Fix Your Upper Back With These Three Steps
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to back pain, the lower back gets a lot of attention, but what about when it’s nearer the neck and shoulders?
Reaching for better health
In this short video, Liv describes and shows three exercises:
Exercise 1: Thoracic Pullover (Dumbbell Pullover)
Purpose: Improves overhead reach and shoulder mobility.
Equipment: light weight, yoga block, or foam roller.
Steps:
- Lie on the floor with the foam roller/block beneath the upper back.
- Hold the weight in both hands, arms extended upward.
- Inhale deeply and reach the weight toward the ceiling.
- Exhale and arc your spine over the block, moving the weight backward.
- Keep core tension to maintain a neutral lower back position.
- Perform 10 repetitions.
Exercise 2: Rotational Mobility Stretch
Purpose: enhances torso rotation, core strength, and hip mobility.
Equipment: none (or a mat)
Steps:
- Lie on your side with knees stacked at 90° and arms extended in front.
- Hold a weight in the top hand.
- Inhale and lift the top arm toward the ceiling, extending the shoulder blade.
- Exhale and twist your torso, allowing the arm to move toward the floor.
- Modify by extending the bottom leg for a deeper twist if needed.
- Perform 6 reps per side, switching legs and repeating on the other side.
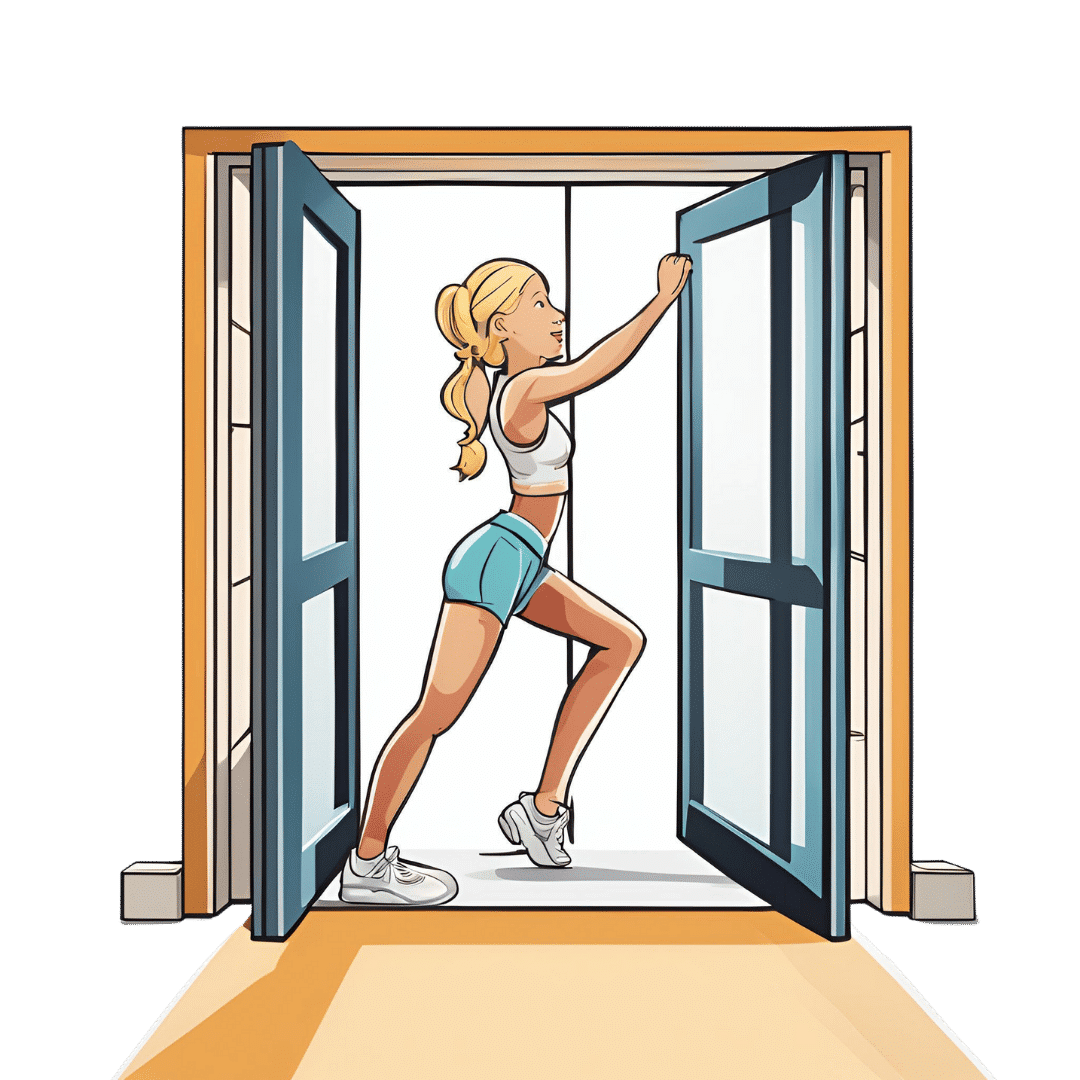
Exercise 3: Doorway/Pole Side Stretch
Purpose: targets multiple areas for a deep, satisfying stretch.
Equipment: door frame, pole, or wall.
Steps:
- Stand at arm’s length from the wall or frame.
- Cross the outer leg (furthest from the wall) behind the inner leg.
- Place the closest hand on the wall and reach the other arm overhead.
- Grip the wall or frame with the top hand, pressing away with the bottom hand.
- Lean into a banana-shaped curve and rotate your chest upward for a deeper stretch.
- Hold for 20–30 seconds per side and repeat 2–3 times.
For more on all of these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Take Your Mental Health As Seriously As General Health!
Sometimes, health and productivity means excelling—sometimes, it means avoiding illness and unproductivity. Both are essential, and today we’re going to tackle some ground-up stuff. If you don’t need it right now, great; we suggest to read it for when and if you do. But how likely is it that you will?
- One in four of us are affected by serious mental health issues in any given year.
- One in five of us have suicidal thoughts at some point in our lifetime.
- One in six of us are affected to at least some extent by the most commonly-reported mental health issues, anxiety and depression, in any given week.
…and that’s just what’s reported, of course. These stats are from a UK-based source but can be considered indicative generally. Jokes aside, the UK is not a special case and is not measurably worse for people’s mental health than, say, the US or Canada.
While this is not an inherently cheery topic, we think it’s an important one.
Depression, which we’re going to focus on today, is very very much a killer to both health and productivity, after all.
One of the most commonly-used measures of depression is known by the snappy name of “PHQ9”. It stands for “Patient Health Questionnaire Nine”, and you can take it anonymously online for free (without signing up for anything; it’s right there on the page already):
Take The PHQ9 Test Here! (under 2 minutes, immediate results)
There’s a chance you took that test and your score was, well, depressing. There’s also a chance you’re doing just peachy, or maybe somewhere in between. PHQ9 scores can fluctuate over time (because they focus on the past two weeks, and also rely on self-reports in the moment), so you might want to bookmark it to test again periodically. It can be interesting to track over time.
In the event that you’re struggling (or: in case one day you find yourself struggling, or want to be able to support a loved one who is struggling), some top tips that are useful:
Accept that it’s a medical condition like any other
Which means some important things:
- You/they are not lazy or otherwise being a bad person by being depressed
- You/they will probably get better at some point, especially if help is available
- You/they cannot, however, “just snap out of it”; illness doesn’t work that way
- Medication might help (it also might not)
Do what you can, how you can, when you can
Everyone knows the advice to exercise as a remedy for depression, and indeed, exercise helps many. Unfortunately, it’s not always that easy.
Did you ever see the 80s kids’ movie “The Neverending Story”? There’s a scene in which the young hero Atreyu must traverse the “Swamp of Sadness”, and while he has a magical talisman that protects him, his beloved horse Artax is not so lucky; he slows down, and eventually stops still, sinking slowly into the swamp. Atreyu pulls at him and begs him to keep going, but—despite being many times bigger and stronger than Atreyu, the horse just sinks into the swamp, literally drowning in despair.
See the scene: The Neverending Story movie clip – Artax and the Swamp of Sadness (1984)
Wow, they really don’t make kids’ movies like they used to, do they?
But, depression is very much like that, and advice “exercise to feel less depressed!” falls short of actually being helpful, when one is too depressed to do it.
If you’re in the position of supporting someone who’s depressed, the best tool in your toolbox will be not “here’s why you should do this” (they don’t care; not because they’re an uncaring person by nature, but because they are physiologically impeded from caring about themself at this time), but rather:
“please do this with me”
The reason this has a better chance of working is because the depressed person will in all likelihood be unable to care enough to raise and/or maintain an objection, and while they can’t remember why they should care about themself, they’re more likely to remember that they should care about you, and so will go with your want/need more easily than with their own. It’s not a magic bullet, but it’s worth a shot.
What if I’m the depressed person, though?
Honestly, the same, if there’s someone around you that you do care about; do what you can to look after you, for them, if that means you can find some extra motivation.
But I’m all alone… what now?
Firstly, you don’t have to be alone. There are free services that you can access, for example:
- US: https://nami.org/help
- Canada: https://www.wellnesstogether.ca/en-CA
- UK: https://www.samaritans.org/
…which varyingly offer advice, free phone services, webchats, and the like.
But also, there are ways you can look after yourself a little bit; do the things you’d advise someone else to do, even if you’re sure they won’t work:
- Take a little walk around the block
- Put the lights on when you’re not sleeping
- For that matter, get out of bed when you’re not sleeping. Literally lie on the floor if necessary, but change your location.
- Change your bedding, or at least your clothes
- If changing the bedding is too much, change just the pillowcase
- If changing your clothes is too much, change just one item of clothing
- Drink some water; it won’t magically cure you, but you’ll be in slightly better order
- On the topic of water, splash some on your face, if showering/bathing is too much right now
- Do something creative (that’s not self-harm). You may scoff at the notion of “art therapy” helping, but this is a way to get at least some of the lights on in areas of your brain that are a little dark right now. Worst case scenario is it’ll be a distraction from your problems, so give it a try.
- Find a connection to community—whatever that means to you—even if you don’t feel you can join it right now. Discover that there are people out there who would welcome you if you were able to go join them. Maybe one day you will!
- Hiding from the world? That’s probably not healthy, but while you’re hiding, take the time to read those books (write those books, if you’re so inclined), learn that new language, take up chess, take up baking, whatever. If you can find something that means anything to you, go with that for now, ride that wave. Motivation’s hard to come by during depression and you might let many things slide; you might as well get something out of this period if you can.
If you’re not depressed right now but you know you’re predisposed to such / can slip that way?
Write yourself instructions now. Copy the above list if you like.
Most of all: have a “things to do when I don’t feel like doing anything” list.
If you only take one piece of advice from today’s newsletter, let that one be it!
Share This Post
-
Can apps and digital resources support your child with autism or ADHD?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Neurodevelopmental conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism affect about one in ten children. These conditions impact development, behaviour and wellbeing.
But children with these conditions and their caregivers often can’t get the support they need. Families report difficulties accessing health-care providers and experience long wait lists to receive care.
Digital tools, such as apps and websites, are often viewed as a solution to these gaps. With a single click or a download, families might be able to access information to support their child.
There are lots of digital tools available, but it’s hard to know what is and isn’t useful. Our new study evaluated freely available digital resources for child neurodevelopment and mental health to understand their quality and evidence base.
We found many resources were functional and engaging. However, resources often lacked evidence for the information provided and the claimed positive impact on children and families.
This is a common problem in the digital resource field, where the high expectations and claims of impact from digital tools to change health care have not yet been realised.
Fabio Principe/Shutterstock What type of resources?
Our study identified 3,435 separate resources, of which 112 (43 apps and 69 websites) met our criteria for review. These resources all claimed to provide information or supports for child neurodevelopment, mental health or wellbeing.
Resources had to be freely available, in English and have actionable information for children and families.
The most common focus was on autism, representing 17% of all resources. Resources suggested they provided strategies to promote speech, language and social development, and to support challenging behaviours.
Other common areas included language and communication (14%), and ADHD (10%).
Resources had various purposes, including journalling and providing advice, scheduling support, and delivering activities and strategies for parents. Resources delivered information interactively, with some apps organising content into structured modules.
Resources also provided options for alternative and assistive communication for people with language or communication challenges.
Most apps were functional and accessible
Our first question was about how engaging and accessible the information was. Resources that are hard to use aren’t used frequently, regardless of the information quality.
We evaluated aesthetics, including whether digital tools were easy to use and navigate, stylistically consistent, with clean and appealing graphics for users.
Most resources were rated as highly engaging, with strong accessibility and functionality.
Most apps and websites we evaluated were engaging. jamesteohart/Shutterstock But many lacked quality information
We ranked resources on various features from 1 (inadequate) to 5 (excellent), with a ranking of 3 considered acceptable. These ratings looked at how credible the resource was and whether there was evidence supporting it.
Despite their functionality, 37% of reviewed apps did not meet the minimum acceptable standards for information quality. This means many apps could not be recommended. Most websites fared better than apps.
There also wasn’t a lot of scientific evidence to suggest using either apps or digital resources actually helped families. Studies show long-term engagement with digital tools is rare, and downloads don’t correspond to frequent usage or benefits.
Digital tools are often viewed as a panacea to health-care gaps, but the evidence is yet to show they fill such gaps. Digital health is a fast-moving field and resources are often made available before they have been properly evaluated.
What should you look for in digital resources?
We found the highest quality resources were developed in collaboration with institutions, such as health, university or government groups.
One highly rated resource was the Raising Children’s Network and the associated app, Raising Healthy Minds. These are co-developed with a university and hospital, and by people with appropriate qualifications.
This resource provides information to support children’s overall health, development and wellbeing, with dedicated sections addressing neurodevelopmental needs and concerns.
The Raising Children Network provides resources for child health, including neurodevelopmental needs. Raising Children Network screenshot Our research shows parents can assess whether digital resources are high quality by checking they are:
- factually correct. Look for where the app or resource is getting its information. Does the author have the qualifications and training to provide the information? Are they a registered health expert who is accountable to a regulatory body (such as AHPRA, the Australian Health Practitioners Regulation Agency) for providing information that does not cause harm?
- consistent across multiple credible sources, such as health institutions.
- linked to supporting information. Look for reliable links to reputable institutions. Links to peer-reviewed scientific journals are often helpful as those articles will also usually describe the limitations of the research presented.
- up-to-date. Apps should be frequently updated. For websites, dates of update are usually found on the homepage or at the bottom of individual pages.
Check when information was last updated. fizkes/Shutterstock Beware of red flags
Some things to watch out for are:
- testimonials and anecdotes without evidence and scientific links to back the anecdotes up. If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
- no information provided about conflicts of interest. Organisations gain when you click on their links or take their advice (financial, reputation and brand development). Think about what they gain when you use their information to help keep a balanced perspective.
Remember, the app’s star rating doesn’t mean it will contain factual information from a reliable source or be helpful for you and your child.
The role of digital tools
Digital tools won’t usually replace a health professional, but they can support care in many different ways. They may be used to help to educate and prepare for meetings, and to collaborate with health providers.
They may also be used to collect information about daily needs. Studies show reporting on sleep in children can be notoriously difficult, for example. But tracking sleep behaviour with actigraphy, where movement and activity patterns are measured using a wearable device, can provide information to support clinical care. With the promise of artificial intelligence, there will also be new opportunities to support daily living.
Our findings reflect a broader problem for digital health, however. Much investment is often made in developing products to drive use, with spurious claims of health benefits.
What’s needed is a system that prioritises the funding, implementation and evaluation of tools to demonstrate benefits for families. Only then may we realise the potential of digital tools to benefit those who use them.
Kelsie Boulton, Senior Research Fellow in Child Neurodevelopment, Brain and Mind Centre, University of Sydney and Adam Guastella, Professor and Clinical Psychologist, Michael Crouch Chair in Child and Youth Mental Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
10 Simple Japanese Habits For Healthier & Longer Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You don’t have to be Japanese or live in Okinawa to enjoy the benefits of healthy longevity. A lot of it comes down to simple habits:
Easy to implement
We’ll not keep the 10 habits a mystery; they are:
- Start the day with hot water: drinking hot water in the morning helps with hydration, warming the body, and aiding digestion.
- Enjoy a hearty breakfast: Japanese breakfasts are traditionally filling, nutritious, and help promote energy and longevity. Typical components include rice, miso soup, fish, and pickles.
- Take balanced meals: Japanese education emphasizes nutrition from a young age, promoting balanced meals with proteins, fiber, and vitamins & minerals.
- Enjoy fermented foods: fermented foods, such as nattō and soy-based condiments, support digestion, heart health, and the immune system.
- Drink green tea and matcha: both are rich in health benefits; preparing matcha mindfully adds a peaceful ritual to daily life too.
- Keep the “80% full” rule: “hara hachi bu” encourages eating until 80% full, which can improve longevity and, of course, prevent overeating.
- Use multiple small dishes: small servings and a variety of dishes help prevent overeating and ensure a diverse intake of nutrients.
- Gratitude before and after meals: saying “itadakimasu” and “gochisousama” promotes mindful eating, and afterwards, good digestion. Speaking Japanese is of course not the key factor here, but rather, do give yourself a moment of reflection before and after meals.
- Use vinegar in cooking: vinegar, often used in sushi rice and sauces like ponzu, adds flavor and offers health benefits, mostly pertaining to blood sugar balance.
- Eat slowly: Eating at a slower pace will improve digestion, and can enhance satiety and prevent accidentally overeating.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Get More Out Of What’s On Your Plate
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How Useful Is Hydrotherapy?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hyyyyyyydromatic…
Hydrotherapy is a very broad term, and refers to any (external) use of water as part of a physical therapy. Today we’re going to look at some of the top ways this can be beneficial—maybe you’ll know them all already, but maybe there’s something you hadn’t thought about or done decently; let’s find out!
Notwithstanding the vague nature of the umbrella term, some brave researchers have done a lot of work to bring us lots of information about what works and what doesn’t, so we’ll be using this to guide us today. For example:
Scientific Evidence-Based Effects of Hydrotherapy on Various Systems of the Body
Swimming (and similar)
An obvious one, this can for most people be a very good full-body exercise, that’s exactly as strenuous (or not) as you want/need it to be.
It can be cardio, it can be resistance, it can be endurance, it can be high-intensity interval training, it can be mobility work, it can be just support for an aching body that gets to enjoy being in the closest to zero-gravity we can get without being in freefall or in space.
See also: How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Depending on what’s available for you locally (pool with a shallow area, for example), it can also be a place to do some exercises normally performed on land, but with your weight being partially supported (and as a counterpoint, a little resistance added to movement), and no meaningful risk of falling.
Tip: check out your local facilities, to see if they offer water aerobics classes; because the water necessitates slow movement, this can look a lot like tai chi to watch, but it’s great for mobility and balance.
Water circuit therapy
This isn’t circuit training! Rather, it’s a mixture of thermo- and cryotherapy, that is to say, alternating warm and cold water immersion. This can also be interspersed with the use of a sauna, of course.
See also:
- Ice Baths: To Dip Or Not To Dip?
- Saunas: Health Benefits (& Caveats)
- The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
this last one is about thermal shock-mediated hormesis, which sounds drastic, but it’s what we’re doing here with the hot and cold, and it’s good for most people!
Pain relief
Most of the research for this has to do with childbirth pain rather than, for example, back pain, but the science is promising:
Post-exercise recovery
It can be tempting to sink into a hot bath, or at least enjoy a good hot shower, after strenuous exercise. But does it help recovery too? The answer is probably yes:
Effect of hot water immersion on acute physiological responses following resistance exercise
For more on that (and other means of improving post-exercise recovery), check out our previous main feature:
How To Speed Up Recovery After A Workout (According To Actual Science)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
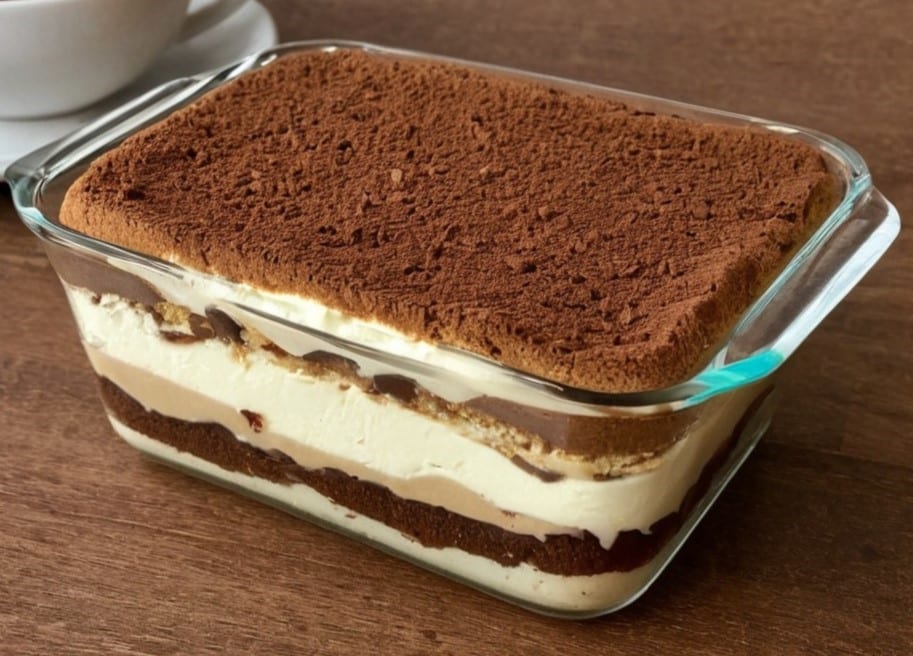
Healthy Tiramisu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tiramisu (literally “pick-me-up”, “tira-mi-su”) is a delightful dish that, in its traditional form, is also a trainwreck for the health, being loaded with inflammatory cream and sugar, not to mention the cholesterol content. Here we recreate the dish in healthy fashion, being loaded with protein, fiber, and healthy fats, not to mention that the optional sweetener is an essential amino acid. The coffee and cocoa, of course, are full of antioxidants too. All in all, what’s not celebrate?
You will need
- 2 cups silken tofu (no need to press it) (do not substitute with any firmer tofu or it will not work)
- 1 cup oat cream (you can buy this ready-made, or make it yourself by blending oats in water until you get the desired consistency) (you can also just use dairy cream, but that will be less healthy)
- 1 cup almond flour (also simply called “ground almonds”)
- 1 cup espresso ristretto, or otherwise the strongest black coffee you have facility to make
- ¼ cup unsweetened cocoa powder, plus more for dusting
- 1 pack savoiardi biscuits, also called “ladyfinger” biscuits (this was the only part we couldn’t make healthy—if you figure out a way to make it healthy, let us know!) (if vegan, obviously use a vegan substitute biscuit; this writer uses Lotus/Biscoff biscuits, which work well)
- 1 tsp vanilla essence
- ½ tsp almond essence
- Optional: glycine, per taste
- Garnish: roasted coffee beans
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add glycine to the coffee first if you want the overall dish to be sweeter. Glycine has approximately the same sweetness as sugar, and can be used as a 1:1 substitution. Use that information as you see fit.
2) Blend the tofu and the oat cream together in a high-speed blender until smooth. It should have a consistency like cake-batter; if it is too liquidy, add small amounts of almond flour until it is thicker. If it’s too thick, add oat cream until it isn’t. If you want it to be sweeter than it is, add glycine to taste. When happy with its taste and consistency, divide it evenly into two bowls.
3) Add the vanilla essence and almond essence to one bowl, and the cocoa powder to the other, mixing well (in a food processor, or just by using a whisk)
4) Coat the base of a glass dish (such as a Pyrex oven dish, but any dish is fine, and any glass dish will allow for viewing the pretty layers we’ll be making) with a very thin layer of almond flour (if you want sweetness there, you can mix some glycine in with the almond flour first).
4) One by one, soak the biscuits briefly in the coffee, and use them to line to base of the dish.
5) Add a thin layer of chocolate cream, ensuring the surface is as flat as possible. Dust it with cocoa powder, to increase the surface tension.
6) Add a thin layer of vanilla-and-almond cream, ensuring the surface is as flat as possible. Dust it with cocoa powder, to increase the surface tension.
7) Stop and assess: do you have enough ingredients left to repeat these layers? It will depend on the size and shape dish you used. If you do, repeat them, finishing with a vanilla-and-almond cream layer.
8) Dust the final layer with cocoa powder if you haven’t already, and add the coffee bean garnish, if using.
9) Refrigerate for at least 8 hours, and if you have time to prepare it the day before you will eat it, that is best of all.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Easily Digestible Vegetarian Protein Sources
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- The Sweet Truth About Glycine
- Tiramisu Crunch Bites ← craving tiramisu but not keen on all that effort? Enjoy these!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Happens To Your Body When You Do Squats Every Day-Not Just For Legs!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Squat Every Day? Yes, Please!
It’s back to basics with this video (below). Passion for Health’s video, “What Happens To Your Body When You Do Squats Every Day-Not Just For Legs!” really brings home how squats aren’t just a one-trick pony for your legs.
The humble bodyweight squat is shown to contribute to everything from bolstering all-around lower body strength to bettering bone density and increasing metabolism.
Indeed, squats are so powerful that we reviewed a whole book that focuses just on the topic of squatting. Other, broader books on exercise also focus on the positive impacts that squatting can make.
A proper squat goes beyond your legs, engaging your core, enhancing joint health, and, some argue, can lead to improved balance and circulation.
(Plus, they’re easy to execute, given they can be done anywhere, without any equipment).
This is probably why Luigi Fontana and Dr Rangan Chatterjee have spoken about the benefits of squatting.
How Should We Start?
The video goes beyond the ‘why’ and delves into the ‘how’, offering step-by-step squatting techniques.
It answers the burning question: should you really be doing squats every day?
(Hint: the answer is most likely “yes”).
Of course, some of us may not be able to squat, and for those, we’ll feature alternatives in a future article.
For beginners, the advice is to start slow, aiming for 10 repetitions. You can gradually increase that count as you feel your muscles strengthen. Experienced gym-goers might push for 20 or more reps, adding variations like jump squats for an extra challenge.
The key takeaway is to listen to your body and ensure rest days for muscle recovery.
At the end of the day, Passion for Health’s video is a treasure trove for squat lovers, from novices to the seasoned, and insists on the importance of form, frequency, and listening to one’s body.
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: