DVT Risk Management Beyond The Socks
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I know I am at higher risk of DVT after having hip surgery, any advice beside compression stockings?❞
First of all, a swift and easy recovery to you!
Surgery indeed increases the risk of deep vein thrombosis (henceforth: DVT), and hip or knee surgery especially so, for obvious reasons.
There are other risk factors you can’t control, like genetics (family history of DVT as an indicator) and age, but there are some that you can, including:
- smoking (so, ideally don’t; do speak to your doctor before quitting though, in case withdrawal might be temporarily worse for you than smoking)
- obesity (so, losing weight is good if overweight, but if this is going to happen, it’ll mostly happen in the kitchen not the gym, which may be a relief as you’re probably not the very most up for exercise at present)
- See also: Lose Weight, But Healthily
- sedentariness (so, while you’re probably not running marathons right now, please do try to keep moving, even if only gently)
Beyond that, yes compression socks, but also frequent gentle massage can help a lot to avoid clots forming.
Also, no surprises, a healthy diet will help, especially one that’s good for general heart health. Check out for example the Mediterranean DASH diet:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet
Also, obviously, speak with your doctor/pharmacist if you haven’t already about possible medications, including checking whether any of your current medications increase the risk and could be swapped for something that doesn’t.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Joy of Saying No – by Natalie Lue
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Superficially, this seems an odd topic for an entire book. “Just say no”, after all, surely! But it’s not so simple as that, is it?
Lue looks into what underpins people-pleasing, first. Then, she breaks it down into five distinct styles of people-pleasing that each come from slightly different motivations and ways of perceiving how we interact with those around us.
Lest this seem overly complicated, those five styles are what she calls: gooding, efforting, avoiding, saving, suffering.
She then looks out how to have a healthier relationship with our yes/no decisions; first by observing, then by creating healthy boundaries. “Healthy” is key here; this isn’t about being a jerk to everyone! Quite the contrary, it involves being honest about what we can and cannot reasonably take on.
The last section is about improving and troubleshooting this process, and constitutes a lot of the greatest value of the book, since this is where people tend to err the most.
Bottom line: this book is informative, clear, and helpful. And far from disappointing everyone with “no”, we can learn to really de-stress our relationships with others—and ourselves.
Share This Post
-
Frozen/Thawed/Refrozen Meat: How Much Is Safety, And How Much Is Taste?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What You Can (And Can’t) Safely Do With Frozen Meat
Yesterday, we asked you:
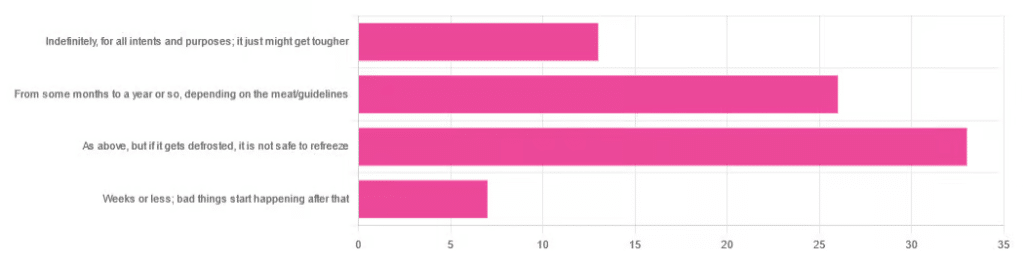
❝You have meat in the freezer. How long is it really safe to keep it?❞
…and got a range of answers, mostly indicating to a) follow the instructions (a very safe general policy) and b) do not refreeze if thawed because that would be unsafe. Fewer respondents indicated that meat could be kept for much longer than guidelines say, or conversely, that it should only be kept for weeks or less.
So, what does the science say?
Meat can be kept indefinitely (for all intents and purposes) in a freezer; it just might get tougher: True or False?
False, assuming we are talking about a normal household electrical freezer that bottoms out at about -18℃ / 0℉.
Fun fact: cryobiologists cryopreserve tissue samples (so basically, meat) at -196℃ / -320℉, and down at those temperatures, the tissues will last a lot longer than you will (and, for all practical purposes: indefinitely). There are other complications with doing so (such as getting the sample through the glass transition point without cracking it during the vitrification process) but those are beyond the scope of this article.
If you remember back to your physics or perhaps chemistry classes at school, you’ll know that molecules move more quickly at higher temperatures, and more slowly at lower ones, only approaching true stillness as they near absolute zero (-273℃ / -459℉ / 0K ← we’re not saying it’s ok, although it is; rather, that is zero kelvin; no degree sign is used with kelvins)
That means that when food is frozen, the internal processes aren’t truly paused; it’s just slowed to a point of near imperceptibility.
So, all the way up at the relatively warm temperatures of a household freezer, a lot of processes are still going on.
What this means in practical terms: those guidelines saying “keep in the freezer for up to 4 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 9 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 12 months” etc are being honest with you.
More or less, anyway! They’ll usually underestimate a little to be on the safe side—but so should you.
Bad things start happening within weeks at most: True or False?
False, for all practical purposes. Again, assuming a normal and properly-working household freezer as described above.
(True, technically but misleadingly: the bad things never stopped; they just slowed down to a near imperceptible pace—again, as described above)
By “bad” here we should clarify we mean “dangerous”. One subscriber wrote:
❝Meat starts losing color and flavor after being in the freezer for too long. I keep meat in the freezer for about 2 months at the most❞
…and as a matter of taste, that’s fair enough!
It is unsafe to refreeze meat that has been thawed: True or False?
False! Assuming it has otherwise been kept chilled, just the same as for fresh meat.
Food poisoning comes from bacteria, and there is nothing about the meat previously having been frozen that will make it now have more bacteria.
That means, for example…
- if it was thawed (but chilled) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been chilled for that period of time (so probably: use it or freeze it, unless it’s been more than a few days)
- if it was thawed (and at room temperature) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been at room temperature for that period of time (so probably: throw it out, unless the period of time is very small indeed)
The USDA gives for 2 hours max at room temperature before considering it unsalvageable, by the way.
However! Whenever you freeze meat (or almost anything with cells, really), ice crystals will form in and between cells. How much ice crystallization occurs depends on several variables, with how much water there is present in the food is usually the biggest factor (remember that animal cells are—just like us—mostly water).
Those ice crystals will damage the cell walls, causing the food to lose structural integrity. When you thaw it out, the ice crystals will disappear but the damage will be left behind (this is what “freezer burn” is).
So if your food seems a little “squishy” after having been frozen and thawed, that’s why. It’s not rotten; it’s just been stabbed countless times on a microscopic level.
The more times you freeze and thaw and refreeze food, the more this will happen. Your food will degrade in structural integrity each time, but the safety of it won’t have changed meaningfully.
Want to know more?
Further reading:
You can thaw and refreeze meat: five food safety myths busted
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Power of Hormones – by Dr. Max Nieuwdorp
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First a quick note on the author: he’s an MD & PhD, internist, endocrinologist, and professor. He knows his stuff.
There are a lot of books with “the new science of” in the title, and they don’t often pertain to science that is actually new, and in this case, for the most part the science contained within this book is quite well-established.
A strength of this book is that it’s not talking about hormones in just one specific aspect (e.g. menopause, pregnancy, etc) but rather, in the full span of human health, across the spectra of ages and sexes—and yes, also covering hormones that are not sex hormones, so for example also demystifying the different happiness-related neurotransmitters, as well as the hormones responsible for hunger and satiety, weight loss and gain, sleep and wakefulness, etc.
Which is all very good, because there’s a lot of overlap and several hormones fall into several categories there.
Moreover, the book covers how your personal cocktail of hormones impacts how you look, feel, behave, and more—there’s a lot about chronic health issues here too, and how to use the information in this book to if not outright cure, then at least ameliorate, many conditions.
Bottom line: this is an information-dense book with a lot of details great and small; if you read this, you’ll come away with a much better understanding of hormones than you had previously!
Click here to check out The Power of Hormones, and harness that power for yourself!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why We Get Fat: And What to Do About It – by Gary Taubes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Taubes’ “The Case Against Sugar“. What does this one bring differently?
Mostly, it’s a different focus. Unsurprisingly, Taubes’ underlying argument is the same: sugar is the biggest dietary health hazard we face. However, this book looks at it specifically through the lens of weight loss, or avoiding weight gain.
Taubes argues for low-carb in general; he doesn’t frame it specifically as the ketogenic diet here, but that is what he is advocating. However, he also acknowledges that not all carbs are created equal, and looks at several categories that are relatively better or worse for our insulin response, and thus, fat management.
If the book has a fault it’s that it does argue a bit too much for eating large quantities of meat, based on Weston Price’s outdated and poorly-conducted research. However, if one chooses to disregard that, the arguments for a low-carb diet for weight management remain strong.
Bottom line: if you’d like to cut some fat without eating less (or exercising more), this book offers a good, well-explained guide for doing so.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Snooze-Button Controversy
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
To Snooze Or Not To Snooze? (Science Has Answers)
This is Dr. Jennifer Kanaan. She’s a medical doctor with a focus on pulmonary critical care, sleep disorders, and sleep medicine.
What does she want to tell us?
She wants us to be wary of the many news articles that have jumped on a certain recent sleep study, such as:
- Is hitting the snooze button really a bad idea? Study sheds light on the impact of morning alarms on sleep and cognition
- Hitting Snooze May Help You Feel Less Sleepy and More Alert, Research Says
- Is it okay to press the snooze button?
- Hitting Snooze May Help You Feel Less Sleepy and More Alert, Research Says
- Hitting the snooze button on your alarm doesn’t make you more tired
For the curious, here is the paper itself, by Dr. Tina Sundelin et al. It’s actually two studies, by the way, but one paper:
The authors of this study concluded:
❝There were no clear effects of snoozing on the cortisol awakening response, morning sleepiness, mood, or overnight sleep architecture.
A brief snooze period may thus help alleviate sleep inertia, without substantially disturbing sleep, for late chronotypes and those with morning drowsiness.❞
Notably, people tend to snooze because an alarm clock will, if not “smart” about it, wake us up mid sleep-cycle more often than not, and that will produce a short “sleep hangover”. By snoozing, we are basically re-rolling the dice on being woken up between sleep cycles, and thus feeling more refreshed.
What’s Dr. Kanaan’s counterpoint?
Dr. Kanaan says:
❝If you’re coming in and out of sleep for 30 minutes, after the alarm goes off the first time, you’re costing yourself 30 minutes of uninterrupted, quality, restorative sleep. This study doesn’t change that fact.❞
She advises that rather than snoozing, we should prioritize getting good sleep in the first place, and once we do wake up, mid sleep-cycle or not, get sunlight. That way, our brain will start promptly scrubbing melatonin and producing the appropriate wakefulness hormones instead. That means serotonin, and also a spike of cortisol.
Remember: cortisol is only bad when it’s chronically elevated. It’s fine, and even beneficial, to have a short spike of cortisol. We make it for a reason!
If you’d like to hear more from Dr. Kanaan, you might like this interview with her at the University of Connecticut:
Want the best of both worlds?
A great option to avoid getting woken in the middle of a sleep cycle, and also not needing to hit snooze, is a sunrise alarm clock. Specifics of these devices vary, but for example, the kind this writer has starts gently glowing an hour before the set alarm time,and gradually gets brighter and lighter over the course of the hour.
We don’t sell them, but here’s an example sunrise alarm clock on Amazon, for your convenience
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I want to eat healthily. So why do I crave sugar, salt and carbs?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all want to eat healthily, especially as we reset our health goals at the start of a new year. But sometimes these plans are sabotaged by powerful cravings for sweet, salty or carb-heavy foods.
So why do you crave these foods when you’re trying to improve your diet or lose weight? And what can you do about it?
There are many reasons for craving specific foods, but let’s focus on four common ones:
1. Blood sugar crashes
Sugar is a key energy source for all animals, and its taste is one of the most basic sensory experiences. Even without specific sweet taste receptors on the tongue, a strong preference for sugar can develop, indicating a mechanism beyond taste alone.
Neurons responding to sugar are activated when sugar is delivered to the gut. This can increase appetite and make you want to consume more. Giving into cravings also drives an appetite for more sugar.
In the long term, research suggests a high-sugar diet can affect mood, digestion and inflammation in the gut.
While there’s a lot of variation between individuals, regularly eating sugary and high-carb foods can lead to rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. When your blood sugar drops, your body can respond by craving quick sources of energy, often in the form of sugar and carbs because these deliver the fastest, most easily accessible form of energy.
2. Drops in dopamine and serotonin
Certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, are involved in the reward and pleasure centres of the brain. Eating sugary and carb-rich foods can trigger the release of dopamine, creating a pleasurable experience and reinforcing the craving.
Serotonin, the feel-good hormone, suppresses appetite. Natural changes in serotonin can influence daily fluctuations in mood, energy levels and attention. It’s also associated with eating more carb-rich snacks in the afternoon.
Do you get 3pm sugar cravings? Serotonin could play a role.
Marcus Aurelius/PexelsLow carb diets may reduce serotonin and lower mood. However, a recent systematic review suggests little association between these diets and risk for anxiety and depression.
Compared to men, women tend to crave more carb rich foods. Feeling irritable, tired, depressed or experiencing carb cravings are part of premenstrual symptoms and could be linked to reduced serotonin levels.
3. Loss of fluids and drops in blood sugar and salt
Sometimes our bodies crave the things they’re missing, such as hydration or even salt. A low-carb diet, for example, depletes insulin levels, decreasing sodium and water retention.
Very low-carb diets, like ketogenic diets, induce “ketosis”, a metabolic state where the body switches to using fat as its primary energy source, moving away from the usual dependence on carbohydrates.
Ketosis is often associated with increased urine production, further contributing to potential fluid loss, electrolyte imbalances and salt cravings.
4. High levels of stress or emotional turmoil
Stress, boredom and emotional turmoil can lead to cravings for comfort foods. This is because stress-related hormones can impact our appetite, satiety (feeling full) and food preferences.
The stress hormone cortisol, in particular, can drive cravings for sweet comfort foods.
A 2001 study of 59 premenopausal women subjected to stress revealed that the stress led to higher calorie consumption.
A more recent study found chronic stress, when paired with high-calorie diet, increases food intake and a preference for sweet foods. This shows the importance of a healthy diet during stress to prevent weight gain.
What can you do about cravings?
Here are four tips to curb cravings:
1) don’t cut out whole food groups. Aim for a well-balanced diet and make sure you include:
- sufficient protein in your meals to help you feel full and reduce the urge to snack on sugary and carb-rich foods. Older adults should aim for 20–40g protein per meal with a particular focus on breakfast and lunch and an overall daily protein intake of at least 0.8g per kg of body weight for muscle health
- fibre-rich foods, such as vegetables and whole grains. These make you feel full and stabilise your blood sugar levels. Examples include broccoli, quinoa, brown rice, oats, beans, lentils and bran cereals. Substitute refined carbs high in sugar like processed snack bars, soft drink or baked goods for more complex ones like whole grain bread or wholewheat muffins, or nut and seed bars or energy bites made with chia seeds and oats
2) manage your stress levels. Practise stress-reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to manage emotional triggers for cravings. Practising mindful eating, by eating slowly and tuning into bodily sensations, can also reduce daily calorie intake and curb cravings and stress-driven eating
3) get enough sleep. Aim for seven to eight hours of quality sleep per night, with a minimum of seven hours. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate hunger and cravings
4) control your portions. If you decide to indulge in a treat, control your portion size to avoid overindulging.
Overcoming cravings for sugar, salt and carbs when trying to eat healthily or lose weight is undoubtedly a formidable challenge. Remember, it’s a journey, and setbacks may occur. Be patient with yourself – your success is not defined by occasional cravings but by your ability to manage and overcome them.
Hayley O’Neill, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: