Cynthia’s Thoughts on Intermittent Fasting
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Myth of Breakfast and Snacking
Here at 10almonds we love addressing misconceptions in the health world.
When it comes to eating habits and fasting, we’ve written our own pieces on how to break your fast (otherwise known as break-fast, or breakfast), alongside a general breakdown of intermittent fasting, and a much-requested piece on fasting specifically for women.
Cynthia Thurlow, though, instead of just writing a few articles, has dedicated the majority of her working years to intermittent fasting and, in her TEDx talk (below), makes a strong argument challenging the long-held belief that breakfast is the most important meal of the day.
Cynthia Thurlow’s Two Main Points
Thurlow argues that it’s not what you eat but when you eat that has a more profound impact on health and aging. And she argues this is crucial regardless of your age.
Complementing her views on fasting are her views on snacking; she argues that snacking all day long is outdated advice and can overtax the digestive system, leading to various health issues.
Practical Tips for Starting Intermittent Fasting
To begin intermittent fasting, Thurlow suggests starting with a 12-13 hour fasting window and gradually increasing it to 16 hours.
In terms of food choice, she recommends eating whole, unprocessed foods during eating periods as well as staying well-hydrated with water, coffee, or tea.
But you won’t see results immediately; Thurlow advises giving the strategy a solid 30 days to see results and consulting a healthcare provider if there are any existing health conditions.
You can dive deeper and join the 15 million other people who have listened to her thoughts on fasting by watching her TEDx talk below:
How was the video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hair-Loss Remedies, By Science
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
10almonds Gets Hairy
Hair loss is a thing that at some point affects most men and a large minority of women. It can be a source of considerable dysphoria for both, as it’s often seen as a loss of virility/femininity respectively, and is societally stigmatized in various ways.
Today we’re going to focus on the most common kind: androgenic alopecia, which is called “male pattern baldness” in men and “female pattern baldness” in women, despite being the same thing.
We won’t spend a lot of time on the science of why this happens (we’re going to focus on the remedies instead), but suffice it to say that genes and hormones both play a role, with dihydrogen testosterone (DHT) being the primary villain in this case.
We’ve talked before about the science of 5α-reductase inhibitors to block the conversion of regular testosterone* to DHT, its more potent form:
One Man’s Saw Palmetto Is Another Woman’s Serenoa Repens…
*We all make this to a greater or lesser degree, unless we have had our ovaries/testes removed.
Finasteride
Finasteride is a 5α-reductase inhibitor that performs similarly to saw palmetto, but comes in tiny pills instead of needing to take a much higher dose of supplement (5mg of finasteride is comparable in efficacy to a little over 300mg of saw palmetto).
Does it work? Yes!
Any drawbacks? A few:
- It’ll take 3–6 months to start seeing effects. This is because of the hormonal life-cycle of human hairs.
- Common side-effects include ED.
- It is popularly labelled/prescribed as “only for men”
On that latter point: the warnings about this are severe, detailing how women must not take it, must not even touch it if it has been cut up or crushed.
However… That’s because it can carry a big risk to our unborn fetuses. So, if we are confident we definitely don’t have one of those, it’s not actually applicable to us.
That said, finasteride’s results in women aren’t nearly so clear-cut as in men (though also, there has been less research, largely because of the above). Here’s an interesting breakdown in more words than we have room for here:
Finasteride for Women: Everything You Need to Know
Spironolactone
This one’s generally prescribed to women, not men, largely because it’s the drug sometimes popularly known as a “chemical castration” drug, which isn’t typically great marketing for men (although it can be applied topically, which will have less of an effect on the rest of the body). For women, this risk is simply not an issue.
We’ll be brief on this one, but we’ll just drop this, so that you know it’s an option that works:
❝Spironolactone is an effective and safe treatment of androgenic alopecia which can enhance the efficacy when combined with other conventional treatments such as minoxidil.
Topical spironolactone is safer than oral administration and is suitable for both male and female patients, and is expected to become a common drug for those who do not have a good response to minoxidil❞
Minoxidil
This one is available (to men and women) without prescription. It’s applied topically, and works by shortcutting the hair’s hormonal growth cycle, to reduce the resting phase and kick it into a growth phase.
Does it work? Yes!
Any drawbacks? A few:
- Whereas you’ll remember finasteride takes 3–6 months to see any effect, this one will have an effect very quickly
- Specifically, the immediate effect is: your rate of hair loss will appear to dramatically speed up
- This happens because when hairs are kicked into their growth phase if they were in a resting phase, the first part of that growth phase is to shed each old hair to make room for the new one
- You’ll then need the same 3–6 months as with finasteride, to see the regrowth effects
- If you stop using it, you will immediately shed whatever hair you gained by this method
Why do people choose this over finasteride? For one of three reasons, mainly:
- They are women, and not offered finasteride
- They are men, and do not want the side effects of finasteride
- They just saw an ad and tried it
As to how it works:
Some final notes:
There are some other contraindications and warnings with each of these drugs by the way, so do speak with your doctor/pharmacist. For example:
- Finasteride can tax the liver a little
- Spironolactone can reduce bone turnover
- Minoxidil is a hypotensive; this shouldn’t be an issue for most people, but for some people it could be a problem
There are other hair loss remedies and practices, but the above three are the heavy-hitters, so that’s what we spent our time/space on today. We’ll perhaps cover the less powerful (but less risky) options one of these days.
Meanwhile, take care!
Share This Post
-
A Surprisingly Powerful Tool: Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing (EMDR)
What skeletons are in your closet? As life goes on, most of accumulate bad experiences as well as good ones, to a greater or lesser degree. From clear cases of classic PTSD, to the widely underexamined many-headed beast that is C-PTSD*, our past does affect our present. Is there, then, any chance for our future being different?
*PTSD is typically associated with military veterans, for example, or sexual assault survivors. There was a clear, indisputable, Bad Thing™ that was experienced, and it left a psychological scar. When something happens to remind us of that—say, there are fireworks, or somebody touches us a certain way—it’ll trigger an immediate strong response of some kind.
These days the word “triggered” has been popularly misappropriated to mean any adverse emotional reaction, often to something trivial.
But, not all trauma is so clear. If PTSD refers to the result of that one time you were smashed with a sledgehammer, C-PTSD (Complex PTSD) refers to the result of having been hit with a rolled-up newspaper every few days for fifteen years, say.
This might have been…
- childhood emotional neglect
- a parent with a hair-trigger temper
- bullying at school
- extended financial hardship as a young adult
- “just” being told or shown all too often that your best was never good enough
- the persistent threat (real or imagined) of doom of some kind
- the often-reinforced idea that you might lose everything at any moment
If you’re reading this list and thinking “that’s just life though”, you might be in the estimated 1 in 5 people with (often undiagnosed) C-PTSD.
For more on C-PTSD, see our previous main feature:
So, what does eye movement have to do with this?
Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing (EMDR) is a therapeutic technique whereby a traumatic experience (however small or large; it could be the memory of that one time you said something very regrettable, or it could be some horror we couldn’t describe here) is recalled, and then “detoothed” by doing a bit of neurological jiggery-pokery.
How the neurological jiggery-pokery works:
By engaging the brain in what’s called bilateral stimulation (which can be achieved in various ways, but a common one is moving the eyes rapidly from side to side, hence the name), the event can be re-processed, in much the same way that we do when dreaming, and relegated safely to the past.
This doesn’t mean you’ll forget the event; you’d need to do different exercises for that.
See also our previous main feature:
The Dark Side Of Memory (And How To Make Your Life Better)
That’s not the only aspect of EMDR, though…
EMDR is not just about recalling traumatic events while moving your eyes from side-to-side. What an easy fix that would be! There’s a little more to it.
The process also involves (ideally with the help of a trained professional) examining what other memories, thoughts, feelings, come to mind while doing that. Sometimes, a response we have today associated with, for example, a feeling of helplessness, or rage in conflict, or shame, or anything really, can be connected to previous instances of feeling the same thing. And, each of those events will reinforce—and be reinforced by—the others.
An example of this could be an adult who struggles with substance abuse (perhaps alcohol, say), using it as a crutch to avoid feelings of [insert static here; we don’t know what the feelings are because they’re being avoided], that were first created by, and gradually snowballed from, some adverse reaction to something they did long ago as a child, then reinforced at various times later in life, until finally this adult doesn’t know what to do, but they do know they must hide it at all costs, or suffer the adverse reaction again. Which obviously isn’t a way to actually overcome anything.
EMDR, therefore, seeks to not just “detooth” a singular traumatic memory, but rather, render harmless the whole thread of memories.
Needless to say, this kind of therapy can be quite an emotionally taxing experience, so again, we recommend trying it only under the guidance of a professional.
Is this an evidence-based approach?
Yes! It’s not without its controversy, but that’s how it is in the dog-eat-dog world of academia in general and perhaps psychotherapy in particular. To give a note to some of why it has some controversy, here’s a great freely-available paper that presents “both sides” (it’s more than two sides, really); the premises and claims, the criticisms, and explanations for why the criticisms aren’t necessarily actually problems—all by a wide variety of independent research teams:
Research on Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing (EMDR) as a Treatment for PTSD
To give an idea of the breadth of applications for EMDR, and the evidence of the effectiveness of same, here are a few additional studies/reviews (there are many):
- An Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) Group Intervention for Syrian Refugees With Post-traumatic Stress Symptoms: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy vs. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing for Treating Panic Disorder: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy in the treatment of depression: a matched pairs study in an inpatient setting
- Emergency room intervention to prevent post concussion-like symptoms and post-traumatic stress disorder. A pilot randomized controlled study of a brief eye movement desensitization and reprocessing intervention versus reassurance or usual care
As for what the American Psychiatric Association says about it:
❝After assessing the 120 outcome studies pertaining to the focus areas, we conclude that for two of the areas (i.e., PTSD in children and adolescents and EMDR early interventions research) the strength of the evidence is rated at the highest level, whereas the other areas obtain the second highest level.❞
Source: The current status of EMDR therapy, specific target areas, and goals for the future
Want to learn more?
To learn a lot more than we could include here, check out the APA’s treatment guidelines (they are written in a fashion that is very accessible to a layperson):
APA | Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) Therapy
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Try This At Home: ABI Test For Clogged Arteries
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Arterial plaque is a big deal, and statistically it’s more of a risk as we get older, often coming to a head around age 72 for women and 65 for men—these are the median ages at which people who are going to get heart attacks, get them. Or get it, because sometimes one is all it takes.
The Ankle-Brachial Index Test
Dr. Brewer recommends a home test for detecting arterial plaque called the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI), which uses a blood pressure monitor. The test involves measuring blood pressure in both the arms and ankles, then calculating the ratio of these measurements:
- A healthy ABI score is between 1.0 and 1.4; anything outside this range may indicate arterial problems.
- Low ABI scores (below 0.8) suggest plaque is likely obstructing blood flow
- High ABI scores (above 1.4) may indicate artery hardening
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), associated with poor ABI results (be they high or low), can cause a whole lot of problems that are definitely better tackled sooner rather than later—remember that atherosclerosis is a self-worsening thing once it gets going, because narrower walls means it’s even easier for more stuff to get stuck in there (and thus, the new stuff that got stuck also becomes part of the walls, and the problem gets worse).
If you need a blood pressure monitor, by the way, here’s an example product on Amazon.
Do note also that yes, if you have plaque obstructing blood flow and hardened arteries, your scores may cancel out and give you a “healthy” score, despite your arteries being very much not healthy. For this reason, this test can be used to raise the alarm, but not to give the “all clear”.
For more on all of the above, plus a demonstration and more in-depth explanation of the test, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Fitness Walking and Bodyweight Exercises – by Frank S. Ring
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of exercise manuals assume that the reader has a “basic” body (nothing Olympian, but nothing damaged either). As we get older, increasingly few of us fall into the “but nothing damaged either” category!
Here’s where Ring brings to bear his decades of experience as a coach and educator, and also his personal recovery from a serious back injury.
The book covers direct, actionable exercise advice (with all manner of detail), and also offers mental health tips he’s learned along the way.
Ring, like us, is a big fan of keeping things simple, so he focusses on “the core four” of bodyweight exercises:
- Pushups
- Squats
- Lunges
- Planks
These four exercises get a whole chapter devoted to them, though! Because there are ways to make each exercise easier or harder, or have different benefits. For example, adjustments include:
- Body angle
- Points of contact
- Speed
- Pausing
- Range of motion
This, in effect, makes a few square meters of floor (and perhaps a chair or bench) your fully-equipped gym.
As for walking? Ring enjoys and extols the health benefits, and/but also uses his walks a lot for assorted mental exercises, and recommends we try them too.
A fine book for anyone who wants to gain and/or maintain good health, but doesn’t pressingly want to join a gym or start pumping iron!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
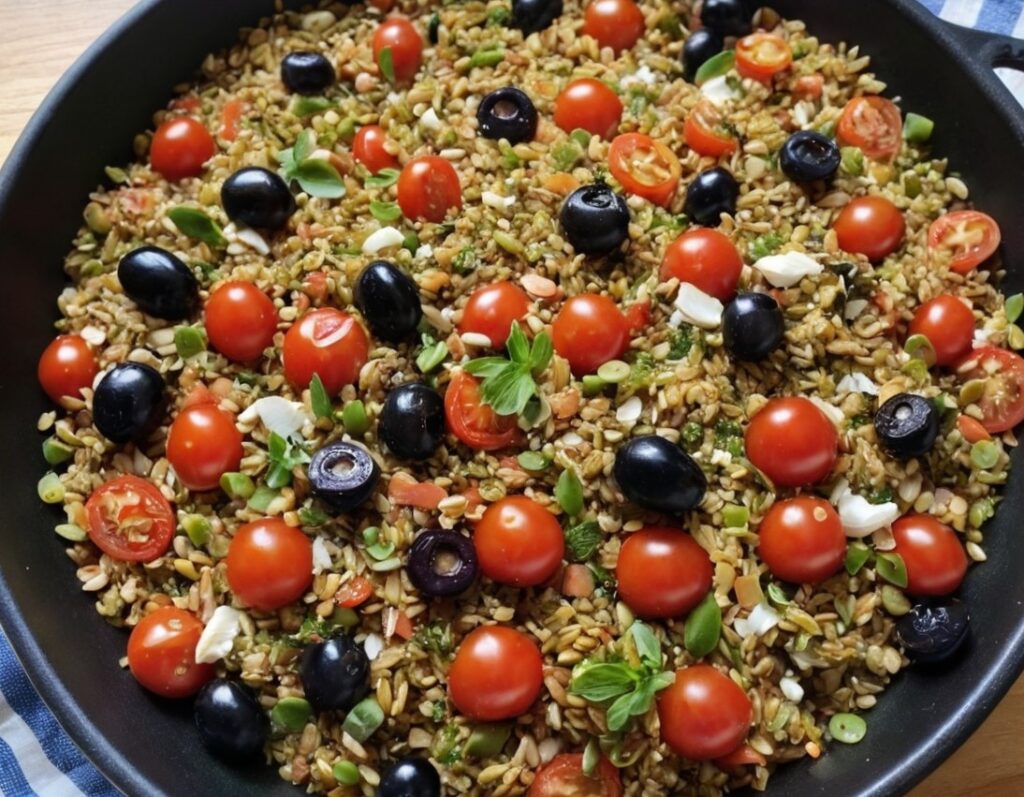
Freekeh Tomato Feast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber-dense freekeh stars in this traditional Palestinian dish, and the whole recipe is very gut-healthy, not to mention delicious and filling, as well as boasting generous amounts of lycopene and other phytonutrients:
You will need
- 1 cup dried freekeh (if avoiding gluten, substitute a gluten-free grain, or pseudograin such as buckwheat; if making such a substitution, then also add 1 tbsp nutritional yeast—for the flavor as well as the nutrients)
- 1 medium onion, thinly sliced
- 1 2oz can anchovies (if vegan/vegetarian, substitute 1 can kimchi)
- 1 14oz can cherry tomatoes
- 1 cup halved cherry tomatoes, fresh
- ½ cup black olives, pitted
- 1 5oz jar roasted peppers, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 sprig fresh thyme
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Place a heavy-based (cast iron, if you have it) sauté pan over a medium heat. Add some olive oil, then the onion, stirring for about 5 minutes.
2) Add the anchovies, herbs and spices (including the garlic), and stir well to combine. The anchovies will probably soon melt into the onion; that’s fine.
3) Add the canned tomatoes (but not the fresh), followed by the freekeh, stirring well again to combine.
4) Add 2 cups boiling water, and simmer with the lid on for about 40 minutes. Stir occasionally and check the water isn’t getting too low; top it up if it’s getting dry and the freekeh isn’t tender yet.
5) Add the fresh chopped cherry tomatoes and the chopped peppers from the jar, as well as the olives. Stir for just another 2 minutes, enough to let the latest ingredients warm through.
6) Serve, adding a garnish if you wish:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Meditation for Fidgety Skeptics – by Dan Harris
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you already meditate regularly, this book isn’t aimed at you (though you may learn a thing or two anyway—this reviewer, who has practiced meditation for the past 30 years, learned a thing!).
However, if you’re—as the title suggests—someone who hasn’t so far been inclined towards meditation, you could get the most out of this one. We’ll say more on this (obviously), but first, there’s one other group that may benefit from this book:
If you have already practiced meditation, and/or already understand and want its benefits, but never really made it stick as a habit.
Now, onto what you’ll get:
- A fair scientific overview of meditation as an increasingly evidence-based way to reduce stress and increase both happiness and productivity
- A good grounding in what meditation is and isn’t
- A how-to guide for building up a consistent meditation habit that won’t get kiboshed when you have a particularly hectic day—or a cold.
- An assortment of very common (and some less common) meditative practices to try
- Some great auxiliary tools to build cognitive restructuring into your meditation
We don’t usually cite other people’s reviews, but we love that one Amazon reviewer wrote:
❝I am 3 weeks into daily meditation practice, and I already notice that I am no longer constantly wishing for undercarriage rocket launchers while driving. I will always think your driving sucks, but I no longer wish you a violent death because of it. Yes, I live in Boston❞
Bottom line: if you’re not already meditating daily, this is definitely a book for you. And if you are, you may learn a thing or two anyway!
Click here to get your copy of Meditation For Fidgety Skeptics from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: