Cucumber Canapés-Crudités
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s time to party with these delicious snacks, which are great as an hors d’œuvre, amuse-bouche, or part of a buffet. And like all our offerings, they’re very healthy too—in this case, especially for the gut and heart!
You will need
- 1 cucumber, sliced
- 1 cup pitted Kalamata olives (or other black olives)
- 1 cup sun-dried tomatoes
- 2 oz feta cheese (or vegan equivalent, or pine nuts)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp fresh basil, chopped
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Make the first topping by combining the olives, half the olive oil, and half the black pepper, into a food processor and blending until it is a coarse pâté.
2) Make the second topping by doing the same with the tomatoes, basil, feta cheese (or substitution), and the other half of the olive oil and black pepper, again until it is a coarse pâté.
3) Assemble the canapés-crudités by topping the cucumber slices alternately with the two toppings, and serve:
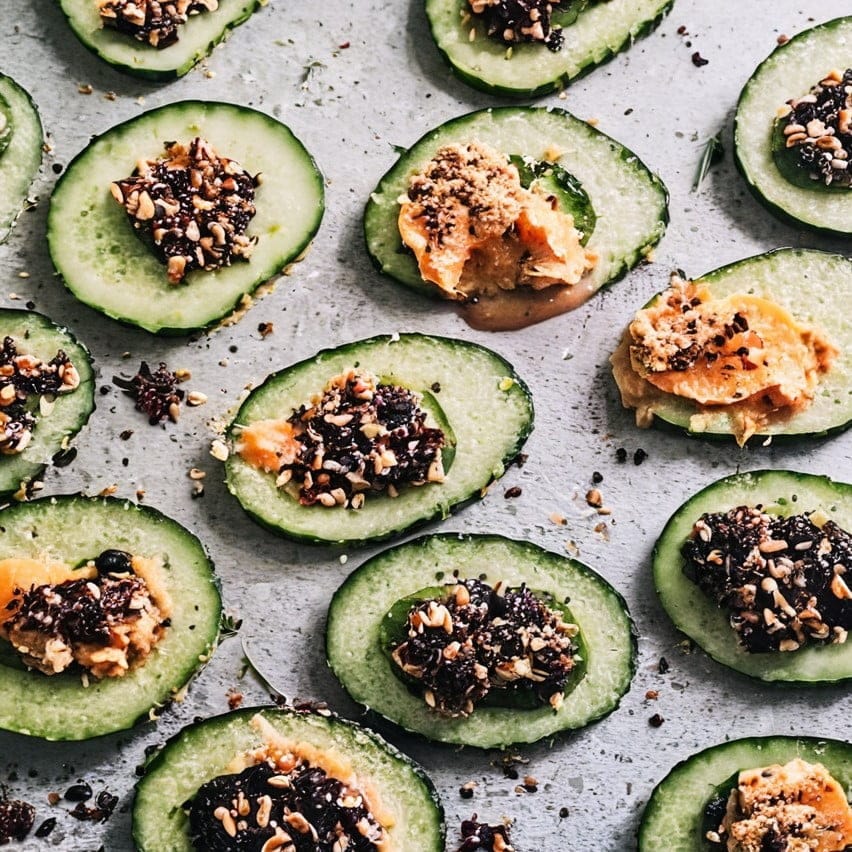

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?! ← yes, you can get this benefit by eating cucumber
- Black Olives vs Green Olives – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess!
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More ← tomatoes are very rich in lycopene
- Herbs for Evidence-Based Health & Healing ←Basil features here
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Blackberries vs Grapes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing blackberries to grapes, we picked the blackberries.
Why?
It’s not even close:
In terms of macros, blackberries have more than 5x the fiber, for about half the carbs, resulting in a notably lower glycemic index. They also have more than 2x the protein, but unlike the fiber, it’s not much in either fruit, so we might disregard it. Still, an easy win for blackberries either way.
In the category of vitamins, blackberries have more of vitamins A, B3, B5, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while grapes have more of vitamins B1, B2, and B6. Another clear win for blackberries.
When it comes to minerals, blackberries have a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while grapes have slightly more manganese and potassium. Once again, blackberries emerge victorious.
Looking at polyphenols, both have an abundance of many polyphenols, but blackberries have more, both in types and in total mass (mg/100g).
Thus, blackberries overwhelmingly win the day, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like:
Can We Drink To Good Health? ← while there are polyphenols such as resveratrol in red wine that per se would boost heart health, there’s so little per glass that you may need 100–1000 glasses per day to get the dosage that provides benefits in mouse studies.
If you’re not a mouse, you might even need more than that!
To this end, many people prefer resveratrol supplementation ← link is to an example product on Amazon, but there are plenty more so feel free to shop around 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
CBD Oil’s Many Benefits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
CBD Oil: What Does The Science Say?
First, a quick legal (and practical) note:
CBD and THC are both derived from the hemp or cannabis plant, but only the latter has euphoriant psychoactive effects, i.e., will get you high. We’re writing here about CBD derived from hemp and not containing THC (thus, will not get you high).
Laws and regulations differ far too much from place to place for us to try to advise here, so please check your own local laws and regulations. And also, while you’re at it, with your doctor and/or pharmacist.
As ever, this newsletter is for purposes of education and enjoyment, and does not constitute any kind of legal (or medical) advice.
With that in mind, onwards to today’s research review…
CBD for Pain Relief
CBD has been popularly touted as a pain relief panacea, and there are a lot of pop-science articles out there “debunking” this, but…
The science seems to back it up. We couldn’t find studies refuting the claim (of CBD as a viable pain relief option). We did, however, find research showing it was good against:
Note that that latter (itself a research review, not a single study, hence covering a lot of bases) describes it matter-of-factly, with no caveats or weasel-words, as:
“CBD, a non-euphoriant, anti-inflammatory analgesic with CB1 receptor antagonist and endocannabinoid modulating effects”
As a quick note: all of the above is about the topical use of CBD oil, not any kind of ingestion
CBD for Anxiety/Depression
There’s a well-cited study with what honestly we think was a bit of a small sample size, but compelling results within that:
A study published in the Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry tested the anxiety levels of 57 men in a simulated public speaking test.
Compared to placebo…
- Those who received 300mg of CBD experienced significantly reduced anxiety during the test.
- Those who received either 150mg or 600mg of CBD experienced more anxiety during the test than the 300mg group
- This means there’s a sweet spot to the dosage
There was also a clinical study that found CBD to have anti-depressant effects.
The methodology was a lot more robust, but the subjects were mice. We can’t have everything in one study, apparently! There is probably a paucity of human volunteers to have their brain slices looked at after tests, though.
Anyway, what makes this study interesting is that it measured quite an assortment of biological markers in the brain, and found that the CBD had a similar physiological effect to the antidepressant imipramine.
CBD for Treating Opioid Addiction
There are a lot of studies for this, both animal and human, but we’d like to put the spotlight on a human study (with the participation of heroin users) that found:
❝Within one week, CBD significantly reduced cravings, anxiety, resting heart rate, and salivary cortisol levels. No serious adverse effects were found.❞
This is groundbreaking because the very thing about heroin is that it’s so addictive and the body rapidly needs more and more of it. You might think “duh”, but most people don’t realize this part:
Heroin is attractive because it offers (and delivers) an immediate guaranteed “downer”, instant relaxation… with none of the bad side effects of, for example, alcohol. No nausea, no hangover, nothing.
The problem is that the body gets tolerant to heroin very quickly, meaning your doses need to get bigger and more frequent to have the same effect.
Before you know it, what seemed like an affordable “self-medication for a stressful life” is very much out of control! Many doctors have personally found this out the hard way.
So, it’s ruinous:
- first to your financial health, as the costs rapidly spiral
- then to your physical health, as you either suffer from withdrawal or eventually overdose
Consequently, heroin is an incredibly easy drug to get hooked onto, and incredibly difficult to get back off.
So CBD offering relief is really a game-changer.
And more…
CBD has been well-studied and found to be effective for a lot of things, more than we could hope to cover in a single edition here.
Some further reading that may interest you includes:
- CBD against Diabetes in mice / in vitro / in humans
- CBD against neurological diseases (in general, in humans)
- CBD against arthritis in mice / in humans
- CBD specifically against the pain of rheumatoid arthritis / of osteoarthritis
Let us know if there’s any of these (or other) conditions you’d like us to look more into the CBD-related research for, because there’s a lot! You can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom
Read (and shop, if you want and it’s permitted where you are):
10 Best CBD Oils of 2023, According to the Forbes Health Advisory Board
Share This Post
-
Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer – by Dr. Patrick Walsh & Janet Farrar Worthington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate cancer is not glamorous or fun, and neither is this book.
Nevertheless, it’s a disease that affects 12% of men in general, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing every year after that.
So, if you have a prostate or love someone who has one, this book is worthwhile reading—yes, even as a preventative.
Like many cancers, prostate cancer is easy to treat if caught very early, becomes harder to treat as it goes, and almost impossible to cure if it gets as far as metastasis (i.e., it spread). Like all cancers, it’s better off avoided entirely if possible.
This book covers all the stages:
- How to avoid it
- How to check for it
- How to “nip it in the bud”
- Why some might want to delay treatment (!)
- What options are available afterwards
This latter is quite extensive, and covers not just surgery, but radiation, thermo- or cryoablation, and hormone therapy.
And as for surgery, not just “remove the tumor”, but other options like radical prostatectomy, and even orchiectomy. Not many men will choose to have their testicles removed to stop them from feeding the prostate, but the point is that this book is comprehensive.
It’s asking whenever possible “is there another option?” and exploring all options, with information and without judgment, at each stage.
The writing style (likely co-author Worthington’s influence; she is an award-winning science-writer) is very “for the layman”, and that’s really helpful in demystifying a lot of what can be quite opaque in the field of oncology.
Bottom line: absolutely not an enjoyable read, but a potentially lifesaving one, especially given the odds we mentioned up top.
Click here to check out Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide To Surviving Prostate Cancer, and be prepared!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Live Life in Crescendo – by Stephen Covey and Cynthia Covey-Haller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Stephen Covey is of course best known for his “7 Habits of Highly Effective People“, while the dozen books he wrote afterwards, not including this one, did not get the same acclaim.
Not including this one, because this one was published posthumously and, notwithstanding the order of the names on the cover, in all likelihood his daughter wrote most of.
And yet! The very spirit of this book is in defiance of 7 Habits being his “early career” magnum opus. We say “early career”, because he was 57 already when that was published, but it was one of his earlier books.
In this work the authors lay out the case for how “your most important work is always ahead of you“, and that it is perfectly possible to “live life in crescendo“, and keep on giving whatever it is that we want to give to the world.
We also learn, mostly through storytelling, of how people are infinitely more important than things, and that it is there that we should put our investments. And that while adversity may not make us stronger, it just means we may need to change our approach, to continue to be productive in whatever way is meaningful to us.
Bottom line: if ever you wonder how your future could live up to your past (in a good way), this is the book to get you thinking.
Click here to check out Live Life in Crescendo, and figure out what your next great work will be!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10almonds Tells The Tea…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s Bust Some Myths!
It’s too late after puberty, hormones won’t change xyz
While yes, many adult trans people dearly wish they’d been able to medically transition before going through the “wrong” puberty, the truth is that a lot of changes will still occur later… even to “unchangeable” things like the skeleton.
The body is remaking itself throughout life, and hormones tell it how to do that. Some parts are just quicker or slower than others. Also: the skeleton is pulled-on constantly by our muscles, and in a battle of muscle vs bone, muscle will always win over time.
Examples of this include:
- trans men building bigger bones to support their bigger muscles
- trans women getting smaller, with wider hips and a pelvic tilt
Trans people have sporting advantages
Assuming at least a year’s cross-sex hormonal treatment, there is no useful advantage to being trans when engaging in a sport. There are small advantages and disadvantages (which goes for any person’s body, really). For example:
- Trans women will tend to be taller than cis women on average…
- …but that larger frame is now being powered by smaller muscles, because they shrink much quicker than the skeleton.
- Trans men taking T are the only athletes allowed to take testosterone…
- …but they will still often be smaller than their fellow male competitors, for example.
Read: Do Trans Women Athletes Have Advantages? (A rather balanced expert overview, which does also cover trans men)
There’s a trans population explosion; it’s a social contagion epidemic!
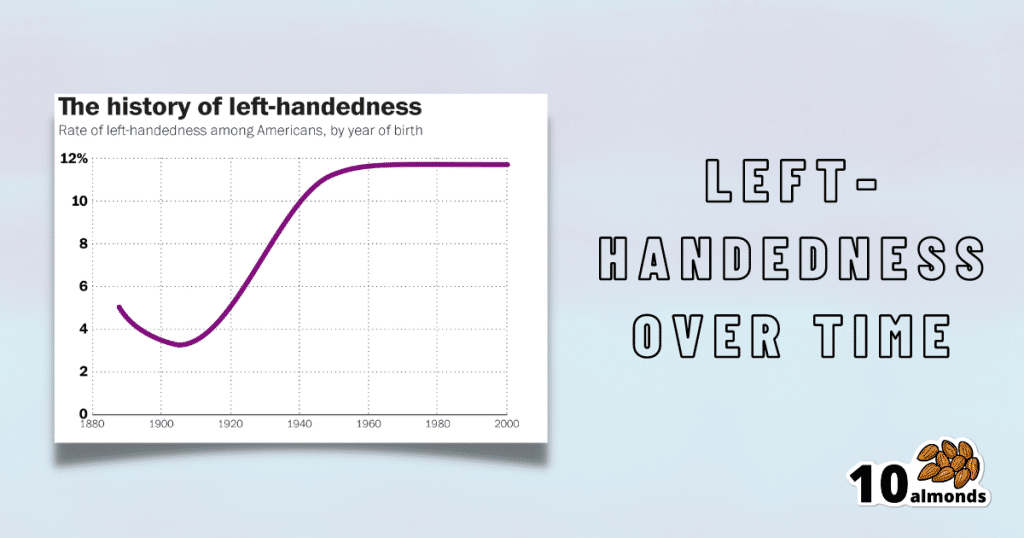
Source for figures: The Overall Rate Of Left-Handedness (Researchgate)
Left-handed people used to make up around 3% of the population… Until the 1920s, when that figure jumped sharply upwards, before plateauing at around 12% in around 1960, where it’s stayed since. What happened?! Simple, schools stopped forcing children to use their right hand.
Today, people ask for trans healthcare because they know it exists! Decades ago, it wasn’t such common knowledge.
The same explanation can be applied to other “population explosions” such as for autism and ADHD.
Fun fact: Mt. Everest was “discovered” in 1852, but scientists suspect it probably existed long before then! People whose ancestors were living on it long before 1852 also agree. Sometimes something exists for a long time, and only comes to wider public awareness later.
Transgender healthcare is too readily available, especially to children!
To believe some press outlets, you’d think:
- HRT is available from school vending machines,
- kids can get a walk-in top surgery at recess,
- and there’s an after-school sterilization club.
In reality, while availability varies from place to place, trans healthcare is heavily gatekept. Even adults have trouble getting it, often having to wait years and/or pay large sums of money… and get permission from a flock of doctors, psychologists, and the like. For those under the age of 18, it’s almost impossible in many places, even with parental support.
Puberty-blockers shouldn’t be given to teenagers, as the effects are irreversible
Quick question: who do you think should be given puberty-blockers? For whom do you think they were developed? Not adults, for sure! They were not developed for trans teens either, but for cis pre-teens with precocious puberty, to keep puberty at bay, to do it correctly later. Nobody argues they’re unsafe for much younger cis children, and only object when it’s trans teens.
They’re not only safe and reversible, but also self-reversing. Stop taking them, and the normally scheduled puberty promptly ensues by itself. For trans kids, the desired effect is to buy the kid time to make an informed and well-considered decision. After all, the effects of the wrong puberty are really difficult to undo!
A lot of people rush medical transition and regret it!
Trans people wish it could be rushed! It’s a lot harder to get gender-affirming care as a trans person, than it is to get the same (or comparable) care as a cis person. Yes, cis people get gender-affirming care, from hormones to surgeries, and have done for a long time.
As for regret… Medical transition has around a 1% regret rate. For comparison, hip replacement has a 4.8% regret rate and knee replacement has a 17.1% regret rate.
A medical procedure with a 99% success rate would generally be considered a miracle cure!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Feel Great, Lose Weight – by Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that losing weight sustainably tends to be harder than simply losing weight. We know that weight loss needs to come with lifestyle change. But how to get there?
One of the biggest problems that we might face while trying to lose weight is that our “metabolic thermostat” has got stuck at the wrong place. Trying to move it just makes our bodies think we are starving, and everything gets even worse. We can’t even “mind over matter” our way through it with willpower, because our bodies will do impressive things on a cellular level in an attempt to save us… Things that are as extraordinary as they are extraordinarily unhelpful.
Dr. Rangan Chatterjee is here to help us cut through that.
In this book, he covers how our metabolic thermostat got stuck in the wrong place, and how to gently tease it back into a better position.
Some advices won’t be big surprises—go for a whole foods diet, avoiding processed food, for example. Probably not a shocker.
Others are counterintuitive, but he explains how they work—exercising less while moving more, for instance. Sounds crazy, but we assure you there’s a metabolic explanation for it that’s beyond the scope of this review. And there’s plenty more where that came from, too.
Bottom line: if your weight has been either slowly rising, or else very stable but at a higher point than you’d like, Dr. Chatterjee can help you move the bar back to where you want it—and keep it there.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: