Cross That Bridge – by Samuel J. Lucas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Books of this genre usually have several chapters of fluff before getting to the point. You know the sort:
- Let me tell you about some cherry-picked celebrity stories that overlook survivorship bias
- Let me tell you my life story, the bad parts
- My life story continued, the good parts now
- What this book can do for you, an imaginative pep talk that keeps circling back to me
…then there will be two or three chapters of the actual advertised content, and then a closing chapter that’s another pep talk.
This book, in contrast, throws that out of the window. Instead, Lucas provides a ground-up structure… within which, he makes a point of giving value in each section:
- exercises
- summaries
- actionable advice
For those who like outlines, lists, and overviews (as we do!), this is perfect. There are also plenty of exercises to do, so for those who like exercises, this book will be great too!
Caveat: occasionally, the book’s actionable advices are direct but unclear, for example:
- Use the potential and power of tea, to solve problems
Context: there was no context. This was a bullet-pointed item, with no explanation. It was not a callback to anything earlier; this is the first (and only) reference to tea.
However! The book as a whole is a treasure trove of genuine tips, tools, and voice-of-experience wisdom. Occasional comments may leave you scratching your head, but if you take value from the rest, then the book was already more than worth its while.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are Electrolyte Supplements Worth It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When To Take Electrolytes (And When We Shouldn’t!)
Any sports nutrition outlet will sell electrolyte supplements. Sometimes in the form of sports drinks that claim to be more hydrating than water, or tablets that can be dissolved in water to make the same. How do they work, and should we be drinking them?
What are electrolytes?
They’re called “electrolytes” because they are ionized particles (so, they have a positive or negative electrical charge, depending on which kind of ion they are) that are usually combined in the form of salts.
The “first halves” of the salts include:
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
The “second halves” of the salts include:
- Chloride
- Phosphate
- Bicarbonate
- Nitrate
It doesn’t matter too much which way they’re combined, provided we get what we need. Specifically, the body needs them in a careful balance. Too much or too little, and bad things will start happening to us.
If we live in a temperate climate with a moderate lifestyle and a balanced diet, and have healthy working kidneys, usually our kidneys will keep them all in balance.
Why might we need to supplement?
Firstly, of course, you might have a dietary deficiency. Magnesium deficiency in particular is very common in North America, as people simply do not eat as much greenery as they ideally would.
But, also, you might sweat out your electrolytes, in which case, you will need to replace them.
In particular, endurance training and High Intensity Interval Training are likely to prompt this.
However… Are you in a rush? Because if not, you might just want to recover more slowly:
❝Vigorous exercise and warm/hot temperatures induce sweat production, which loses both water and electrolytes. Both water and sodium need to be replaced to re-establish “normal” total body water (euhydration).
This replacement can be by normal eating and drinking practices if there is no urgency for recovery.
But if rapid recovery (<24 h) is desired or severe hypohydration (>5% body mass) is encountered, aggressive drinking of fluids and consuming electrolytes should be encouraged to facilitate recovery❞
Source: Fluid and electrolyte needs for training, competition, and recovery
Should we just supplement anyway, as a “catch-all” to be sure?
Probably not. In particular, it is easy to get too much sodium in one’s diet, let alone by supplementation.And, oversupplementation of calcium is very common, and causes its own health problems. See:
To look directly to the science on this one, we see a general consensus amongst research reviews: “this is complicated and can go either way depending on what else people are doing”:
- Trace minerals intake: risks and benefits for cardiovascular health
- Electrolyte minerals intake and cardiovascular health
Well, that’s not helpful. Any clearer pointers?
Yes! Researchers Latzka and Mountain put together a very practical list of tips. Rather, they didn’t put it as a list, but the following bullet points are information extracted directly from their abstract, though we’ve also linked the full article below:
- It is recommended that individuals begin exercise when adequately hydrated.
- This can be facilitated by drinking 400 mL to 600 mL of fluid 2 hours before beginning exercise and drinking sufficient fluid during exercise to prevent dehydration from exceeding 2% body weight.
- A practical recommendation is to drink small amounts of fluid (150-300 mL) every 15 to 20 minutes of exercise, varying the volume depending on sweating rate.
- During exercise lasting less than 90 minutes, water alone is sufficient for fluid replacement
- During prolonged exercise lasting longer than 90 minutes, commercially available carbohydrate electrolyte beverages should be considered to provide an exogenous carbohydrate source to sustain carbohydrate oxidation and endurance performance.
- Electrolyte supplementation is generally not necessary because dietary intake is adequate to offset electrolytes lost in sweat and urine; however, during initial days of hot-weather training or when meals are not calorically adequate, supplemental salt intake may be indicated to sustain sodium balance.
Source: Water and electrolyte requirements for exercise
Bonus tip:
We’ve talked before about the specific age-related benefits of creatine supplementation, but if you’re doing endurance training or HIIT, you might also want to consider a creatine-electrolyte combination sports drink (even if you make it yourself):
Where can I get electrolyte supplements?
They’re easy to find in any sports nutrition store, or you can buy them online; here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience
You can also opt for natural and/or homemade electrolyte drinks:
Healthline | 8 Healthy Drinks Rich in Electrolytes
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Little Treatments, Big Effects – by Dr. Jessica Schleider
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author, a clinical psychologist, discusses how mental healthcare has come a very long way, yet still has a long way to go. While advocating for top-down reforms, she does have a stopgap solution:
Find ways to significantly improve people’s mental health in a single-session intervention.
This seems like a tall order, but her method is based on good science, and also, most people will agree from experience that big changes can happen to someone in the space of moments, at pivotal turning points in life—they just have to be the right moments.
Dr. Schleider recommends that therapists train in (and then offer) this method, but she does also give comprehensive advice for self-therapy of this kind too.
These self-therapy directions, ways to induce those life-pivoting moments for the better, are perhaps the greatest value that the book gives us.
Bottom line: if you’d like a lot of the benefits of therapy without getting therapy, this book can definitely point you in the right direction, in a manner that won’t be a drain on your time or your wallet.
Share This Post
-
Reduce Caffeine’s Impact on Kidneys
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Avid coffee drinker so very interested in the results Also question Is there something that you could take or eat that would prevent the caffeine from stimulating the kidneys? I tried to drink decaf from morning to night not a good result! Thanks❞
That is a good question! The simple answer is “no” (but keep reading, because all is not lost)
There’s no way (that we yet know of) to proof the kidneys against the stimulating effect of caffeine. This is especially relevant because part of caffeine’s stimulating effect is noradrenergic, and that “ren” in the middle there? It’s about the kidneys. This is just because the adrenal gland is situated next to them (actually, it’s pretty much sitting on top of them), hence the name, but it does mean that the kidneys are about the hardest thing in the body to have not effected by caffeine.
However! The effects of caffeine in general can be softened a little with l-theanine (found in tea, or it can be taken as a supplement). It doesn’t stop it from working, but it makes the curve of the effect a little gentler, and so it can reduce some unwanted side effects.
You can read more about l-theanine here:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How To Get Your First Pull-Up
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pull-ups are a great compound exercise that works most of the upper body. However, it can be frustrating for many, if unable to do more than dangle and struggle while not going anywhere. That’s not actually bad, by the way! Of course it’s not great athletic performance, but in terms of exercise, “dangling and struggling while not going anywhere” is an isometric exercise that has plenty of benefits of its own. However, for those who would rather go up in the world, personal trainer Meg Gallagher shows the way:
The Only Way Is Up?
Gallagher offers a few methods; the first is simply an improvement on the “dangling and struggling while not going anywhere” method, but doing it with good form. It’s called the…
Hollow body hold:
- Hang from the bar with legs and feet together.
- Maintain a posterior pelvic tilt (i.e. don’t let your hips roll forwards, and don’t let your butt stick out more than is necessary by mere virtue of having a butt)
- Engage your core by shortening the space between your ribs and pelvis.
- Turn on your abs and lats, with your head slightly behind the bar.
- Practice the hollow body hang instead of dead hangs to build grip and core strength.
Another method is now moving on from the hollow body hold, and shows that in fact, up is not the only way. It’s called…
Negative pull-ups:
- Jump up to get your chin over the bar, then slowly lower yourself in a controlled manner.
- Prioritize negative pull-ups over other exercises to build strength.
- You can use modifications like resistance bands or feet assistance if necessary to extend the duration of your negative pull-up, but these are “crutches”, so try to move on from them as soon as you reasonably can—same if your gym has an “assisted pull-up” machine, consisting of a moving platform with a variable counterweight, mimicking how a pull-up would feel if your body were lighter.
- Practice resisting throughout the entire range of motion.
To give a sense of direction, Gallagher offers the following program:
- On day 1, test how long you can resist the negative pull-up (e.g., 10 seconds).
- For each session, multiply your time by 2 (e.g., 10 seconds × 2 = 20 seconds total).
- Break the total volume into as many sets as needed (e.g., 2 sets of 10 seconds or 4 sets of 5 seconds).
- After each session, add 2 seconds to the total volume for the next session.
- Aim for 3 sessions per week for 3–4 weeks, increasing by 2 seconds each session.
- When you reach about 25 seconds, you should be close to performing your first pull-up.
For more on all of this, plus a few other things to try, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong?
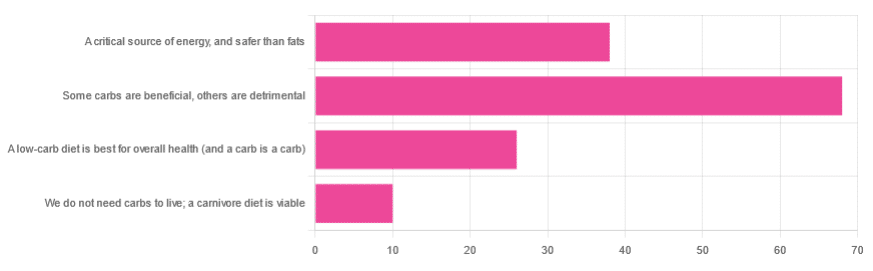
We asked you for your health-related view of carbs, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses
- About 48% said “Some carbs are beneficial; others are detrimental”
- About 27% said “Carbs are a critical source of energy, and safer than fats”
- About 18% said “A low-carb diet is best for overall health (and a carb is a carb)”
- About 7% said “We do not need carbs to live; a carnivore diet is viable”
But what does the science say?
Carbs are a critical source of energy, and safer than fats: True or False?
True and False, respectively! That is: they are a critical source of energy, and carbs and fats both have an important place in our diet.
❝Diets that focus too heavily on a single macronutrient, whether extreme protein, carbohydrate, or fat intake, may adversely impact health.❞
Source: Low carb or high carb? Everything in moderation … until further notice
(the aforementioned lead author Dr. de Souza, by the way, served as an external advisor to the World Health Organization’s Nutrition Guidelines Advisory Committee)
Some carbs are beneficial; others are detrimental: True or False?
True! Glycemic index is important here. There’s a big difference between eating a raw carrot and drinking high-fructose corn syrup:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
While some say grains and/or starchy vegetables are bad, best current science recommends:
- Eat some whole grains regularly, but they should not be the main bulk of your meal (non-wheat grains are generally better)
- Starchy vegetables are not a critical food group, but in moderation they are fine.
To this end, the Mediterranean Diet is the current gold standard of healthful eating, per general scientific consensus:
A low-carb diet is best for overall health (and a carb is a carb): True or False?
True-ish and False, respectively. We covered the “a carb is a carb” falsehood earlier, so we’ll look at “a low-carb diet is best”.
Simply put: it can be. One of the biggest problems facing the low-carb diet though is that adherence tends to be poor—that is to say, people crave their carby comfort foods and eat more carbs again. As for the efficacy of a low-carb diet in the context of goals such as weight loss and glycemic control, the evidence is mixed:
❝There is probably little to no difference in weight reduction and changes in cardiovascular risk factors up to two years’ follow-up, when overweight and obese participants without and with T2DM are randomised to either low-carbohydrate or balanced-carbohydrate weight-reducing diets❞
Source: Low-carbohydrate versus balanced-carbohydrate diets for reducing weight and cardiovascular risk
❝On the basis of moderate to low certainty evidence, patients adhering to an LCD for six months may experience remission of diabetes without adverse consequences.
Limitations include continued debate around what constitutes remission of diabetes, as well as the efficacy, safety, and dietary satisfaction of longer term LCDs❞
~ Dr. Joshua Goldenberg et al.
Source: Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission
❝There should be no “one-size-fits-all” eating pattern for different patient´s profiles with diabetes.
It is clinically complex to suggest an ideal percentage of calories from carbohydrates, protein and lipids recommended for all patients with diabetes.❞
Source: Current Evidence Regarding Low-carb Diets for The Metabolic Control of Type-2 Diabetes
We do not need carbs to live; a carnivore diet is viable: True or False?
False. For a simple explanation:
The Carnivore Diet: Can You Have Too Much Meat?
There isn’t a lot of science studying the effects of consuming no plant products, largely because such a study, if anything other than observational population studies, would be unethical. Observational population studies, meanwhile, are not practical because there are so few people who try this, and those who do, do not persist after their first few hospitalizations.
Putting aside the “Carnivore Diet” as a dangerous unscientific fad, if you are inclined to meat-eating, there is some merit to the Paleo Diet, at least for short-term weight loss even if not necessarily long-term health:
What’s The Real Deal With The Paleo Diet?
For longer-term health, we refer you back up to the aforementioned Mediterranean Diet.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer – by Dr. Patrick Walsh & Janet Farrar Worthington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate cancer is not glamorous or fun, and neither is this book.
Nevertheless, it’s a disease that affects 12% of men in general, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing every year after that.
So, if you have a prostate or love someone who has one, this book is worthwhile reading—yes, even as a preventative.
Like many cancers, prostate cancer is easy to treat if caught very early, becomes harder to treat as it goes, and almost impossible to cure if it gets as far as metastasis (i.e., it spread). Like all cancers, it’s better off avoided entirely if possible.
This book covers all the stages:
- How to avoid it
- How to check for it
- How to “nip it in the bud”
- Why some might want to delay treatment (!)
- What options are available afterwards
This latter is quite extensive, and covers not just surgery, but radiation, thermo- or cryoablation, and hormone therapy.
And as for surgery, not just “remove the tumor”, but other options like radical prostatectomy, and even orchiectomy. Not many men will choose to have their testicles removed to stop them from feeding the prostate, but the point is that this book is comprehensive.
It’s asking whenever possible “is there another option?” and exploring all options, with information and without judgment, at each stage.
The writing style (likely co-author Worthington’s influence; she is an award-winning science-writer) is very “for the layman”, and that’s really helpful in demystifying a lot of what can be quite opaque in the field of oncology.
Bottom line: absolutely not an enjoyable read, but a potentially lifesaving one, especially given the odds we mentioned up top.
Click here to check out Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide To Surviving Prostate Cancer, and be prepared!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: