Cottage cheese is back and all over TikTok. Two dietitians explain why social media’s obsessed
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You might remember cottage cheese from your childhood. Back then, it was considered “diet food”. You ate it out of the tub, with celery or spread it on crackers for a low-calorie snack. Then cottage cheese went out of fashion.
But cottage cheese is having a resurgence. In recent months, Google searches for “cottage cheese” have risen to the highest levels since 2004.
Social media influencers have been promoting its benefits on TikTok and Instagram with hashtags such as #cottagecheese, #cottagecheeseforlife, and #cottagecheeserecipe. Sales of cottage cheese around the world have skyrocketed.
Let’s see why cottage cheese is having such a moment.
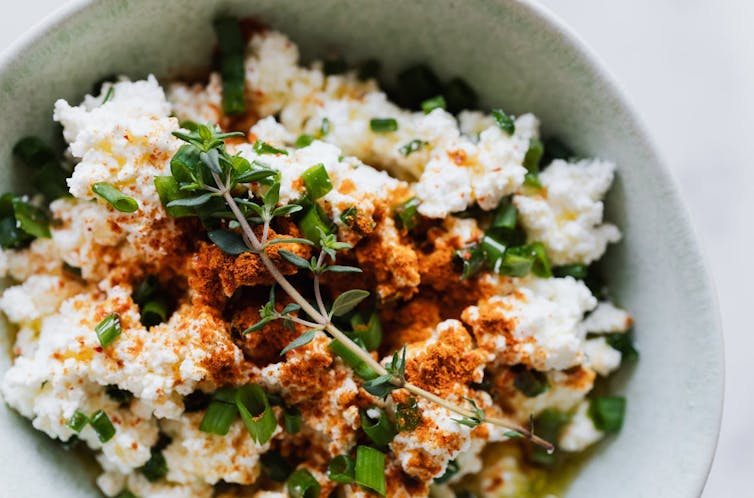

What is cottage cheese?
Cottage cheese is a fresh dairy cheese product with a mild flavour and a slightly tangy taste. It is made by curdling cow’s milk, then draining the whey, leaving behind the curds. These curds are usually small and lumpy, and the texture can vary from creamy to dry, depending on the amount of whey left in the cheese.
The term “cottage cheese” is said to have originated because the cheese was generally made in cottage-type houses from leftover milk, after making butter.
Cottage cheese is cheap, costing about A$12 per kilogram in the supermarket, similar to ricotta cheese.
It’s also surprisingly simple to make at home using freely available recipes. All you need is milk, salt and a splash of vinegar.
We’re using cottage cheese in new ways
It’s difficult to know what started the latest cottage cheese trend. But the creativity of social media means people are sharing alternative ways to use cottage cheese, changing people’s views from it being boring and lacking flavour to it being versatile and healthy.
People are spreading cottage cheese on toast and using it to make dishes such as porridge, dips, salads, bread and flatbreads. They’re using it in cakes and scones, and in desserts such as mousse and ice cream.
Is cottage cheese healthy?
Compared with other cheeses, cottage cheese is low in fat and therefore energy (kilojoules or kJ). This makes it a smart choice for people looking to cut down on their daily energy intake.
For example, 100 grams of cottage cheese contains about 556kJ. The same amount of cheddar contains 1,254kJ and parmesan 1,565kJ.
Many cheeses are rich in protein but they often contain higher amounts of kilojoules due to their fat content. But cottage cheese has substantial amounts of protein with fewer kilojoules.
This makes cottage cheese an ideal option for people aiming to maximise their protein intake without eating large amounts of kilojoules.
Some 100g of cottage cheese provides 17g protein. This is about the same found in three eggs, 60g chicken breast or 320 millilitres (about 300g) full-fat yoghurt.

Cottage cheese also contains high levels of vitamin B12 (important for healthy brain function), riboflavin (supports healthy skin and eyes), phosphorus (helps build strong bones and teeth) and folate (essential for cell growth).
However, cottage cheese is lower in calcium compared with other cheeses. It contains just 89 milligrams per 100g. This compares with parmesan (948mg), haloumi (620mg) and ricotta (170mg).
You’ve convinced me. How can I use cottage cheese?
Beyond its excellent nutrition profile, the resurgence of cottage cheese is enabling people to experiment in the kitchen. Its neutral flavour and varied textures – ranging from smooth to chunky – makes it suitable for a range of dishes, from sweet to savoury.
TikTok and Instagram have some great recipes. You could start with an old faithful recipe of celery and cottage cheese, and work your way towards new options such as cottage cheese ice cream.
The healthiest recipes will be those that combine cottage cheese with wholefoods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, and lean protein sources.
For instance, you can make a cottage cheese wrap then fill it with vegetables and a lean source of protein (such as chicken or fish).
Other combinations include cottage cheese salad dressings, vegetable dips and egg salads.
Cottage cheese’s rise in popularity is well deserved. Including more cottage cheese in your diet is a smart choice for getting a high dose of protein without adding processed ingredients or too much energy. Embrace the trend and get creative in the kitchen.
Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland and Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Makkō-Hō – by Haruka Nagai
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve all heard the claims, “Fluent in 3 Months!”, “Russian in Two Weeks!”, “Overnight Mandarin Chinese”, “15-Minute Arabic!”, “Instant Italian!”.
We see the same in the world of health and fitness too. So how does this one’s claim of “five minutes’ physical fitness” hold up?
Well, it is 5 minutes per day. And indeed, the author writes:
❝The total time [to do these exercises], then, is only one minute and thirty seconds. This series I call one round. When it has been completed, execute another complete round. You should find the exercises easier to do the second time. Executed this way, the exercsies will prove very effective, though they take only three minutes in all. After you have leaned back into the final position, you must remain in that posture for one minute. That brings the total time to four minutes. Even when [some small additions] are added, it takes only five minutes at most.❞
The exercises themselves are from makkō-hō, which is a kind of Japanese dynamic yoga. They involve repetitions of (mostly) moving stretches with good form, and are excellent for mobility and general health, keeping us supple and robust as we get older.
The text descriptions are clear, as are the diagrams and photos. The language is a little dated, as this book was written in the 1970s, but the techniques themselves are timeless.
Bottom line: consider it a 5-minute anti-aging regimen. And, as Nagai says, “the person who cannot find 5 minutes out of 24 hours, was never truly interested in their health”.
Click here to check out Makkō-Hō and schedule your five minutes!
Share This Post
-
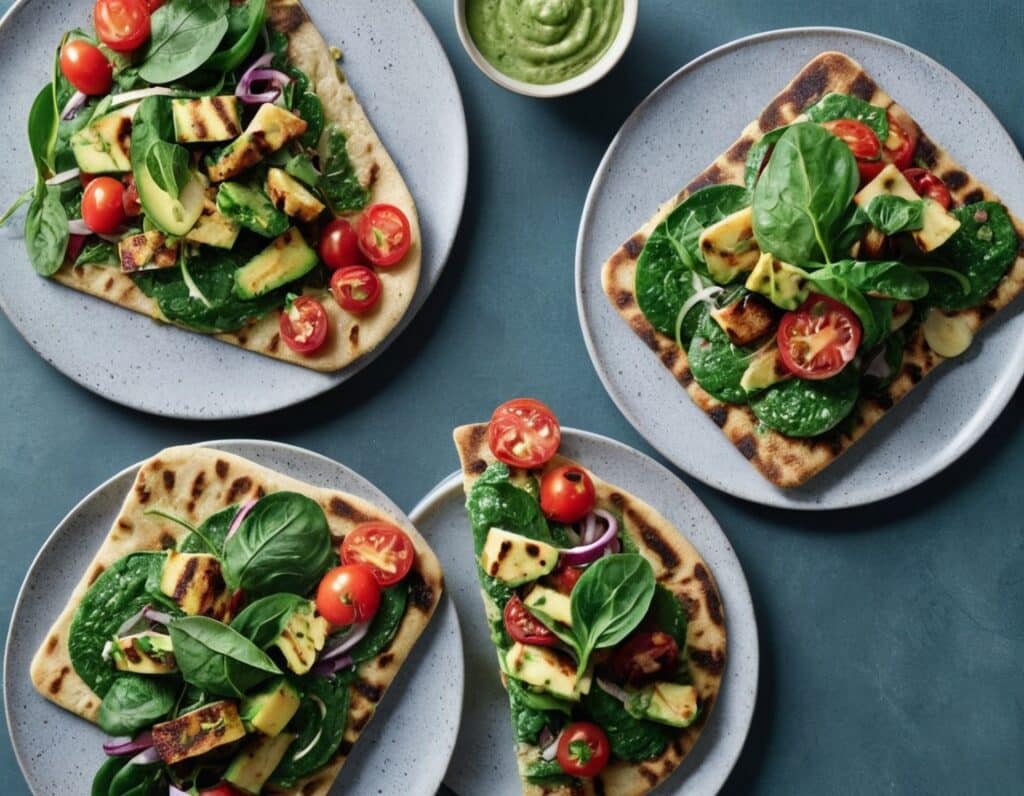
Green Paneer Flatbreads
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These are versatile little snacks that can be eaten alone or served as part of a buffet; great for warm summer nights!
You will need
- 1 lb block of paneer (you can also use our plant-based high-protein paneer recipe)
- 7 oz unsweetened yogurt (your choice what kind; plant-based is fine; live cultured is best)
- 1 tomato, thinly sliced
- ½ red onion, thinly sliced
- 2 oz spinach leaves
- 1 tbsp lime juice
- 1 tsp red chili powder
- 4 wholewheat flatbreads
And then the marinade:
- 3 oz spinach
- ½ bulb garlic
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp coriander seeds
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt (MSG being the preferable and healthier option)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- Juice of ½ lime
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the marinade ingredients in a blender.
2) Cut the paneer into long cuboid chapes (similar to fish fingers) and put them in a bowl. Pour ⅔ of the marinade over them, and gently mix to coat evenly.
3) Heat a ridged griddle pan, and when hot, add the paneer and cook for 1–2 minutes each side without stirring, jiggling, or doing anything other than turning once per uncooked side.
4) Combine the onion, tomato, spinach leaves, lime choice, and chili powder to make the salad.
5) Add the remaining marinade to the yogurt to make a green dip.
6) Toast your flatbreads under the grill.
5) Assemble, putting the paneer and salad with a spoonful of the dip on the flatbread, and serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- High-Protein Plant-Based Paneer
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
No Time to Panic – by Matt Gutman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Matt Gutman is not a doctor or a psychologist. He’s a journalist, accustomed to asking questions and then asking more probing questions, unrelenting until he gets the answers he’s looking for.
This book is the result of what happened when he needed to overcome his own anxiety and panic attacks, and went on an incisive investigative journey.
The style is as clear and accessible as you’d expect of a journalist, and presents a very human exploration, nonetheless organized in a way that will be useful to the reader.
It’s said that “experience is a great teacher, but she sends hefty bills”. In this case as in many, it’s good to learn from someone else’s experience!
By the end of the book, you’ll have a good grounding in most approaches to dealing with anxiety and panic attacks, and an idea of efficacy/applicability, and what to expect.
Bottom line: without claiming any magic bullet, this book presents six key strategies that Gutman found to work, along with his experiences of what didn’t. Valuable reading if you want to curb your own anxiety, or want to be able to help/support someone else with theirs.
Click here to check out No Time To Panic, and find the peace you deserve!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
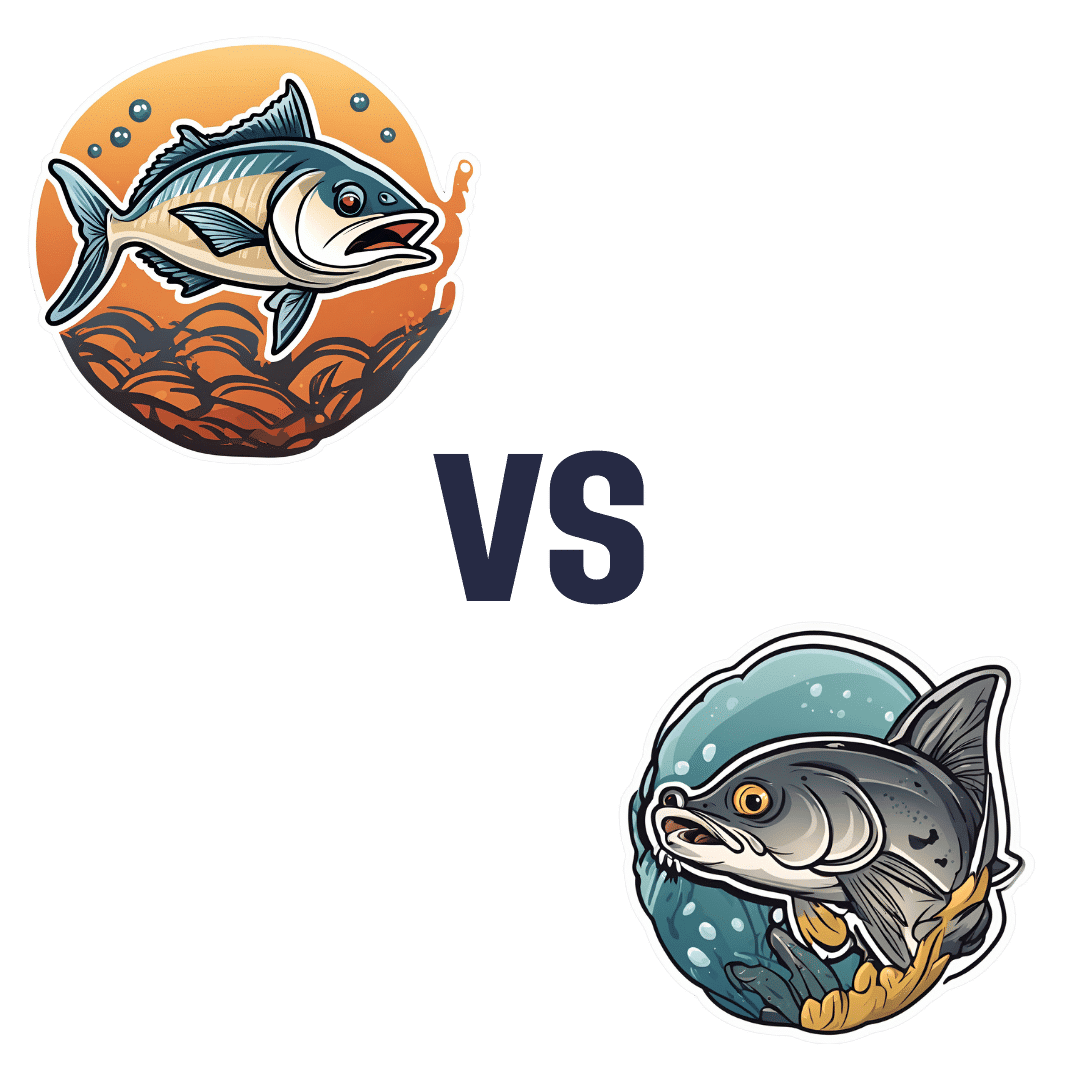
Tuna vs Catfish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tuna to catfish, we picked the tuna.
Why?
Today in “that which is more expensive and/or harder to get is not necessarily healthier”…
Looking at their macros, tuna has more protein and less fat (and overall, less saturated fat, and also less cholesterol).
In the category of vitamins, both are good but tuna distinguishes itself: tuna has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, and D, while catfish has more of vitamins B5, B9, B12, E, and K. They are both approximately equal in choline, and as an extra note in tuna’s favor (already winning 6:5), tuna is a very good source of vitamin D, while catfish barely contains any. All in all: a moderate, but convincing, win for tuna.
When it comes to minerals, things are clearer still: tuna has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while catfish has more calcium, manganese, and zinc. Oh, and catfish is also higher in one other mineral: sodium, which most people in industrialized countries need less of, on average. So, a 6:3 win for tuna, before we even take into account the sodium content (which makes the win for tuna even stronger).
In short: tuna wins the day in every category!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught (It Makes Quite A Difference)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Loneliness Does To Your Brain And Body
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Spoiler: it’s nothing good (but it can be addressed!)
Not something to be ignored
Loneliness raises the risk of heart disease by 29% and the risk of stroke by 32%. It also brings about higher susceptibility to illness (flu, COVID, chronic pain, etc), as well as poor sleep quality and cognitive decline, possibly leading to dementia. Not only that, but it also promotes inflammation, and premature death (comparable to smoking).
This is because the lack of meaningful social connections activates the body’s stress response, which in turn increases paranoia, suspicion, and social withdrawal—which makes it harder to seek the social interaction needed to alleviate it.
On a neurological level, cortisol levels become imbalanced, and a faltering dopamine response leads to impulsive behaviors (e.g., drinking, gambling) to try to make up for it. Decreased serotonin, oxytocin, and natural opioids reduce feelings of happiness and negate pain relief.
As for combatting it, the first-line remedy is the obvious one: connecting with others improves emotional and physical wellbeing. However, it is recommended to aim for deep, meaningful connections that make you happy rather than just socializing for its own sake. It’s perfectly possible to be lonely in a crowd, after all.
A second-line remedy is to simply mitigate the harm by means of such things as art therapy and time in nature—they can’t completely replace human connection, but they can at least improve the neurophysiological situation (which in turn, might be enough of a stop-gap solution to enable a return to human connection).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Quit Drinking – by Rebecca Dolton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many “quit drinking” books focus on tips you’ve heard already—cut down like this, rearrange your habits like that, make yourself accountable like so, add a reward element this way, etc.
Dolton takes a different approach.
She focuses instead on the underlying processes of addiction, so as to not merely understand them to fight them, but also to use them against the addiction itself.
This is not just a social or behavioral analysis, by the way, and goes into some detail into the physiological factors of the addiction—including such things as the little-talked about relationship between addiction and gut flora. Candida albans, found in most if not all humans to some extent, gets really out of control when given certain kinds of sugars (including those from alcohol); it grows, eventually puts roots through the intestinal walls (ouch!) and the more it grows, the more it demands the sugars it craves, so the more you feed it.
Quite a motivator to not listen to such cravings! It’s not even you that wants it, it’s the Candida!
Anyway, that’s just one example; there are many. The point here is that this is a well-researched, well-written book that sets itself apart from many of its genre.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: