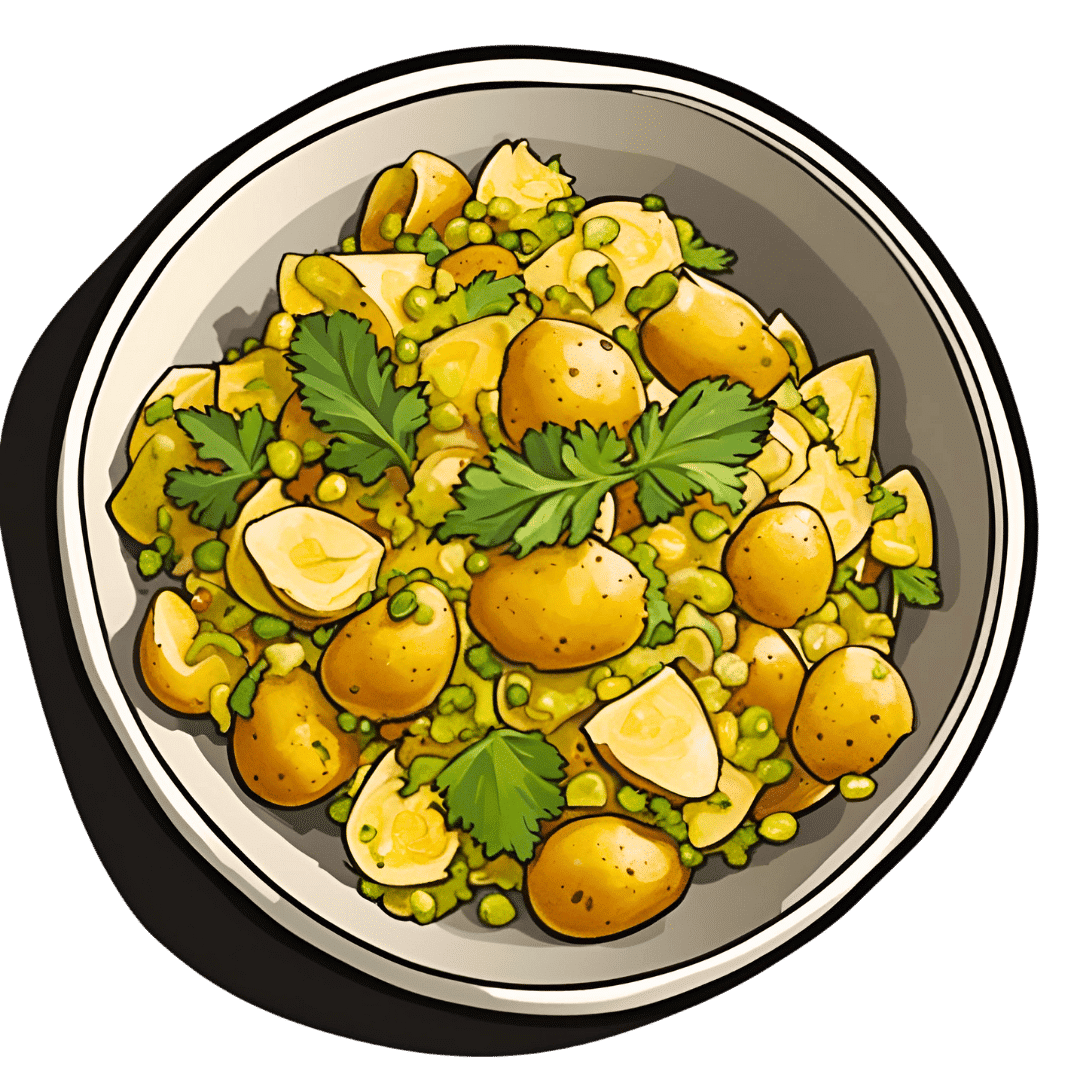
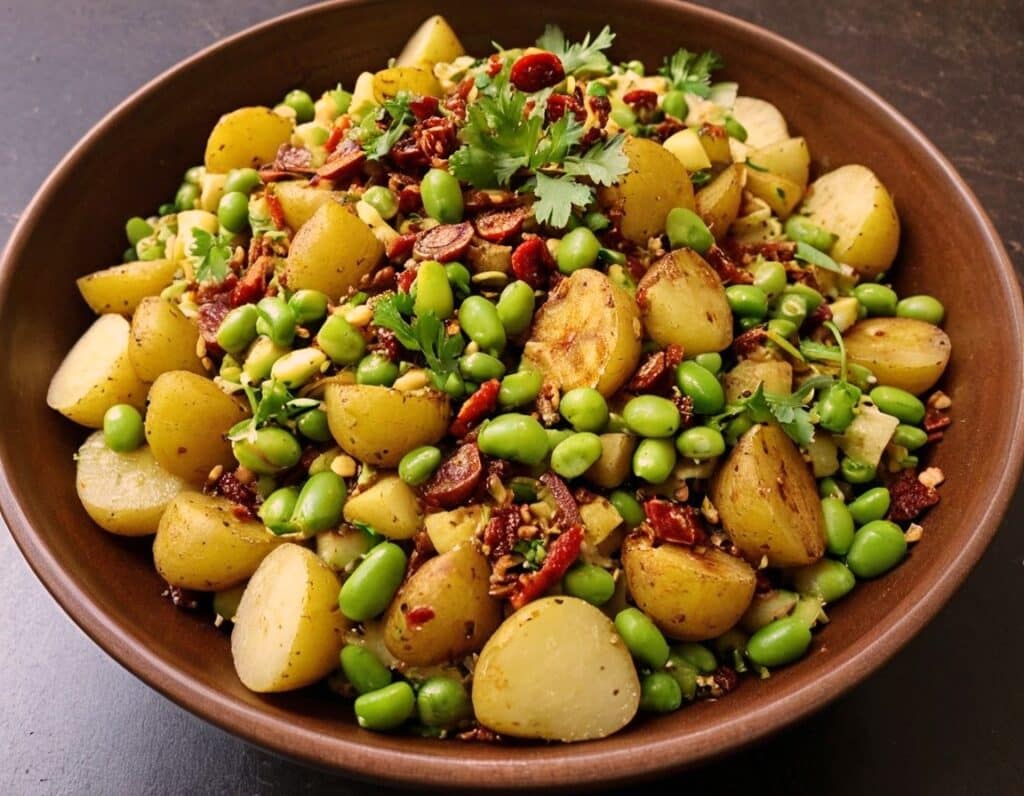
Chaat Masala Spiced Potato Salad With Beans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is an especially gut-healthy dish; the cooked-and-cooled potatoes are not rich with resistant starches (that’s good), the beans bring protein (as well as more fiber and micronutrients), and many of the spices bring their own benefits. A flavorful addition to your table!
You will need
- 1 lb new potatoes, boiled or steamed, with skin on, quartered, cooled ← this is a bit of a “mini recipe”, but we expect you can handle it
- 5 oz blanched broad beans
- 2 oz sun-dried tomatoes, chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp amchoor
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground ginger
- 1 tsp ground asafoetida
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red chili powder
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Juice of ½ lemon
And then…
- To garnish: finely chopped cilantro, or if you have the “cilantro tastes like soap” gene, then substitute with parsley
- To serve: a nice chutney; you can use our Spiced Fruit & Nut Chutney recipe
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix all the ingredients from the main section, ensuring an even distribution on the spices.
2) Add the garnish, and serve with the chutney. That’s it. There was more work in the prep (and potentially, finding all the ingredients) today.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored all five today!
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More ← don’t underestimate those sun-dried tomatoes, either!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How can I stop overthinking everything? A clinical psychologist offers solutions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As a clinical psychologist, I often have clients say they are having trouble with thoughts “on a loop” in their head, which they find difficult to manage.
While rumination and overthinking are often considered the same thing, they are slightly different (though linked). Rumination is having thoughts on repeat in our minds. This can lead to overthinking – analysing those thoughts without finding solutions or solving the problem.
It’s like a vinyl record playing the same part of the song over and over. With a record, this is usually because of a scratch. Why we overthink is a little more complicated.
We’re on the lookout for threats
Our brains are hardwired to look for threats, to make a plan to address those threats and keep us safe. Those perceived threats may be based on past experiences, or may be the “what ifs” we imagine could happen in the future.
Our “what ifs” are usually negative outcomes. These are what we call “hot thoughts” – they bring up a lot of emotion (particularly sadness, worry or anger), which means we can easily get stuck on those thoughts and keep going over them.
However, because they are about things that have either already happened or might happen in the future (but are not happening now), we cannot fix the problem, so we keep going over the same thoughts.
Who overthinks?
Most people find themselves in situations at one time or another when they overthink.
Some people are more likely to ruminate. People who have had prior challenges or experienced trauma may have come to expect threats and look for them more than people who have not had adversities.
Deep thinkers, people who are prone to anxiety or low mood, and those who are sensitive or feel emotions deeply are also more likely to ruminate and overthink.
We all overthink from time to time, but some people are more prone to rumination.
BĀBI/UnsplashAlso, when we are stressed, our emotions tend to be stronger and last longer, and our thoughts can be less accurate, which means we can get stuck on thoughts more than we would usually.
Being run down or physically unwell can also mean our thoughts are harder to tackle and manage.
Acknowledge your feelings
When thoughts go on repeat, it is helpful to use both emotion-focused and problem-focused strategies.
Being emotion-focused means figuring out how we feel about something and addressing those feelings. For example, we might feel regret, anger or sadness about something that has happened, or worry about something that might happen.
Acknowledging those emotions, using self-care techniques and accessing social support to talk about and manage your feelings will be helpful.
The second part is being problem-focused. Looking at what you would do differently (if the thoughts are about something from your past) and making a plan for dealing with future possibilities your thoughts are raising.
But it is difficult to plan for all eventualities, so this strategy has limited usefulness.
What is more helpful is to make a plan for one or two of the more likely possibilities and accept there may be things that happen you haven’t thought of.
Think about why these thoughts are showing up
Our feelings and experiences are information; it is important to ask what this information is telling you and why these thoughts are showing up now.
For example, university has just started again. Parents of high school leavers might be lying awake at night (which is when rumination and overthinking is common) worrying about their young person.
Think of what the information is telling you.
TheVisualsYouNeed/ShutterstockKnowing how you would respond to some more likely possibilities (such as they will need money, they might be lonely or homesick) might be helpful.
But overthinking is also a sign of a new stage in both your lives, and needing to accept less control over your child’s choices and lives, while wanting the best for them. Recognising this means you can also talk about those feelings with others.
Let the thoughts go
A useful way to manage rumination or overthinking is “change, accept, and let go”.
Challenge and change aspects of your thoughts where you can. For example, the chance that your young person will run out of money and have no food and starve (overthinking tends to lead to your brain coming up with catastrophic outcomes!) is not likely.
You could plan to check in with your child regularly about how they are coping financially and encourage them to access budgeting support from university services.
Your thoughts are just ideas. They are not necessarily true or accurate, but when we overthink and have them on repeat, they can start to feel true because they become familiar. Coming up with a more realistic thought can help stop the loop of the unhelpful thought.
Accepting your emotions and finding ways to manage those (good self-care, social support, communication with those close to you) will also be helpful. As will accepting that life inevitably involves a lack of complete control over outcomes and possibilities life may throw at us. What we do have control over is our reactions and behaviours.
Remember, you have a 100% success rate of getting through challenges up until this point. You might have wanted to do things differently (and can plan to do that) but nevertheless, you coped and got through.
So, the last part is letting go of the need to know exactly how things will turn out, and believing in your ability (and sometimes others’) to cope.
What else can you do?
A stressed out and tired brain will be more likely to overthink, leading to more stress and creating a cycle that can affect your wellbeing.
So it’s important to manage your stress levels by eating and sleeping well, moving your body, doing things you enjoy, seeing people you care about, and doing things that fuel your soul and spirit.
Find ways to manage your stress levels.
antoniodiaz/ShutterstockDistraction – with pleasurable activities and people who bring you joy – can also get your thoughts off repeat.
If you do find overthinking is affecting your life, and your levels of anxiety are rising or your mood is dropping (your sleep, appetite and enjoyment of life and people is being negatively affected), it might be time to talk to someone and get some strategies to manage.
When things become too difficult to manage yourself (or with the help of those close to you), a therapist can provide tools that have been proven to be helpful. Some helpful tools to manage worry and your thoughts can also be found here.
When you find yourself overthinking, think about why you are having “hot thoughts”, acknowledge your feelings and do some future-focused problem solving. But also accept life can be unpredictable and focus on having faith in your ability to cope.
Kirsty Ross, Associate Professor and Senior Clinical Psychologist, Massey University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Physical Exercises That Build Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Jim Kwik: from broken brain to brain coach
Image from Kwik Learning This is Jim Kwik. He suffered a traumatic brain injury as a small child, and later taught himself to read and write by reading comic books. He became fascinated with the process of learning, and in his late 20s he set up Kwik Learning, to teach accelerated learning in classrooms and companies, which he continued until 2009 when he launched his online learning platform. His courses have now been enjoyed by people in 195 countries.
So, since accelerated learning is his thing, you might wonder…
What does he have to share that we can benefit from in the next five minutes?
Three brain exercises to improve memory and concentration
A lot of problems we have with working memory are a case of executive dysfunction, but there are tricks we can use to get our brains into gear and make them cumulatively stronger:
First exercise
You can strengthen your corpus callosum (the little bridge between the two hemispheres of the brain) by performing a simple kinesiological exercise, such as alternating touching your left elbow to your right knee, and touching your right elbow to your left knee.
Do it for about a minute, but the goal here is not a cardio exercise, it’s accuracy!
You want to touch your elbow and opposite knee to each other as precisely as possible each time. Not missing slightly off to the side, not falling slightly short, not hitting it too hard.
Second exercise
Put your hands out in front of you, as though you’re about to type at a keyboard. Now, turn your hands palm-upwards. Now back to where they were. Now palm-upwards again. Got it? Good.
That’s not the exercise, the exercise is:
You’re now going to do the same thing, but do it twice as quickly with one hand than the other. So they’ll still be flipping to the same basic “beat”, put it in musical terms, the tempo on one hand will now be twice that of the other. When you get the hang of that, switch hands and do the other side.
This is again about the corpus callosum, but it’s now adding an extra level of challenge because of holding the two rhythms separately, which is also working the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex.
The pre-frontal cortex in particular is incredibly important to executive function, self-discipline, and being able to “do” delayed gratification. So this exercise is really important!
Third exercise
This one works the same features of the brain, but most people find it harder. So, consider it a level-up on the previous:
Imagine there’s a bicycle wheel in front of you (as though the bike is facing you at chest-height). Turn the wheel towards you with your hands, one on each side.
Now, do the same thing, but each of your hands is going in the opposite direction. So one is turning the wheel towards you; the other is turning it away from you.
Now, do the same thing, but one hand goes twice as quickly as the other.
Switch sides.
Why is this harder for most people than the previous? Because the previous involved processing discrete (distinct from each other) movements while this one involves analog continuous movements.
It’s like reading an analog clock vs a digital clock, but while using both halves of your brain, your corpus callosum, your pre-frontal cortex, and the motor cortex too.
Want to learn more?
You might enjoy his book, which as well as offering exercises like the above, also offers a lot about learning strategies, memory processes, and generally building a quicker more efficient brain:
Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life
Share This Post
-
Curious Kids: what are the main factors in forming someone’s personality?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“What are the main factors in forming someone’s personality?” – Emma, age 10, from Shanghai
Hello Emma, and thank you for this very interesting question!
Let’s start by exploring what we mean by personality. Have you noticed no two people are completely alike? We all see, experience, and understand the world in different ways.
For example, some people love spending time with friends and being the centre of attention, whereas other people are more shy and enjoy having time to themselves.
Your unique personality is shaped by your genes as well as various influences in your environment. And your personality plays an important role in how you interact with the world.
The big five
Did you know there are scientists who spend time researching personality? Their research is concerned with describing the ways people differ from each other, and understanding how these differences could be important for other parts of life such as our health and how well we do in school or at work.
There are many different perspectives on personality. A widely accepted viewpoint based on a lot of research is called the five factor model or the “big five”. According to this theory, a great deal of a person’s personality can be summarised in terms of where they sit on five dimensions, called traits:
- the introversion-extraversion trait refers to how much someone is outgoing and social (extroverted) or prefers being with smaller groups of friends or focusing on their own thoughts (introverted)
- agreeableness captures how much someone tends to be cooperative and helps others
- openness to experience refers to how much a person is creative and enjoys experiencing new things
- neuroticism describes a person’s tendency to experience negative feelings, like worrying about things that could go wrong
- conscientiousness encompasses how much a person is organised, responsible, and dedicated to things that are important to them, like schoolwork or training for a sports team.
A person can have high, low, or moderate levels of each of these traits. And understanding whether someone has higher or lower levels of the big five can tell us a lot about how we might expect them to behave in different situations.
So what shapes our personalities?
A number of factors shape our personalities, including our genes and social environment.
Our bodies are made up of many very small structures called cells. Within these cells are genes. We inherit genes from our parents, and they carry the information needed to make our bodies and personalities. So, your personality may be a bit like your parents’ personalities. For example, if you’re an outgoing sort of person who loves to meet new people, perhaps one or both of your parents are very social too.
Our personalities are influenced by the genes we get from our parents.
KieferPix/ShutterstockPersonalities are also affected by our environment, such as our experiences and our relationships with family and friends. For example, some research has shown our relationships with our parents can influence our personality. If we have loving and warm relationships, we may be more agreeable and open. But if our relationships are hurtful or stressful, this may increase our neuroticism.
Another study showed that, over time, young children who were more physically active were less introverted (less shy) and less likely to get very upset when things don’t go their way, compared to children who were less physically active. Although we don’t know why this is for sure, one possible explanation is that playing sport leads to reduced shyness because it introduces children to different people.
While we’re learning more about personality development all the time, research in this area presents quite a few challenges. Many different biological, cultural and environmental influences shape our development, and these factors can interact with each other in complex ways.
Is our personality fixed once we become adults?
Although we develop most of our personality when we are young, and people’s personalities tend to become more stable as they get older, it is possible for aspects of a person’s personality to change, even when they are fully grown.
A good example of this can be seen among people who seek treatment for conditions like anxiety or depression. People who respond well to working with a psychologist can show decreases in neuroticism, indicating they become less likely to worry a lot or feel strong negative feelings when something stressful happens.
Hello, Curious Kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to mailto:[email protected]
Tim Windsor, Professor, Director, Generations Research Initiative, College of Education, Psychology and Social Work, Flinders University and Natalie Goulter, Lecturer, College of Education, Psychology and Social Work, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
15 Easy Japanese Habits That Will Transform Your Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The original title says “no-cost habits”, but in fairness, for most of us food is not usually free (alas). So, we will say “easy” instead, because they are indeed easy to build into your life:
15 Healthy Habits To Adopt
We’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Intermittent fasting: naturally fasting for at least 12 hours overnight improves digestion and sleep quality.
- Fermented foods: regularly consuming fermented foods (like kimchi, or even just sauces like miso and shio koji) supports gut health.
- Rice & legumes over wheat: choosing wholegrain rice as a staple reduces bloating and benefits skin health (lentils are even better).
- Big breakfast, light dinner: eating a heavier breakfast and a lighter dinner gives energy in the morning and allows digestion to rest at night.
- Balancing indulgences: enjoying social meals without guilt and balancing food intake the next day.
- Daily gentle exercise: doing at least 15 minutes of yoga, Pilates, or light walking for long-term health.
- Daily baths: taking a warm bath boosts blood circulation and relaxation.
- Eating seasonal & diverse foods: including a variety of fresh, seasonal ingredients for balanced nutrition.
- Consistent morning routine: waking up at the same time, cleansing and moisturizing, and having a proper breakfast.
- Enjoying soup with meals: consuming nutrient-rich soups with vegetables and protein to prevent overeating.
- Chewing food thoroughly: eating slowly and chewing well aids digestion and enhances enjoyment.
- Light seasoning in food: avoiding overly salty or flavorful meals to appreciate natural tastes.
- Maintaining good posture: paying attention to posture during daily activities for better overall health.
- Prioritizing protein intake: eating protein-rich foods like tofu, beans, eggs, and fish, to maintain skin firmness as well as muscletone.
- Confidence in aging: focusing on internal well-being over external opinions and embracing health at every age.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Water: For Health, for Healing, for Life – by Dr. Fereydoon Batmanghelidj
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Notwithstanding the cover’s declaration of “you’re not sick, you’re thirsty”, in fact this book largely makes the argument that both are often the case simultaneously, and that dehydration plays a bigger role in disease pathogenesis and progression than it is credited for.
You may be wondering: is this 304 pages to say “drink some water”?
And the answer is: yes, somewhat. However, it also goes into detail of how and why it is relevant in each case, which means that there will be, once you have read this, more chance of your dehydrated and thus acutely-less-functional brain going “oh, I remember what this is” rather than just soldiering on dehydrated because you are too dehydrated to remember to hydrate.
The strength of the book really is in motivation; understanding why things happen the way they do and thus why they matter, is a huge part of then actually being motivated to do something about it. And let’s face it, a “yes, I will focus on my hydration” health kick is typically sustained for less time than many more noticeable (e.g. diet and exercise) healthy lifestyle adjustments, precisely because there’s less there to focus on so it gets forgotten.
The style is a little dated (the book is from 2003, and the style feels like it is from the 80s, which is when the author was doing most of his research, before launching his first book, which we haven’t read-and-reviewed yet, in 1992) but perfectly clear and pleasant to read.
Bottom line: this book may well get you to actually drink more water
Click here to check out Water: For Health, for Healing, for Life, and get hydrating!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Love Changes Your Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When we fall in love, have a romantic attachment, or have a sad breakup, there’s a lot going on neurochemically, and also with different parts of the brain taking the wheel. Dr. Shannon Odell explains:
The neurochemistry of love
Of course, not every love will follow this exact pattern, but here’s perhaps the most common one:
Infatuation stage: This early phase is characterized by obsessive thoughts and a strong desire to be with the person. The ventral tegmental area (VTA), the brain’s reward center, becomes highly active, releasing dopamine, one of the feel-good neurotransmitters, which makes love feel intoxicating, similar to addictive substances. Additionally, activity in the prefrontal cortex, responsible for critical thinking and judgment, decreases, causing people to see their partners through “rose-tinted glasses”. However, this intense stage usually lasts only a few months.
Attachment stage: As the relationship progresses, it shifts into a more stable and long-lasting phase. This stage is driven by oxytocin and vasopressin, hormones that promote trust/bonding and arousal, respectively. These same hormones also play a role in family and friendship connections. Oxytocin, in particular, reduces stress hormones, which is why spending time with a loved one can feel so calming.
Heartbreak stage: When a relationship ends, the insular cortex processes emotional and physical pain, making heartbreak feel as painful as a physical injury. Meanwhile, the VTA remains active, leading to intense longing and cravings for the lost partner, similar to withdrawal symptoms. The stress axis also activates, causing distress and restlessness. Over time, higher brain regions help regulate these emotions. Healing strategies such as exercise, socializing, and listening to music can help by triggering dopamine release and easing the pain of heartbreak.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: