Canned Tuna vs Canned Sardines – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing canned tuna to canned sardines, we picked the sardines.
Why?
This comparison is unfair, but practical—because both are sold next to each other in the supermarket and often used for similar things.
It’s unfair because in a can of tuna, there is tuna meat, whereas in a can of sardines, there is sardine meat, skin, and bones.
Consequently, sardines outperform tuna in almost everything, because a lot of nutrients are in the skin and bones.
To be completely unambiguous:
Sardines have more vitamins and minerals by far (special shout-out to calcium, of which sardines contain 6000% more), and more choline (which is sometimes reckoned as a vitamin, sometimes not).
Tuna does have marginally more protein, and less fat. If you are trying to limit your cholesterol intake, then that could be an argument for choosing tuna over sardines.
All in all: the sardines are more nutrient dense by far, are good sources of vitamins and minerals that tuna contains less of (and in many cases only trace amounts of), and for most people this will more than offset the difference in cholesterol, especially if having not more than one can per day.
About that skin and bones…
That’s where the real benefit for your joints lies, by the way!
See: We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Coffee, From A Blood Sugar Management Perspective
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our favorite French biochemist (Jessie Inchauspé) is back, and this time, she’s tackling a topic near and dear to this writer’s heart: coffee ☕💕
What to consider
Depending on how you like your coffee, some or all of these may apply to you:
- Is coffee healthy? Coffee is generally healthy, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes by improving fat burning in the liver and protecting beta cells in the pancreas.
- Does it spike blood sugars? Usually not so long as it’s black and unsweetened. Black coffee can cause small glucose spikes in some people due to stress-induced glucose release, but only if it contains caffeine.
- When is it best to drink it? Drinking coffee after breakfast, especially after a poor night’s sleep, can actually reduce glucose and insulin spikes.
- What about milk? All milks cause some glucose and insulin spikes. While oat milk is generally healthy, for blood sugar purposes unsweetened nut milks or even whole cow’s milk (but not skimmed; it needs the fat) are better options as they cause smaller spikes.
- What about sweetening? Adding sugar to coffee, especially on an empty stomach, obviously leads to large glucose spikes. Alternative sweeteners like stevia or sweet cinnamon are fine substitutes.
For more details on all of those things, plus why Kenyan coffee specifically may be the best for blood sugars, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Burden of Getting Medical Care Can Exhaust Older Patients
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Susanne Gilliam, 67, was walking down her driveway to get the mail in January when she slipped and fell on a patch of black ice.
Pain shot through her left knee and ankle. After summoning her husband on her phone, with difficulty she made it back to the house.
And then began the run-around that so many people face when they interact with America’s uncoordinated health care system.
Gilliam’s orthopedic surgeon, who managed previous difficulties with her left knee, saw her that afternoon but told her “I don’t do ankles.”
He referred her to an ankle specialist who ordered a new set of X-rays and an MRI. For convenience’s sake, Gilliam asked to get the scans at a hospital near her home in Sudbury, Massachusetts. But the hospital didn’t have the doctor’s order when she called for an appointment. It came through only after several more calls.
Coordinating the care she needs to recover, including physical therapy, became a part-time job for Gilliam. (Therapists work on only one body part per session, so she has needed separate visits for her knee and for her ankle several times a week.)
“The burden of arranging everything I need — it’s huge,” Gilliam told me. “It leaves you with such a sense of mental and physical exhaustion.”
The toll the American health care system extracts is, in some respects, the price of extraordinary progress in medicine. But it’s also evidence of the poor fit between older adults’ capacities and the health care system’s demands.
“The good news is we know so much more and can do so much more for people with various conditions,” said Thomas H. Lee, chief medical officer at Press Ganey, a consulting firm that tracks patients’ experiences with health care. “The bad news is the system has gotten overwhelmingly complex.”
That complexity is compounded by the proliferation of guidelines for separate medical conditions, financial incentives that reward more medical care, and specialization among clinicians, said Ishani Ganguli, an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School.
“It’s not uncommon for older patients to have three or more heart specialists who schedule regular appointments and tests,” she said. If someone has multiple medical problems — say, heart disease, diabetes, and glaucoma — interactions with the health care system multiply.
Ganguli is the author of a new study showing that Medicare patients spend about three weeks a year having medical tests, visiting doctors, undergoing treatments or medical procedures, seeking care in emergency rooms, or spending time in the hospital or rehabilitation facilities. (The data is from 2019, before the covid pandemic disrupted care patterns. If any services were received, that counted as a day of health care contact.)
That study found that slightly more than 1 in 10 seniors, including those recovering from or managing serious illnesses, spent a much larger portion of their lives getting care — at least 50 days a year.
“Some of this may be very beneficial and valuable for people, and some of it may be less essential,” Ganguli said. “We don’t talk enough about what we’re asking older adults to do and whether that’s realistic.”
Victor Montori, a professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, has for many years raised an alarm about the “treatment burden” that patients experience. In addition to time spent receiving health care, this burden includes arranging appointments, finding transportation to medical visits, getting and taking medications, communicating with insurance companies, paying medical bills, monitoring health at home, and following recommendations such as dietary changes.
Four years ago — in a paper titled “Is My Patient Overwhelmed?” — Montori and several colleagues found that 40% of patients with chronic conditions such as asthma, diabetes, and neurological disorders “considered their treatment burden unsustainable.”
When this happens, people stop following medical advice and report having a poorer quality of life, the researchers found. Especially vulnerable are older adults with multiple medical conditions and low levels of education who are economically insecure and socially isolated.
Older patients’ difficulties are compounded by medical practices’ increased use of digital phone systems and electronic patient portals — both frustrating for many seniors to navigate — and the time pressures afflicting physicians. “It’s harder and harder for patients to gain access to clinicians who can problem-solve with them and answer questions,” Montori said.
Meanwhile, clinicians rarely ask patients about their capacity to perform the work they’re being asked to do. “We often have little sense of the complexity of our patients’ lives and even less insight into how the treatments we provide (to reach goal-directed guidelines) fit within the web of our patients’ daily experiences,” several physicians wrote in a 2022 paper on reducing treatment burden.
Consider what Jean Hartnett, 53, of Omaha, Nebraska, and her eight siblings went through after their 88-year-old mother had a stroke in February 2021 while shopping at Walmart.
At the time, the older woman was looking after Hartnett’s father, who had kidney disease and needed help with daily activities such as showering and going to the bathroom.
During the year after the stroke, both of Hartnett’s parents — fiercely independent farmers who lived in Hubbard, Nebraska — suffered setbacks, and medical crises became common. When a physician changed her mom’s or dad’s plan of care, new medications, supplies, and medical equipment had to be procured, and new rounds of occupational, physical, and speech therapy arranged.
Neither parent could be left alone if the other needed medical attention.
“It wasn’t unusual for me to be bringing one parent home from the hospital or doctor’s visit and passing the ambulance or a family member on the highway taking the other one in,” Hartnett explained. “An incredible amount of coordination needed to happen.”
Hartnett moved in with her parents during the last six weeks of her father’s life, after doctors decided he was too weak to undertake dialysis. He passed away in March 2022. Her mother died months later in July.
So, what can older adults and family caregivers do to ease the burdens of health care?
To start, be candid with your doctor if you think a treatment plan isn’t feasible and explain why you feel that way, said Elizabeth Rogers, an assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Minnesota Medical School.
“Be sure to discuss your health priorities and trade-offs: what you might gain and what you might lose by forgoing certain tests or treatments,” she said. Ask which interventions are most important in terms of keeping you healthy, and which might be expendable.
Doctors can adjust your treatment plan, discontinue medications that aren’t yielding significant benefits, and arrange virtual visits if you can manage the technological requirements. (Many older adults can’t.)
Ask if a social worker or a patient navigator can help you arrange multiple appointments and tests on the same day to minimize the burden of going to and from medical centers. These professionals can also help you connect with community resources, such as transportation services, that might be of help. (Most medical centers have staff of this kind, but physician practices do not.)
If you don’t understand how to do what your doctor wants you to do, ask questions: What will this involve on my part? How much time will this take? What kind of resources will I need to do this? And ask for written materials, such as self-management plans for asthma or diabetes, that can help you understand what’s expected.
“I would ask a clinician, ‘If I chose this treatment option, what does that mean not only for my cancer or heart disease, but also for the time I’ll spend getting care?’” said Ganguli of Harvard. “If they don’t have an answer, ask if they can come up with an estimate.”
We’re eager to hear from readers about questions you’d like answered, problems you’ve been having with your care, and advice you need in dealing with the health care system. Visit http://kffhealthnews.org/columnists to submit your requests or tips.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
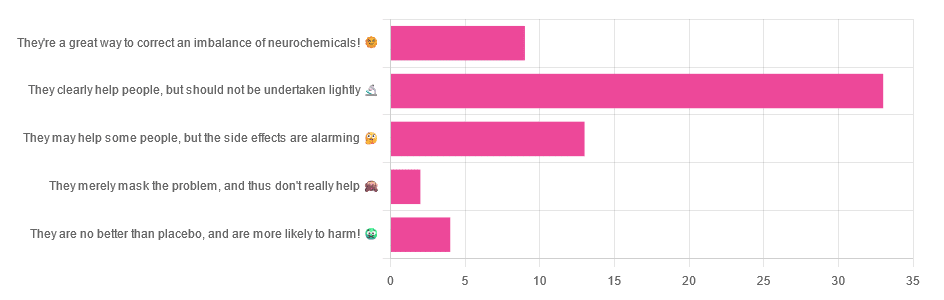
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on antidepressants, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- Just over half of respondents said “They clearly help people, but should not be undertaken lightly”
- Just over a fifth of respondents said “They may help some people, but the side effects are alarming”
- Just under a sixth of respondents said “They’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals”
- Four respondents said “They are no better than placebo, and are more likely to harm”
- Two respondents said “They merely mask the problem, and thus don’t really help”
So what does the science say?
❝They are no better than placebo, and are more likely to harm? True or False?❞
True or False depending on who you are and what you’re taking. Different antidepressants can work on many different systems with different mechanisms of action. This means if and only if you’re not taking the “right” antidepressant for you, then yes, you will get only placebo benefits:
- Placebo Effect in the Treatment of Depression and Anxiety ← randomly assigned antidepressants are, shockingly, luck of the draw in usefulness
- Antidepressants versus placebo in major depression: an overview ← “wow this science is messy”
- Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs: a systematic review and network meta-analysis ← “oh look, it makes a difference which antidepressant we give to people”
Rather than dismissing antidepressants as worthless, therefore, it is a good idea to find out (by examination or trial and error) what kind of antidepressant you need, if you indeed do need such.
Otherwise it is like getting a flu shot and being surprised when you still catch a cold!
❝They merely mask the problem, and thus don’t really help: True or False?❞
False, categorically.
The problem in depressed people is the depressed mood. This may be influenced by other factors, and antidepressants indeed won’t help directly with those, but they can enable the person to better tackle them (more on this later).
❝They may help some people, but the side-effects are alarming: True or False?❞
True or False depending on more factors than we can cover here.
Side-effects vary from drug to drug and person to person, of course. As does tolerability and acceptability, since to some extent these things are subjective.
One person’s dealbreaker may be another person’s shrugworthy minor inconvenience at most.
❝They’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals: True or False?❞
True! Contingently.
That is to say: they’re a great way to correct an imbalance of neurochemicals if and only if your problem is (at least partly) an imbalance of neurochemicals. If it’s not, then your brain can have all the neurotransmitters it needs, and you will still be depressed, because (for example) the other factors* influencing your depression have not changed.
*common examples include low self-esteem, poor physical health, socioeconomic adversity, and ostensibly bleak prospects for the future.
For those for whom the problem is/was partly a neurochemical imbalance and partly other factors, the greatest help the antidepressants give is getting the brain into sufficient working order to be able to tackle those other factors.
Want to know more about the different kinds?
Here’s a helpful side-by-side comparison of common antidepressants, what type they are, and other considerations:
Mind | Comparing Antidepressants
Want a drug-free approach?
You might like our previous main feature:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Wakefulness, Cognitive Enhancement, AND Improved Mood?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Old Drug, New Tricks?
Modafinil (also known by brand names including Modalert and Provigil) is a dopamine uptake inhibitor.
What does that mean? It means it won’t put any extra dopamine in your brain, but it will slow down the rate at which your brain removes naturally-occuring dopamine.
The result is that your brain will get to make more use of the dopamine it does have.
(dopamine is a neutrotransmitter that allows you to feel wakeful and happy, and perform complex cognitive tasks)
Modafinil is prescribed for treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness. Often that’s caused by shift work sleep disorder, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy.
Read: Overview of the Clinical Uses, Pharmacology, and Safety of Modafinil
Many studies done on humans (rather than rats) have been military experiments to reduce the effects of sleep deprivation:
Click Here To See A Military Study On Modafinil!
They’ve found modafinil to be helpful, and more effective and more long-lasting than caffeine, without the same “crash” later. This is for two reasons:
1) while caffeine works by blocking adenosine (so you don’t feel how tired you are) and by constricting blood vessels (so you feel more ready-for-action), modafinil works by allowing your brain to accumulate more dopamine (so you’re genuinely more wakeful, and you get to keep the dopamine)
2) the biological half-life of modafinil is 12–15 hours, as opposed to 4–8 hours* for caffeine.
*Note: a lot of sources quote 5–6 hours for caffeine, but this average is misleading. In reality, we are each genetically predetermined to be either a fast caffeine metabolizer (nearer 4 hours) or a slow caffeine metabolizer (nearer 8 hours).
What’s a biological half-life (also called: elimination half-life)?
A substance’s biological half-life is the time it takes for the amount in the body to be reduced by exactly half.
For example: Let’s say you’re a fast caffeine metabolizer and you have a double-espresso (containing 100mg caffeine) at 8am.
By midday, you’ll have 50mg of caffeine left in your body. So far, so simple.
By 4pm you might expect it to be gone, but instead you have 25mg remaining (because the amount halves every four hours).
By 8pm, you have 12.5mg remaining.
When midnight comes and you’re tucking yourself into bed, you still have 6.25mg of caffeine remaining from your morning coffee!
Use as a nootropic
Many healthy people who are not sleep-deprived use modafinil “off-label” as a nootropic (i.e., a cognitive enhancer).
Read: Modafinil for cognitive neuroenhancement in healthy non-sleep-deprived subjects: A systematic review
Important Note: modafinil is prescription-controlled, and only FDA-approved for sleep disorders.
To get around this, a lot of perfectly healthy biohackers describe the symptoms of sleep pattern disorder to their doctor, to get a prescription.
We do not recommend lying to your healthcare provider, and nor do we recommend turning to the online “grey market”.
Such websites often use anonymized private doctors to prescribe on an “informed consent” basis, rather than making a full examination. Those websites then dispense the prescribed medicines directly to the patient with no further questions asked (i.e. very questionable practices).
Caveat emptor!
A new mood-brightener?
Modafinil was recently tested head-to-head against Citalapram for the treatment of depression, and scored well:
See its head-to-head scores here!
How does it work? Modafinil does for dopamine what a lot of anti-depressants do for serotonin. Both dopamine and serotonin promote happiness and wakefulness.
This is very promising, especially as modafinil (in most people, at least) has fewer unwanted side-effects than a lot of common anti-depressant medications.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Train For The Event Of Your Life!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mobility As A Sporting Pursuit
As we get older, it becomes increasingly important to treat life like a sporting event. By this we mean:
As an “athlete of life”, there are always events coming up for which we need to train. Many of these events will be surprise tests!
Such events/tests might include:
- Not slipping in the shower and breaking a hip (or worse)
- Reaching an item from a high shelf without tearing a ligament
- Getting out of the car at an awkward angle without popping a vertebra
- Climbing stairs without passing out light-headed at the top
- Descending stairs without making it a sled-ride-without-a-sled
…and many more.
Train for these athletic events now
Not necessarily this very second; we appreciate you finishing reading first. But, now generally in your life, not after the first time you fail such a test; it can (and if we’re not attentive: will) indeed happen to us all.
With regard to falling, you might like to revisit our…
…which covers how to not fall, and to not injure yourself if you do.
You’ll also want to be able to keep control of your legs (without them buckling) all the way between standing and being on the ground.
Slav squats or sitting squats (same exercise, different names, amongst others) are great for building and maintaining this kind of strength and suppleness:
(Click here for a refresher if you haven’t recently seen Zuzka’s excellent video explaining how to do this, especially if it’s initially difficult for you, “The Most Anti-Aging Exercise”)
this exercise is, by the way, great for pretty much everything below the waist!
You will also want to do resistance exercises to keep your body robust:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And as for those shoulders? If it is convenient for you to go swimming, then backstroke is awesome for increasing and maintaining shoulder mobility (and strength).
If swimming isn’t a viable option for you, then doing the same motion with your arms, while standing, will build the same flexibility. If you do it while holding a small weight (even just 1kg is fine, but feel free to increase if you so wish and safely can) in each hand will build the necessary strength as you go too.
As for why even just 1kg is fine: read on
About that “and strength”, by the way…
Stretching is not everything. Stretching is great, but mobility without strength (in that joint!) is just asking for dislocation.
You don’t have to be built like the Terminator, but you do need to have the structural integrity to move your body and then a little bit more weight than that (or else any extra physical work could be enough to tip you to breaking point) without incurring damage from the strain. So, it needs to not be a strain! See again, the aforementioned resistance exercises.
That said, even very gentle exercise helps too; see for example the impact of walking on osteoporosis:
Living near green spaces linked to higher bone density and lower osteoporosis risk
and…
So you don’t have to run marathons—although you can if you want:
Marathons in Mid- and Later-Life
…to keep your hips and more in good order.
Want to test yourself now?
Check out:
Building & Maintaining Mobility
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Top 10 Causes Of High Blood Pressure
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As Dr. Frita Fisher explains, these are actually the top 10 known causes of high blood pressure. Number zero on the list would be “primary hypertension”, which means high blood pressure with no clear underlying cause.
Superficially, this feels a little like the sometime practice of writing the catch-all “heart failure” as the cause of death on a death certificate, because yes, that heart sure did stop beating. But in reality, primary hypertension is most likely often caused by such things as unmanaged chronic stress—something that doesn’t show up on most health screenings.
Dr. Fisher’s Top 10
- Thyroid disease: both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can cause high blood pressure.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: characterized by snoring, daytime sleepiness, and headaches, this condition can lead to hypertension.
- Chronic kidney disease: diseases ranging from diabetic nephropathy to renal vascular disease can cause high blood pressure.
- Elevated cortisol levels: conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or disease, which involve high cortisol levels, can lead to hypertension—as can a lifestyle with a lot of chronic stress, but that’s less readily diagnosed as such than something one can tell from a blood test.
- Elevated aldosterone levels: excess aldosterone from the adrenal glands causes the body to retain salt and water, increasing blood pressure, because more stuff = more pressure.
- Brain tumor: tumors that increase intracranial pressure can cause a rise in blood pressure to ensure adequate brain perfusion. In these cases, the hypertension is keeping you alive—unless it kills you first. If this seems like a strange bodily response, remember that our bodily response to an infection is often fever, to kill off the infection which can’t survive at such high temperatures (but neither can we, so it becomes a game of chicken with our life on the line), so sometimes our body does kill us with one thing while trying to save us from another.
- Coarctation of the aorta: this congenital heart defect results in narrowing of the aorta, leading to hypertension, especially in the upper body.
- Pregnancy: pregnancy can either induce or worsen existing hypertension.
- Obesity: excess weight increases blood flow and pressure on arteries, raising the risk of hypertension and associated conditions, e.g. diabetes etc.
- Drugs: certain medications and recreational drugs (including, counterintuitively, alcohol!) can elevate blood pressure.
For more information on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: