Are Brain Chips Safe?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ready For Cyborgization?
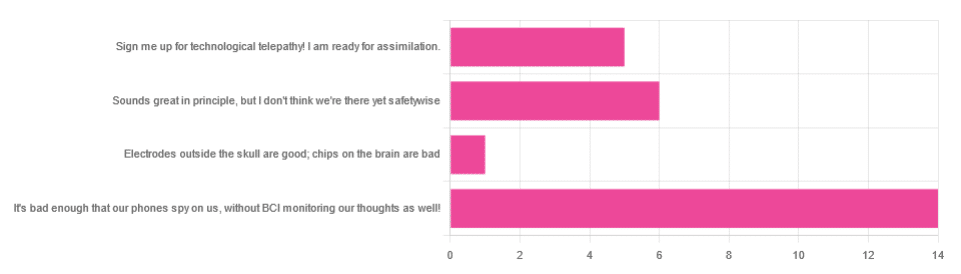
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your views on Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs), such as the Utah Array and Neuralink’s chips on/in brains that allow direct communication between brains and computers, so that (for example) a paralysed person can use a device to communicate, or manipulate a prosthetic limb or two.
We didn’t get as many votes as usual; it’s possible that yesterday’s newsletter ended up in a lot of spam filters due to repeated use of a word in “extra ______ olive oil” in its main feature!
However, of the answers we did get…
- About 54% said “It’s bad enough that our phones spy on us, without BCI monitoring our thoughts as well!”
- About 23% said “Sounds great in principle, but I don’t think we’re there yet safetywise”
- About 19% said “Sign me up for technological telepathy! I am ready for assimilation”
- One (1) person said “Electrode outside the skull are good; chips on the brain are bad”
But what does the science say?
We’re not there yet safetywise: True or False?
True, in our opinion, when it comes to the latest implants, anyway. While it’s very difficult to prove a negative (it could be that everything goes perfectly in human trials), “extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence”, and so far this seems to be lacking.
The stage before human trials is usually animal trials, starting with small creatures and working up to non-human primates if appropriate, before finally humans.
- Good news: the latest hot-topic BCI device (Neuralink) was tested on animals!
- Bad news: to say it did not go well would be an understatement
The Gruesome Story of How Neuralink’s Monkeys Actually Died
The above is a Wired article, and we tend to go for more objective sources, however we chose this one because it links to very many objective sources, including an open letter from the Physicians’ Committee for Responsible Medicine, which basically confirms everything in the Wired article. There are lots of links to primary (medical and legal) sources, too.
Electrodes outside the skull are good; chips on/in the brain are bad: True or False?
True or False depending on how they’re done. The Utah Array (an older BCI implant, now 20 years old, though it’s been updated many times since) has had a good safety record, after being used by a few dozen people with paralysis to control devices:
How the Utah Array is advancing BCI science
The Utah Array works on the same general principle as Neuralink, but the mechanics of its implementation are very different:
- The Utah Array involves a tiny bundle of microelectrodes (held together by a rigid structure that looks a bit like a nanoscale hairbrush) put in place by a brain surgeon, and that’s that.
- The Neuralink has a dynamic web of electrodes, implanted by a little robot that acts like a tiny sewing machine to implant many polymer threads, each containing its own a bunch of electrodes.
In theory, the latter is much more advanced. In practice, so far, the former has a much better safety record.
I am right to be a little worried about giving companies access to my brain: True or False?
True or False, depending on the nature of your concern.
For privacy: current BCI devices have quite simple switches operated consciously by the user. So while technically any such device that then runs its data through Bluetooth or WiFi could be hacked, this risk is no greater than using a wireless mouse and/or keyboard, because it has access to about the same amount of information.
For safety: yes, probably there is cause to be worried. Likely the first waves of commercial users of any given BCI device will be severely disabled people who are more likely to waive their rights in the hope of a life-changing assistance device, and likely some of those will suffer if things go wrong.
Which on the one hand, is their gamble to make. And on the other hand, makes rushing to human trials, for companies that do that, a little more predatory.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Dopamine Myth
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Dopamine Myth
There’s a popular misconception that, since dopamine is heavily involved in addictions, it’s the cause.
We see this most often in the context of non-chemical addictions, such as:
- gambling
- videogames
- social media
And yes, those things will promote dopamine production, and yes, that will feel good. But dopamine isn’t the problem.
Myth: The Dopamine Detox
There’s a trend we’ve mentioned before (it got a video segment a few Fridays back) about the idea of a “dopamine detox“, and how unscientific the idea is.
For a start…
- You cannot detox from dopamine, because dopamine is not a toxin
- You cannot abstain from dopamine, because your brain regulates your dopamine levels to keep them correct*
- If you could abstain from dopamine (and did), you would die, horribly.
*unless you have a serious mental illness, for example:
- forms of schizophrenia and/or psychosis that involve too much dopamine, or
- forms of depression and/or neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s (and several kinds of dementia) in which you have too little dopamine
- bipolar disorder in which dopamine levels can swing too far each way
See also: Dopamine fasting: misunderstanding science spawns a maladaptive fad
Myth: Dopamine is all about pleasure
Dopamine is a pleasure-giving neurotransmitter, but it serves more purposes than that! It also plays a central role in many neurological processes, including:
- Motivation
- Learning and memory
- Motor functions
- Language faculties
- Linear task processing
Note for example how someone taking dopaminergic drugs (prescription or otherwise; could be anything from modafinil to cocaine) is not blissed out… They’re probably in a good mood, sure, but they’re focused, organized, quick-thinking, and so forth! This is not an ad for cocaine; cocaine is very bad for the health. But you see the features? So, what if we could have a little more dopamine… healthily?
Dopamine—à la carte
Let’s look at the examples we gave earlier of non-chemical addictions that are dopaminergic in nature:
- gambling
- videogames
- social media
They’re not actually that rewarding, are they?
- Gamblers lose more than they win
- Gamers cease to care about a game once they have won
- Social media more often results in “doomscrolling”
This is because what prompts the most dopamine is actually the anticipation of reward… not the thing itself, whose reward-pleasure is very fleeting. Nobody looks back at an hour of doomscrolling and thinks “well, that was fun; I’m glad I did that”.
See the science: Liking, Wanting and the Incentive-Sensitization Theory of Addiction
But what if we anticipated a reward from things that are not deleterious to health and productivity? Things that are neutral, or even good for us?
Examples of this include:
- Sex! (remember though, it’s not a race to the finish-line)
- Good, nourishing food (bonus: some foods boost dopamine production nutritionally)
- Exercise/sport (also prompts release of endorphins, win/win!)
- Gamified learning apps (e.g. Duolingo)
- Gamified health/productivity apps (anything with bells and whistles and things that go “ding” and measure streaks etc)
Want to know more?
That’s all we have time for today, but you might want to check out:
10 Best Ways to Increase Dopamine Levels Naturally ← Science-based and well-sourced article!
Share This Post
-
Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing chickpeas to black beans, we picked the black beans.
Why?
They’re both great! But we consider the nutritional profile of black beans to be better:
In terms of macros, black beans have a little more protein, while chickpeas have more carbohydrates. Generally speaking, people are not usually short of carbs in their diet, so we’ll go with the one with more protein. Black beans also have more fiber, which is important for heart health and more.
In the category of micronutrients, black beans have twice as much potassium and twice as much calcium, as well as twice as much magnesium. Chickpeas, meanwhile are better for manganese and slightly higher in B vitamins, but B vitamins are everywhere (especially vitamin B5, pantothenic acid; that’s literally where its name comes from, it means “from everywhere”), so we don’t consider that as much of a plus as the black beans doubling up on potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
So, do enjoy both, but if you’re going to pick, or lean more heavily on one, we recommend the black beans
Further reading
See also:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Easily Digestible Vegetarian Protein Sources
- What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Focusing On Health In Our Sixties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What happens when you age in your sixties?❞
The good news is, a lot of that depends on you!
But, speaking on averages:
While it’s common for people to describe being over 50 as being “over the hill”, halfway to a hundred, and many greetings cards and such reflect this… Biologically speaking, our 60s are more relevant as being halfway to our likely optimal lifespan of 120. Humans love round numbers, but nature doesn’t care for such.
- In our 60s, we’re now usually the “wrong” side of the menopausal metabolic slump (usually starting at 45–55 and taking 5–10 years), or the corresponding “andropause” where testosterone levels drop (usually starting at 45 and a slow decline for 10–15 years).
- In our 60s, women will now be at a higher risk of osteoporosis, due to the above. The risk is not nearly so severe for men.
- In our 60s, if we’re ever going to get cancer, this is the most likely decade for us to find out.
- In our 60s, approximately half of us will suffer some form of hearing loss
- In our 60s, our body has all but stopped making new T-cells, which means our immune defenses drop (this is why many vaccines/boosters are offered to over-60s, but not to younger people)
While at first glance this does not seem a cheery outlook, knowledge is power.
- We can take HRT to avoid the health impact of the menopause/andropause
- We can take extra care to look after our bone health and avoid osteoporosis
- We can make sure we get the appropriate cancer screenings when we should
- We can take hearing tests, and if appropriate find the right hearing aids for us
- We can also learn to lip-read (this writer relies heavily on lip-reading!)
- We can take advantage of those extra vaccinations/boosters
- We can take extra care to boost immune health, too
Your body has no idea how many times you’ve flown around the sun and nor does it care. What actually makes a difference to it, is how it has been treated.
See also: Milestone Medical Tests You Should Take in Your 60s, 70s, and Beyond
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Brain Power – by Michael Gelb & Kelly Howell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s most important when it comes to brain health? Is it the right diet? Supplements? Brain-training? Attitude? Sleep? Physical exercise? Social connections? Something else?
This book covers a lot of bases, including all of the above and more. The authors are not scientists by training and this is not a book of science, so much as a book of aggregated science-based advice from other sources. The authors did consult with many scientists, and their input is shown throughout.
In the category of criticism, nothing here goes very deeply into the science, and there’s also nothing you wouldn’t find we’ve previously written about in a 10almonds article somewhere. But all the same, it’s good to have a wide variety of brain-healthy advices all in one place.
Bottom line: if you’re looking for a one-stop-shop “look after your brain as you age” guide, then this is a good one.
Click here to check out Brain Power, and improve your mind as you age!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Real Superfoods – by Ocean Robbins & Nichole Dandrea-Russert
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of the two authors, the former is a professional public speaker, and the latter is a professional dietician. As a result, we get a book that is polished and well-presented, while actually having a core of good solid science (backed up with plenty of references).
The book is divided into two parts; the first part has 9 chapters pertaining to 9 categories of superfood (with more details about top-tier examples of each, within), and the second part has 143 pages of recipes.
And yes, as usual, a couple of the recipes are “granola” and “smoothie”, but when are they not? Most of the recipes are worthwhile, though, with a lot of good dishes that should please most people.
Bottom line: this is half pop-science presentation of superfoods, and half cookbook featuring those ingredients. Definitely a good way to increase your consumption of superfoods, and get the most out of your diet.
Click here to check out Real Superfoods, and power up your health!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Neurologists Debunk 11 Brain Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Neuroscientists Dr. Santoshi Billakota and Dr. Brad Kamitaki debunk 11 myths about the brain. How many did you know?
From the top
Without further ado, the myths are…
- “We only use 10% of our brains”: False! We use most parts of our brain at different times, depending on the activity. PET/MRI scans show widespread usage.
- “The bigger the brain, the smarter the creature”: False! While there’s often a correlation, intelligence depends on brain complexity and development of specific regions, not overall size. For this reason get, for example, some corvids that are more intelligent than some dogs.
- “IQ tests are an accurate measure of intelligence”: False! IQ tests measure limited aspects of intelligence and are influenced by external factors like test conditions and education.
- “Video games rot your brain”: False! Video games can improve problem-solving, strategy, and team-building skills when played in moderation.
- “Memory gets worse as you age”: Partly false. While episodic memory may decline, semantic and procedural memory often improve with age.
- “Left-brained people are logical, and right-brained people are creative”: False! Both hemispheres work together, and personality or skills are influenced by environment and experiences, not brain hemispheres.
- “You can’t prevent a stroke”: False! Strokes can often be prevented by managing risk factors like blood pressure, cholesterol, and lifestyle choices.
- “Eating fish makes you smarter”: False! Eating fish, especially those rich in omega-3s, can support brain health but won’t increase intelligence.
- “You can always trust your senses”: False! Senses can be deceptive and influenced by emotions, memories, or neurological conditions.
- “Different sexes have different brains”: False! Structurally, brains are the same regardless of chromosomal sex; differences arise from environmental (including hormonal) and experiential factors—and even there, there’s more than enough overlap that we are far from categorizable as sexually dimorphic.
- “If you have a seizure, you have epilepsy”: False! A seizure can occur from various causes, but epilepsy is defined by recurrent unprovoked seizures and requires specific diagnosis and treatment.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Dopamine Myth ← a bonus 12th myth!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: