Body Language (In The Real World)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Forget What You Think You Know About Body Language
…unless it’s about a specific person whose habits and mannerisms you know intimately, in which case, you probably have enough personal data stored up to actually recognize patterns à la “when my spouse does this, then…”, and probably do know what’s going on.
For everyone else… our body language can be as unique as our idiolect
What’s an idiolect? It’s any one given person’s way of speaking/writing, in their natural state (i.e. without having to adjust their style for some reason, for example in a public-facing role at work, where style often becomes much narrower and more consciously-chosen).
Extreme example first
To give an extreme example of how non-verbal communication can be very different than a person thinks, there’s an anecdote floating around the web of someone whose non-verbal autistic kid would, when he liked someone who was visiting the house, hide their shoes when they were about to leave, to cause them to stay longer. Then one day some relative visited and when she suggested that she “should be going sometime soon”, he hurried to bring her her shoes. She left, happy that the kid liked her (he did not).
The above misunderstanding happened because the visitor had the previous life experience of “a person who brings me things is being helpful, and if they do it of their own free will, it’s because they like me”.
In other words…
Generalizations are often sound… In general
…which does not help us when dealing with individuals, which as it turns out, everyone is.
Clenched fists = tense and angry… Except when it’s just what’s comfortable for someone, or they have circulation issues, or this, or that, or the other.
Pacing = agitated… Except when it’s just someone who finds the body in motion more comfortable
Relaxed arms and hands = at ease and unthreatening… Unless it’s a practitioner of various martial arts for whom that is their default ready-for-action state.
Folded arms = closed-off, cold, distant… Or it was just somewhere to put one’s hands.
Lack of eye contact = deceitful, hiding something… Unless it’s actually for any one of a wide number of reasons, which brings us to our next section:
A liar’s “tells”
Again, if you know someone intimately and know what signs are associated with deceit in them, then great, that’s a thing you know. But for people in general…
A lot of what is repeated about “how to know if someone is lying” has seeped into public consciousness from “what police use to justify their belief that someone is lying”.
This is why many of the traditional “this person is lying” signs are based around behaviors that show up when in fact “this person is afraid, under pressure, and talking to an authority figure who has the power to ruin their life”:
Research on Non-verbal Signs of Lies and Deceit: A Blind Alley
But what about eye-accessing cues? They have science to them, right?
For any unfamiliar: this is about the theory that when we are accessing different parts of our mind (such as memory or creativity, thus truthfulness or lying), our eyes move one way or another according to what faculty we’re accessing.
Does it work? No
But, if you carefully calibrate it for a specific person, such as by asking them questions along the lines of “describe your front door” or “describe your ideal holiday”, to see which ways they look for recall or creativity… Then also no:
The Eyes Don’t Have It: Lie Detection and Neuro-Linguistic Programming
How can we know what non-verbal communication means, then?
With strangers? We can’t, simply. It’s on us to be open-minded, with a healthy balance of optimism and wariness.
With people we know? We can build up a picture over time, learn the person’s patterns. Best of all, we can ask them. In the moment, and in general.
For more on optimizing interpersonal communication, check out:
Save Time With Better Communication
…and the flipside of that:
The Problem With Active Listening (And How To Do It Better)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
A Hospital Kept a Brain-Damaged Patient on Life Support to Boost Statistics. His Sister Is Now Suing for Malpractice.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ProPublica is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative newsroom. Sign up for The Big Story newsletter to receive stories like this one in your inbox.
In 2018, Darryl Young was hoping for a new lease on life when he received a heart transplant at a New Jersey hospital after years of congestive heart failure. But he suffered brain damage during the procedure and never woke up.
The following year, a ProPublica investigation revealed that Young’s case was part of a pattern of heart transplants that had gone awry at Newark Beth Israel Medical Center in 2018. The spate of bad outcomes had pushed the center’s percentage of patients still alive one year after surgery — a key benchmark — below the national average. Medical staff were under pressure to boost that metric. ProPublica published audio recordings from meetings in which staff discussed the need to keep Young alive for a year, because they feared another hit to the program’s survival rate would attract scrutiny from regulators. On the recordings, the transplant program’s director, Dr. Mark Zucker, cautioned his team against offering Young’s family the option of switching from aggressive care to comfort care, in which no lifesaving efforts would be made. He acknowledged these actions were “very unethical.”
ProPublica’s revelations horrified Young’s sister Andrea Young, who said she was never given the full picture of her brother’s condition, as did the findings of a subsequent federal regulator’s probe that determined that the hospital was putting patients in “immediate jeopardy.” Last month, she filed a medical malpractice lawsuit against the hospital and members of her brother’s medical team.
The lawsuit alleges that Newark Beth Israel staff were “negligent and deviated from accepted standards of practice,” leading to Young’s tragic medical outcome.
Defendants in the lawsuit haven’t yet filed responses to the complaint in court documents. But spokesperson Linda Kamateh said in an email that “Newark Beth Israel Medical Center is one of the top heart transplant programs in the nation and we are committed to serving our patients with the highest quality of care. As this case is in active litigation, we are unable to provide further detail.” Zucker, who is no longer on staff at Newark Beth Israel, didn’t respond to requests for comment. His attorney also didn’t respond to calls and emails requesting comment.
Zucker also didn’t respond to requests for comment from ProPublica in 2018; Newark Beth Israel at the time said in a statement, made on behalf of Zucker and other staff, that “disclosures of select portions of lengthy and highly complex medical discussions, when taken out of context, may distort the intent of conversations.”
The lawsuit alleges that Young suffered brain damage as a result of severely low blood pressure during the transplant surgery. In 2019, when the federal Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services scrutinized the heart transplant program following ProPublica’s investigation, the regulators found that the hospital had failed to implement corrective measures even after patients suffered, leading to further harm. For example, one patient’s kidneys failed after a transplant procedure in August 2018, and medical staff made recommendations internally to increase the frequency of blood pressure measurement during the procedure, according to the lawsuit. The lawsuit alleges that the hospital didn’t implement its own recommendations and that one month later, “these failures were repeated” in Young’s surgery, leading to brain damage.
The lawsuit also alleges that Young wasn’t asked whether he had an advance directive, such as a preference for a do-not-resuscitate order, despite a hospital policy stating that patients should be asked at the time of admission. The lawsuit also noted that CMS’ investigation found that Andrea Young was not informed of her brother’s condition.
Andrea Young said she understands that mistakes can happen during medical procedures, “however, it’s their duty and their responsibility to be honest and let the family know exactly what went wrong.” Young said she had to fight to find out what was going on with her brother, at one point going to the library and trying to study medical books so she could ask the right questions. “I remember as clear as if it were yesterday, being so desperate for answers,” she said.
Andrea Young said that she was motivated to file the lawsuit because she wants accountability. “Especially with the doctors never, from the outset, being forthcoming and truthful about the circumstances of my brother’s condition, not only is that wrong and unethical, but it took a lot away from our entire family,” she said. “The most important thing to me is that those responsible be held accountable.”
ProPublica’s revelation of “a facility putting its existence over that of a patient is a scary concept,” said attorney Jonathan Lomurro, who’s representing Andrea Young in this case with co-counsel Christian LoPiano. Besides seeking damages for Darryl Young’s children, “we want to call attention to this so it doesn’t happen again,” Lomurro said.
The lawsuit further alleges that medical staff at Newark Beth Israel invaded Young’s privacy and violated the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, more commonly known as HIPAA, by sharing details of his case with the media without his permission. “We want people to be whistleblowers and want information out,” but that information should be told to patients and their family members directly, Lomurro said.
The 2019 CMS investigation determined that Newark Beth Israel’s program placed patients in “immediate jeopardy,” the most serious level of violation, and required the hospital to implement corrective plans. Newark Beth Israel did not agree with all of the regulator’s findings and in a statement at the time said that the CMS team lacked the “evidence, expertise and experience” to assess and diagnose patient outcomes.
The hospital did carry out the corrective plans and continues to operate a heart transplant program today. The most recent federal data, based on procedures from January 2021 through June 2023, shows that the one year probability of survival for a patient at Newark Beth is lower than the national average. It also shows that the number of graft failures, including deaths, in that time period was higher than the expected number of deaths for the program.
Andrea Young said she’s struggled with a feeling of emptiness in the years after her brother’s surgery. They were close and called each other daily. “There’s nothing in the world that can bring my brother back, so the only solace I will have is for the ones responsible to be held accountable,” she said. Darryl Young died on Sept 12, 2022, having never woken up after the transplant surgery.
A separate medical malpractice lawsuit filed in 2020 by the wife of another Newark Beth Israel heart transplant patient who died after receiving an organ infected with a parasitic disease is ongoing. The hospital has denied the allegations in court filing. The state of New Jersey, employer of the pathologists named in the case, settled for $1.7 million this month, according to the plaintiff’s attorney Christian LoPiano. The rest of the case is ongoing.
Share This Post
-
Coffee, From A Blood Sugar Management Perspective
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our favorite French biochemist (Jessie Inchauspé) is back, and this time, she’s tackling a topic near and dear to this writer’s heart: coffee ☕💕
What to consider
Depending on how you like your coffee, some or all of these may apply to you:
- Is coffee healthy? Coffee is generally healthy, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes by improving fat burning in the liver and protecting beta cells in the pancreas.
- Does it spike blood sugars? Usually not so long as it’s black and unsweetened. Black coffee can cause small glucose spikes in some people due to stress-induced glucose release, but only if it contains caffeine.
- When is it best to drink it? Drinking coffee after breakfast, especially after a poor night’s sleep, can actually reduce glucose and insulin spikes.
- What about milk? All milks cause some glucose and insulin spikes. While oat milk is generally healthy, for blood sugar purposes unsweetened nut milks or even whole cow’s milk (but not skimmed; it needs the fat) are better options as they cause smaller spikes.
- What about sweetening? Adding sugar to coffee, especially on an empty stomach, obviously leads to large glucose spikes. Alternative sweeteners like stevia or sweet cinnamon are fine substitutes.
For more details on all of those things, plus why Kenyan coffee specifically may be the best for blood sugars, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Addiction Myths That Are Hard To Quit
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Which Addiction-Quitting Methods Work Best?
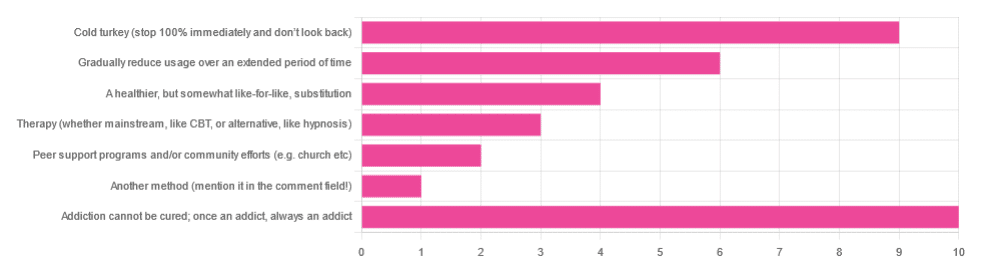
In Tuesday’s newsletter we asked you what, in your opinion, is the best way to cure an addiction. We got the above-depicted, below-described, interesting distribution of responses:
- About 29% said: “Addiction cannot be cured; once an addict, always an addict”
- About 26% said “Cold turkey (stop 100% and don’t look back)”
- About 17% said “Gradually reduce usage over an extended period of time”
- About 11% said “A healthier, but somewhat like-for-like, substitution”
- About 9% said “Therapy (whether mainstream, like CBT, or alternative, like hypnosis)”
- About 6% said “Peer support programs and/or community efforts (e.g. church etc)”
- About 3% said “Another method (mention it in the comment field)” and then did not mention it in the comment field
So what does the science say?
Addiction cannot be cured; once an addict, always an addict: True or False?
False, which some of the people who voted for it seemed to know, as some went on to add in the comment field what they thought was the best way to overcome the addiction.
The widespread belief that “once an addict, always an addict” is a “popular truism” in the same sense as “once a cheater, always a cheater”. It’s an observation of behavioral probability phrased as a strong generalization, but it’s not actually any kind of special unbreakable law of the universe.
And, certainly the notion that one cannot be cured keeps membership in many 12-step programs and similar going—because if you’re never cured, then you need to stick around.
However…
❝What is the definition of addiction?
Addiction is a treatable, chronic medical disease involving complex interactions among brain circuits, genetics, the environment, and an individual’s life experiences. People with addiction use substances or engage in behaviors that become compulsive and often continue despite harmful consequences.
Prevention efforts and treatment approaches for addiction are generally as successful as those for other chronic diseases.❞
~ American Society of Addiction Medicine
Or if we want peer-reviewed source science, rather than appeal to mere authority as above, then:
❝What is drug addiction?
Addiction is defined as a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use despite adverse consequences. It is considered a brain disorder, because it involves functional changes to brain circuits involved in reward, stress, and self-control. Those changes may last a long time after a person has stopped taking drugs.
Addiction is a lot like other diseases, such as heart disease. Both disrupt the normal, healthy functioning of an organ in the body, both have serious harmful effects, and both are, in many cases, preventable and treatable.❞
~ Nora D. Volkow (Director, National Institute of Drug Abuse)
Read more: Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction
In short: part of the definition of addiction is the continued use; if the effects of the substance are no longer active in your physiology, and you are no longer using, then you are not addicted.
Just because you would probably become addicted again if you used again does not make you addicted when neither the substance nor its after-effects are remaining in your body. Otherwise, we could define all people as addicted to all things based on “well if they use in the future they will probably become addicted”.
This means: the effects of addiction can and often will last for long after cessation of use, but ultimately, addiction can be treated and cured.
(yes, you should still abstain from the thing to which you were formerly addicted though, or you indeed most probably will become addicted again)
Cold turkey is best: True or False?
True if and only if certain conditions are met, and then only for certain addictions. For all other situations… False.
To decide whether cold turkey is a safe approach (before even considering “effective”), the first thing to check is how dangerous the withdrawal symptoms are. In some cases (e.g. alcohol, cocaine, heroin, and others), the withdrawal symptoms can kill.
That doesn’t mean they will kill, so knowing (or being!) someone who quit this way does not refute this science by counterexample. The mortality rates that we saw while researching varied from 8% to 37%, so most people did not die, but do you really want (yourself or a loved one) to play those odds unnecessarily?
See also: Detoxification and Substance Abuse Treatment
Even in those cases where it is considered completely safe for most people to quit cold turkey, such as smoking, it is only effective when the quitter has appropriate reliable medical support, e.g.
- Without support: 3–5% success rate
- With support: 22% success rate
And yes, that 22% was for the “abrupt cessation” group; the “gradual cessation” group had a success rate of 15.5%. On which note…
Gradual reduction is the best approach: True or False?
False based on the above data, in the case of addictions where abrupt cessation is safe. True in other cases where abrupt cessation is not safe.
Because if you quit abruptly and then die from the withdrawal symptoms, then well, technically you did stay off the substance for the rest of your life, but we can’t really claim that as a success!
A healthier, but somewhat like-for-like substitution is best: True or False?
True where such is possible!
This is why, for example, medical institutions recommend the use of buprenorphine (e.g. Naloxone) in the case of opioid addiction. It’s a partial opioid receptor agonist, meaning it does some of the job of opioids, while being less dangerous:
It’s also why vaping—despite itself being a health hazard—is recommended as a method of quitting smoking:
Similarly, “zero alcohol drinks that seem like alcohol” are a popular way to stop drinking alcohol, alongside other methods:
This is also why it’s recommended that if you have multiple addictions, to quit one thing at a time, unless for example multiple doctors are telling you otherwise for some specific-to-your-situation reason.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Boundary-Setting Beyond “No”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
More Than A “No”
A lot of people struggle with boundary-setting, and it’s not always the way you might think.
The person who “can’t say no” to people probably comes to mind, but the problem is more far-reaching than that, and it’s rooted in not being clear over what a boundary actually is.
For example: “Don’t bring him here again!”
Pretty clear, right?
And while it is indeed clear, it’s not a boundary; it’s a command. Which may or may not be obeyed, and at the end of the day, what right have we to command people in general?
Same goes for less dramatic things like “Don’t talk to me about xyz”, which can still be important or trivial, depending on whether the topic of xyz is deeply traumatizing for you, or mildly annoying, or something else entirely.
Why this becomes a problem
It becomes a problem not because of any lack of clarity about your wishes, but rather, because it opens the floor for a debate. The listener may be given to wonder whether your right to not experience xyz is greater or lesser than their right to do/say/etc xyz.
“My right to swing my fist ends where someone else’s nose begins”
…does not help here, firstly because both sides will believe themself (or nobody) to be the injured party; for the fist-swinger, the other person’s nose made a vicious assault on their freedom. Or secondly, maybe there was some higher principle at stake; a reason why violence was justified. And then ten levels of philosophical debate. We see this a lot when it comes to freedom of expression, and vigorous debate over whether this entails freedom from social consequences of one’s words/actions.
How a good boundary-setting works (if this, then that)
Consider two signs:
- No trespassing!
- Trespassers will be shot!
Superficially, the second just seems like a more violent rendition of the first. But in fact, the second is more informationally useful: it explains what will happen if the boundary is not respected, and allows the reader to make their own informed decision with regard to what to do with that information.
We can employ this method (and can even do so gently, if we so wish and hopefully we mostly do wish to be gentle) when it comes to social and interpersonal boundary-setting:
- If you bring him here again, I will refuse you entrance
- If you bring up that topic again, I will ask you to leave
- If you do that, I will never speak to you again
- If you don’t stop drinking, I will divorce you
This “if-this-then-that” model does the very first thing that any good boundary does: make itself clear.
It doesn’t rely on moral arguments; it doesn’t invite debate. For example in that last case, it doesn’t argue that the partner doesn’t have the right to drink—it simply expresses what the speaker will exercise their own right to do, in that eventuality.
(as an aside, the situation that occurs when one is enmeshed with someone who is dependent on a substance is a complex topic, and if you’re interested in that, check out: Codependency Isn’t What Most People Think)
Back on track: boundary-setting is not about what’s right or good—it’s about nothing more nor less than a clear delineation between what we will and won’t accept, and how we’ll enforce that.
We can also, in particularly personal boundary-setting (such as with sexual boundaries’ oft-claimed “gray areas”), fix an improperly-set boundary that forgot to do the above, e.g:
“How about [proposition]?”
“No thank you” ← casually worded answer; contextually reasonable, and yet not a clear boundary per what we discussed above
“Come on, I think you’d like it”
“I said no. No means no. Ask me again and I will [consequences that are appropriate and actionable]”What’s “appropriate and actionable” may vary a lot from one situation to another, but it’s important that it’s something you can do and are prepared to do and will do if the condition for doing it is met.
Anything less than that is not a boundary—it’s just a request.
Note: this does not require that we have power, by the way. If we have zero power in a situation, well, that definitely sucks, but even then we can still express what is actionable, e.g. “I will never trust you again”.
“Price of entry”
You may have wondered, upon reading “boundary-setting is not about what’s right or good—it’s about nothing more nor less than a clear delineation between what we will and won’t accept, and how we’ll enforce that”, can’t that be used to control and manipulate people, essentially coercing them to do or not do things with the threat of consequences (specifically: bad ones)?
And the answer is: yes, yes it can.
But that’s where the flipside comes into play—the other person gets to set their boundaries, too.
For all of us, if we have any boundaries at all, there is a “price of entry” and all who want to be in our lives, or be close to us, have to decide for themselves whether that price of entry is worth it.
- If a person says “do not talk about topic xyz to me or I will leave”, that is a price of entry for being close to them.
- If you are passionate about talking about topic xyz to the point that you are unwilling to shelve it when in their presence, then that is the price of entry for being close to you.
- If one or more of you is not willing to pay the price of entry, then guess what, you’re just not going to be close.
In cases of forced proximity (e.g. workplaces or families) this is likely to get resolved by the workplace’s own rules (i.e. the price of entry that you agreed to when signing a contract to work there), and if something like that doesn’t exist (such as in families), well, that forced proximity is going to reach a breaking point, and somebody may discover it wasn’t enforceable after all.
See also: Family Estrangement: More Common Than Most People Think
…which also details how to fix it, where possible.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Sprout Book – by Doug Evans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sprouting seeds are more nutritious than most people think, and “seeds” is also a much broader category than people think. Beyond even chia and sunflower and such, this book bids us remember that onions do not just appear on supermarket shelves fully formed (to give just one example of many); most plants come from seeds and of those, most can be usefully sprouted.
The author, most well-known for his tech companies, here is selling us a very low-tech health kick with very little profit to be found except for our health. By sprouting seeds of many kinds at home, we can enjoy powerful superfoods that are not only better than, but also cheaper than, most supplements.
Nor are the benefits of sprouting things marginal; we’re not talking about a 1–10% increase in bioavailable so much as what’s often a 100–1000% increase.
After explaining the science and giving a primer on sprouting things for oneself, there is a wide selection of recipes, but the biggest benefit of the book is in just getting the reader up-and-running with at-home sprouting.
Bottom line: if you like the idea of letting food be your medicine and even like the idea of essentially growing your own food with zero gardening skills, then this is an excellent book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Green Tea Allergies and Capsules
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Hey Sheila – As always, your articles are superb !! So, I have a topic that I’d love you guys to discuss: green tea. I used to try + drink it years ago but I always got an allergic reaction to it. So the question I’d like answered is: Will I still get the same allergic reaction if I take the capsules ? Also, because it’s caffeinated, will taking it interfere with iron pills, other vitamins + meds ? I read that the health benefits of the decaffeinated tea/capsules are not as great as the caffeinated. Any info would be greatly appreciated !! Thanks much !!❞
Hi! I’m not Sheila, but I’ll answer this one in the first person as I’ve had a similar issue:
I found long ago that taking any kind of tea (not herbal infusions, but true teas, e.g. green tea, black tea, red tea, etc) on an empty stomach made me want to throw up. The feeling would subside within about half an hour, but I learned it was far better to circumvent it by just not taking tea on an empty stomach.
However! I take an l-theanine supplement when I wake up, to complement my morning coffee, and have never had a problem with that. Of course, my physiology is not your physiology, and this “shouldn’t” be happening to either of us in the first place, so it’s not something there’s a lot of scientific literature about, and we just have to figure out what works for us.
This last Monday I wrote (inspired in part by your query) about l-theanine supplementation, and how it doesn’t require caffeine to unlock its benefits after all, by the way. So that’s that part in order.
I can’t speak for interactions with your other supplements or medications without knowing what they are, but I’m not aware of any known issue, beyond that l-theanine will tend to give a gentler curve to the expression of some neurotransmitters. So, if for example you’re talking anything that affects that (e.g. antidepressants, antipsychotics, ADHD meds, sleepy/wakefulness meds, etc) then checking with your doctor is best.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: