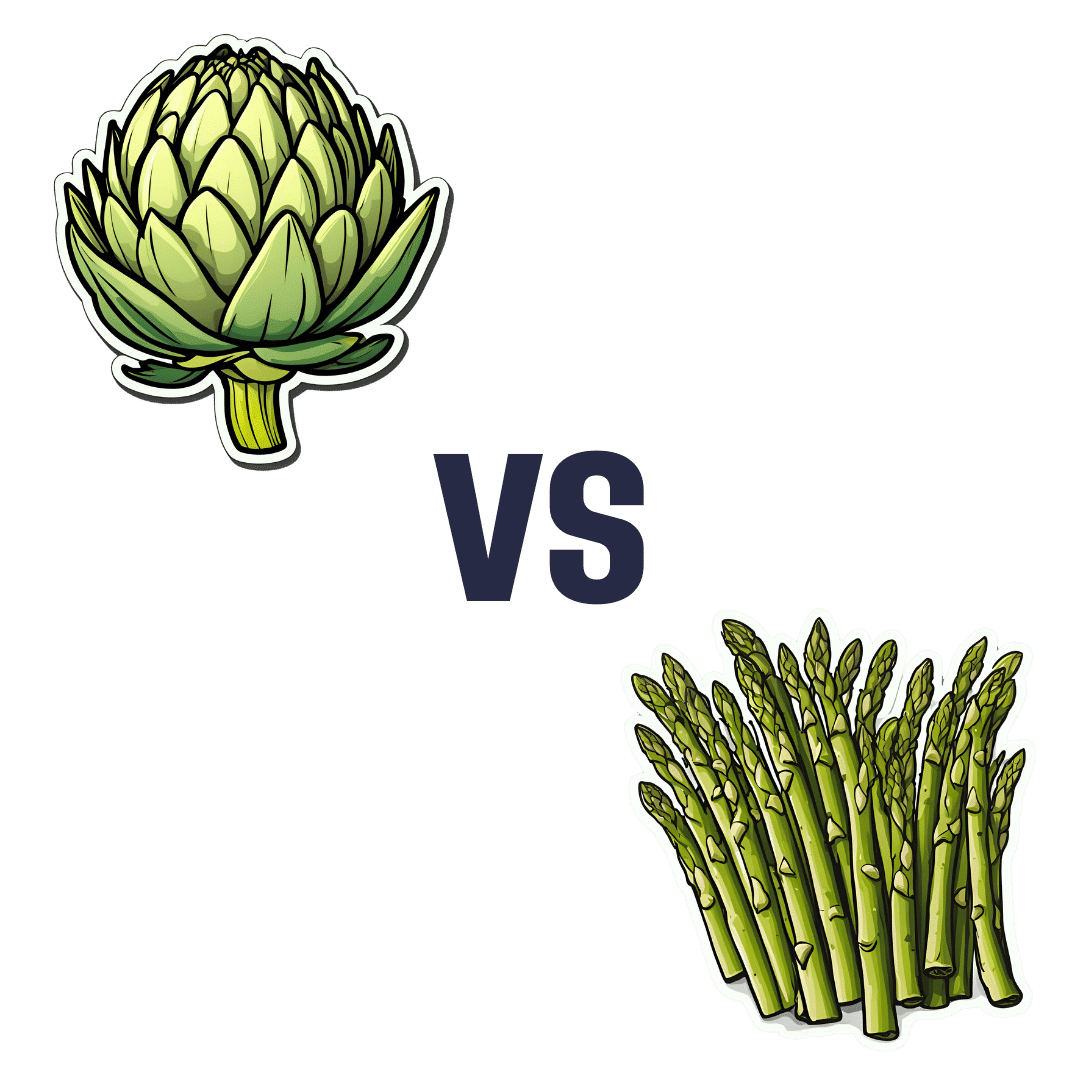
Artichoke vs Asparagus – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing artichoke to asparagus, we picked the artichoke.
Why?
Both are great and it was close!
In terms of macros, artichoke has a little more protein and around 3x the carbs and fiber: the ratio there means that both vegetables have an identical glycemic index, so we’ll go with the “most food per food” reckoning of nutritional density, and call it for the artichoke.
When it comes to vitamins, artichoke has more of vitamins B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline, while asparagus has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, E, and K. Both very respectable nutritional sets, but artichoke gets a marginal 6:5 win on strength of numbers.
In the category of minerals, artichoke has more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while asparagus has more iron, selenium, and zinc. A clearer 6:3 win for artichoke this time.
Once again, both of these are great foods, so by all means enjoy either or both. But if you’re looking for the nutritionally densest option, it’s the artichoke!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Water’s Counterintuitive Properties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Why are we told to drink more water for everything, even if sometimes it seems like the last thing we need? Bloated? Drink water. Diarrhea? Drink water. Nose running like a tap? Drink water❞
While water will not fix every ill, it can fix a lot, or at least stop it from being worse!
Our bodies are famously over 60% water (exact figure will depend on how well-hydrated you are, obviously, as well as your body composition in terms of muscle and fat). Our cells (which are mostly full of mostly water) need replacing all the time, and almost everything that needs transporting almost anywhere is taken there by blood (which is also mostly water). And if we need something moving out of the body? Water is usually going to be a large part of how it gets ejected.
In the cases of the examples you gave…
- Bloating: bloating is often a matter of water retention, which often happens as a result of having too much salt, and/or sometimes too much fat. So the body’s homeostatic system (the system that tries to maintain all kinds of equilibrium, keeping salt balance, temperature, pH, and many other things in their respective “Goldilocks zones”) tries to add more water to where it’s needed to balance out the salt etc.
- Consequently, drinking more water means the body will note “ok, balance restored, no need to keep retaining water there, excess salts being safely removed using all this lovely water”.
- Diarrhea: this is usually a case of a bacterial infection, though there can be other causes. Whether for that reason or another, the body has decided that it needs to give your gut an absolute wash-out, and it can only do that from the inside—so it uses as much of the body’s water as it needs to do that.
- Consequently, drinking more water means that you are replenishing the water that the body has already 100% committed to using. If you don’t drink water, you’ll still have diarrhea, you’ll just start to get dangerously dehydrated.
- Runny nose: this is usually a case of either fighting a genuine infection, or else fighting something mistaken for a pathogen (e.g. pollen, or some other allergen). The mucus is an important part of the body’s defense: it traps the microbes (be they bacteria, virus, whatever) and water-slides them out of the body.
- Consequently, drinking more water means the body can keep the water-slide going. Otherwise, you’ll just get gradually more dehydrated (because as with diarrhea, your body will prioritize this function over maintaining water reserves—water reserves are there to be used if necessary, is the body’s philosophy) and if the well runs dry, you’ll just be dehydrated and have a higher pathogen-count still in your body.
Some previous 10almonds articles that might interest you:
- Hydration Mythbusting
- When To Take Electrolytes (And When We Shouldn’t!)
- Keeping Your Kidneys Healthy (Especially After 60)
Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Share This Post
- Bloating: bloating is often a matter of water retention, which often happens as a result of having too much salt, and/or sometimes too much fat. So the body’s homeostatic system (the system that tries to maintain all kinds of equilibrium, keeping salt balance, temperature, pH, and many other things in their respective “Goldilocks zones”) tries to add more water to where it’s needed to balance out the salt etc.
-
Shoe Wear Patterns: What They Mean, Why It Matters, & How To Fix It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you look under your shoes, do you notice how the tread is worn more in some places than others? Specific patterns of shoe wear correspond to how our body applies force, weight, and rotational movement. This reveals how we move, and uneven wear can indicate problematic movement dynamics.
The clues in your shoes
Common shoe wear patterns include:
- Diagonal wear on the outside of the heel: caused by foot angle, leg position, and instability, leading to joint stress.
- Rotational wear at specific points: due to internal or external rotation, often originating from the hip, pelvis, or torso.
- Wear above the big toe: caused by excessive toe lifting, often associated with a “lighter” or kicking leg.
Fixing movement issues to prevent wear involves correcting posture, improving balance, and adjusting how the legs land during walking/running.
Key fixes include:
- Aligning the center of gravity properly to prevent leg overcompensation.
- Ensuring feet land under the hips and not far in front.
- Stabilizing the torso to avoid unnecessary rotation.
- Engaging the glutes effectively to reduce hip flexor dominance and improve leg mechanics.
- Maintaining even weight distribution on both legs to prevent excessive lifting or twisting.
Posture and walking mechanics are vital to reducing uneven wear, but meaningful, lasting change takes time and focused effort, to build new habits.
For more on all this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
On This Bright Day – by Dr. Susan Thompson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is principally aimed at those who have struggled with emotional/comfort eating, over-eating, and/or compulsive eating of some kind.
However, its advices go for the “little compulsions” too, the many small unhealthy choices that add up. Thus, this book has value for most if not all of us.
The format is: each day has a little quotation, followed by a short discussion of that, which is then underlined by an affirmation for the day.
The main thrust of the book is to promote mindful eating, and it does this well with daily reminders that are helpful without being preachy.
Bottom line: if you enjoy “daily reader” type books and would like a daily reminder to practice mindful eating, then this book is for you!
Click here to check out On This Bright Day, and enjoy your food mindfully, every day!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Purple Parsnip’s Bioactive Brain Benefits (& more)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This Root Might Be A Guardian Angel
Sometimes we go searching for supplements to research; sometimes supplements present themselves for examination! In this case, our attention was grabbed by a headline:
Angelica gigas extract emerges as a potential treatment for vascular disease
Angelica who?
Angelica gigas, also called the purple parsnip (amongst other names), is a flowering plant native to Korea. It has assorted medicinal properties, and in this case, it was its heart-healthy benefits that were making news:
❝Ultimately, this study presents clearly evidence that Angelica gigas extract is a promising natural product-based functional food/herbal medicine candidate for preventing or regulating hyperlipidemic cardiovascular complications❞
But it has a lot more to offer…
The root has various bioactive metabolites, but the compounds that most studies are most interested in are decursin and decursinol, for their neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement effects:
❝[C]rude extracts and isolated components from the root of A. gigas exhibited neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement effects.
Neuronal damage or death is the most important factor for many neurodegenerative diseases.
In addition, recent studies have clearly demonstrated the possible mechanisms behind the neuroprotective action of extracts/compounds from the root of A. gigas.❞
That middle paragraph there? That’s one of the main pathogenic processes of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Multiple Sclerosis.
Angelica gigas attenuates (reduces the force of) that process:
❝The published reports revealed that the extracts and isolated components from the root of A. gigas showed neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement properties through various mechanisms such as anti-apoptosis, antioxidative actions, inhibiting mRNA and protein expressions of inflammatory mediators and regulating a number of signaling pathways.
In conclusion, the A. gigas root can serve as an effective neuroprotective agent by modulating various pathophysiological processes❞
Read more: Neuroprotective and Cognitive Enhancement Potentials of Angelica gigas Nakai Root: A Review
Beyond neuroprotection & cognitive enhancement
…and also beyond its protection against vascular disease, which is what got our attention…
Angelica gigas also has antioxidant properties, anti-cancer properties, and general immune-boosting properties.
We’ve only so much room, so: those links above will take you to example studies for those things, but there are plenty more where they came from, so we’re quite confident in this one.
Of course, what has antioxidant properties is usually anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-aging, because these things are reliant on many of the same processes as each other, with a lot of overlap.
Where can we get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
“I Stretched Every Day For 30 Days: Game Changer!”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How much can an unflexible person really improve in just 20 minutes per day for a month? Makari Espe finds out:
Consistency really is key
We’re supposed to stretch at least 3 times per week; for many people, the reality is often more like 2 times per year (often the 1st and 2nd of January).
So, how quickly can such neglect be turned around?
Upon initial testing, she found she was even less flexible than thought, and set about her work:
The stretches she used were from random 20-minute full body stretch videos on YouTube, of which there are many, but she used a different one each day. As she went along, she found some favorite kinds of stretching and some favorite instructors, and settled on mostly Peloton stretching videos—she also switched to evening stretching sessions instead of morning.
Along the way, she already noticed gradual improvement in mobility and reduced body tension, and after 3 weeks, it had become a habit that she started craving.
The final test? There’s a marked improvement; see the video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Yoga Teacher: “If I wanted to get flexible in 2025, here’s what I’d do”
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hashimoto’s Food Pharmacology – by Dr. Izabella Wentz
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author is a doctor of pharmacology, and we’ve featured her before as an expert on Hashimoto’s, which she has. She has recommendations about specific blood tests and medications, but in this book she’s mainly focussing on what she calls the “three Rs” of managing hypothyroidism:
- Remove the causes and triggers of your hypothyroidism, so far as possible
- Repair the damage caused to your body, especially your gut
- Replace the thyroid hormones and related things in which your body has become deficient
To this end, she provides recipes that avoid processed meats and unfermented dairy, and include plenty of nutrient-dense whole foods specifically tailored to meet the nutritional needs of someone with hypothyroidism.
A nice bonus of the presentation of recipes (of which there are 125, if we include things like “mint tea” and “tomato sauce” and “hot lemon water” as recipes) is explaining the thyroid-supporting elements of each recipe.
A downside for some will be that if you are vegetarian/vegan, this book is very much not, and since many recipes are paleo-style meat dishes, substitutions will change the nutritional profile completely.
Bottom line: if you have hypothyroidism (especially if: Hashimoto’s) and like meat, this will be a great recipe book for you.
Click here to check out Hashimoto’s Food Pharmacology, and get cooking!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: