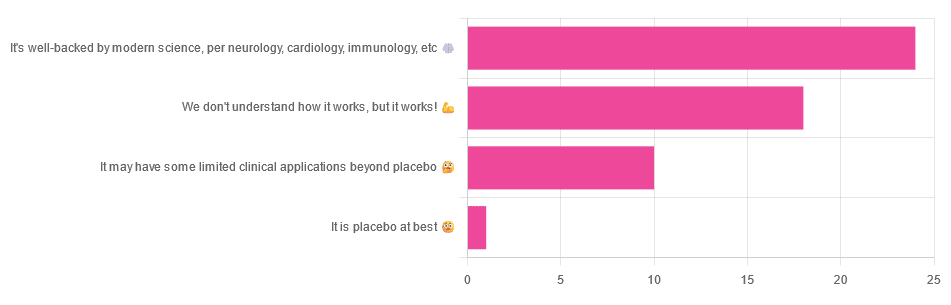
Self-Care That’s Not Just Self-Indulgence
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Self-Care That’s Not Just Self-Indulgence
Self-care is often seen as an excuse for self-indulgence. Worse, it’s often used as an excuse for self-indulgence—in ways that can end up making us feel worse.
It’s a bit like dietary “cheat days”. If your diet needs cheat days, your diet probably isn’t right for you!
How to recognize the difference between self-care and self-indulgence?
Statistically, the majority of our subscribers are parents (whose children are now mostly grown up, but still, the point is that parenting experience has been gleaned), and/or are or have been caregivers of some form or other.
When a small child is ill, we (hopefully!) look after them carefully:
- We don’t expect too much of them, but…
- …we do expect them to adhere to things consistent with their recovery.
Critically: an important part of self-care is that it actually should be care.
Let’s spell something out: neglect is not care!
How this works for physical and mental health
If you overdo it in physical exercise, it’s right and correct to take a break to recover, and during that time, do things that will hasten one’s recovery. For example:
Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise
But it’s well-known that if you just do nothing, your condition will likely deteriorate. Also, “a break to recover” is going to be as short as is necessary to recover. Then you’ll ease back into exercise, but you will get back to it.
For mental health it’s just the same. If we for whatever reason need to take a step back, it’s right and correct to do take a break to recover, and during that time, do things that will hasten one’s recovery.
Sometimes, if for example it’s just a case of burnout, rest is the best medicine, and even rest can be an active process. See for example:
How To Rest More Efficiently (Yes, Really)
So the question to ask, when it comes to self-care vs self-indulgence, is:
“Is this activity helping me to get better?”
Some examples:
Probably not great self-care activities:
- Oversleeping (unless you were sleep-deprived, in which case, it’s better to get an earlier night than a later morning, if possible)
- Overeating (comfort-eating is a thing, but your actual problems will still be there)
- Mindless activities (mindless scrolling, TV-watching, game-playing, etc)
Probably better self-care activities:
- Enjoyable physical activity (whatever that may be for you)
- Preparing your favorite food, and then enjoying it mindfully
- Engaging in a personal project that might not be that important, but it’s fulfilling to you (hobbies etc can fall into this category)
- Scheduling some time, and committing some resources, to tackling whatever problem(s) you are facing that’s prompting you to need this self-care.
- Doing the tasks you want to hide away from, but making them fun.
What’s your go-to self-care? We love to hear from you, so feel free to hit “reply” to this email, or use the handy feedback form at the bottom!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Long-Covid Patients Are Frustrated That Federal Research Hasn’t Found New Treatments
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Erica Hayes, 40, has not felt healthy since November 2020 when she first fell ill with covid.
Hayes is too sick to work, so she has spent much of the last four years sitting on her beige couch, often curled up under an electric blanket.
“My blood flow now sucks, so my hands and my feet are freezing. Even if I’m sweating, my toes are cold,” said Hayes, who lives in Western Pennsylvania. She misses feeling well enough to play with her 9-year-old son or attend her 17-year-old son’s baseball games.
Along with claiming the lives of 1.2 million Americans, the covid-19 pandemic has been described as a mass disabling event. Hayes is one of millions of Americans who suffer from long covid. Depending on the patient, the condition can rob someone of energy, scramble the autonomic nervous system, or fog their memory, among many other http://symptoms.in/ addition to the brain fog and chronic fatigue, Hayes’ constellation of symptoms includes frequent hives and migraines. Also, her tongue is constantly swollen and dry.
“I’ve had multiple doctors look at it and tell me they don’t know what’s going on,” Hayes said about her tongue.
Estimates of prevalence range considerably, depending on how researchers define long covid in a given study, but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention puts it at 17 million adults.
Despite long covid’s vast reach, the federal government’s investment in researching the disease — to the tune of $1.15 billion as of December — has so far failed to bring any new treatments to market.
This disappoints and angers the patient community, who say the National Institutes of Health should focus on ways to stop their suffering instead of simply trying to understand why they’re suffering.
“It’s unconscionable that more than four years since this began, we still don’t have one FDA-approved drug,” said Meighan Stone, executive director of the Long COVID Campaign, a patient-led advocacy organization. Stone was among several people with long covid who spoke at a workshop hosted by the NIH in September where patients, clinicians, and researchers discussed their priorities and frustrations around the agency’s approach to long-covid research.
Some doctors and researchers are also critical of the agency’s research initiative, called RECOVER, or Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery. Without clinical trials, physicians specializing in treating long covid must rely on hunches to guide their clinical decisions, said Ziyad Al-Aly, chief of research and development with the VA St Louis Healthcare System.
“What [RECOVER] lacks, really, is clarity of vision and clarity of purpose,” said Al-Aly, saying he agrees that the NIH has had enough time and money to produce more meaningful progress.
Now the NIH is starting to determine how to allocate an additional $662 million of funding for long-covid research, $300 million of which is earmarked for clinical trials. These funds will be allocated over the next four http://years.at/ the end of October, RECOVER issued a request for clinical trial ideas that look at potential therapies, including medications, saying its goal is “to work rapidly, collaboratively, and transparently to advance treatments for Long COVID.”
This turn suggests the NIH has begun to respond to patients. This has stirred cautious optimism among those who say that the agency’s approach to long covid has lacked urgency in the search for effective treatments.Stone calls this $300 million a down payment. She warns it’s going to take a lot more money to help people like Hayes regain some degree of health.“There really is a burden to make up this lost time now,” Stone said.
The NIH told KFF Health News and NPR via email that it recognizes the urgency in finding treatments. But to do that, there needs to be an understanding of the biological mechanisms that are making people sick, which is difficult to do with post-infectious conditions.
That’s why it has funded research into how long covid affects lung function, or trying to understand why only some people are afflicted with the condition.
Good Science Takes Time
In December 2020, Congress appropriated $1.15 billion for the NIH to launch RECOVER, raising hopes in the long-covid patient community.
Then-NIH Director Francis Collins explained that RECOVER’s goal was to better understand long covid as a disease and that clinical trials of potential treatments would come later.
According to RECOVER’s website, it has funded eight clinical trials to test the safety and effectiveness of an experimental treatment or intervention. Just one of those trials has published results.
On the other hand, RECOVER has supported more than 200 observational studies, such as research on how long covid affects pulmonary function and on which symptoms are most common. And the initiative has funded more than 40 pathobiology studies, which focus on the basic cellular and molecular mechanisms of long covid.
RECOVER’s website says this research has led to crucial insights on the risk factors for developing long covid and on understanding how the disease interacts with preexisting conditions.
It notes that observational studies are important in helping scientists to design and launch evidence-based clinical trials.
Good science takes time, said Leora Horwitz, the co-principal investigator for the RECOVER-Adult Observational Cohort at New York University. And long covid is an “exceedingly complicated” illness that appears to affect nearly every organ system, she said.
This makes it more difficult to study than many other diseases. Because long covid harms the body in so many ways, with widely variable symptoms, it’s harder to identify precise targets for treatment.
“I also will remind you that we’re only three, four years into this pandemic for most people,” Horwitz said. “We’ve been spending much more money than this, yearly, for 30, 40 years on other conditions.”
NYU received nearly $470 million of RECOVER funds in 2021, which the institution is using to spearhead the collection of data and biospecimens from up to 40,000 patients. Horwitz said nearly 30,000 are enrolled so far.
This vast repository, Horwitz said, supports ongoing observational research, allowing scientists to understand what is happening biologically to people who don’t recover after an initial infection — and that will help determine which clinical trials for treatments are worth undertaking.
“Simply trying treatments because they are available without any evidence about whether or why they may be effective reduces the likelihood of successful trials and may put patients at risk of harm,” she said.
Delayed Hopes or Incremental Progress?
The NIH told KFF Health News and NPR that patients and caregivers have been central to RECOVER from the beginning, “playing critical roles in designing studies and clinical trials, responding to surveys, serving on governance and publication groups, and guiding the initiative.”But the consensus from patient advocacy groups is that RECOVER should have done more to prioritize clinical trials from the outset. Patients also say RECOVER leadership ignored their priorities and experiences when determining which studies to fund.
RECOVER has scored some gains, said JD Davids, co-director of Long COVID Justice. This includes findings on differences in long covid between adults and kids.But Davids said the NIH shouldn’t have named the initiative “RECOVER,” since it wasn’t designed as a streamlined effort to develop treatments.
“The name’s a little cruel and misleading,” he said.
RECOVER’s initial allocation of $1.15 billion probably wasn’t enough to develop a new medication to treat long covid, said Ezekiel J. Emanuel, co-director of the University of Pennsylvania’s Healthcare Transformation Institute.
But, he said, the results of preliminary clinical trials could have spurred pharmaceutical companies to fund more studies on drug development and test how existing drugs influence a patient’s immune response.
Emanuel is one of the authors of a March 2022 covid roadmap report. He notes that RECOVER’s lack of focus on new treatments was a problem. “Only 15% of the budget is for clinical studies. That is a failure in itself — a failure of having the right priorities,” he told KFF Health News and NPR via email.
And though the NYU biobank has been impactful, Emanuel said there needs to be more focus on how existing drugs influence immune response.
He said some clinical trials that RECOVER has funded are “ridiculous,” because they’ve focused on symptom amelioration, for example to study the benefits of over-the-counter medication to improve sleep. Other studies looked at non-pharmacological interventions, such as exercise and “brain training” to help with cognitive fog.
People with long covid say this type of clinical research contributes to what many describe as the “gaslighting” they experience from doctors, who sometimes blame a patient’s symptoms on anxiety or depression, rather than acknowledging long covid as a real illness with a physiological basis.
“I’m just disgusted,” said long-covid patient Hayes. “You wouldn’t tell somebody with diabetes to breathe through it.”
Chimére L. Sweeney, director and founder of the Black Long Covid Experience, said she’s even taken breaks from seeking treatment after getting fed up with being told that her symptoms were due to her diet or mental health.
“You’re at the whim of somebody who may not even understand the spectrum of long covid,” Sweeney said.
Insurance Battles Over Experimental Treatments
Since there are still no long-covid treatments approved by the Food and Drug Administration, anything a physician prescribes is classified as either experimental — for unproven treatments — or an off-label use of a drug approved for other conditions. This means patients can struggle to get insurance to cover prescriptions.
Michael Brode, medical director for UT Health Austin’s Post-COVID-19 Program — said he writes many appeal letters. And some people pay for their own treatment.
For example, intravenous immunoglobulin therapy, low-dose naltrexone, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy are all promising treatments, he said.
For hyperbaric oxygen, two small, randomized controlled studies show improvements for the chronic fatigue and brain fog that often plague long-covid patients. The theory is that higher oxygen concentration and increased air pressure can help heal tissues that were damaged during a covid infection.
However, the out-of-pocket cost for a series of sessions in a hyperbaric chamber can run as much as $8,000, Brode said.
“Am I going to look a patient in the eye and say, ‘You need to spend that money for an unproven treatment’?” he said. “I don’t want to hype up a treatment that is still experimental. But I also don’t want to hide it.”
There’s a host of pharmaceuticals that have promising off-label uses for long covid, said microbiologist Amy Proal, president and chief scientific officer at the Massachusetts-based PolyBio Research Foundation. For instance, she’s collaborating on a clinical study that repurposes two HIV drugs to treat long covid.
Proal said research on treatments can move forward based on what’s already understood about the disease. For instance, she said that scientists have evidence — partly due to RECOVER research — that some patients continue to harbor small amounts of viral material after a covid infection. She has not received RECOVER funds but is researching antivirals.
But to vet a range of possible treatments for the millions suffering now — and to develop new drugs specifically targeting long covid — clinical trials are needed. And that requires money.
Hayes said she would definitely volunteer for an experimental drug trial. For now, though, “in order to not be absolutely miserable,” she said she focuses on what she can do, like having dinner with her http://family.at/ the same time, Hayes doesn’t want to spend the rest of her life on a beige couch.
RECOVER’s deadline to submit research proposals for potential long-covid treatments is Feb. 1.
This article is from a partnership that includes NPR and KFF Health News.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Is thunderstorm asthma becoming more common?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When spring arrives, so do warnings about thunderstorm asthma. But a decade ago, most of us hadn’t heard of it.
So where did thunderstorm asthma come from? Is it a new phenomenon?
In 2016, the world’s most catastrophic thunderstorm asthma event took Melbourne by surprise. An increase in warnings and monitoring is partly a response to this.
But there are also signs climate change may be exacerbating the likelihood of thunderstorm asthma, with more extreme weather, extended pollen seasons and a rise in Australians reporting hay fever.
A landmark catastrophe
The first time many Australians heard of thunderstorm asthma was in November 2016, when a major event rocked Melbourne.
During a late night storm, an estimated 10,000 people were rushed to hospitals with severe asthma attacks. With thousands of calls on emergency lines, ambulances and emergency departments were unprepared to handle the rapid increase in people needing urgent medical care. Tragically, ten of those people died.
This was the most catastrophic thunderstorm asthma event in recorded history and the first time deaths have ever occurred anywhere in the world.
In response, the Victorian Department of Health implemented initiatives, including public awareness campaigns and improvements to health and emergency services, to be ready for future thunderstorm asthma events.
A network of pollen monitoring stations was also set up across the state to gather data that helps to predict future events.
A problem for decades
While this event was unexpected, it wasn’t the first time we’d had thunderstorm asthma in Australia – we’ve actually known about it for decades.
Melbourne reported its first instance of thunderstorm asthma back in 1984, only a year after this phenomenon was first discovered in Birmingham in the United Kingdom.
Thunderstorm asthma has since been reported in other parts of Australia, including Canberra and New South Wales. But it is still most common in Melbourne. Compared to any other city (or country) the gap is significant: over a quarter of all known events worldwide have occurred in Melbourne.
Why Melbourne?
Melbourne’s location makes it a hotspot for these kinds of events. Winds coming from the north of Melbourne tend to be dry and hot as they come from deserts in the centre of Australia, while winds from the south are cooler as they come from the ocean.
When hot and cool air mix above Melbourne, it creates the perfect conditions for thunderstorms to form.
Northern winds also blow a lot of pollen from farmlands into the city, in particular grass pollen. This is not only the most common cause of seasonal hay fever in Melbourne but also a major trigger of thunderstorm asthma.
Why grass pollen?
There’s a particular reason grass pollen is the main culprit behind thunderstorm asthma in Australia. During storms there is a lot of moisture in the air. Grass pollen will absorb this moisture, making it swell up like a water balloon.
If pollen absorbs too much water whilst airborne, it can burst or “rupture,” releasing hundreds of microscopic particles into the air that can be swept by powerful winds.
Normally, when you breathe in pollen it gets stuck in your upper airway – for example, your nose and throat. This is what causes typical hay fever symptoms such as sneezing or runny nose.
But the microscopic particles released from ruptured grass pollen are much smaller and don’t get stuck as easily in the upper airway. Instead, they can travel deep into your airways until they reach your lungs. This may trigger more severe symptoms, such as wheezing or difficulty breathing, even in people with no prior history of asthma.
So who is at risk?
You might think asthma is the biggest risk factor for thunderstorm asthma. In fact, the biggest risk factor is hay fever.
Up to 99% of patients who went to the emergency department during the Melbourne 2016 event had hay fever, while a majority (60%) had no prior diagnosis of asthma.
Every single person hospitalised was allergic to at least one type of grass pollen. All had a sensitivity to ryegrass.
Is thunderstorm asthma becoming more common?
Thunderstorm asthma events are rare, with just 26 events officially recorded worldwide.
However there is evidence these events could become more frequent and severe in coming years, due to climate change. Higher temperatures and pollution could be making plants produce more pollen and pollen seasons last much longer.
Extreme weather events, including thunderstorms, are also expected to become more common and severe.
In addition, there are signs rates that hay fever may be increasing. The number of Australians reporting allergy symptoms have risen from 15% in 2008 to 24% in 2022. Similar trends in other countries has been linked to climate change.
How can I prepare?
Here are three ways you can reduce your risk of thunderstorm asthma:
- stock up on allergy medication and set up an asthma action plan with your GP
- check daily pollen forecasts for the estimated pollen level and risk of a thunderstorm asthma event in your local area
- on days with high pollen or a high risk of thunderstorm asthma, spend less time outside or wear a surgical face mask to reduce your symptoms.
Kira Morgan Hughes, PhD Candidate in Allergy and Asthma, School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How Does One Test Acupuncture Against Placebo Anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture
We asked you for your opinions on acupuncture, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of answers:
- A little under half of all respondents voted for “It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc”
- Slightly fewer respondents voted for “We don’t understand how it works, but it works!”
- A little under a fifth of respondents voted for “It may have some limited clinical applications beyond placebo”
- One (1) respondent voted for for “It’s placebo at best”
When we did a main feature about homeopathy, a couple of subscribers wrote to say that they were confused as to what homeopathy was, so this time, we’ll start with a quick definition first.
First, what is acupuncture? For the convenience of a quick definition so that we can move on to the science, let’s borrow from Wikipedia:
❝Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine in which thin needles are inserted into the body.
Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery.❞
Now, that’s not a promising start, but we will not be deterred! We will instead examine the science itself, rather than relying on tertiary sources like Wikipedia.
It’s worth noting before we move on, however, that there is vigorous debate behind the scenes of that article. The gist of the argument is:
- On one side: “Acupuncture is not pseudoscience/quackery! This has long been disproved and there are peer-reviewed research papers on the subject.”
- On the other: “Yes, but only in disreputable quack journals created specifically for that purpose”
The latter counterclaim is a) potentially a “no true Scotsman” rhetorical ploy b) potentially true regardless
Some counterclaims exhibit specific sinophobia, per “if the source is Chinese, don’t believe it”. That’s not helpful either.
Well, the waters sure are muddy. Where to begin? Let’s start with a relatively easy one:
It may have some clinical applications beyond placebo: True or False?
True! Admittedly, “may” is doing some of the heavy lifting here, but we’ll take what we can get to get us going.
One of the least controversial uses of acupuncture is to alleviate chronic pain. Dr. Vickers et al, in a study published under the auspices of JAMA (a very respectable journal, and based in the US, not China), found:
❝Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic pain and is therefore a reasonable referral option. Significant differences between true and sham acupuncture indicate that acupuncture is more than a placebo.
However, these differences are relatively modest, suggesting that factors in addition to the specific effects of needling are important contributors to the therapeutic effects of acupuncture❞
Source: Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis
If you’re feeling sharp today, you may be wondering how the differences are described as “significant” and “relatively modest” in the same text. That’s because these words have different meanings in academic literature:
- Significant = p<0.05, where p is the probability of the achieved results occurring randomly
- Modest = the differences between the test group and the control group were small
In other words, “significant modest differences” means “the sample sizes were large, and the test group reliably got slightly better results than placebo”
We don’t understand how it works, but it works: True or False
Broadly False. When it works, we generally have an idea how.
Placebo is, of course, the main explanation. And even in examples such as the above, how is placebo acupuncture given?
By inserting acupuncture needles off-target rather than in accord with established meridians and points (the lines and dots that, per Traditional Chinese Medicine, indicate the flow of qi, our body’s vital energy, and welling-points of such).
So, if a patient feels that needles are being inserted randomly, they may no longer have the same confidence that they aren’t in the control group receiving placebo, which could explain the “modest” difference, without there being anything “to” acupuncture beyond placebo. After all, placebo works less well if you believe you are only receiving placebo!
Indeed, a (Korean, for the record) group of researchers wrote about this—and how this confounding factor cuts both ways:
❝Given the current research evidence that sham acupuncture can exert not only the originally expected non-specific effects but also sham acupuncture-specific effects, it would be misleading to simply regard sham acupuncture as the same as placebo.
Therefore, researchers should be cautious when using the term sham acupuncture in clinical investigations.❞
Source: Sham Acupuncture Is Not Just a Placebo
It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc: True or False?
False, for the most part.
While yes, the meridians and points of acupuncture charts broadly correspond to nerves and vasculature, there is no evidence that inserting needles into those points does anything for one’s qi, itself a concept that has not made it into Western science—as a unified concept, anyway…
Note that our bodies are indeed full of energy. Electrical energy in our nerves, chemical energy in every living cell, kinetic energy in all our moving parts. Even, to stretch the point a bit, gravitational potential energy based on our mass.
All of these things could broadly be described as qi, if we so wish. Indeed, the ki in the Japanese martial art of aikido is the latter kinds; kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy based on our mass. Same goes, therefore for the ki in kiatsu, a kind of Japanese massage, while the ki in reiki, a Japanese spiritual healing practice, is rather more mystical.
The qi in Chinese qigong is mostly about oxygen, thus indirectly chemical energy, and the electrical energy of the nerves that are receiving oxygenated blood at higher or lower levels.
On the other hand, the efficacy of the use of acupuncture for various kinds of pain is well-enough evidenced. Indeed, even the UK’s famously thrifty NHS (that certainly would not spend money on something it did not find to work) offers it as a complementary therapy for some kinds of pain:
❝Western medical acupuncture (dry needling) is the use of acupuncture following a medical diagnosis. It involves stimulating sensory nerves under the skin and in the muscles.
This results in the body producing natural substances, such as pain-relieving endorphins. It’s likely that these naturally released substances are responsible for the beneficial effects experienced with acupuncture.❞
Source: NHS | Acupuncture
Meanwhile, the NIH’s National Cancer Institute recommends it… But not as a cancer treatment.
Rather, they recommend it as a complementary therapy for pain management, and also against nausea, for which there is also evidence that it can help.
Frustratingly, while they mention that there is lots of evidence for this, they don’t actually link the studies they’re citing, or give enough information to find them. Instead, they say things like “seven randomized clinical trials found that…” and provide links that look reassuring until one finds, upon clicking on them, that it’s just a link to the definition of “randomized clinical trial”:
Source: NIH | Nactional Cancer Institute | Acupuncture (PDQ®)–Patient Version
However, doing our own searches finds many studies (mostly in specialized, potentially biased, journals such as the Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies) finding significant modest outperformance of [what passes for] placebo.
Sometimes, the existence of papers with promising titles, and statements of how acupuncture might work for things other than relief of pain and nausea, hides the fact that the papers themselves do not, in fact, contain any evidence to support the hypothesis. Here’s an example:
❝The underlying mechanisms behind the benefits of acupuncture may be linked with the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (adrenal) axis and activation of the Wnt/β-catenin and OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathways.
In summary, strong evidence may still come from prospective and well-designed clinical trials to shed light on the potential role of acupuncture in preserving bone loss❞
Source: Acupuncture for Osteoporosis: a Review of Its Clinical and Preclinical Studies
So, here they offered a very sciencey hypothesis, and to support that hypothesis, “strong evidence may still come”.
“We must keep faith” is not usually considered evidence worthy of inclusion in a paper!
PS: the above link is just to the abstract, because the “Full Text” link offered in that abstract leads to a completely unrelated article about HIV/AIDS-related cryptococcosis, in a completely different journal, nothing to do with acupuncture or osteoporosis).
Again, this is not the kind of professionalism we expect from peer-reviewed academic journals.
Bottom line:
Acupuncture reliably performs slightly better than sham acupuncture for the management of pain, and may also help against nausea.
Beyond placebo and the stimulation of endorphin release, there is no consistently reliable evidence that is has any other discernible medical effect by any mechanism known to Western science—though there are plenty of hypotheses.
That said, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, and the logistical difficulty of testing acupuncture against placebo makes for slow research. Maybe one day we’ll know more.
For now:
- If you find it helps you: great! Enjoy
- If you think it might help you: try it! By a licensed professional with a good reputation, please.
- If you are not inclined to having needles put in you unnecessarily: skip it! Extant science suggests that at worst, you’ll be missing out on slight relief of pain/nausea.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cacao to carob, we picked the cacao.
Why?
It’s close, and may depend a little on your priorities!
In terms of macros, the cacao has more protein and fat, while the carob has more carbohydrates, mostly sugar. Since people will not generally eat this by the spoonful, and will instead either make drinks or cook with it, we can’t speak for the glycemic index or general health impact of the sugars. As for the fats, on the one hand the cacao does contain saturated fat; on the other, this merely means that different saturated fat will usually be added to the carob if making something with it. Still, slight win for the carob on the fat front. Protein, of course, is entirely in cacao’s favor.
In the category of vitamins and minerals, they’re about equal on vitamins, while cacao wins easily on the mineral front, boasting more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus.
While both have a generous antioxidant content, this one’s another win for cacao, with about 3x the active polyphenols and flavonoids.
In short: both are good, consumed in moderation and before adding unhealthy extra ingredients—but we say cacao comes out the winner.
If you’re looking specifically for the above-depicted products, by the way, here they are:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
- Chocolate & Health
- The Truth About Chocolate & Skin Health
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Goji Berries vs Blueberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing goji berries to blueberries, we picked the goji berries.
Why?
As you might have guessed, both are very good options:
- Both have plenty of vitamins and minerals, and/but goji berries have more. How much more? It varies, but for example about 5x more vitamin C, about 25x more iron, about 30x more calcium, about 50x more vitamin A.
- Blueberries beat goji berries with some vitamins (B, E, K), but only in quite small amounts.
- Both are great sources of antioxidants, and/but goji berries have 2–4 times the antioxidants that blueberries do.
- Goji berries do have more sugar, but since they have about 4x more sugar and 5x more fiber, we’re still calling this a win for goji berries on the glycemic index front (and indeed, the GI of goji berries is lower).
In short: blueberries are great, but goji berries beat them in most metrics.
Want to read more?
Check out our previous main features, detailing some of the science, and also where to get them:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Brain Alarm Signs That Warn Of Dementia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to predicting age-related cognitive impairment:
First there are genetic factors to take into account (such as the APOE4 gene for Alzheimer’s), as well as things such as age and sex.
When it comes to sex, by the way, what matters here is hormones, which is why [it seems; this as technically as yet unproven with full rigor, but the hypothesis is sound and there is a body of evidence gradually being accumulated to support it] postmenopausal women with untreated menopause get Alzheimer’s at a higher rate and deteriorate more quickly:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Next, there are obviously modifiable lifestyle factors to take into account, things that will reduce your risk such as getting good sleep, good diet, good exercise, and abstaining from alcohol and smoking, as well as oft-forgotten things such as keeping cognitively active and, equally importantly, socially active:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
(the article outlines what matters the most in each of the above areas, by the way, so that you can get the most bang-for-buck in terms of lifestyle adjustments)
Lastly (in the category of risk factors), there are things to watch out for in the blood such as hypertension and high cholesterol.
Nipping it in the blood
In new research (so new it is still ongoing, but being at year 2 of a 4-year prospective study, they have published a paper with their results so far), researchers have:
- started with the premise “dementia is preceded by mild cognitive impairment”
- then, asked the question “what are the biometric signs of mild cognitive impairment?”
Using such tools as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) while the participants performed cognitive tasks, they were able to record changes in plasma levels of extracellular vesicles, assessing them with small-particle flow cytometry.
Translating from sciencese: they gave the participants mental tasks, and while they completed them, the researchers scanned their brains and monitored blood flow and the brain’s ability to compensate for any lack of it.
What they found:
- in young adults, blood flow increased, facilitating neurovascular coupling (this is good)
- in older adults, blood flow did not increase as much, but they engaged other areas of the brain to compensate, by what’s called functional connectivity (this is next best)
- in those with mild cognitive impairment, blood flow was reduced, and they did not have the ability to compensate by functional connectivity (this is not good)
They also performed a liquid biopsy, which sounds alarming but it just means they took some blood, and tested this for density of cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles (CEEVs), which—in more prosaic words—are bits from the cells lining the blood vessels in the brain.
People with mild cognitive impairment had more of these brain bits in their blood than those without.
You can read the paper itself here:
What this means
The science here is obviously still young (being as it is still in progress), but this will likely contribute greatly to early warning signs of dementia, by catching mild cognitive impairment in its early stages, by means of a simple blood test, instead of years of wondering before getting a dementia diagnosis.
And of course, forewarned is forearmed, so if this is something that could be done as a matter of routine upon hitting the age of, say, 65 and then periodically thereafter, it would catch a lot of cases while there’s still more time to turn things around.
As for how to turn things around, well, we imagine you have now read our “How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk” article linked up top (if not, we recommend checking it out), and there is also…
Do Try This At Home: The 12-Week Brain Fitness Program To Measurably Boost Your Brain
Take care!
When it comes to predicting age-related cognitive impairment:
First there are genetic factors to take into account (such as the APOE4 gene for Alzheimer’s), as well as things such as age and sex.
When it comes to sex, by the way, what matters here is hormones, which is why [it seems; this as technically as yet unproven with full rigor, but the hypothesis is sound and there is a body of evidence gradually being accumulated to support it] postmenopausal women with untreated menopause get Alzheimer’s at a higher rate and deteriorate more quickly:
Alzheimer’s Sex Differences May Not Be What They Appear
Next, there are obviously modifiable lifestyle factors to take into account, things that will reduce your risk such as getting good sleep, good diet, good exercise, and abstaining from alcohol and smoking, as well as oft-forgotten things such as keeping cognitively active and, equally importantly, socially active:
How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
(the article outlines what matters the most in each of the above areas, by the way, so that you can get the most bang-for-buck in terms of lifestyle adjustments)
Lastly (in the category of risk factors), there are things to watch out for in the blood such as hypertension and high cholesterol.
Nipping it in the blood
In new research (so new it is still ongoing, but being at year 2 of a 4-year prospective study, they have published a paper with their results so far), researchers have:
- started with the premise “dementia is preceded by mild cognitive impairment”
- then, asked the question “what are the biometric signs of mild cognitive impairment?”
Using such tools as functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) while the participants performed cognitive tasks, they were able to record changes in plasma levels of extracellular vesicles, assessing them with small-particle flow cytometry.
Translating from sciencese: they gave the participants mental tasks, and while they completed them, the researchers scanned their brains and monitored blood flow and the brain’s ability to compensate for any lack of it.
What they found:
- in young adults, blood flow increased, facilitating neurovascular coupling (this is good)
- in older adults, blood flow did not increase as much, but they engaged other areas of the brain to compensate, by what’s called functional connectivity (this is next best)
- in those with mild cognitive impairment, blood flow was reduced, and they did not have the ability to compensate by functional connectivity (this is not good)
They also performed a liquid biopsy, which sounds alarming but it just means they took some blood, and tested this for density of cerebrovascular endothelial extracellular vesicles (CEEVs), which—in more prosaic words—are bits from the cells lining the blood vessels in the brain.
People with mild cognitive impairment had more of these brain bits in their blood than those without.
You can read the paper itself here:
What this means
The science here is obviously still young (being as it is still in progress), but this will likely contribute greatly to early warning signs of dementia, by catching mild cognitive impairment in its early stages, by means of a simple blood test, instead of years of wondering before getting a dementia diagnosis.
And of course, forewarned is forearmed, so if this is something that could be done as a matter of routine upon hitting the age of, say, 65 and then periodically thereafter, it would catch a lot of cases while there’s still more time to turn things around.
As for how to turn things around, well, we imagine you have now read our “How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk” article linked up top (if not, we recommend checking it out), and there is also…
Do Try This At Home: The 12-Week Brain Fitness Program To Measurably Boost Your Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: