Pine Nuts vs Pecans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pine nuts to pecans, we picked the pine nuts.
Why?
Both have their merits!
In terms of macros, pine nuts have more protein while pecans have more fiber. They’re about equal on fats, although pine nuts have more polyunsaturated fat and pecans have more monounsaturated fat, of which, both are healthy. They’re also about equal on carbs. So really it comes down to the subjective choice between prioritizing protein and prioritizing fiber. On principle, we pick fiber, which gives the win to pecans, but your preference in this regard may differ; prioritizing the protein would give the win to pine nuts.
In the category of vitamins, pine nuts have more of vitamins B2, B3, B9, E, K, and choline, while pecans have more of vitamins A, B1, B5, B6, and C. Thus, a 6:5 marginal win for pine nuts.
Looking at the minerals, pine nuts have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while pecans have more calcium and selenium. An easy win for pine nuts this time.
Adding up the sections makes for a win for pine nuts, but of course, enjoy either or (preferably) both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
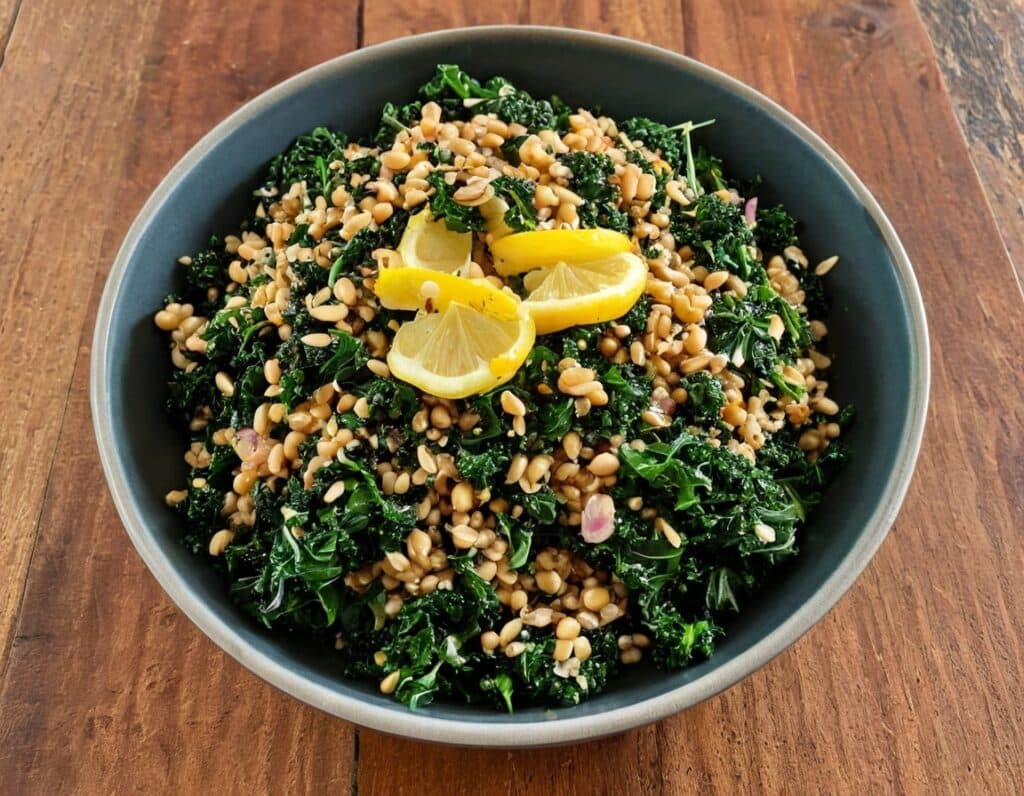
SMOL Bowl With Sautéed Greens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whole grains are good, and gluten is bad for some people. Today’s dish has four whole grains, and no gluten (assuming no cross-contamination, so look for the gluten-free label if that’s important to you). Breafast? Brunch? Lunch? Supper, even? This is good at any time of day, packed with nutrients and full of flavor!
You will need (per person)
- 1 cup mixed cooked grains of equal parts sorghum, millet, oats, lentils (SMOL)—these can be cooked in bulk in advance and frozen in portions, as it’s often good to used mixed grains, and these four are a great combination for many purposes.
- ½ cup low sodium vegetable stock (ideally you made this yourself from vegetable offcuts you kept in the freezer until you had enough for this purpose, but failing that, low-sodium stock cubes can be bought at most large supermarkets).
- ½ cup finely chopped red onion
- 6 oz cavolo nero, finely chopped
- 1 small carrot, finely chopped
- 3 cloves garlic, finely chopped
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- To serve: 1 lemon wedge
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add the stock to a sauté pan over a medium heat, and add the onion, garlic, and carrot. Stir frequently for about 7 minutes.
2) Add the cavolo nero and miso paste, stirring for another 4 minutes. If there is any liquid remaining, drain it off now.
3) Warm the SMOL mixture (microwave is fine) and spoon it into a bowl, topping with the nutritional yeast and black pepper. Finally, add the hot cavolo nero mixture.
4) Serve with the lemon wedge on the side, to add a dash of lemon at will.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Accidental falls in the older adult population: What academic research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Accidental falls are among the leading causes of injury and death among adults 65 years and older worldwide. As the aging population grows, researchers expect to see an increase in the number of fall injuries and related health spending.
Falls aren’t unique to older adults. Nealy 684,000 people die from falls each year globally. Another 37.3 million people each year require medical attention after a fall, according to the World Health Organization. But adults 65 and older account for the greatest number of falls.
In the United States, more than 1 in 4 older adults fall each year, according to the National Institute on Aging. One in 10 report a fall injury. And the risk of falling increases with age.
In 2022, health care spending for nonfatal falls among older adults was $80 billion, according to a 2024 study published in the journal Injury Prevention.
Meanwhile, the fall death rate in this population increased by 41% between 2012 and 2021, according to the latest CDC data.
“Unfortunately, fall-related deaths are increasing and we’re not sure why that is,” says Dr. Jennifer L. Vincenzo, an associate professor at the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in the department of physical therapy and the Center for Implementation Research. “So, we’re trying to work more on prevention.”
Vincenzo advises journalists to write about how accidental falls can be prevented. Remind your audiences that accidental falls are not an inevitable consequence of aging, and that while we do decline in many areas with age, there are things we can do to minimize the risk of falls, she says. And expand your coverage beyond the national Falls Prevention Awareness Week, which is always during the first week of fall — Sept. 23 to 27 this year.
Below, we explore falls among older people from different angles, including injury costs, prevention strategies and various disparities. We have paired each angle with data and research studies to inform your reporting.
Falls in older adults
In 2020, 14 million older adults in the U.S. reported falling during the previous year. In 2021, more than 38,700 older adults died due to unintentional falls, according to the CDC.
A fall could be immediately fatal for an older adult, but many times it’s the complications from a fall that lead to death.
The majority of hip fractures in older adults are caused by falls, Vincenzo says, and “it could be that people aren’t able to recover [from the injury], losing function, maybe getting pneumonia because they’re not moving around, or getting pressure injuries,” she says.
In addition, “sometimes people restrict their movement and activities after a fall, which they think is protective, but leads to further functional declines and increases in fall risk,” she adds.
Factors that can cause a fall include:
- Poor eyesight, reflexes and hearing. “If you cannot hear as well, anytime you’re doing something in your environment and there’s a noise, it will be really hard for you to focus on hearing what that noise is and what it means and also moving at the same time,” Vincenzo says.
- Loss of strength, balance, and mobility with age, which can lessen one’s ability to prevent a fall when slipping or tripping.
- Fear of falling, which usually indicates decreased balance.
- Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or problems with nerves or feet that can affect balance.
- Conditions like incontinence that cause rushed movement to the bathroom.
- Cognitive impairment or certain types of dementia.
- Unsafe footwear such as backless shoes or high heels.
- Medications or medication interactions that can cause dizziness or confusion.
- Safety hazards in the home or outdoors, such as poor lighting, steps and slippery surfaces.
Related Research
Nonfatal and Fatal Falls Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — United States, 2020–2021
Ramakrishna Kakara, Gwen Bergen, Elizabeth Burns and Mark Stevens. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, September 2023.Summary: Researchers analyzed data from the 2020 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System — a landline and mobile phone survey conducted each year in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia — and data from the 2021 National Vital Statistics System to identify patterns of injury and death due to falls in the U.S. by sex and state for adults 65 years and older. Among the findings:
- The percentage of women who reported falling was 28.9%, compared with 26.1% of men.
- Death rates from falls were higher among white and American Indian or Alaska Native older adults than among older adults from other racial and ethnic groups.
- In 2020, the percentage of older adults who reported falling during the past year ranged from 19.9% in Illinois to 38.0% in Alaska. The national estimate for 18 states was 27.6%.
- In 2021, the unintentional fall-related death rate among older adults ranged from 30.7 per 100,000 older adults in Alabama to 176.5 in Wisconsin. The national estimate for 26 states was 78.
“Although common, falls among older adults are preventable,” the authors write. “Health care providers can talk with patients about their fall risk and how falls can be prevented.”
Trends in Nonfatal Falls and Fall-Related Injuries Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years — United States, 2012-2018
Briana Moreland, Ramakrishna Kakara and Ankita Henry. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, July 2020.Summary: Researchers compared data from the 2018 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Among the findings:
- The percentage of older adults reporting a fall increased from 2012 to 2016, then slightly decreased from 2016 to 2018.
- Even with this decrease in 2018, older adults reported 35.6 million falls. Among those falls, 8.4 million resulted in an injury that limited regular activities for at least one day or resulted in a medical visit.
“Despite no significant changes in the rate of fall-related injuries from 2012 to 2018, the number of fall-related injuries and health care costs can be expected to increase as the proportion of older adults in the United States grows,” the authors write.
Understanding Modifiable and Unmodifiable Older Adult Fall Risk Factors to Create Effective Prevention Strategies
Gwen Bergen, et al. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine, October 2019.Summary: Researchers used data from the 2016 U.S. Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System to better understand the association between falls and fall injuries in older adults and factors such as health, state and demographic characteristics. Among the findings:
- Depression had the strongest association with falls and fall injuries. About 40% of older adults who reported depression also reported at least one fall; 15% reported at least one fall injury.
- Falls and depression have several factors in common, including cognitive impairment, slow walking speed, poor balance, slow reaction time, weakness, low energy and low levels of activity.
- Other factors associated with an increased risk of falling include diabetes, vision problems and arthritis.
“The multiple characteristics associated with falls suggest that a comprehensive approach to reducing fall risk, which includes screening and assessing older adult patients to determine their unique, modifiable risk factors and then prescribing tailored care plans that include evidence-based interventions, is needed,” the authors write.
Health care use and cost
In addition to being the leading cause of injury, falls are the leading cause of hospitalization in older adults. Each year, about 3 million older adults visit the emergency department due to falls. More than 1 million get hospitalized.
In 2021, falls led to more than 38,000 deaths in adults 65 and older, according to the CDC.
The annual financial medical toll of falls among adults 65 years and older is expected to be more than $101 billion by 2030, according to the National Council on Aging, an organization advocating for older Americans.
Related research
Healthcare Spending for Non-Fatal Falls Among Older Adults, USA
Yara K. Haddad, et al. Injury Prevention, July 2024.Summary: In 2015, health care spending related to falls among older adults was roughly $50 billion. This study aims to update the estimate, using the 2017, 2019 and 2021 Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey, the most comprehensive and complete survey available on the Medicare population. Among the findings:
- In 2020, health care spending for non-fatal falls among older adults was $80 billion.
- Medicare paid $53.3 billion of the $80 billion, followed by $23.2 billion paid by private insurance or patients and $3.5 billion by Medicaid.
“The burden of falls on healthcare systems and healthcare spending will continue to rise if the risk of falls among the aging population is not properly addressed,” the authors write. “Many older adult falls can be prevented by addressing modifiable fall risk factors, including health and functional characteristics.”
Cost of Emergency Department and Inpatient Visits for Fall Injuries in Older Adults Lisa Reider, et al. Injury, February 2024.
Summary: The researchers analyzed data from the 2016-2018 National Inpatient Sample and National Emergency Department Sample, which are large, publicly available patient databases in the U.S. that include all insurance payers such as Medicare and private insurance. Among the findings:
- During 2016-2018, more than 920,000 older adults were admitted to the hospital and 2.3 million visited the emergency department due to falls. The combined annual cost was $19.2 billion.
- More than half of hospital admissions were due to bone fractures. About 14% of these admissions were due to multiple fractures and cost $2.5 billion.
“The $20 billion in annual acute treatment costs attributed to fall injury indicate an urgent need to implement evidence-based fall prevention interventions and underscores the importance of newly launched [emergency department]-based fall prevention efforts and investments in geriatric emergency departments,” the authors write.
Hip Fracture-Related Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations and Deaths by Mechanism of Injury Among Adults Aged 65 and Older, United States 2019
Briana L. Moreland, Jaswinder K. Legha, Karen E. Thomas and Elizabeth R. Burns. Journal of Aging and Health, June 2024.Summary: The researchers calculated hip fracture-related U.S. emergency department visits, hospitalizations and deaths among older adults, using data from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project and the National Vital Statistics System. Among the findings:
- In 2019, there were 318,797 emergency department visits, 290,130 hospitalizations and 7,731 deaths related to hip fractures among older adults.
- Nearly 88% of emergency department visits and hospitalizations and 83% of deaths related to hip fractures were caused by falls.
- These rates were highest among those living in rural areas and among adults 85 and older. More specifically, among adults 85 and older, the rate of hip fracture-related emergency department visits was nine times higher than among adults between 65 and 74 years old.
“Falls are common among older adults, but many are preventable,” the authors write. “Primary care providers can prevent falls among their older patients by screening for fall risk annually or after a fall, assessing modifiable risk factors such as strength and balance issues, and offering evidence-based interventions to reduce older adults’ risk of falls.”
Fall prevention
Several factors, including exercising, managing medication, checking vision and making homes safer can help prevent falls among older adults.
“Exercise is one of the best interventions we know of to prevent falls,” Vincenzo says. But “walking in and of itself will not help people to prevent falls and may even increase their risk of falling if they are at high risk of falls.”
The National Council on Aging also has a list of evidence-based fall prevention programs, including activities and exercises that are shown to be effective.
The National Institute on Aging has a room-by-room guide on preventing falls at home. Some examples include installing grab bars near toilets and on the inside and outside of the tub and shower, sitting down while preparing food to prevent fatigue, and keeping electrical cords near walls and away from walking paths.
There are also national and international initiatives to help prevent falls.
Stopping Elderly Accidents, Deaths and Injuries, or STEADI, is an initiative by the CDC’s Injury Center to help health care providers who treat older adults. It helps providers screen patients for fall risk, assess their fall risk factors and reduce their risk by using strategies that research has shown to be effective. STEADI’s guidelines are in line with the American and British Geriatric Societies’ Clinical Practice Guidelines for fall prevention.
“We’re making some iterations right now to STEADI that will come out in the next couple of years based on the World Falls Guidelines, as well as based on clinical providers’ feedback on how to make [STEADI] more feasible,” Vincenzo says.
The World Falls Guidelines is an international initiative to prevent falls in older adults. The guidelines are the result of the work of 14 international experts who came together in 2019 to consider whether new guidelines on fall prevention were needed. The task force then brought together 96 experts from 39 countries across five continents to create the guidelines.
The CDC’s STEADI initiative has a screening questionnaire for consumers to check their risk of falls, as does the National Council on Aging.
On the policy side, U.S. Rep. Carol Miller, R-W.V., and Melanie Stansbury, D-N.M., introduced the Stopping Addiction and Falls for the Elderly (SAFE) Act in March 2024. The bill would allow occupational and physical therapists to assess fall risks in older adults as part of the Medicare Annual Wellness Benefit. The bill was sent to the House Subcommittee on Health in the same month.
Meanwhile, older adults’ attitudes toward falls and fall prevention are also pivotal. For many, coming to terms with being at risk of falls and making changes such as using a cane, installing railings at home or changing medications isn’t easy for all older adults, studies show.
“Fall is a four-letter F-word in a way to older adults,” says Vincenzo, who started her career as a physical therapist. “It makes them feel ‘old.’ So, it’s a challenge on multiple fronts: U.S. health care infrastructure, clinical and community resources and facilitating health behavior change.”
Related research
Environmental Interventions for Preventing Falls in Older People Living in the Community
Lindy Clemson, et al. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, March 2023.Summary: This review includes 22 studies from 10 countries involving a total of 8,463 older adults who live in the community, which includes their own home, a retirement facility or an assisted living facility, but not a hospital or nursing home. Among the findings:
- Removing fall hazards at home reduced the number of falls by 38% among older adults at a high risk of having a fall, including those who have had a fall in the past year, have been hospitalized or need support with daily activities. Examples of fall hazards at home include a stairway without railings, a slippery pathway or poor lighting.
- It’s unclear whether checking prescriptions for eyeglasses, wearing special footwear or installing bed alarm systems reduces the rate of falls.
- It’s also not clear whether educating older adults about fall risks reduces their fall risk.
The Influence of Older Adults’ Beliefs and Attitudes on Adopting Fall Prevention Behaviors
Judy A. Stevens, David A. Sleet and Laurence Z. Rubenstein. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. January 2017.Summary: Persuading older adults to adopt interventions that reduce their fall risk is challenging. Their attitudes and beliefs about falls play a large role in how well they accept and adopt fall prevention strategies, the authors write. Among the common attitudes and beliefs:
- Many older adults believe that falls “just happen,” are a normal result of aging or are simply due to bad luck.
- Many don’t acknowledge or recognize their fall risk.
- For many, falls are considered to be relevant only for frail or very old people.
- Many believe that their home environment or daily activities can be a risk for fall, but do not consider biological factors such as dizziness or muscle weakness.
- For many, fall prevention simply consists of “being careful” or holding on to things when moving about the house.
“To reduce falls, health care practitioners have to help patients understand and acknowledge their fall risk while emphasizing the positive benefits of fall prevention,” the authors write. “They should offer patients individualized fall prevention interventions as well as provide ongoing support to help patients adopt and maintain fall prevention strategies and behaviors to reduce their fall risk. Implementing prevention programs such as CDC’s STEADI can help providers discuss the importance of falls and fall prevention with their older patients.”
Reframing Fall Prevention and Risk Management as a Chronic Condition Through the Lens of the Expanded Chronic Care Model: Will Integrating Clinical Care and Public Health Improve Outcomes?
Jennifer L. Vincenzo, Gwen Bergen, Colleen M. Casey and Elizabeth Eckstrom. The Gerontologist, June 2024.Summary: The authors recommend approaching fall prevention from the lens of chronic disease management programs because falls and fall risk are chronic issues for many older adults.
“Policymakers, health systems, and community partners can consider aligning fall risk management with the [Expanded Chronic Care Model], as has been done for diabetes,” the authors write. “This can help translate high-quality research on the effectiveness of fall prevention interventions into daily practice for older adults to alter the trajectory of older adult falls and fall-related injuries.”
Disparities
Older adults face several barriers to reducing their fall risk. Accessing health care services and paying for services such as physical therapy is not feasible for everyone. Some may lack transportation resources to go to and from medical appointments. Social isolation can increase the risk of death from falls. In addition, physicians may not have the time to fit in a fall risk screening while treating older patients for other health concerns.
Moreover, implementing fall risk screening, assessment and intervention in the current U.S. health care structure remains a challenge, Vincenzo says.
Related research
Mortality Due to Falls by County, Age Group, Race, and Ethnicity in the USA, 2000-19: A Systematic Analysis of Health Disparities
Parkes Kendrick, et al. The Lancet Public Health, August 2024.Summary: Researchers analyzed death registration data from the U.S. National Vital Statistics System and population data from the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics to estimate annual fall-related mortality. The data spanned from 2000 to 2019 and includes all age groups. Among the findings:
- The disparities between racial and ethnic populations varied widely by age group. Deaths from falls among younger adults were highest for the American Indian/Alaska Native population, while among older adults it was highest for the white population.
- For older adults, deaths from falls were particularly high in the white population within clusters of counties across states including Florida, Minnesota and Wisconsin.
- One factor that could contribute to higher death rates among white older adults is social isolation, the authors write. “Studies suggest that older Black and Latino adults are more likely to have close social support compared with older white adults, while AIAN and Asian individuals might be more likely to live in multigenerational households,” they write.
“Among older adults, current prevention techniques might need to be restructured to reduce frailty by implementing early prevention and emphasizing particularly successful interventions. Improving social isolation and evaluating the effectiveness of prevention programs among minoritized populations are also key,” the authors write.
Demographic Comparisons of Self-Reported Fall Risk Factors Among Older Adults Attending Outpatient Rehabilitation
Mariana Wingood, et al. Clinical Interventions in Aging, February 2024.Summary: Researchers analyzed the electronic health record data of 108,751 older adults attending outpatient rehabilitation within a large U.S. health care system across seven states, between 2018 and 2022. Among the findings:
- More than 44% of the older adults were at risk of falls; nearly 35% had a history of falls.
- The most common risk factors for falls were diminished strength, gait and balance.
- Compared to white older adults, Native American/Alaska Natives had the highest prevalence of fall history (43.8%) and Hispanics had the highest prevalence of falls with injury (56.1%).
“Findings indicate that rehabilitation providers should perform screenings for these impairments, including incontinence and medication among females, loss of feeling in the feet among males, and all Stay Independent Questionnaire-related fall risk factors among Native American/Alaska Natives, Hispanics, and Blacks,” the authors write.
Resources and articles
- National Institute on Aging
- National Council on Aging
- Gerontological Society of America
- Home Health Agencies Failed To Report Over Half of Falls With Major Injury and Hospitalization Among Their Medicare Patients, a 2023 report from the U.S Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Inspector General.
- 6 tips for improving new coverage of older people, a tip sheet from The Journalist’s Resource.
- Crosswalk and pedestrian safety: What you need to know from recent research, from The Journalist’s Resource.
- Aging-in-place technology challenges and trends, a resource from the Association of Health Care Journalists.
- Successful aging at home: what reporters should know, a resource from the Association of Health Care Journalists.
This article first appeared on The Journalist’s Resource and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
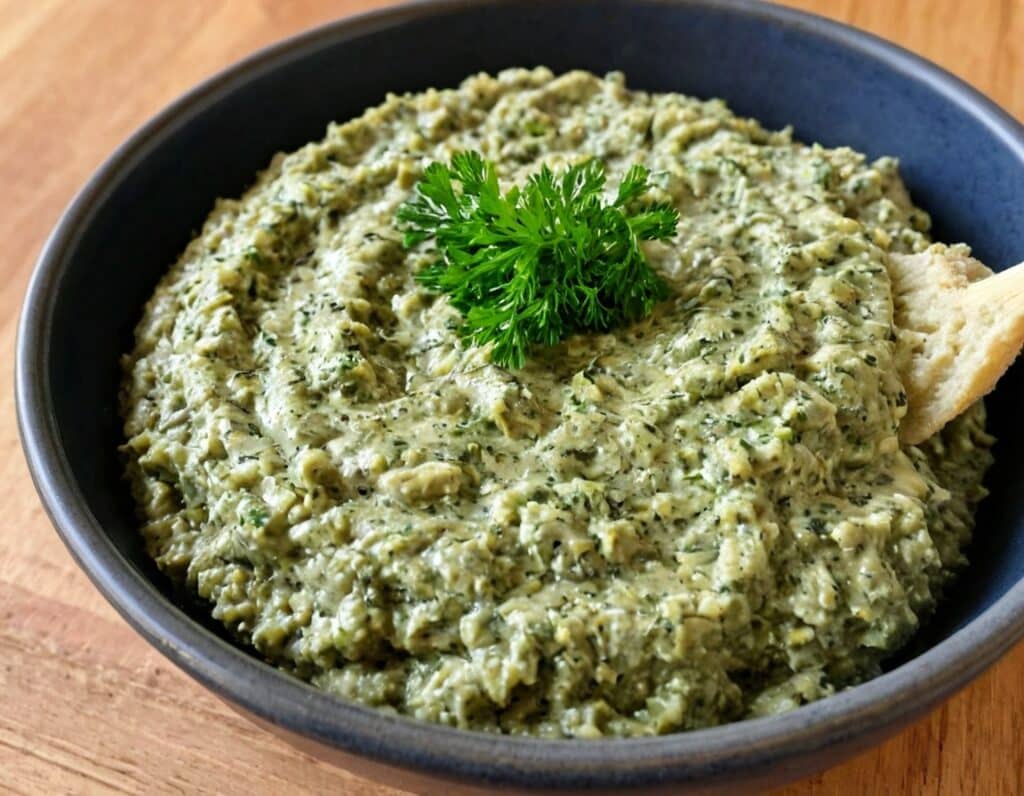
Superfood Kale & Dill Pâté
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us could do with eating more greens a lot of the time, but it’s not always easy to include them. This kale and dill pâté brings a healthy dose of green in luxurious style, along with abundant phytochemicals and more!
You will need
- 2 handfuls kale, stalks removed
- 1 cup soft cheese (you can use our Healthy Plant-Based Cream Cheese recipe if you like)
- 2 tbsp fresh dill, chopped
- 1 tsp capers
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Steam the kale for about 5 minutes or until wilted and soft. Run under cold water to halt the cooking process.
2) Combine all the ingredients, including the kale you just blanched, in a food processor and blitz to make a smooth pâté.
3) Serve with oatcakes or vegetable sticks, or keep in the fridge to enjoy it later:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Heart Health Calculator Entry Issue
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I tried to use your calculator for heart health, and was unable to enter in my height or weight. Is there another way to calculate? Why will that field not populate?❞
(this is in reference to yesterday’s main feature “How Are You, Really? And How Old Is Your Heart?“)
How strange! We tested it in several desktop browsers and several mobile browsers, and were unable to find any version that didn’t work. That includes switching between metric and imperial units, per preference; both appear to work fine. Do be aware that it’ll only take numerical imput, though.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Heal & Reenergize Your Brain With Optimized Sleep Cycles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes 8 hours sleep can result in grogginess while 6 hours can result in waking up fresh as a daisy, so what gives? Dr. Tracey Marks explains, in this short video.
Getting more than Zs in
Sleep involves 90-minute cycles, usually in 4 stages:
- Stage 1: (drowsy state): brief muscle jerks; lasts a few minutes.
- Stage 2: (light sleep): sleep spindles for memory consolidation; 50% of total sleep.
- Stage 3 (deep sleep): tissue repair, immune support, brain toxin removal via the glymphatic system.
- Stage 4 (REM sleep): emotional processing, creativity, problem-solving, and dreaming.
Some things can disrupt some or all of those. To give a few common examples:
- Alcohol: impairs REM sleep.
- Caffeine: hinders deep sleep even if consumed hours before bed.
- Screentime: delays sleep onset due to blue light (but not by much); the greater problem is that it can also disrupt REM sleep due to mental stimulation.
To optimize things, Dr. Marks recommends:
- 90-minute rule: plan sleep to align with full cycles (e.g: 22:30 to 06:00 = 7½ hours, which is 5x 90-minute cycles).
- Smart alarms: use sleep-tracking apps with built-in alarm, to wake you up during light sleep phases.
- Strategic naps: keep naps to 20 minutes or a full 90-minute cycle.
- Pink noise: improves deep sleep.
- Meal timing: avoid eating within 3 hours of bedtime.
- Natural light: get morning light exposure in the morning to strengthen circadian rhythm.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
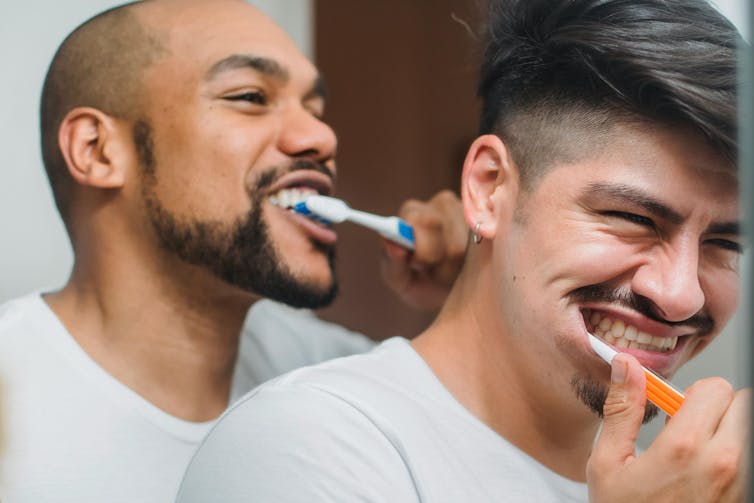
Yes, you do need to clean your tongue. Here’s how and why
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Has your doctor asked you to stick out your tongue and say “aaah”? While the GP assesses your throat, they’re also checking out your tongue, which can reveal a lot about your health.
The doctor will look for any changes in the tongue’s surface or how it moves. This can indicate issues in the mouth itself, as well as the state of your overall health and immunity.
But there’s no need to wait for a trip to the doctor. Cleaning your tongue twice a day can help you check how your tongue looks and feels – and improve your breath.
luisrsphoto/Shutterstock What does a healthy tongue look like?
Our tongue plays a crucial role in eating, talking and other vital functions. It is not a single muscle but rather a muscular organ, made up of eight muscle pairs that help it move.
The surface of the tongue is covered by tiny bumps that can be seen and felt, called papillae, giving it a rough surface.
These are sometimes mistaken for taste buds – they’re not. Of your 200,000-300,000 papillae, only a small fraction contain taste buds. Adults have up to 10,000 taste buds and they are invisible to the naked eye, concentrated mainly on the tip, sides and back of the tongue. https://www.youtube.com/embed/uYvpUl7li9Y?wmode=transparent&start=0
A healthy tongue is pink although the shade may vary from person to person, ranging from dark to light pink.
A small amount of white coating can be normal. But significant changes or discolouration may indicate a disease or other issues.
How should I clean my tongue?
Cleaning your tongue only takes around 10-15 seconds, but it’s is a good way to check in with your health and can easily be incorporated into your teeth brushing routine.
Build-up can occur if you stop brushing or scraping your tongue even for a few days. Anthony Shkraba/Pexels You can clean your tongue by gently scrubbing it with a regular toothbrush. This dislodges any food debris and helps prevent microbes building up on its rough textured surface.
Or you can use a special tongue scraper. These curved instruments are made of metal or plastic, and can be used alone or accompanied by scrubbing with your toothbrush.
Your co-workers will thank you as well – cleaning your tongue can help combat stinky breath. Tongue scrapers are particularly effective at removing the bacteria that commonly causes bad breath, hidden in the tongue’s surface.
What’s that stuff on my tongue?
So, you’re checking your tongue during your twice-daily clean, and you notice something different. Noting these signs is the first step. If you observe any changes and they worry you, you should talk to your GP.
Here’s what your tongue might be telling you.
White coating
Developing a white coating on the tongue’s surface is one of the most common changes in healthy people. This can happen if you stop brushing or scraping the tongue, even for a few days.
In this case, food debris and microbes have accumulated and caused plaque. Gentle scrubbing or scraping will remove this coating. Removing microbes reduces the risk of chronic infections, which can be transferred to other organs and cause serious illnesses.
Scrubbing or scraping your tongue only takes around ten seconds and can be done while brushing your teeth. Ketut Subiyanto/Pexels Yellow coating
This may indicate oral thrush, a fungal infection that leaves a raw surface when scrubbed.
Oral thrush is common in elderly people who take multiple medications or have diabetes. It can also affect children and young adults after an illness, due to the temporary suppression of the immune system or antibiotic use.
If you have oral thrush, a doctor will usually prescribe a course of anti-fungal medication for at least a month.
Black coating
Smoking or consuming a lot of strong-coloured food and drink – such as tea and coffee, or dishes with tumeric – can cause a furry appearance. This is known as a black hairy tongue. It’s not hair, but an overgrowth of bacteria which may indicate poor oral hygiene.
Smoking can add to poor oral hygiene and make the tongue look black. Sophon Nawit/Shutterstock Pink patches
Pink patches surrounded by a white border can make your tongue look like a map – this is called “geographic tongue”. It’s not known what causes this condition, which usually doesn’t require treatment.
Pain and inflammation
A red, sore tongue can indicate a range of issues, including:
- nutritional deficiencies such as folic acid or vitamin B12
- diseases including pernicious anaemia, Kawasaki disease and scarlet fever
- inflammation known as glossitis
- injury from hot beverages or food
- ulcers, including cold sores and canker sores
- burning mouth syndrome.
Dryness
Many medications can cause dry mouth, also called xerostomia. These include antidepressants, anti-psychotics, muscle relaxants, pain killers, antihistamines and diuretics. If your mouth is very dry, it may hurt.
What about cancer?
White or red patches on the tongue that can’t be scraped off, are long-standing or growing need to checked out by a dental professional as soon as possible, as do painless ulcers. These are at a higher risk of turning into cancer, compared to other parts of the mouth.
Oral cancers have low survival rates due to delayed detection – and they are on the rise. So checking your tongue for changes in colour, texture, sore spots or ulcers is critical.
Dileep Sharma, Professor and Head of Discipline – Oral Health, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: