Almonds vs Peanuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almonds to peanuts, we picked the almonds.
Why?
No, it’s not just our pro-almonds bias… But it’s also not as one-sided, nutritionally speaking, as you might think!
In terms of macros, almonds have a lot more fiber, and moderately more carbs, the ratio of which give almonds the lower glycemic index. On the other hand, peanuts have a little more protein. Both of these nuts are equally fatty, but peanuts have the higher saturated fat content. All in all, we say the biggest deciding factor is the fiber, and hand this one to the almonds.
In the category of vitamins, almonds have more of vitamins B2 and E, while peanuts have more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, B7, and B9. An easy win for peanuts this time.
When it comes to minerals, almonds have more calcium, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while peanuts have more copper, iron, selenium, and zinc. Thus, a 5:4 marginal win for almonds.
Adding up the sections makes for an overall win for almonds, but as you can see, it was close and peanuts certainly have their merits too, so by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Unless you are allergic, in which case, obviously please don’t do that.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wholewheat Bread vs Seeded White – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing wholewheat bread to seeded bread, we picked the wholewheat.
Why?
First, we will acknowledge that this is a false dichotomy; it is possible to have seeded wholewheat bread. However, it is very common to have wholewheat bread that isn’t seeded, and white bread that is seeded. So, it’s important to be able to decide which is the healthier option, since very often, this false dichotomy is what’s on offer.
We will also advise checking labels (or the baker, if getting from a bakery) to ensure that visibly brown bread is actually wholewheat, and not just dyed brown with caramel coloring or such (yes, that is a thing that some companies do).
Now, as for why we chose the wholewheat over the seeded white…
In terms of macronutrients, wholewheat bread has (on average; individual breads may vary of course) has 2x the protein and a lot more fiber.
Those seeds in seeded bread? They just aren’t enough to make a big impact on the overall nutritional value of the bread in those regards. Per slice, you are getting, what, 10 seeds maybe? This is not a meaningful dietary source of much.
Seeded bread does have proportionally more healthy fats, but the doses are still so low as to make it not worth the while; it just looks like a lot of expressed as a percentage of comparison, because of the wholewheat bread has trace amounts, and the seeded bread has several times those trace amounts, it’s still a tiny amount. So, we’d recommend looking to other sources for those healthy fats.
Maybe dip your bread, of whatever kind, into extra virgin olive oil, for example.
Wholewheat bread of course also has a lower glycemic index. Those seeds in seeded white bread don’t really slow it down at all, because they’re not digested until later.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong?
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Is stress turning my hair grey?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When we start to go grey depends a lot on genetics.
Your first grey hairs usually appear anywhere between your twenties and fifties. For men, grey hairs normally start at the temples and sideburns. Women tend to start greying on the hairline, especially at the front.
The most rapid greying usually happens between ages 50 and 60. But does anything we do speed up the process? And is there anything we can do to slow it down?
You’ve probably heard that plucking, dyeing and stress can make your hair go grey – and that redheads don’t. Here’s what the science says.
Oksana Klymenko/Shutterstock What gives hair its colour?
Each strand of hair is produced by a hair follicle, a tunnel-like opening in your skin. Follicles contain two different kinds of stem cells:
- keratinocytes, which produce keratin, the protein that makes and regenerates hair strands
- melanocytes, which produce melanin, the pigment that colours your hair and skin.
There are two main types of melanin that determine hair colour. Eumelanin is a black-brown pigment and pheomelanin is a red-yellow pigment.
The amount of the different pigments determines hair colour. Black and brown hair has mostly eumelanin, red hair has the most pheomelanin, and blonde hair has just a small amount of both.
So what makes our hair turn grey?
As we age, it’s normal for cells to become less active. In the hair follicle, this means stem cells produce less melanin – turning our hair grey – and less keratin, causing hair thinning and loss.
As less melanin is produced, there is less pigment to give the hair its colour. Grey hair has very little melanin, while white hair has none left.
Unpigmented hair looks grey, white or silver because light reflects off the keratin, which is pale yellow.
Grey hair is thicker, coarser and stiffer than hair with pigment. This is because the shape of the hair follicle becomes irregular as the stem cells change with age.
Interestingly, grey hair also grows faster than pigmented hair, but it uses more energy in the process.
Can stress turn our hair grey?
Yes, stress can cause your hair to turn grey. This happens when oxidative stress damages hair follicles and stem cells and stops them producing melanin.
Oxidative stress is an imbalance of too many damaging free radical chemicals and not enough protective antioxidant chemicals in the body. It can be caused by psychological or emotional stress as well as autoimmune diseases.
Environmental factors such as exposure to UV and pollution, as well as smoking and some drugs, can also play a role.
Melanocytes are more susceptible to damage than keratinocytes because of the complex steps in melanin production. This explains why ageing and stress usually cause hair greying before hair loss.
Scientists have been able to link less pigmented sections of a hair strand to stressful events in a person’s life. In younger people, whose stems cells still produced melanin, colour returned to the hair after the stressful event passed.
4 popular ideas about grey hair – and what science says
1. Does plucking a grey hair make more grow back in its place?
No. When you pluck a hair, you might notice a small bulb at the end that was attached to your scalp. This is the root. It grows from the hair follicle.
Plucking a hair pulls the root out of the follicle. But the follicle itself is the opening in your skin and can’t be plucked out. Each hair follicle can only grow a single hair.
It’s possible frequent plucking could make your hair grey earlier, if the cells that produce melanin are damaged or exhausted from too much regrowth.
2. Can my hair can turn grey overnight?
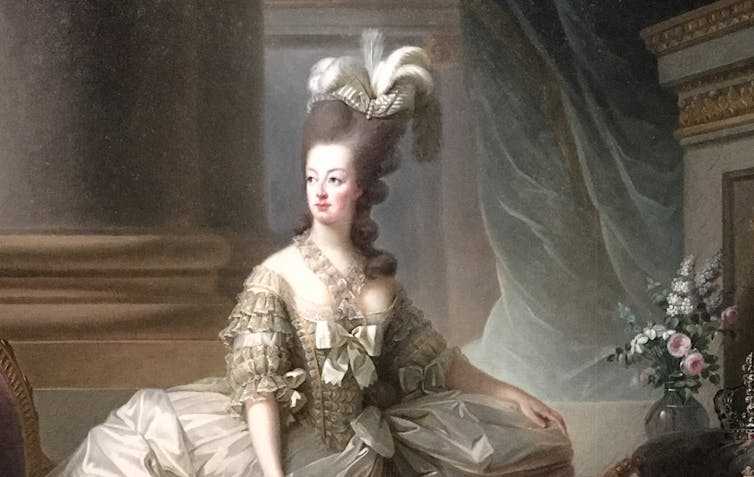
Legend says Marie Antoinette’s hair went completely white the night before the French queen faced the guillotine – but this is a myth.
It is not possible for hair to turn grey overnight, as in the legend about Marie Antoinette. Yann Caradec/Wikimedia, CC BY-NC-SA Melanin in hair strands is chemically stable, meaning it can’t transform instantly.
Acute psychological stress does rapidly deplete melanocyte stem cells in mice. But the effect doesn’t show up immediately. Instead, grey hair becomes visible as the strand grows – at a rate of about 1 cm per month.
Not all hair is in the growing phase at any one time, meaning it can’t all go grey at the same time.
3. Will dyeing make my hair go grey faster?
This depends on the dye.
Temporary and semi-permanent dyes should not cause early greying because they just coat the hair strand without changing its structure. But permanent products cause a chemical reaction with the hair, using an oxidising agent such as hydrogen peroxide.
Accumulation of hydrogen peroxide and other hair dye chemicals in the hair follicle can damage melanocytes and keratinocytes, which can cause greying and hair loss.
4. Is it true redheads don’t go grey?
People with red hair also lose melanin as they age, but differently to those with black or brown hair.
This is because the red-yellow and black-brown pigments are chemically different.
Producing the brown-black pigment eumelanin is more complex and takes more energy, making it more susceptible to damage.
Producing the red-yellow pigment (pheomelanin) causes less oxidative stress, and is more simple. This means it is easier for stem cells to continue to produce pheomelanin, even as they reduce their activity with ageing.
With ageing, red hair tends to fade into strawberry blonde and silvery-white. Grey colour is due to less eumelanin activity, so is more common in those with black and brown hair.
Your genetics determine when you’ll start going grey. But you may be able to avoid premature greying by staying healthy, reducing stress and avoiding smoking, too much alcohol and UV exposure.
Eating a healthy diet may also help because vitamin B12, copper, iron, calcium and zinc all influence melanin production and hair pigmentation.
Theresa Larkin, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Best Form Of Sugar During Exercise
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝What is the best form of sugar for an energy kick during exercise? Both type of sugar eg glicoae fructose dextrose etc and medium, ie drink, gel, solids etc❞
Great question! Let’s be clear first that we’re going to answer this specifically for the context of during exercise.
Because, if you’re not actively exercising strenuously right at the time when you’re taking the various things we’re going to be talking about, the results will not be the same.
For scenarios that are anything less than “I am exercising right now and my muscles (not joints, or anything else) are feeling the burn”, then instead please see this:
Snacks & Hacks: Eating For Energy (In Ways That Actually Work)
Because, to answer your question, we’re going to be going 100% against the first piece of advice in that article, which was “Skip the quasi-injectables”, i.e., anything marketed as very quick release. Those things are useful for diabetics to have handy just in case of needing to urgently correct a hypo, but for most people most of the time, they’re not. See also:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
However…
When strenuously exercising in a way that is taxing our muscles, we do not have to worry about the usual problem of messing up our glucose metabolism by overloading our body with sugars faster than it can use it (thus: it has to hurriedly convert glucose and shove it anywhere it’ll fit to put it away, which is very bad for us), because right now, in the exercise scenario we’re describing, the body is already running its fastest metabolism and is grabbing glucose anywhere it can find it.
Which brings us to our first key: the best type of sugar for this purpose is glucose. Because:
- glucose: the body can use immediately and easily convert whatever’s spare to glycogen (a polysaccharide of glucose) for storage
- fructose: the body cannot use immediately and any conversion of fructose to glycogen has to happen in the liver, so if you take too much fructose (without anything to slow it down, such as the fiber in whole fruit), you’re not only not going to get usable energy (the sugar is just going to be there in your bloodstream, circulating, not getting used, because it doesn’t trigger insulin release and insulin is the gatekeeper that allows sugar to be used), but also, it’s going to tax the liver, which if done to excess, is how we get non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- sucrose: is just a disaccharide of glucose and fructose, so it first gets broken down into those, and then its constituent parts get processed as above. Other disaccharides you’ll see mentioned sometimes are maltose and lactose, but again, they’re just an extra step removed from useful metabolism, so to save space, we’ll leave it at that for those today.
- dextrose: is just glucose, but when the labeller is feeling fancy. It’s technically informational because it specifies what isomer of glucose it is, but basically all glucose found in food is d-glucose, i.e. dextrose. Other isomers of glucose can be synthesized (very expensively) in laboratories or potentially found in obscure places (the universe is vast and weird), but in short: unless someone’s going to extreme lengths to get something else, all glucose we encounter is dextrose, and all (absolutely all) dextrose is glucose.
We’d like to show scientific papers contesting these head-to-head for empirical proof, but since the above is basic chemistry and physiology, all we could find is papers taking this for granted and stating in their initial premise that sports drinks, gels, bars usually contain glucose as their main sugar, potentially with some fructose and sucrose. Like this one:
A Comprehensive Study on Sports and Energy Drinks
As for how to take it, again this is the complete opposite of our usual health advice of “don’t drink your calories”, because in this case, for once…
(and again, we must emphasize: only while actively doing strenuous exercise that is making specifically your muscles burn, not your joints or anything else; if your joints are burning you need to rest and definitely don’t spike your blood sugars because that will worsen inflammation)
…just this once, we do want those sugars to be zipping straight into the blood. Which means: liquid is best for this purpose.
And when we say liquid: gel is the same as a drink, so far as the body is concerned, provided the body in question is adequately hydrated (i.e., you are also drinking water).
Here are a pair of studies (by the same team, with the same general methodology), testing things head-to-head, with endurance cyclists on 6-hour stationary cycle rides:
CHO Oxidation from a CHO Gel Compared with a Drink during Exercise
Meanwhile, liquid beat solid, but only significantly so from the 90-minute mark onwards, and even that significant difference was modest (i.e. it’s clinically significant, it’s a statistically reliable result and improbable as random happenstance, but the actual size of the difference was not huge):
Oxidation of Solid versus Liquid CHO Sources during Exercise
We would hypothesize that the reason that liquids only barely outperformed solids for this task is precisely because the solids in question were also designed for the task. When a company makes a fast-release energy bar, they don’t load it with fiber to slow it down. Which differentiates this greatly from, say, getting one’s sugars from whole fruit.
If the study had compared apples to apple juice, we hypothesize the results would have been very different. But alas, if that study has been done, we couldn’t find it.
Today has been all about what’s best during exercise, so let’s quickly finish with a note on what’s best before and after:
Before: What To Eat, Take, And Do Before A Workout
After: Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Tilapia vs Cod – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tilapia to cod, we picked the tilapia.
Why?
Another case of “that which is more expensive is not necessarily the healthier”!
In terms of macros, tilapia has more protein and fats, as well as more omega-3 (and omega-6). On the downside, tilapia does have relatively more saturated fat, but at 0.94g/100g, it’s not exactly butter.
The vitamins category sees that tilapia has more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B12, D, and K, while cod has more of vitamins B6, B9, and choline. A moderate win for tilapia.
When it comes to minerals, things are most divided; tilapia has more copper, iron, phosphorus, potassium, manganese, and selenium, while cod has more magnesium and zinc. An easy win for tilapia.
One other thing to note is that both of these fish contain mercury these days (and it’s worth noting: cod has nearly 10x more mercury). Mercury is, of course, not exactly a health food.
So, excessive consumption of either is not recommended, but out of the two, tilapia is definitely the one to pick.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught: Know The Health Differences
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Blueberries vs Cranberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing blueberries to cranberries, we picked the blueberries.
Why?
It’s close!
In terms of macros, blueberries have slightly more protein and carbs, while cranberries have slightly more fiber. We say the extra fiber’s more important than the (even more minimally) extra protein, so this is the slightest of marginal wins for cranberries in this category.
In the category of vitamins, blueberries have much more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B9, K, and choline, while cranberries have slightly more of vitamins A, B5, B6, C, and E. That’s a 6:5 win for blueberries, and also, the margins of difference were much greater for blueberries’ vitamins, making this a clearer win for blueberries.
When it comes to minerals, blueberries have slightly more iron, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc, while cranberries have slightly more calcium. The margins of difference are small in both cases, but this is a 4:1 win for blueberries.
Both of these berries are famously full of antioxidants; blueberries have more antioxidant power overall, though cranberries have some specific benefits such as being better than antibiotics against UTIs—though there are some contraindications too; check out the link below for more on that!
All in all, meanwhile, we say that adding up the sections here makes for a win for blueberries, but by all means, enjoy either or both (unless one of the contraindications below applies to you).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Health Benefits Of Cranberries (But: You’d Better Watch Out)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ashwagandha: The Root of All Even-Mindedness?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ashwagandha: The Root Of All Even-Mindedness?
In the past few years, Ashwagandha root has been enjoying popular use in consumer products ranging from specialist nootropic supplement stacks, to supermarket teas and hot chocolates.
This herb is considered to have a calming effect, but the science goes a lot deeper than that. Let’s take a look!
Last summer, a systematic review was conducted, that asked the question:
Does Ashwagandha supplementation have a beneficial effect on the management of anxiety and stress?
While they broadly found the answer was “yes”, they expressed low confidence, and even went so far as to say there was contradictory evidence. We (10almonds) were not able to find any contradictory evidence, and their own full article had been made inaccessible to the public, so we couldn’t double-check theirs.
We promptly did our own research review, and we found many studies this year supporting Ashwaghanda’s use for the management of anxiety and stress, amongst other benefits.
First, know: Ashwagandha’s scientific name is “Withania somnifera”, so if you see that (or a derivative of it) mentioned in a paper or extract, it’s the same thing.
Onto the benefits…
A study from the same summer investigated “the efficacy of Withania somnifera supplementation on adults’ cognition and mood”, and declared that:
“in conclusion, Ashwagandha supplementation may improve the physiological, cognitive, and psychological effects of stress.”
We notice the legalistic “may improve”, but the data itself seems more compelling than that, because the study showed that it in fact “did improve” those things. Specifically, Ashwagandha out-performed placebo in most things they measured, and most (statistically) significantly, reduced cortisol output measurably. Cortisol, for any unfamiliar, is “the stress hormone”.
Another study that looked into its anti-stress properties is this one:
Ashwagandha Modulates Stress, Sleep Dynamics, and Mental Clarity
This study showed that Ashwagandha significantly outperformed placebo in many ways, including:
- sleep quality
- cognitive function
- energy, and
- perceptions of stress management.
Ashwagandha is popular among students, because it alleviates stress while also promising benefits to memory, attention, and thinking. So, this study on students caught our eye:
Their findings demonstrated that Ashwagandha increased college students’ perceived well-being through supporting sustained energy, heightened mental clarity, and enhanced sleep quality.
That was about perceived well-being and based on self-reports, though
So: what about hard science?
A later study (in September) found supplementation with 400 mg of Ashwagandha improved executive function, helped sustain attention, and increased short-term/working memory.
Read the study: Effects of Acute Ashwagandha Ingestion on Cognitive Function
❝But aside from the benefits regarding stress, anxiety, sleep quality, cognitive function, energy levels, attention, executive function, and memory, what has Ashwagandha ever done for us?❞
Well, there have been studies investigating its worth against depression, like this one:
Can Traditional Treatment Such as Ashwagandha Be Beneficial in Treating Depression?
Their broad answer: Ashwagandha works against depression, but they don’t know how it works.
They did add: “Studies also show that ashwagandha may bolster the immune system, increase stamina, fight inflammation and infection, combat tumors*, reduce stress, revive the libido, protect the liver and soothe jangled nerves.
That’s quite a lot, including a lot of physical benefits we’ve not explored in this research review which was more about Ashwagandha’s use as a nootropic!
We’ve been focusing on the more mainstream, well-studied benefits, but for any interested in Ashwagandha’s anti-cancer potential, here’s an example:
Evaluating anticancer properties of [Ashwagandha Extract]-a potent phytochemical
In summary:
There is a huge weight of evidence (of which we’ve barely skimmed the surface here in this newsletter, but there’s only so much we can include, so we try to whittle it down to the highest quality most recent most relevant research) to indicate that Ashwagandha is effective…
- Against stress
- Against anxiety
- Against depression
- For sleep quality
- For memory (working, short-term, and long-term)
- For mental clarity
- For attention
- For stamina
- For energy levels
- For libido
- For immune response
- Against inflammation
- Against cancer
- And more*
*(seriously, this is not hyperbole… We didn’t even look at its liver-protective functions, for instance)
Bottom line:
You’d probably like some Ashwagandha now, right? We know we would.
We don’t sell it (or anything else, for that matter), but happily the Internet does:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: