Simple Wall Pilates for Seniors – by Grace Clark
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While the cover illustration makes this look a little too simple, in fact there’s a lot of value in this book, with exercises ranging from things like that on the cover, to the “wall downward dog”. But the actual exercises (of which there are 29) themselves are only a part of the book (taking about 70 pages of it with clear illustrations).
There’s also a lot about important Pilates principles to apply, such as breathing, correct body alignment (if you don’t already do Pilates, you will not have this, as Pilates alignment is quite specific), flexibility, balance, stability, coordination, range of motion, isometric exercise considerations, endurance, and more.
Unlike a lot of “…for seniors” books, this is not a watered down barely-does-anything version of the “real” exercises, but rather, would present most the same challenges to a 20-year-old reader; it’s just that the focus here is more on matters that tend to concern an older rather than younger demographic. That 20-something may be busy building their butt, for instance, while the 80-year-old is building their bones. No reason both shouldn’t do both, of course, but the focus is age-specific.
The author guides us through working up from easy things to hard, breaking stuff down so that we can progress at our own pace, such that even the most cautious or enthusiastic reader can start at an appropriate point and proceed accordingly.
She also talks us through a 28-day program (as promised by the subtitle), and advice on how to keep it going without plateauing, how to set realistic goals, how to tailor it to our abilities as we go, track our progress, and so forth.
The style is clear and instructional, and one thing that sets this apart from a lot of Pilates books is that the education comes from an angle not of “trust me”, but rather from well-sourced claims with bibliography whose list spans 5 pages at the end.
Bottom line: if you’d like to progressively increase your strength, stability, and more—with no gym equipment, just a wall—then this book will have you see improvements in the 28 days it promises, and thereafter.
Click here to check out Simple Wall Pilates For Seniors, and experience the difference!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
World Menopause Day Health News Round-Up
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In order to provide variety in this week’s round-up, not all of this is menopause-related, but it is all important:
Menopause & CVD
Untreated menopause is associated with higher incidence of heart disease, and higher mortality. People often forget about how much estrogen does for us (well, for those of us with a physiology running on estrogen, anyway; gentlemen, your testosterone is fine for you), and think it is “just” a sex hormone, but it’s a lot more.
Read in full: Menopause transition linked to increased heart disease risk
Related: What Menopause Does To The Heart
Extraterrestrial medical technology
The much lower gravity in Earth orbit has allowed for tissue engineering techniques that Earth’s normal gravity imposes limitations on. This is big news, because it means that rather than replacing a whole liver, tissue implants could be grafted, allowing the extant liver to repair itself (something livers are famously good at, but they need enough undamaged base material to work with).
Read in full: How liver tissue from the International Space Station may transform tissue engineering
Related: How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
One thing and then another
As if endometriosis weren’t unpleasant enough in and of itself, the endothelial dysfunction inherent to it also raises cardiovascular disease risk. This is important, because while endometriosis has (like many maladies predominantly affecting women) generally been shrugged off by the medical world as an unhappy inconvenience but not life-threatening, now we know it comes with extra existential risks too:
Read in full: Understanding cardiovascular risks in endometriosis patients
Related: What You Need To Know About Endometriosis
Push-button meditation
Unlike mindfulness meditation, listening to music is a very passive experience, and thus requires less effort from the user. And yet, it has been associated with lower perceived pain levels, lower self-reported anxiety levels, less opioid use, and measurably lower heart-rate.
Read in full: Listening to music may speed up recovery from surgery, research suggests
Related: Nobody Likes Surgery, But Here’s How To Make It Much Less Bad
Cholesterol in menopause: quality over quantity
Much like previous research has shown that the quantity of LDL is not nearly so predictive of health outcomes in women as it is in men, this study into HDL and menopausal women shows that quantity of HDL does not matter nearly so much as the quality of it.
Read in full: HDL quality, not quantity, contribute to the first sign of Alzheimer’s disease in women
Related: Statins: His & Hers? ← consistent with the above, statins (to lower LDL cholesterol) generally help more for men and produce more adverse side effects for women. So again, a case of “the actual amount of cholesterol isn’t so important for women as for men”.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
PlantYou: Scrappy Cooking – by Carleigh Bodrug
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a book that took “whole foods plant-based diet” and ran with it.
“Whole foods”, you say? Carleigh Bodrug has you covered in this guide to using pretty much everything.
One of the greatest strengths of the book is its “Got this? Make that” section, for using up those odds and ends that you’d normally toss.
You may be thinking: “ok, but if to use this unusual ingredient I have to buy four other ingredients to make this recipe, generating waste from those other ingredients, then this was a bad idea”, but fear not.
Bodrug covers that too, and in many cases leftover “would get wasted” ingredients can get turned into stuff that can go into longer-term storage one way or another, to use at leisure.
Which also means that on the day “there’s nothing in the house to eat” and you don’t want to go grocery-shopping, or if some global disaster causes the supply lines to fail and the stores become empty (that could never happen though, right?), you will have the mystical ability to conjure a good meal out of assorted odds and ends that you stored because of this book.
Bottom line: if you love food and hate food waste, this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out Scrappy Cooking, and do domestic magic!
Share This Post
-
Parsnips vs Potatoes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing parsnips to potatoes, we picked the parsnips.
Why?
To be more specific, we’re looking at russet potatoes, and in both cases we’re looking at cooked without fat or salt, skin on. In other words, the basic nutritional values of these plants in edible form, without adding anything. With this in mind, once we get to the root of things, there’s a clear winner:
Looking at the macros first, potatoes have more carbs while parsnips have more fiber. Potatoes do have more protein too, but given the small numbers involved when it comes to protein we don’t think this is enough of a plus to outweigh the extra fiber in the parsnips.
In the category of vitamins, again a champion emerges: parsnips have more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B9, C, E, and K, while potatoes have more of vitamins B3, B6, and choline. So, a 7:3 win for parsnips.
When it comes to minerals, parsnips have more calcium copper, manganese, selenium, and zinc, while potatoes have more iron and potassium. Potatoes do also have more sodium, but for most people most of the time, this is not a plus, healthwise. Disregarding the sodium, this category sees a 5:2 win for parsnips.
In short: as with most starchy vegetables, enjoy both in moderation if you feel so inclined, but if you’re picking one, then parsnips are the nutritionally best choice here.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why do I poo in the morning? A gut expert explains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
No, you’re not imagining it. People really are more likely to poo in the morning, shortly after breakfast. Researchers have actually studied this.
But why mornings? What if you tend to poo later in the day? And is it worth training yourself to be a morning pooper?
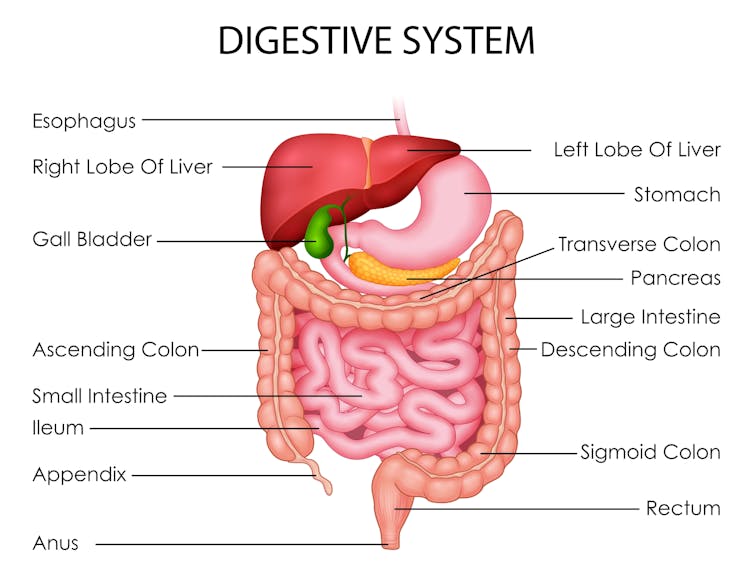
To understand what makes us poo when we do, we need to consider a range of factors including our body clock, gut muscles and what we have for breakfast.
Here’s what the science says.
H_Ko/Shutterstock So morning poos are real?
In a UK study from the early 1990s, researchers asked nearly 2,000 men and women in Bristol about their bowel habits.
The most common time to poo was in the early morning. The peak time was 7-8am for men and about an hour later for women. The researchers speculated that the earlier time for men was because they woke up earlier for work.
About a decade later, a Chinese study found a similar pattern. Some 77% of the almost 2,500 participants said they did a poo in the morning.
But why the morning?
There are a few reasons. The first involves our circadian rhythm – our 24-hour internal clock that helps regulate bodily processes, such as digestion.
For healthy people, our internal clock means the muscular contractions in our colon follow a distinct rhythm.
There’s minimal activity in the night. The deeper and more restful our sleep, the fewer of these muscle contractions we have. It’s one reason why we don’t tend to poo in our sleep.
Your lower gut is a muscular tube that contracts more strongly at certain times of day. Vectomart/Shutterstock But there’s increasing activity during the day. Contractions in our colon are most active in the morning after waking up and after any meal.
One particular type of colon contraction partly controlled by our internal clock are known as “mass movements”. These are powerful contractions that push poo down to the rectum to prepare for the poo to be expelled from the body, but don’t always result in a bowel movement. In healthy people, these contractions occur a few times a day. They are more frequent in the morning than in the evening, and after meals.
Breakfast is also a trigger for us to poo. When we eat and drink our stomach stretches, which triggers the “gastrocolic reflex”. This reflex stimulates the colon to forcefully contract and can lead you to push existing poo in the colon out of the body. We know the gastrocolic reflex is strongest in the morning. So that explains why breakfast can be such a powerful trigger for a bowel motion.
Then there’s our morning coffee. This is a very powerful stimulant of contractions in the sigmoid colon (the last part of the colon before the rectum) and of the rectum itself. This leads to a bowel motion.
How important are morning poos?
Large international surveys show the vast majority of people will poo between three times a day and three times a week.
This still leaves a lot of people who don’t have regular bowel habits, are regular but poo at different frequencies, or who don’t always poo in the morning.
So if you’re healthy, it’s much more important that your bowel habits are comfortable and regular for you. Bowel motions do not have to occur once a day in the morning.
Morning poos are also not a good thing for everyone. Some people with irritable bowel syndrome feel the urgent need to poo in the morning – often several times after getting up, during and after breakfast. This can be quite distressing. It appears this early-morning rush to poo is due to overstimulation of colon contractions in the morning.
Can you train yourself to be regular?
Yes, for example, to help treat constipation using the gastrocolic reflex. Children and elderly people with constipation can use the toilet immediately after eating breakfast to relieve symptoms. And for adults with constipation, drinking coffee regularly can help stimulate the gut, particularly in the morning.
A disturbed circadian rhythm can also lead to irregular bowel motions and people more likely to poo in the evenings. So better sleep habits can not only help people get a better night’s sleep, it can help them get into a more regular bowel routine.
A regular morning coffee can help relieve constipation. Caterina Trimarchi/Shutterstock Regular physical activity and avoiding sitting down a lot are also important in stimulating bowel movements, particularly in people with constipation.
We know stress can contribute to irregular bowel habits. So minimising stress and focusing on relaxation can help bowel habits become more regular.
Fibre from fruits and vegetables also helps make bowel motions more regular.
Finally, ensuring adequate hydration helps minimise the chance of developing constipation, and helps make bowel motions more regular.
Monitoring your bowel habits
Most of us consider pooing in the morning to be regular. But there’s a wide variation in normal so don’t be concerned if your poos don’t follow this pattern. It’s more important your poos are comfortable and regular for you.
If there’s a major change in the regularity of your bowel habits that’s concerning you, see your GP. The reason might be as simple as a change in diet or starting a new medication.
But sometimes this can signify an important change in the health of your gut. So your GP may need to arrange further investigations, which could include blood tests or imaging.
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tuna vs Catfish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tuna to catfish, we picked the tuna.
Why?
Today in “that which is more expensive and/or harder to get is not necessarily healthier”…
Looking at their macros, tuna has more protein and less fat (and overall, less saturated fat, and also less cholesterol).
In the category of vitamins, both are good but tuna distinguishes itself: tuna has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, and D, while catfish has more of vitamins B5, B9, B12, E, and K. They are both approximately equal in choline, and as an extra note in tuna’s favor (already winning 6:5), tuna is a very good source of vitamin D, while catfish barely contains any. All in all: a moderate, but convincing, win for tuna.
When it comes to minerals, things are clearer still: tuna has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while catfish has more calcium, manganese, and zinc. Oh, and catfish is also higher in one other mineral: sodium, which most people in industrialized countries need less of, on average. So, a 6:3 win for tuna, before we even take into account the sodium content (which makes the win for tuna even stronger).
In short: tuna wins the day in every category!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught (It Makes Quite A Difference)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Egg Whites vs Whole Eggs – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing egg whites to whole eggs, we picked the whole eggs.
Why?
Egg whites are mostly protein. Egg yolks are mostly fat, with some protein.
However, fat ≠ bad, and the yolk is also where the choline is stored, which itself (as well as its benefits for your brain) will tend to reduce fat storage in the body.
Furthermore, the yolk contains an assortment of vitamins, minerals, and essential amino acids. After all, the yolk is there specifically to contain everything needed to turn a cluster of cells into a small bird.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: