Generation M – by Dr. Jessica Shepherd
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Menopause is something that very few people are adequately prepared for despite its predictability, and also something that very many people then neglect to take seriously enough.
Dr. Shepherd encourages a more proactive approach throughout all stages of menopause and beyond; she discusses “the preseason, the main event, and the after-party” (perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause), which is important, because typically people take up an interest in perimenopause, are treating it like a marathon by menopause, and when it comes to postmenopause, it’s easy to think “well, that’s behind me now”, and it’s not, because untreated menopause will continue to have (mostly deleterious) cumulative effects until death.
As for HRT, there’s a chapter on that of course, going into quite some detail. There is also plenty of attention given to popular concerns such as managing weight changes and libido changes, as well as oft-neglected topics such as brain changes, as well as things considered more cosmetic but that can have a big impact on mental health, such as skin and hair.
The style throughout is pop-science; friendly without skimping on detail and including plenty of good science.
Bottom line: if you’d like a fairly comprehensive overview of the changes that occur from perimenopause all the way to menopause and well beyond, then this is a great book for that.
Click here to check out Generation M, and live well at every stage of life!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Brain-Skin Doctor
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of Brains And Breakouts
Today’s spotlight is on Dr. Claudia Aguirre. She’s a molecular neuroscientist, and today she’s going to be educating us about skin.
What? Why?
When we say “neuroscience”, we generally think of the brain. And indeed, that’s a very important part of it.
We might think about eyes, which are basically an extension of the brain.
We don’t usually think about skin, which (just like our eyes) is constantly feeding us a lot of information about our surroundings, via a little under three million nerve endings. Guess where the other ends of those nerves lead!
There’s a constant two-way communication going on between our brain and our skin.
What does she want us to know?
Psychodermatology
The brain and the skin talk to each other, and maladies of one can impact the other:
- Directly, e.g. stress prompting skin breakouts (actually this is a several-step process physiologically, but for the sake of brevity we’ll call this direct)
- Indirectly, e.g. nervous disorders that result in people scratching or picking at their skin, which prompts a whole vicious cycle of one thing making the other worse
Read more: Psychodermatology: The Brain-Skin Connection
To address both kinds of problems, clearly something beyond moisturizer is needed!
Mindfulness (meditation and beyond)
Mindfulness is a well-evidenced healthful practice for many reasons, and Dr. Aguirra argues the case for it being good for our skin too.
As she points out,
❝Cultural stress and anxiety can trigger or aggravate many skin conditions—from acne to eczema to herpes, psoriasis, and rosacea.
Conversely, a disfiguring skin condition can trigger stress, anxiety, depression, and even suicide.
Chronic, generalized anxiety can create chronic inflammation and exacerbate inflammatory skin conditions, such as those I mentioned previously.
Chronic stress can result in chronic anxiety, hypervigilance, poor sleep, and a whole cascade of effects resulting in a constant breakdown of tissues and organs, including the skin.❞
So, she recommends mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), for the above reasons, along with others!
Read more: Mind Matters
How to do it: No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
And as for “and beyond?”
Do you remember in the beginning of the pandemic, when people were briefly much more consciously trying to avoid touching their faces so much? That, too, is mindfulness. It may have been a stressed and anxious mindfulness for many*, but mindfulness nonetheless.
*which is why “mindfulness-based stress reduction” is not a redundant tautology repeated more than once unnecessarily, one time after another 😉
So: do try to keep aware of what you are doing to your skin, and so far as is reasonably practicable, only do the things that are good for it!
The skin as an endocrine organ
Nerves are not the only messengers in the body; hormones do a lot of our body’s internal communication too. And not just the ones everyone remembers are hormones (e.g. estrogen, testosterone, although yes, they do both have a big impact on skin too), but also many more, including some made in the skin itself!
Dr. Aguirra gives us a rundown of common conditions, the hormones behind them, and what we can do if we don’t want them:
Read more: Rethinking The Skin As An Endocrine Organ
Take-away advice:
For healthy skin, we need to do more than just hydrate, get good sleep, have good nutrition, and get a little sun (but not too much).
- We should also practice mindfulness-based stress reduction, and seek help for more serious mental health issues.
- We should also remember the part our hormones play in our skin, and not just the obvious ones.
Did you know that vitamin D is also a hormone, by the way? It’s not the only hormone at play in your skin by a long way, but it is an important one:
Society for Endocrinology | Vitamin D
Want to know more?
You might like this interview with Dr. Aguirre:
The Brain in Our Skin: An Interview with Dr. Claudia Aguirre
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Grapefruit vs Lemon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing grapefruit to lemon, we picked the lemon.
Why?
Grapefruit has its merits, but in the battle of the citrus fruits, lemons come out on top nutritionally:
In terms of macros, grapefruit has more carbs while lemons have more fiber. So, while both have a low glycemic index, lemon is still the winner by the numbers.
Looking at the vitamins, here we say grapefruit’s strengths: grapefruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, and choline, while lemon has more of vitamins B6 and C. So, a 4:2 win for grapefruit here.
In the category of minerals, lemons retake the lead: grapefruit has more zinc, while lemon has more calcium, copper, iron, manganese, and selenium.
One final consideration that’s not shown in the nutritional values, is that grapefruit contains high levels of furanocoumarin, which can inhibit cytochrome P-450 3A4 isoenzyme and P-glycoptrotein transporters in the intestine and liver—slowing down their drug metabolism capabilities, thus effectively increasing the bioavailability of many drugs manifold.
This may sound superficially like a good thing (improving bioavailability of things we want), but in practice it means that in the case of many drugs, if you take them with (or near in time to) grapefruit or grapefruit juice, then congratulations, you just took an overdose. This happens with a lot of meds for blood pressure, cholesterol (including statins), calcium channel-blockers, anti-depressants, benzo-family drugs, beta-blockers, and more. Oh, and Viagra, too. Which latter might sound funny, but remember, Viagra’s mechanism of action is blood pressure modulation, and that is not something you want to mess around with unduly. So, do check with your pharmacist to know if you’re on any meds that would be affected by grapefruit or grapefruit juice!
PS: the same substance is quite available in pummelos and sour oranges (but not meaningfully in sweet oranges); you can see a chart here showing the relative furanocoumarin contents of many citrus fruits, or lack thereof as the case may be, as it is for lemons and most limes)
Adding up the sections gives us a clear win for lemons, but by all means enjoy either or both; just watch out for that furanocoumarin content of grapefruit if you’re on any meds affected by such (again, do check with your pharmacist, as our list was far from exhaustive—and yes, this question is one that a pharmacist will answer more easily and accurately than a doctor will).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← citrus fruits in general make the list; they inhibit tumor growth and kill cancer cells; regular consumption is also associated with a lower cancer risk 🙂
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
When “Normal” Health Is Not What You Want
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝When going to sleep, I try to breathe through my nose (since everyone says that’s best). But when I wake I often find that I am breathing through my mouth. Is that normal, or should I have my nose checked out?❞
It is quite normal, but when it comes to health, “normal” does not always mean “optimal”.
- Good news: it is correctable!
- Bad news: it is correctable by what may be considered rather an extreme practice that comes with its own inconveniences and health risks.
Some people correct this by using medical tape to keep their mouth closed at night, ensuring nose-breathing. Advocates of this say that after using it for a while, nose-breathing in sleep will become automatic.
We know of no hard science to confirm this, and cannot even offer a personal anecdote on this one. Here are some pop-sci articles that do link to the (very few) studies that have been conducted:
- Mouth taping may be a trending sleep hack, but the science behind it is slim
- Mouth Taping for Sleep: Does it Work? And What are the Side Effects?
This writer’s personal approach is simply to do breathing exercises when going to sleep and first thing upon awakening, and settle for imperfection in this regard while asleep.
Meanwhile, take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Early Bird Or Night Owl? Genes vs Environment
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Sliding Slope?
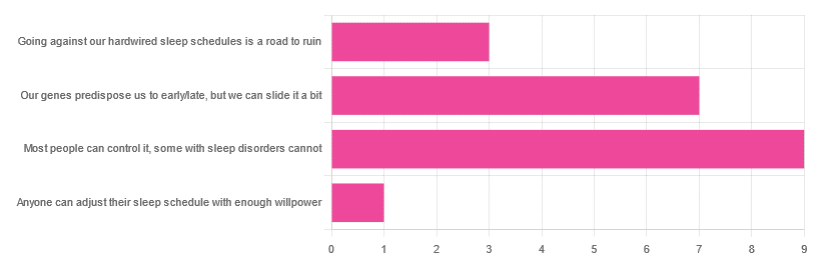
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you how much control you believe we have over our sleep schedule, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- 45% said “most people can control it; some people with sleep disorders cannot
- 35% said “our genes predispose us to early/late, but we can slide it a bit
- 15% said: “going against our hardwired sleep schedules is a road to ruin”
- 5% said “anyone can adjust their sleep schedule with enough willpower”
You may be wondering: what’s with those single-digit numbers in the graph there? And the answer is: Tuesday’s email didn’t go out at the usual time due to a scheduling mistake (sorry!), which is probably what affected the number of responses (poll response levels vary, but are usually a lot higher than this).
Note: yes, this does mean most people who read our newsletter don’t vote. So, not to sound like a politician on the campaign trail, but… Your vote counts! We always love reading your comments when you add those, too—often they provide context that allow us to tailor what we focus on in our articles
However, those are the responses we got, so here we are!
What does the science say?
Anyone can adjust their sleep with enough willpower: True or False?
False, simply. It’s difficult for most people, but for many people with sleep disorders, it is outright impossible.
In a battle of narcolepsy vs willpower, for example, no amount of willpower will stop the brain from switching to sleep mode when it thinks it’s time to sleep:
❝Narcolepsy is the most common neurological cause of chronic sleepiness. The discovery about 20 years ago that narcolepsy is caused by selective loss of the neurons producing orexins sparked great advances in the field
[There is also] developing evidence that narcolepsy is an autoimmune disorder that may be caused by a T cell-mediated attack on the orexin neurons and explain how these new perspectives can inform better therapeutic approaches.❞
~ Dr. Carrie Mahoney et al. (lightly edited for brevity)
Source: The neurobiological basis of narcolepsy
For further reading, especially if this applies to you or a loved one:
Our genes predispose us to early/late, but we can slide it a bit: True or False?
True! First, about our genes predisposing us:
…and also:
Gene distinguishes early birds from night owls and helps predict time of death
Now, as for the “can slide it a bit”, this is really just a function of the general categories of “early bird” and “night owl” spanning periods of time that allow for a few hours’ wiggle-room at either side.
However, it is recommended to make any actual changes more gradually, with the Sleep Foundation going so far as to recommend 30 minutes, or even just 15 minutes, of change per day:
Sleep Foundation | How to Fix Your Sleep Schedule
Going against our hardwired sleep schedule is a road to ruin: True or False?
False, contextually. By this we mean: our “hardwired” sleep schedule is (for most of us), genetically predisposed but not predetermined.
Also, genetic predispositions are not necessarily always good for us; one would not argue, for example, for avoiding going against a genetic predisposition to addiction.
Some genetic predispositions are just plain bad for us, and genes can be a bit of a lottery.
That said, we do recommend getting some insider knowledge (literally), by getting personal genomics tests done, if that’s a viable option for you, so you know what’s really a genetic trait (and what to do with that information) and what’s probably caused by something else (and what to do with that information):
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dating apps could have negative effects on body image and mental health, our research shows
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Around 350 million people globally use dating apps, and they amass an estimated annual revenue of more than US$5 billion. In Australia, 49% of adults report using at least one online dating app or website, with a further 27% having done so in the past.
But while dating apps have helped many people find romantic partners, they’re not all good news.
In a recent review, my colleagues and I found using dating apps may be linked to poorer body image, mental health and wellbeing.
Dikushin Dmitry/Shutterstock We collated the evidence
Our study was a systematic review, where we collated the results of 45 studies that looked at dating app use and how this was linked to body image, mental health or wellbeing.
Body image refers to the perceptions or feelings a person has towards their own appearance, often relating to body size, shape and attractiveness.
Most of the studies we included were published in 2020 onwards. The majority were carried out in Western countries (such as the United States, the United Kingdom and Australia). Just under half of studies included participants of all genders. Interestingly, 44% of studies observed men exclusively, while only 7% included just women.
Of the 45 studies, 29 looked at the impact of dating apps on mental health and wellbeing and 22 considered the impact on body image (some looked at both). Some studies examined differences between users and non-users of dating apps, while others looked at whether intensity of dating app use (how often they’re used, how many apps are used, and so on) makes a difference.
More than 85% of studies (19 of 22) looking at body image found significant negative relationships between dating app use and body image. Just under half of studies (14 of 29) observed negative relationships with mental health and wellbeing.
The studies noted links with problems including body dissatisfaction, disordered eating, depression, anxiety and low self-esteem.
Dating apps are becoming increasingly common. But could their use harm mental health? Rachata Teyparsit/Shutterstock It’s important to note our research has a few limitations. For example, almost all studies included in the review were cross-sectional – studies that analyse data at a particular point in time.
This means researchers were unable to discern whether dating apps actually cause body image, mental health and wellbeing concerns over time, or whether there is simply a correlation. They can’t rule out that in some cases the relationship may go the other way, meaning poor mental health or body image increases a person’s likelihood of using dating apps.
Also, the studies included in the review were mostly conducted in Western regions with predominantly white participants, limiting our ability to generalise the findings to all populations.
Why are dating apps linked to poor body image and mental health?
Despite these limitations, there are plausible reasons to expect there may be a link between dating apps and poorer body image, mental health and wellbeing.
Like a lot of social media, dating apps are overwhelmingly image-centric, meaning they have an emphasis on pictures or videos. Dating app users are initially exposed primarily to photos when browsing, with information such as interests or hobbies accessible only after manually clicking through to profiles.
Because of this, users often evaluate profiles based primarily on the photos attached. Even when a user does click through to another person’s profile, whether or not they “like” someone may still often be determined primarily on the basis of physical appearance.
This emphasis on visual content on dating apps can, in turn, cause users to view their appearance as more important than who they are as a person. This process is called self-objectification.
People who experience self-objectification are more likely to scrutinise their appearance, potentially leading to body dissatisfaction, body shame, or other issues pertaining to body image.
Dating apps are overwhelmingly image-centric. Studio Romantic/Shutterstock There could be several reasons why mental health and wellbeing may be impacted by dating apps, many of which may centre around rejection.
Rejection can come in many forms on dating apps. It can be implied, such as having a lack of matches, or it can be explicit, such as discrimination or abuse. Users who encounter rejection frequently on dating apps may be more likely to experience poorer self-esteem, depressive symptoms or anxiety.
And if rejection is perceived to be based on appearance, this could lead again to body image concerns.
What’s more, the convenience and game-like nature of dating apps may lead people who could benefit from taking a break to keep swiping.
What can app developers do? What can you do?
Developers of dating apps should be seeking ways to protect users against these possible harms. This could, for example, include reducing the prominence of photos on user profiles, and increasing the moderation of discrimination and abuse on their platforms.
The Australian government has developed a code of conduct – to be enforced from April 1 this year – to help moderate and reduce discrimination and abuse on online dating platforms. This is a positive step.
Despite the possible negatives, research has also found dating apps can help build confidence and help users meet new people.
If you use dating apps, my colleagues and I recommend choosing profile images you feel display your personality or interests, or photos with friends, rather than semi-clothed images and selfies. Engage in positive conversations with other users, and block and report anyone who is abusive or discriminatory.
It’s also sensible to take breaks from the apps, particularly if you’re feeling overwhelmed or dejected.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14. The Butterfly Foundation provides support for eating disorders and body image issues, and can be reached on 1800 334 673.
Zac Bowman, PhD Candidate, College of Education, Psychology & Social Work, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Growing Young – by Marta Zaraska
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one will be a slightly mixed review, but we think the book has more than enough of value to make it a very worthwhile read.
The premise of the book is that, as the subtitle suggests, positive social qualities increase personal longevity.
Author (and science journalist) Marta Zaraska looks at a lot of research to back this up, and also did a lot of travelling and digging into stories. This is of great value, because she notes where a lot of misconceptions have arisen.
To give one example, it’s commonly noted that marriage (or as-though-marriage life partnerships) is generally* associated with longer life.
*Statistics suggest that marriage-related longevity is enjoyed by men married to women, and people in same-sex marriages regardless of gender, but is not so much the case for women married to men.
However! Zaraska notes a factor she learned from Gottman’s research (yes, that Gottman), that what matters is not the official status of a relationship, so much as the sense of secure lifelong commitment to it.
These kinds of observations (throughout the book) add an extra layer beyond “common wisdom”, and allow us to better understand what’s really going on. The book’s main weaknesses, meanwhile, are twofold:
- The author is (in this reviewer’s opinion) unduly dismissive of physical health lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise, because they “only” account for a similar bonus to healthy longevity.
- Like many, she does not always consider where correlation might not mean causation. For example, she cites that volunteering free time increases healthspan by 22%, but neglects to note that perhaps it is having the kind of socioeconomic situation that allows one free time to volunteer, that gives the benefit.
Bottom line: the book has its flaws, but we think that only serves to make it more engaging. After all, reading should not be a purely passive activity! Zaraska’s well-studied insights give plenty of pointers for tweaking the social side of anyone’s quest for healthy longevity.
Click here to check out Growing Young, increase your healthspan, and take joy in doing it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: