4 Practices To Build Self-Worth That Lasts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Self-worth is internal, based on who you are, not what you do or external validation. It differs from self-esteem, which is more performance-based. High self-worth doesn’t necessarily mean arrogance, but can lead to more confidence and success. Most importantly, it’ll help you to thrive in what’s actually most important to you, rather than being swept along by what other people want.
A stable foundation
A strong sense of self-worth shapes how you handle boundaries, what you believe you deserve, and what you pursue in life. This matters, because life is unpredictable, so having a resilient internal foundation (like a secure “house”) helps you to weather challenges.
- Self-acceptance and compassion:
- Accept both your positive and negative traits with compassion.
- Don’t judge yourself harshly; allow yourself to accept imperfections without guilt or shame.
- Self-trust:
- Trust yourself to make choices that benefit you and create habits that support long-term well-being—especially if those benefits are cumulative!
- Balance self-care with flexibility to enjoy life without being overly rigid.
- Get uncomfortable:
- Growth happens outside your comfort zone. Step into new, challenging experiences to build self-trust.
- However! Small uncomfortable actions lead to greater confidence and a stronger sense of self. Large uncomfortable actions often doing lead anywhere good.
- Separation of tasks:
- Oftentimes we end up overly preoccupying ourselves with things that are not actually our responsibility. Focus instead on tasks that genuinely belong to you, and let go of trying to control others’ perceptions or tasks.
- Seek internal validation, not external praise. Avoid people-pleasing behavior.
Finally, three things to keep in mind:
- Boundaries: respecting your own boundaries strengthens self-worth, avoiding burnout from people-pleasing.
- Validation: self-worth is independent of how others perceive you; focus on your integrity and personal growth.
- Accountability: take responsibility for your actions but recognize that others’ reactions are beyond your control.
For more on all of these things, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Practise Self-Compassion In Your Relationship (But Watch Out!)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

No, taking drugs like Ozempic isn’t ‘cheating’ at weight loss or the ‘easy way out’
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are taking drugs like Ozempic to lose weight. But what do we actually know about them? This month, The Conversation’s experts explore their rise, impact and potential consequences.
Obesity medication that is effective has been a long time coming. Enter semaglutide (sold as Ozempic and Wegovy), which is helping people improve weight-related health, including lowering the risk of a having a heart attack or stroke, while also silencing “food noise”.
As demand for semaglutide increases, so are claims that taking it is “cheating” at weight loss or the “easy way out”.
We don’t tell people who need statin medication to treat high cholesterol or drugs to manage high blood pressure they’re cheating or taking the easy way out.
Nor should we shame people taking semaglutide. It’s a drug used to treat diabetes and obesity which needs to be taken long term and comes with risks and side effects, as well as benefits. When prescribed for obesity, it’s given alongside advice about diet and exercise.
How does it work?
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA). This means it makes your body’s own glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone, called GLP-1 for short, work better.
GLP-1 gets secreted by cells in your gut when it detects increased nutrient levels after eating. This stimulates insulin production, which lowers blood sugars.
GLP-1 also slows gastric emptying, which makes you feel full, and reduces hunger and feelings of reward after eating.
GLP-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) medications like Ozempic help the body’s own GLP-1 work better by mimicking and extending its action.
Some studies have found less GLP-1 gets released after meals in adults with obesity or type 2 diabetes mellitus compared to adults with normal glucose tolerance. So having less GLP-1 circulating in your blood means you don’t feel as full after eating and get hungry again sooner compared to people who produce more.
GLP-1 has a very short half-life of about two minutes. So GLP-1RA medications were designed to have a very long half-life of about seven days. That’s why semaglutide is given as a weekly injection.
What can users expect? What does the research say?
Higher doses of semaglutide are prescribed to treat obesity compared to type 2 diabetes management (up to 2.4mg versus 2.0mg weekly).
A large group of randomised controlled trials, called STEP trials, all tested weekly 2.4mg semaglutide injections versus different interventions or placebo drugs.
Trials lasting 1.3–2 years consistently found weekly 2.4 mg semaglutide injections led to 6–12% greater weight loss compared to placebo or alternative interventions. The average weight change depended on how long medication treatment lasted and length of follow-up.

Higher doses of semaglutide are prescribed for obesity than for type 2 diabetes. fcm82/Shutterstock Weight reduction due to semaglutide also leads to a reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure of about 4.8 mmHg and 2.5 mmHg respectively, a reduction in triglyceride levels (a type of blood fat) and improved physical function.
Another recent trial in adults with pre-existing heart disease and obesity, but without type 2 diabetes, found adults receiving weekly 2.4mg semaglutide injections had a 20% lower risk of specific cardiovascular events, including having a non-fatal heart attack, a stroke or dying from cardiovascular disease, after three years follow-up.
Who is eligible for semaglutide?
Australia’s regulator, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), has approved semaglutide, sold as Ozempic, for treating type 2 diabetes.
However, due to shortages, the TGA had advised doctors not to start new Ozempic prescriptions for “off-label use” such as obesity treatment and the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme doesn’t currently subsidise off-label use.
The TGA has approved Wegovy to treat obesity but it’s not currently available in Australia.
When it’s available, doctors will be able to prescribe semaglutide to treat obesity in conjunction with lifestyle interventions (including diet, physical activity and psychological support) in adults with obesity (a BMI of 30 or above) or those with a BMI of 27 or above who also have weight-related medical complications.
What else do you need to do during Ozempic treatment?
Checking details of the STEP trial intervention components, it’s clear participants invested a lot of time and effort. In addition to taking medication, people had brief lifestyle counselling sessions with dietitians or other health professionals every four weeks as a minimum in most trials.
Support sessions were designed to help people stick with consuming 2,000 kilojoules (500 calories) less daily compared to their energy needs, and performing 150 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, like brisk walking, dancing and gardening each week.
STEP trials varied in other components, with follow-up time periods varying from 68 to 104 weeks. The aim of these trials was to show the effect of adding the medication on top of other lifestyle counselling.

Trial participants also exercised for 150 minutes a week. Elena Nichizhenova/Shutterstock A review of obesity medication trials found people reported they needed less cognitive behaviour training to help them stick with the reduced energy intake. This is one aspect where drug treatment may make adherence a little easier. Not feeling as hungry and having environmental food cues “switched off” may mean less support is required for goal-setting, self-monitoring food intake and avoiding things that trigger eating.
But what are the side effects?
Semaglutide’s side-effects include nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, constipation, indigestion and abdominal pain.
In one study these led to discontinuation of medication in 6% of people, but interestingly also in 3% of people taking placebos.
More severe side-effects included gallbladder disease, acute pancreatitis, hypoglycaemia, acute kidney disease and injection site reactions.
To reduce risk or severity of side-effects, medication doses are increased very slowly over months. Once the full dose and response are achieved, research indicates you need to take it long term.
Given this long-term commitment, and associated high out-of-pocket cost of medication, when it comes to taking semaglutide to treat obesity, there is no way it can be considered “cheating”.
Read the other articles in The Conversation’s Ozempic series here.
Clare Collins, Laureate Professor in Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post

Dry Needling for Meralgia Paresthetica?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Could you address dry needling, who should administer it, and could it be a remedy for meralgia paresthetica? If not, could you speak to home-based remedies for meralgia paresthetica? Thank you?❞
We’ll need to take a main feature some time to answer this one fully, but we will say some quick things here:
- Dry needling, much like acupuncture, has been found to help with pain relief.
- Meralgia paresthetica, being a neuropathy, may benefit from some things that benefit people with peripheral neuropathy, such as lion’s mane mushroom. There is definitely not research to support this hypothesis yet though (so far as we could find anyway; there is plenty to support lion’s mane helping with nerve regeneration in general, but nothing specific for meralgia paresthetica).
Some previous articles you might enjoy meanwhile:
- Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture
- Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief
- Peripheral Neuropathy: How To Avoid It, Manage It, Treat It
- What Does Lion’s Mane Actually Do, Anyway?
Take care!
Share This Post

The Daily Stoic – by Ryan Holiday & Stephen Hanselman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s this, a philosophy book in a health and productivity newsletter? Well, look at it this way: Aristotle basically wrote the “How To Win Friends And Influence People” of his day, and Plato before him wrote a book about management.
In this (chiefly modern!) book, we see what the later Stoic philosophers had to say about getting the most out of life—which is also what we’re about, here at 10almonds!
We tend to use the word “stoic” in modern English to refer to a person who is resolute in the face of hardship. The traditional meaning does encompass that, but also means a lot more: a whole, rounded, philosophy of life.
Philosophy in general is not an easy thing into which to “dip one’s toe”. No matter where we try to start, it seems, it turns out there were a thousand other things we needed to read first!
This book really gets around that. The format is:
- There’s a theme for each month
- Each month has one lesson per day
- Each daily lesson starts with some words from a renowned stoic philosopher, and then provides commentary on such
- The commentary provides a jumping-off point and serves as a prompt to actually, genuinely, reflect and apply the ideas.
Unlike a lot of “a year of…” day-by-day books, this is not light reading, by the way, and you are getting a weighty tome for your money.
But, the page-length daily lessons are indeed digestible—which, again, is what we like at 10almonds!
Share This Post
Related Posts

Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I was wondering, is the health difference important between extra virgin olive oil and regular?❞
Assuming that by “regular” you mean “virgin and still sold as a food product”, then there are health differences, but they’re not huge. Or at least: not nearly so big as the differences between those and other oils.
Virgin olive oil (sometimes simply sold as “olive oil”, with no claims of virginity) has been extracted by the same means as extra virgin olive oil, that is to say: purely mechanical.
The difference is that extra virgin olive oil comes from the first pressing*, so the free fatty acid content is slightly lower (later checked and validated and having to score under a 0.8% limit for “extra virgin” instead of 2% limit for a mere “virgin”).
*Fun fact: in Arabic, extra virgin is called “البكر الممتاز“, literally “the amazing first-born”, because of this feature!
It’s also slightly higher in mono-unsaturated fatty acids, which is a commensurately slight health improvement.
It’s very slightly lower in saturated fats, which is an especially slight health improvement, as the saturated fats in olive oil are amongst the healthiest saturated fats one can consume.
On which fats are which:
The truth about fats: the good, the bad, and the in-between
And our own previous discussion of saturated fats in particular:
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
Probably the strongest extra health-benefit of extra virgin is that while that first pressing squeezes out oil with the lowest free fatty acid content, it squeezes out oil with the highest polyphenol content, along with other phytonutrients:
If you enjoy olive oil, then springing for extra virgin is worth it if that’s not financially onerous, both for health reasons and taste.
However, if mere “virgin” is what’s available, it’s no big deal to have that instead; it still has a very similar nutritional profile, and most of the same benefits.
Don’t settle for less than “virgin”, though.
While some virgin olive oils aren’t marked as such, if it says “refined” or “blended”, then skip it. These will have been extracted by chemical means and/or blended with completely different oils (e.g. canola, which has a very different nutritional profile), and sometimes with a dash of virgin or extra virgin, for the taste and/or so that they can claim in big writing on the label something like:
a blend of
EXTRA VIRGIN OLIVE OIL
and other oils…despite having only a tiny amount of extra virgin olive oil in it.
Different places have different regulations about what labels can claim.
The main countries that produce olives (and the EU, which contains and/or directly trades with those) have this set of rules:
International Olive Council: Designations and definitions of Olive Oils
…which must be abided by or marketers face heavy fines and sanctions.
In the US, the USDA has its own set of rules based on the above:
USDA | Olive Oil and Olive-Pomace Oil Grades and Standards
…which are voluntary (not protected by law), and marketers can pay to have their goods certified if they want.
So if you’re in the US, look for the USDA certification or it really could be:
- What the USDA calls “US virgin olive oil not fit for human consumption”, which in the IOC is called “lamp oil”*
- crude pomace-oil (oil made from the last bit of olive paste and then chemically treated)
- canola oil with a dash of olive oil
- anything yellow and oily, really
*This technically is virgin olive oil insofar as it was mechanically extracted, but with defects that prevent it from being sold as such, such as having a free fatty acid content above the cut-off, or just a bad taste/smell, or some sort of contamination.
See also: Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols
(the above paper has a handy infographic if you scroll down just a little)
Where can I get some?
Your local supermarket, probably, but if you’d like to get some online, here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Gut Health for Women – by Aurora Bloom
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First things first: though the title says “For Women”, almost all of it applies to men too—and the things that don’t apply, don’t cause a problem. So if you’re cooking for your family that contains one or more men, this is still great.
Bloom gives us a good, simple, practical introduction to gut health. Her overview also covers gut-related ailments beyond the obvious “tummy hurts”. On which note:
A very valuable section of this book covers dealing with any stomach-upsets that do occur… without harming your trillions of tiny friends (friendly gut microbiota). This alone can make a big difference!
The book does of course also cover the things you’d most expect: things to eat or avoid. But it goes beyond that, looking at optimizing and maintaining your gut health. It’s not just dietary advice here, because the gut affects—and is affected by—other lifestyle factors too. Ranges from mindful eating, to a synchronous sleep schedule, to what kinds of exercise are best to keep your gut ticking over nicely.
There’s also a two-week meal plan, and an extensive appendix of resources, not to mention a lengthy bibliography for sourcing health claims (and suggesting further reading).
In short, a fine and well-written guide to optimizing your gut health and enjoying the benefits.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:

Yes, adults can develop food allergies. Here are 4 types you need to know about
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you didn’t have food allergies as a child, is it possible to develop them as an adult? The short answer is yes. But the reasons why are much more complicated.
Preschoolers are about four times more likely to have a food allergy than adults and are more likely to grow out of it as they get older.
It’s hard to get accurate figures on adult food allergy prevalence. The Australian National Allergy Council reports one in 50 adults have food allergies. But a US survey suggested as many as one in ten adults were allergic to at least one food, with some developing allergies in adulthood.
What is a food allergy
Food allergies are immune reactions involving immunoglobulin E (IgE) – an antibody that’s central to triggering allergic responses. These are known as “IgE-mediated food allergies”.
Food allergy symptoms that are not mediated by IgE are usually delayed reactions and called food intolerances or hypersensitivity.
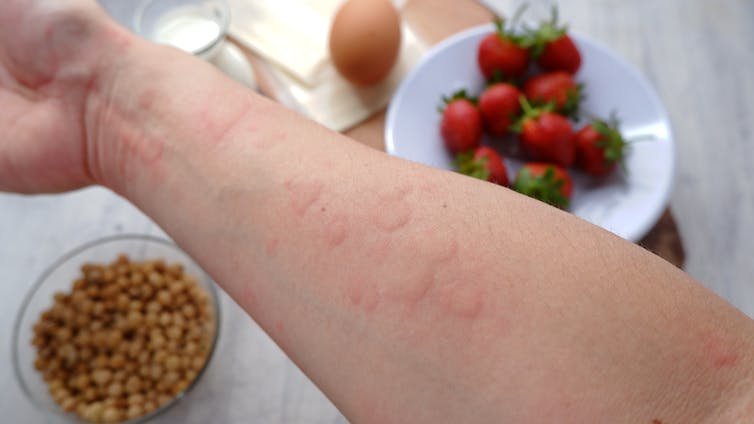
Food allergy symptoms can include hives, swelling, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, throat or chest tightening, trouble breathing, chest pain, rapid heart rate, dizziness, low blood pressure or anaphylaxis.

Symptoms include hives. wisely/Shutterstock IgE-mediated food allergies can be life threatening, so all adults need an action management plan developed in consultation with their medical team.
Here are four IgE-mediated food allergies that can occur in adults – from relatively common ones to rare allergies you’ve probably never heard of.
1. Single food allergies
The most common IgE-mediated food allergies in adults in a US survey were to:
- shellfish (2.9%)
- cow’s milk (1.9%)
- peanut (1.8%)
- tree nuts (1.2%)
- fin fish (0.9%) like barramundi, snapper, salmon, cod and perch.
In these adults, about 45% reported reacting to multiple foods.
This compares to most common childhood food allergies: cow’s milk, egg, peanut and soy.
Overall, adult food allergy prevalence appears to be increasing. Compared to older surveys published in 2003 and 2004, peanut allergy prevalence has increased about three-fold (from 0.6%), while tree nuts and fin fish roughly doubled (from 0.5% each), with shellfish similar (2.5%).
While new adult-onset food allergies are increasing, childhood-onset food allergies are also more likely to be retained into adulthood. Possible reasons for both include low vitamin D status, lack of immune system challenges due to being overly “clean”, heightened sensitisation due to allergen avoidance, and more frequent antibiotic use.

Some adults develop allergies to cow’s milk, while others retain their allergy from childhood. Sarah Swinton/Unsplash 2. Tick-meat allergy
Tick-meat allergy, also called α-Gal syndrome or mammalian meat allergy, is an allergic reaction to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose, or α-Gal for short.
Australian immunologists first reported links between α-Gal syndrome and tick bites in 2009, with cases also reported in the United States, Japan, Europe and South Africa. The US Centers for Disease Control estimates about 450,000 Americans could be affected.
The α-Gal contains a carbohydrate molecule that is bound to a protein molecule in mammals.
The IgE-mediated allergy is triggered after repeated bites from ticks or chigger mites that have bitten those mammals. When tick saliva crosses into your body through the bite, antibodies to α-Gal are produced.
When you subsequently eat foods that contain α-Gal, the allergy is triggered. These triggering foods include meat (lamb, beef, pork, rabbit, kangaroo), dairy products (yoghurt, cheese, ice-cream, cream), animal-origin gelatin added to gummy foods (jelly, lollies, marshmallow), prescription medications and over-the counter supplements containing gelatin (some antibiotics, vitamins and other supplements).
Tick-meat allergy reactions can be hard to recognise because they’re usually delayed, and they can be severe and include anaphylaxis. Allergy organisations produce management guidelines, so always discuss management with your doctor.
3. Fruit-pollen allergy
Fruit-pollen allergy, called pollen food allergy syndrome, is an IgE-mediated allergic reaction.
In susceptible adults, pollen in the air provokes the production of IgE antibodies to antigens in the pollen, but these antigens are similar to ones found in some fruits, vegetables and herbs. The problem is that eating those plants triggers an allergic reaction.
The most allergenic tree pollens are from birch, cypress, Japanese cedar, latex, grass, and ragweed. Their pollen can cross-react with fruit and vegetables, including kiwi, banana, mango, avocado, grapes, celery, carrot and potato, and some herbs such as caraway, coriander, fennel, pepper and paprika.
Fruit-pollen allergy is not common. Prevalence estimates are between 0.03% and 8% depending on the country, but it can be life-threatening. Reactions range from itching or tingling of lips, mouth, tongue and throat, called oral allergy syndrome, to mild hives, to anaphylaxis.
4. Food-dependent, exercise-induced food allergy
During heavy exercise, the stomach produces less acid than usual and gut permeability increases, meaning that small molecules in your gut are more likely to escape across the membrane into your blood. These include food molecules that trigger an IgE reaction.
If the person already has IgE antibodies to the foods eaten before exercise, then the risk of triggering food allergy reactions is increased. This allergy is called food-dependent exercise-induced allergy, with symptoms ranging from hives and swelling, to difficulty breathing and anaphylaxis.

This type of allergy is extremely rare. Ben O’Sullivan/Unsplash Common trigger foods include wheat, seafood, meat, poultry, egg, milk, nuts, grapes, celery and other foods, which could have been eaten many hours before exercising.
To complicate things even further, allergic reactions can occur at lower levels of trigger-food exposure, and be more severe if the person is simultaneously taking non-steroidal inflammatory medications like aspirin, drinking alcohol or is sleep-deprived.
Food-dependent exercise-induced allergy is extremely rare. Surveys have estimated prevalence as between one to 17 cases per 1,000 people worldwide with the highest prevalence between the teenage years to age 35. Those affected often have other allergic conditions such as hay fever, asthma, allergic conjunctivitis and dermatitis.
Allergies are a growing burden
The burden on physical health, psychological health and health costs due to food allergy is increasing. In the US, this financial burden was estimated as $24 billion per year.
Adult food allergy needs to be taken seriously and those with severe symptoms should wear a medical information bracelet or chain and carry an adrenaline auto-injector pen. Concerningly, surveys suggest only about one in four adults with food allergy have an adrenaline pen.
If you have an IgE-mediated food allergy, discuss your management plan with your doctor. You can also find more information at Allergy and Anaphylaxis Australia.
Clare Collins, Laureate Professor in Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: