An Important Way That Love Gets Eroded
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It is unusual for a honeymoon period to last forever, but some relationships fair a lot better than others. Not just in terms of staying together vs separating, but in terms of happiness and satisfaction in the relationship. What’s the secret? There are many, but here’s one of them…
Communication
In this video, the case is made for a specific aspect of communication: airing grievances.
Superficially, this doesn’t seem like a recipe for happiness, but it is one important ingredient—that it’s dangerously easy to let small grievances add up and eat away at one’s love and patience, until one day resentment outweighs attachment, and at that point, it often becomes a case of “checking out before you leave”, remaining in the relationship more due to inertia than volition.
Which, in turn, will likely start to cause resentment on the other side, and eventually things will crumble and/or explode.
In contrast, if we make sure to speak our feelings clearly (10almonds note, not in the video: we think that doing so compassionately is also important), the bad as well as the good, then it means that:
- things don’t stack up and fester (there will less likely be a “final straw” if we are regularly removing straws)
- there is an opportunity for change (in contrast, our partner would be unlikely to adjust anything to correct a problem they don’t know about)
- all but the most inclined-to-anxiety partners can rest easy, because they know that if we had a problem, we’d tell them
This is definitely only one critical aspect of communication; this video for example says nothing about actually being affectionate with one’s partner, or making sure to accept emotional bids for connection (per that story that goes “I knew my marriage was over when he wouldn’t come look at the tomatoes I grew”), but it is one worth considering—even if we at 10almonds would advise being gentle yet honest, and where possible balancing, in aggregate if not in the moment, with positive things (per Gottman’s ratio of 5:1 good moments to bad, being the magic number for marriages that “work”).
For more on why it’s so important to be able to safely air grievances, see:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Seriously Useful Communication Skills! ← this deals with some of the important gaps left by the video
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Reversing Alzheimer’s – by Dr. Heather Sandison
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The title here is bold, isn’t it? But, if the studies so far are anything to go by, she is, indeed, reversing Alzheimer’s. By this we mean: her Alzheimer’s patients have enjoyed a measurable reversal of the symptoms of cognitive decline (this is not something that usually happens).
The science here is actually new, and/but references are given aplenty, including Dr. Sandison’s own research and others—there’s a bibliography of several hundred papers, which we love to see.
Dr. Sandison’s approach is of course multivector, but is far more lifestyle medicine than pills, with diet in particular playing a critical role. Indeed, it’s worth mentioning that she is a naturopathic doctor (not an MD), so that is her focus—though she’s had a lot of MDs looking in on her work too, as you may see in the book. She has found best results in a diet low in carbs, high in healthy fats—and it bears emphasizing, healthy ones. Many other factors are also built in, but this is a book review, not a book summary.
Nor does the book look at diet in isolation; other aspects of lifestyle are also taken into account, as well as various medical pathways, and how to draw up a personalized plan to deal with those.
The book is written with the general assumption that the reader is someone with increased Alzheimer’s risk wishing to reduce that risk, or the relative of someone with Alzheimer’s disease already. However, the information within is beneficial to all.
The style is on the hard end of pop-science; it’s written for the lay reader, but will (appropriately enough) require active engagement to read effectively.
Bottom line: if Alzheimer’s is something that affects or is likely to affect you (directly, or per a loved one), then this is a very good book to have read
Click here top check out Reversing Alzheimer’s, and learn how to do it!
Share This Post
-
Radical Longevity – by Dr. Ann Gittleman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Gittleman takes a comprehensive approach, advising us about avoiding AGEs, freeing up fascia, stimulating cellular rejuvenation, the mind-gut connection, keeping the immune system healthy, and more.
The “plan” promised by the subtitle involves identifying the key factors of nutrition and lifestyle most impactful to you, and adjusting them accordingly, in a multistep, author-walks-the-reader-by-the-hand process.
There’s also, for those who prefer it, a large section (seven chapters) on a body part/system by body part/system approach, e.g. brain health, heart health, revitalizing skin, reversing hair loss, repairing bones, muscles, joints, etc.
The writing style is quite casual,butalso with a mind to education, with its call-out boxes, bullet-point summaries, and so forth. There is a “select references” section, but if one wants to find studies, it’s often necessary to go looking, as there aren’t inline citations.
Bottom line: we’d love to see better referencing, but otherwise this is a top-tier anti-aging book, and a lot more accessible than most, without skimping on depth and breadth.
Click here to check out Radical Longevity, and get rejuvenating radically!
Share This Post
-
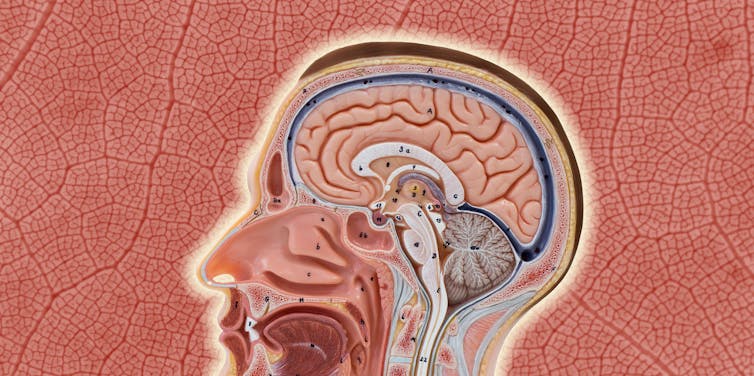
Our blood-brain barrier stops bugs and toxins getting to our brain. Here’s how it works
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our brain is an extremely complex and delicate organ. Our body fiercely protects it by holding onto things that help it and keeping harmful things out, such as bugs that can cause infection and toxins.
It does that though a protective layer called the blood-brain barrier. Here’s how it works, and what it means for drug design.
The Conversation, Rattiya Thongdumhyu/Shutterstock, Petr Ganaj/Pexels First, let’s look at the circulatory system
Adults have roughly 30 trillion cells in their body. Every cell needs a variety of nutrients and oxygen, and they produce waste, which needs to be taken away.
Our circulatory system provides this service, delivering nutrients and removing waste.
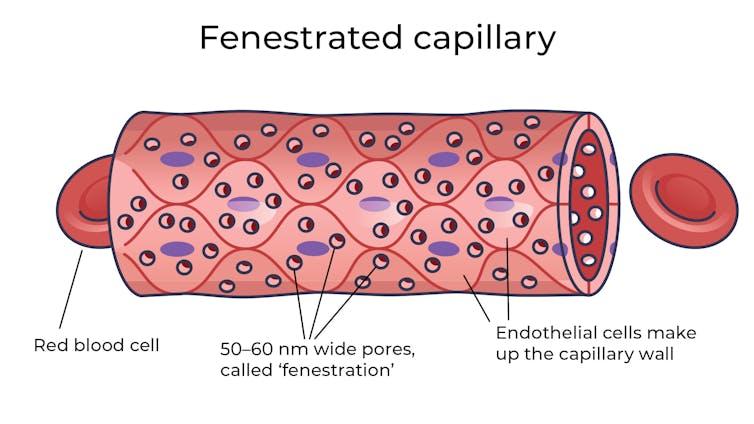
Fenestrated capillaries let nutrients and waste pass through. Vectormine/Shutterstock Where the circulatory system meets your cells, it branches down to tiny tubes called capillaries. These tiny tubes, about one-tenth the width of a human hair, are also made of cells.
But in most capillaries, there are some special features (known as fenestrations) that allow relatively free exchange of nutrients and waste between the blood and the cells of your tissues.
It’s kind of like pizza delivery
One way to think about the way the circulation works is like a pizza delivery person in a big city. On the really big roads (vessels) there are walls and you can’t walk up to the door of the house and pass someone the pizza.
But once you get down to the little suburban streets (capillaries), the design of the streets means you can stop, get off your scooter and walk up to the door to deliver the pizza (nutrients).
We often think of the brain as a spongy mass without much blood in it. In reality, the average brain has about 600 kilometres of blood vessels.
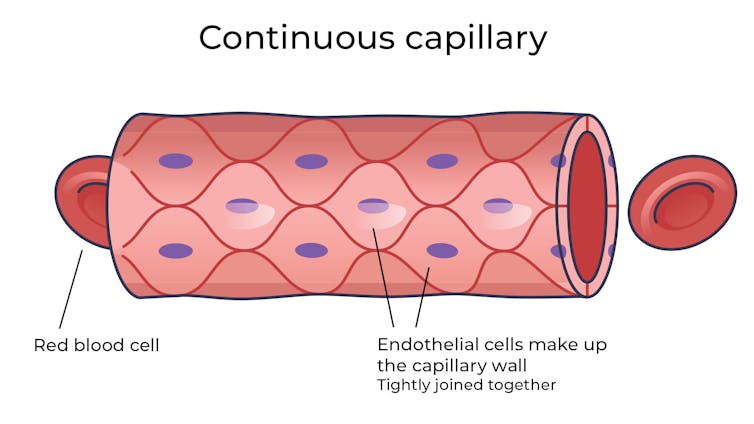
The difference between the capillaries in most of the brain and those elsewhere is that these capillaries are made of specialised cells that are very tightly joined together and limit the free exchange of anything dissolved in your blood. These are sometimes called continuous capillaries.
Continuous capillaries limit the free exchange of anything dissolved in your blood. Vectormine/Shutterstock This is the blood brain barrier. It’s not so much a bag around your brain stopping things from getting in and out but more like walls on all the streets, even the very small ones.
The only way pizza can get in is through special slots and these are just the right shape for the pizza box.
The blood brain barrier is set up so there are specialised transporters (like pizza box slots) for all the required nutrients. So mostly, the only things that can get in are things that there are transporters for or things that look very similar (on a molecular scale).
The analogy does fall down a little bit because the pizza box slot applies to nutrients that dissolve in water. Things that are highly soluble in fat can often bypass the slots in the wall.
Why do we have a blood-brain barrier?
The blood brain barrier is thought to exist for a few reasons.
First, it protects the brain from toxins you might eat (think chemicals that plants make) and viruses that often can infect the rest of your body but usually don’t make it to your brain.
It also provides protection by tightly regulating the movement of nutrients and waste in and out, providing a more stable environment than in the rest of the body.
Lastly, it serves to regulate passage of immune cells, preventing unnecessary inflammation which could damage cells in the brain.
What it means for medicines
One consequence of this tight regulation across the blood brain barrier is that if you want a medicine that gets to the brain, you need to consider how it will get in.
There are a few approaches. Highly fat-soluble molecules can often pass into the brain, so you might design your drug so it is a bit greasy.
The blood-brain barrier stops many medicines getting into the brain. Ron Lach/Pexels Another option is to link your medicine to another molecule that is normally taken up into the brain so it can hitch a ride, or a “pro-drug”, which looks like a molecule that is normally transported.
Using it to our advantage
You can also take advantage of the blood brain barrier.
Opioids used for pain relief often cause constipation. They do this because their target (opioid receptors) are also present in the nervous system of the intestines, where they act to slow movement of the intestinal contents.
Imodium (Loperamide), which is used to treat diarrhoea, is actually an opioid, but it has been specifically designed so it can’t cross the blood brain barrier.
This design means it can act on opioid receptors in the gastrointestinal tract, slowing down the movement of contents, but does not act on brain opioid receptors.
In contrast to Imodium, Ozempic and Victoza (originally designed for type 2 diabetes, but now popular for weight-loss) both have a long fat attached, to improve the length of time they stay in the body.
A consequence of having this long fat attached is that they can cross the blood-brain barrier, where they act to suppress appetite. This is part of the reason they are so effective as weight-loss drugs.
So while the blood brain barrier is important for protecting the brain it presents both a challenge and an opportunity for development of new medicines.
Sebastian Furness, ARC Future Fellow, School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
HIIT, But Make It HIRT
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This May HIRT A Bit
This is Ingrid Clay. She’s a professional athlete, personal trainer, chef*, and science writer.
*A vegan bodybuilding chef, no less:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
For those who prefer reading…
This writer does too 😉
We’ve previously reviewed her book, “Science of HIIT”, and we’re going to be talking a bit about High Intensity Interval Training today.
If you’d like to know a little more about the woman herself first, then…
Centr | Meet Ingrid: Your HIIT HIRT trainer
Yes, that is Centr, as in Chris Hemsworth’s personal training app, where Clay is the resident HIIT & HIRT expert & trainer.
What’s this HIIT & HIRT?
“HIIT” is High Intensity Interval Training, which we’ve written about before:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Basically, it’s a super-efficient way of working out, that gets better results than working out for longer with other methods, especially because of how it raises the metabolism for a couple of hours after training (this effect is called EPOC, by the way—Excessive Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption), and is a good thing.
You can read more about the science of it, in the above-linked main feature.
And HIRT?
“HIRT” is High Intensity Resistance Training, and is resistance training performed with HIIT principles.
See also: Chris Hemsworth’s Trainer Ingrid Clay Explains HIRT
An example is doing 10 reps of a resistance exercise (e.g., a dumbbell press) every minute on odd-numbered minutes, and 10 reps of a different resistance exercise (e.g. dumbbell squats) on even-numbered minutes.
If dumbbells aren’t your thing, it could be resistance bands, or even the floor (press-ups are a resistance exercise!)
For HIRT that’s not also a cardio exercise, gaps between different exercises can be quite minimal, as we only need to confuse the muscles, not the heart. So, effectively, it becomes a specially focused kind of circuit training!
If doing planks though, you might want to check out Clay’s troubleshooting guide:
Want more from Clay?
Here she gives a full 20-minute full-body HIIT HIRT workout:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eating disorders don’t just affect teen girls. The risk may go up around pregnancy and menopause too
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eating disorders impact more than 1.1 million people in Australia, representing 4.5% of the population. These disorders include binge eating disorder, bulimia nervosa, and anorexia nervosa.
Meanwhile, more than 4.1 million people (18.9%) are affected by body dissatisfaction, a major risk factor for some types of eating disorders.
But what image comes to mind first when you think of someone with an eating disorder or body image concerns? Is it a teenage girl? If so, you’re definitely not alone. This is often the image we see in popular media.
Eating disorders and body image concerns are most common in teenage girls, but their prevalence in adults, particularly in women, aged in their 30s, 40s and 50s, is actually close behind.
So what might be going on with girls and women in these particular age groups to create this heightened risk?
Drazen Zigic/Shutterstock The 3 ‘P’s
We can consider women’s risk periods for body image issues and eating disorders as the three “P”s: puberty (teenagers), pregnancy (30s) and perimenopause and menopause (40s, 50s).
A recent report from The Butterfly Foundation showed the three highest prevalence groups for body image concerns are teenage girls aged 15–17 (39.9%), women aged 55–64 (35.7%) and women aged 35–44 (32.6%).
We acknowledge there’s a wide age range for when girls and women will go through these phases of life. For example, a small proportion of women will experience premature menopause before 40, and not all women will become pregnant.
Variations in the way eating disorder symptoms are measured across different studies can make it difficult to draw direct comparisons, but here’s a snapshot of what the evidence tells us.
Puberty
In a review of studies looking at children aged six to adolescents aged 18, 30% of girls in this age group reported disordered eating, compared to 17% of boys. Rates of disordered eating were higher as children got older.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, eating disorder prevalence is estimated at 7.5%. Almost 70% of women are dissatisfied with their body weight and figure in the post-partum period.
Pregnancy can represent a major change in identity and self-perception. Pormezz/Shutterstock Perimenopause
It’s estimated more than 73% of midlife women aged 42–52 are unsatisfied with their body weight. However, only a portion of these women would have been going through the menopause transition at the time of this study.
The prevalence of eating disorders is around 3.5% in women over 40 and 1–2% in men at the same stage.
So what’s going on?
Although we’re not sure of the exact mechanisms underlying eating disorder and body dissatisfaction risk during the three “P”s, it’s likely a combination of factors are at play.
These life stages involve significant reproductive hormonal changes (for example, fluctuations in oestrogen and progesterone) which can lead to increases in appetite or binge eating and changes in body composition. These changes can result in concerns about body weight and shape.
These stages can also represent a major change in identity and self-perception. A girl going through puberty may be concerned about turning into an “adult woman” and changes in attitudes of those around her, such as unwanted sexual attention.
Pregnancy obviously comes with significant body size and shape changes. Pregnant women may also feel their body is no longer their own.
While social pressures to be thin can stop during pregnancy, social expectations arguably return after birth, demanding women “bounce back” to their pre-pregnancy shape and size quickly.
Women going through menopause commonly express concerns about a loss of identity. In combination with changes in body composition and a perception their appearance is departing from youthful beauty ideals, this can intensify body dissatisfaction and increase the risk of eating disorders.
These periods of life can each also be incredibly stressful, both physically and psychologically.
For example, a girl going through puberty may be facing more adult responsibilities and stress at school. A pregnant woman could be taking care of a family while balancing work and other demands. A woman going through menopause could potentially be taking care of multiple generations (teenage children, ageing parents) while navigating the complexities of mid-life.
Research has shown interpersonal problems and stressors can increase the risk of eating disorders.
Body image concerns and eating disorders are not limited to teenage girls. transly/Unsplash, CC BY We need to do better
Unfortunately most of the policy and research attention currently seems to be focused on preventing and treating eating disorders in adolescents rather than adults. There also appears to be a lack of understanding among health professionals about these issues in older women.
In research I (Gemma) led with women who had experienced an eating disorder during menopause, participants expressed frustration with the lack of services that catered to people facing an eating disorder during this life stage. Participants also commonly said health professionals lacked education and training about eating disorders during menopause.
We need to increase awareness among health professionals and the general public about the fact eating disorders and body image concerns can affect women of any age – not just teenage girls. This will hopefully empower more women to seek help without stigma, and enable better support and treatment.
Jaycee Fuller from Bond University contributed to this article.
If this article has raised issues for you, or if you’re concerned about someone you know, call Lifeline on 13 11 14. For concerns around eating disorders or body image visit the Butterfly Foundation website or call the national helpline on 1800 33 4673.
Gemma Sharp, Professor, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow & Senior Clinical Psychologist, The University of Queensland; Amy Burton, Lecturer in Clinical Psychology, University of Technology Sydney, and Megan Lee, Assistant Professor, Psychology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The BAT-pause!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Cold Weather & The Menopause Battle It Out
You may know that (moderate, safe) exposure to the cold allows our body to convert our white and yellow fat into the much healthier brown fat—also called brown adipose tissue, or “BAT” to its friends.
If you didn’t already know that, then well, neither did scientists until about 15 years ago:
The Changed Metabolic World with Human Brown Adipose Tissue: Therapeutic Visions
You can read more about it here:
Cool Temperature Alters Human Fat and Metabolism
This is important, especially because the white fat that gets converted is the kind that makes up most visceral fat—the kind most associated with all-cause mortality:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It ← this is not the same as your subcutaneous fat, the kind that sits directly under your skin and keeps you warm; this is the fat that goes between your organs and of which we should only have a small amount!
The BAT-pause
It’s been known (since before the above discovery) that BAT production slows considerably as we get older. Not too shocking—after all, many metabolic functions slow as we get older, so why should fat regulation be any different?
But! Rodent studies found that this was tied less to age, but to ovarian function: rats who underwent ovariectomies suffered reduced BAT production, regardless of their age.
Naturally, it’s been difficult to recreate such studies in humans, because it’s difficult to find a large sample of young adults willing to have their ovaries whipped out (or even suppressed chemically) to see how badly their metabolism suffers as a result.
Nor can an observational study (for example, of people who incidentally have ovaries removed due to ovarian cancer) usefully be undertaken, because then the cancer itself and any additional cancer treatments would be confounding factors.
Perimenopausal study to the rescue!
A recent (published last month, at time of writing!) study looked at women around the age of menopause, but specifically in cohorts before and after, measuring BAT metabolism.
By dividing the participants into groups based on age and menopausal status, and dividing the post-menopausal group into “takes HRT” and “no HRT” groups, and dividing the pre-menopausal group into “normal ovarian function” and “ovarian production of estrogen suppressed to mimic slightly early menopause” groups (there’s a drug for that), and then having groups exposed to warm and cold temperatures, and measuring BAT metabolism in all cases, they were able to find…
It is about estrogen, not age!
You can read more about the study here:
“Good” fat metabolism changes tied to estrogen loss, not necessarily to aging, shows study
…and the study itself, here:
Brown adipose tissue metabolism in women is dependent on ovarian status
What does this mean for men?
This means nothing directly for (cis) men, sorry.
But to satisfy your likely curiosity: yes, testosterone does at least moderately suppress BAT metabolism—based on rodent studies, anyway, because again it’s difficult to find enough human volunteers willing to have their testicles removed for science (without there being other confounding variables in play, anyway):
Testosterone reduces metabolic brown fat activity in male mice
So, that’s bad per se, but there isn’t much to be done about it, since the rest of your (addressing our male readers here) metabolism runs on testosterone, as do many of your bodily functions, and you would suffer many unwanted effects without it.
However, as men do typically have notably less body fat in general than women (this is regulated by hormones), the effects of changes in BAT metabolism are rather less pronounced in men (per testosterone level changes) than in women (per estrogen level changes), because there’s less overall fat to convert.
In summary…
While menopausal HRT is not necessarily a silver bullet to all metabolic problems, its BAT-maintaining ability is certainly one more thing in its favor.
See also:
Dr. Jen Gunter | What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: