Oral vaccines could provide relief for people who suffer regular UTIs. Here’s how they work
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In a recent TikTok video, Australian media personality Abbie Chatfield shared she was starting a vaccine to protect against urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Huge news for the UTI girlies. I am starting a UTI vaccine tonight for the first time.
Chatfield suffers from recurrent UTIs and has turned to the Uromune vaccine, an emerging option for those seeking relief beyond antibiotics.
But Uromune is not a traditional vaccine injected to your arm. So what is it and how does it work?

First, what are UTIs?
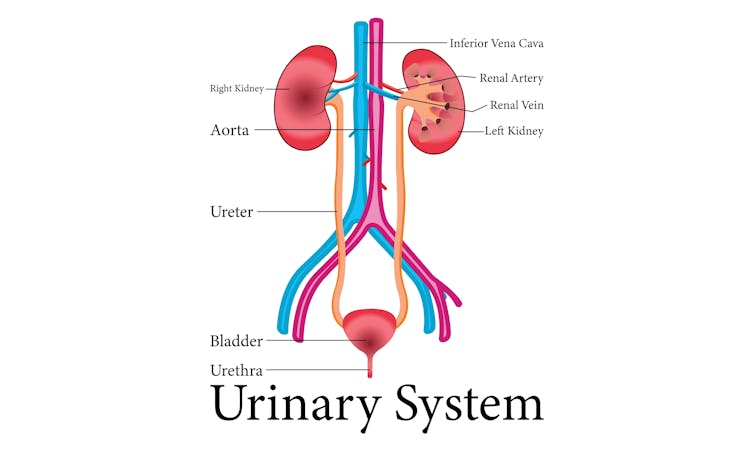
UTIs are caused by bacteria entering the urinary system. This system includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters (thin tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder), and the urethra (the tube through which urine leaves the body).
The most common culprit is Escherichia coli (E. coli), a type of bacteria normally found in the intestines.
While most types of E. coli are harmless in the gut, it can cause infection if it enters the urinary tract. UTIs are particularly prevalent in women due to their shorter urethras, which make it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder.
Roughly 50% of women will experience at least one UTI in their lifetime, and up to half of those will have a recurrence within six months.
The symptoms of a UTI typically include a burning sensation when you wee, frequent urges to go even when the bladder is empty, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or back. If left untreated, a UTI can escalate into a kidney infection, which can require more intensive treatment.
While antibiotics are the go-to treatment for UTIs, the rise of antibiotic resistance and the fact many people experience frequent reinfections has sparked more interest in preventive options, including vaccines.
What is Uromune?
Uromune is a bit different to traditional vaccines that are injected into the muscle. It’s a sublingual spray, which means you spray it under your tongue. Uromune is generally used daily for three months.
It contains inactivated forms of four bacteria that are responsible for most UTIs, including E. coli. By introducing these bacteria in a controlled way, it helps your immune system learn to recognise and fight them off before they cause an infection. It can be classified as an immunotherapy.
A recent study involving 1,104 women found the Uromune vaccine was 91.7% effective at reducing recurrent UTIs after three months, with effectiveness dropping to 57.6% after 12 months.
These results suggest Uromune could provide significant (though time-limited) relief for women dealing with frequent UTIs, however peer-reviewed research remains limited.
Any side effects of Uromune are usually mild and may include dry mouth, slight stomach discomfort, and nausea. These side effects typically go away on their own and very few people stop treatment because of them. In rare cases, some people may experience an allergic reaction.
How can I access it?
In Australia, Uromune has not received full approval from the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), and so it’s not something you can just go and pick up from the pharmacy.
However, Uromune can be accessed via the TGA’s Special Access Scheme or the Authorised Prescriber pathway. This means a GP or specialist can apply for approval to prescribe Uromune for patients with recurrent UTIs. Once the patient has a form from their doctor documenting this approval, they can order the vaccine directly from the manufacturer.

Uromune is not covered under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, meaning patients must cover the full cost out-of-pocket. The cost of a treatment program is around A$320.
Uromune is similarly available through special access programs in places like the United Kingdom and Europe.
Other options in the pipeline
In addition to Uromune, scientists are exploring other promising UTI vaccines.
Uro-Vaxom is an established immunomodulator, a substance that helps regulate or modify the immune system’s response to bacteria. It’s derived from E. coli proteins and has shown success in reducing UTI recurrences in several studies. Uro-Vaxom is typically prescribed as a daily oral capsule taken for 90 days.
FimCH, another vaccine in development, targets something called the adhesin protein that helps E. coli attach to urinary tract cells. FimCH is typically administered through an injection and early clinical trials have shown promising results.
Meanwhile, StroVac, which is already approved in Germany, contains inactivated strains of bacteria such as E. coli and provides protection for up to 12 months, requiring a booster dose after that. This injection works by stimulating the immune system in the bladder, offering temporary protection against recurrent infections.
These vaccines show promise, but challenges like achieving long-term immunity remain. Research is ongoing to improve these options.
No magic bullet, but there’s reason for optimism
While vaccines such as Uromune may not be an accessible or perfect solution for everyone, they offer real hope for people tired of recurring UTIs and endless rounds of antibiotics.
Although the road to long-term relief might still be a bit bumpy, it’s exciting to see innovative treatments like these giving people more options to take control of their health.
Iris Lim, Assistant Professor in Biomedical Science, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bamboo Shoots vs Asparagus – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing bamboo shoots to asparagus, we picked the asparagus.
Why?
Both are great! But asparagus does distinguish itself on nutritional density.
In terms of macros, bamboo starts strong with more protein and fiber, but it’s not a huge amount more; the margins of difference are quite small.
In the category of vitamins, asparagus wins easily with more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B9, C, E, K, and choline. In contrast, bamboo boasts only more vitamin B6. A clear win for asparagus.
The minerals line-up is closer; asparagus has more calcium, iron, magnesium, and selenium, while bamboo shoots have more manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. That’s a 4:4 tie, but asparagus’s margins of difference are larger, and if we need a further tiebreaker, bamboo also contains more sodium, which most people in the industrialized world could do with less of rather than more. So, a small win for asparagus.
In short, adding up the sections… Bamboo shoots, but asparagus scores, and wins the day. Enjoy both, of course, but if making a pick, then asparagus has more bang-for-buck.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Asparagus vs Eggplant – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What Different Kinds of Hair Loss/Thinning Say About Your Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Siobhan Deshauer shows us different kinds of hair loss, what causes them, and what can be done about them:
Many different causes
Here’s how to tell them apart:
- Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss that can occur at any age and affects about 1 in 50 people. It often presents as smooth patches of hair loss and can be treated with steroid injections. Severe cases may require high-dose prednisone, which can restore hair growth over time.
- Discoid lupus is an autoimmune disease that affects the skin, leading to inflammation, scarring, and permanent hair loss. Unlike alopecia areata, it causes visible damage to the scalp and hair follicles. This type of lupus typically does not involve internal organs, unlike systemic lupus.
- Telogen effluvium occurs when a major systemic shock, such as an infection, surgery, or significant stress, triggers many hair follicles to enter the resting phase simultaneously, resulting in delayed hair shedding. The condition is diagnosed with a “hair pull test” and is typically temporary, as the resting phase is followed by normal hair growth phases.
- Allergic reactions to products, such as hair dye containing PPD, can cause hair loss due to scalp irritation and inflammation. An allergic response may trigger hair follicles to enter a resting phase, leading to hair loss by the same mechanism as telogen effluvium. Treatment with steroids can calm the reaction, and hair usually regrows after recovery.
- Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection, can present with varied symptoms, including hair loss in a distinct moth-eaten pattern. Hair loss due to syphilis is reversible and curable with penicillin treatment, with hair regrowth typically occurring a few months after treatment.
- Biotin deficiency is rare due to its production by gut bacteria and presence in foods such as nuts, seeds, and beans such as soybeans. Deficiency can result from excessive consumption of raw egg whites, which block absorption. Severe deficiency causes hair loss and skin issues but can be treated effectively with biotin supplements.
- Iron deficiency anemia can cause hair thinning along with symptoms like fatigue and breathlessness. It often results from inadequate dietary intake, but can also occur after heavy menstrual bleeding. Treatment with iron supplements, or blood transfusions in severe cases, can restore both hair and energy levels, leading to significant improvements.
- Trichotillomania is a psychological condition marked by an uncontrollable urge to pull out one’s hair, often associated with anxiety or depression. Hair patches may show different stages of regrowth. While it can be challenging to manage, the condition can be treated with appropriate psychological and medical support.
- Traction alopecia results from hairstyles that exert prolonged tension on the hair, causing it to thin or fall out. This type of hair loss can be prevented by reducing the strain on the hair. Loosening hairstyles and giving the scalp a break can help hair regrow over time.
- Hypothyroidism causes symptoms like fatigue, dry skin, and hair thinning due to insufficient thyroid hormone production—however, it can be managed with diet, and if necessary, thyroid medications.
- Zinc deficiency may also cause hair loss and a characteristic rash. Treatment with zinc supplements can significantly improve hair growth and other symptoms.
- Medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, Accutane, and anti-seizure medications like valproic acid, are known to cause hair loss as a side effect. This type of hair loss is often reversible once the medication is stopped.
- Male pattern hair loss, or androgenic alopecia, is influenced by testosterone and genetic risk factors—which, contrary to popular belief, can come from either or both sides of the family. Early onset, especially before age 40, is linked to an increased risk of heart disease. However, effective treatments are available, and early intervention is beneficial.
- Female pattern hair loss is basically the same thing as male pattern hair loss (indeed, it is literally still androgenic alopecia), just a) almost always much less severe and b) with a gender-appropriate name. It affects up to 40% of women by age 50 and is characterized by thinning hair at the top of the head. It’s related to hormonal imbalances involving testosterone, such as those seen in PCOS and menopause, amongst other less common causes. Early treatment can be effective, and research is ongoing to develop more targeted therapies.
Dr. Siobhan Deshauer advises, if you’re experiencing hair loss, to monitor other symptoms too if applicable, take photos for tracking, and consult a doctor early for diagnosis and potential treatment.
For more on all of this plus visual illustrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Can a drug like Ozempic help treat addictions to alcohol, opioids or other substances?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Semaglutide (sold as Ozempic, Wegovy and Rybelsus) was initially developed to treat diabetes. It works by stimulating the production of insulin to keep blood sugar levels in check.
This type of drug is increasingly being prescribed for weight loss, despite the fact it was initially approved for another purpose. Recently, there has been growing interest in another possible use: to treat addiction.
Anecdotal reports from patients taking semaglutide for weight loss suggest it reduces their appetite and craving for food, but surprisingly, it also may reduce their desire to drink alcohol, smoke cigarettes or take other drugs.
But does the research evidence back this up?
Animal studies show positive results
Semaglutide works on glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors and is known as a “GLP-1 agonist”.
Animal studies in rodents and monkeys have been overwhelmingly positive. Studies suggest GLP-1 agonists can reduce drug consumption and the rewarding value of drugs, including alcohol, nicotine, cocaine and opioids.
Out team has reviewed the evidence and found more than 30 different pre-clinical studies have been conducted. The majority show positive results in reducing drug and alcohol consumption or cravings. More than half of these studies focus specifically on alcohol use.
However, translating research evidence from animal models to people living with addiction is challenging. Although these results are promising, it’s still too early to tell if it will be safe and effective in humans with alcohol use disorder, nicotine addiction or another drug dependence.
What about research in humans?
Research findings are mixed in human studies.
Only one large randomised controlled trial has been conducted so far on alcohol. This study of 127 people found no difference between exenatide (a GLP-1 agonist) and placebo (a sham treatment) in reducing alcohol use or heavy drinking over 26 weeks.
In fact, everyone in the study reduced their drinking, both people on active medication and in the placebo group.
However, the authors conducted further analyses to examine changes in drinking in relation to weight. They found there was a reduction in drinking for people who had both alcohol use problems and obesity.
For people who started at a normal weight (BMI less than 30), despite initial reductions in drinking, they observed a rebound increase in levels of heavy drinking after four weeks of medication, with an overall increase in heavy drinking days relative to those who took the placebo.
There were no differences between groups for other measures of drinking, such as cravings.
Some studies show a rebound increase in levels of heavy drinking. Deman/Shutterstock In another 12-week trial, researchers found the GLP-1 agonist dulaglutide did not help to reduce smoking.
However, people receiving GLP-1 agonist dulaglutide drank 29% less alcohol than those on the placebo. Over 90% of people in this study also had obesity.
Smaller studies have looked at GLP-1 agonists short-term for cocaine and opioids, with mixed results.
There are currently many other clinical studies of GLP-1 agonists and alcohol and other addictive disorders underway.
While we await findings from bigger studies, it’s difficult to interpret the conflicting results. These differences in treatment response may come from individual differences that affect addiction, including physical and mental health problems.
Larger studies in broader populations of people will tell us more about whether GLP-1 agonists will work for addiction, and if so, for whom.
How might these drugs work for addiction?
The exact way GLP-1 agonists act are not yet well understood, however in addition to reducing consumption (of food or drugs), they also may reduce cravings.
Animal studies show GLP-1 agonists reduce craving for cocaine and opioids.
This may involve a key are of the brain reward circuit, the ventral striatum, with experimenters showing if they directly administer GLP-1 agonists into this region, rats show reduced “craving” for oxycodone or cocaine, possibly through reducing drug-induced dopamine release.
Using human brain imaging, experimenters can elicit craving by showing images (cues) associated with alcohol. The GLP-1 agonist exenatide reduced brain activity in response to an alcohol cue. Researchers saw reduced brain activity in the ventral striatum and septal areas of the brain, which connect to regions that regulate emotion, like the amygdala.
In studies in humans, it remains unclear whether GLP-1 agonists act directly to reduce cravings for alcohol or other drugs. This needs to be directly assessed in future research, alongside any reductions in use.
Are these drugs safe to use for addiction?
Overall, GLP-1 agonists have been shown to be relatively safe in healthy adults, and in people with diabetes or obesity. However side effects do include nausea, digestive troubles and headaches.
And while some people are OK with losing weight as a side effect, others aren’t. If someone is already underweight, for example, this drug might not be suitable for them.
In addition, very few studies have been conducted in people with addictive disorders. Yet some side effects may be more of an issue in people with addiction. Recent research, for instance, points to a rare risk of pancreatitis associated with GLP-1 agonists, and people with alcohol use problems already have a higher risk of this disorder.
Other drugs treatments are currently available
Although emerging research on GLP-1 agonists for addiction is an exciting development, much more research needs to be done to know the risks and benefits of these GLP-1 agonists for people living with addiction.
In the meantime, existing effective medications for addiction remain under-prescribed. Only about 3% of Australians with alcohol dependence, for example, are prescribed medication treatments such as like naltrexone, acamprosate or disulfiram. We need to ensure current medication treatments are accessible and health providers know how to prescribe them.
Continued innovation in addiction treatment is also essential. Our team is leading research towards other individualised and effective medications for alcohol dependence, while others are investigating treatments for nicotine addiction and other drug dependence.
Read the other articles in The Conversation’s Ozempic series here.
Shalini Arunogiri, Addiction Psychiatrist, Associate Professor, Monash University; Leigh Walker, , Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health, and Roberta Anversa, , The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
An apple cider vinegar drink a day? New study shows it might help weight loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Made from fermented apples and naturally high in acetic acid, apple cider vinegar has been popular in recent years for its purported health benefits – from antibacterial properties to antioxidant effects and potential for helping manage blood sugars.
Its origins as a health tonic stretch much further back. Hippocrates used it to treat wounds, fever and skin sores.
An experimental study, released today, looks into whether apple cider vinegar could be effective for weight loss, reduce blood glucose levels and reduce blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides).
The results suggest it could reduce all three – but it might not be as simple as downing an apple cider vinegar drink a day.
What did they do?
A group of scientists in Lebanon did a double-blinded, randomised, clinical trial in a group of overweight and obese young people aged from 12–25 years.
Researchers randomly placed 30 participants in one of four groups. The participants were instructed to consume either 5, 10 or 15ml of apple cider vinegar diluted into 250ml of water each morning before they ate anything for 12 weeks. A control group consumed an inactive drink (a placebo) made (from lactic acid added to water) to look and taste the same.
Typically this sort of study provides high quality evidence as it can show cause and effect – that is the intervention (apple cider vinegar in this case) leads to a certain outcome. The study was also double-blinded, which means neither the participants or the scientists involved with collecting the data knew who was in which group.
So, what did they find?
After a period of three months apple cider vinegar consumption was linked with significant falls in body weight and body mass index (BMI). On average, those who drank apple cider vinegar during that period lost 6–8kg in weight and reduced their BMI by 2.7–3 points, depending on the dose. They also showed significant decreases in the waist and hip circumference.
The authors also report significant decreases in levels of blood glucose, triglycerides, and cholesterol in the apple cider groups. This finding echoes previous studies. The placebo group, who were given water with lactic acid, had much smaller decreases in weight and BMI. There were also no significant decreases in blood glucose and blood lipids.
From animal studies, it is thought the acetic acid in apple cider vinegar may affect the expression of genes involved in burning fats for energy. The new study did not explore whether this mechanism was involved in any weight loss.
Is this good news?
While the study appears promising, there are also reasons for caution.
Firstly, study participants were aged from 12 to 25, so we can’t say whether the results could apply to everyone.
The statistical methods used in the study don’t allow us to confidently say the same amount of weight loss would occur again if the study was done again.
And while the researchers kept records of the participants’ diet and exercise during the study, these were not published in the paper. This makes it difficult to determine if diet or exercise may have had an impact. We don’t know whether participants changed the amount they ate or the types of food they ate, or whether they changed their exercise levels.
The study used a placebo which they tried to make identical in appearance and taste to the active treatment. But people may still be able to determine differences. Researchers may ask participants at the end of a study to guess which group they were in to test the integrity of the placebo. Unfortunately this was not done in this study, so we can’t be certain if the participants knew or not.
Finally, the authors do not report whether anyone dropped out of the study. This could be important and influence results if people who did not lose weight quit due to lack of motivation.
Is that you mother? The enzymes in apple cider vinegar might be health-giving.
ShutterstockAny other concerns?
Apple cider vinegar is acidic and there are concerns it may erode tooth enamel. This can be a problem with any acidic beverages, including fizzy drinks, lemon water and orange juice.
To minimise the risk of acid erosion some dentists recommend the following after drinking acidic drinks:
- rinsing out your mouth with tap water afterwards
- chewing sugar-free gum afterwards to stimulate saliva production
- avoiding brushing your teeth immediately after drinking because it might damage the teeth’s softened top layer
- drink with a straw to minimise contact with the teeth.
Rinsing with water could prevent acid damaging your teeth.
ShutterstockDown the hatch?
This study provides us with some evidence of a link between apple cider vinegar and weight loss. But before health professionals can recommend this as a weight loss strategy we need bigger and better conducted studies across a wider age range.
Such research would need to be done alongside a controlled background diet and exercise across all the participants. This would provide more robust evidence that apple cider vinegar could be a useful aid for weight loss.
Still, if you don’t mind the taste of apple cider vinegar then you could try drinking some for weight loss, alongside a healthy balanced and varied dietary intake. This study does not suggest people can eat whatever they like and drink apple cider vinegar as a way to control weight.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Blood, urine and other bodily fluids: how your leftover pathology samples can be used for medical research
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A doctor’s visit often ends with you leaving with a pathology request form in hand. The request form soon has you filling a sample pot, having blood drawn, or perhaps even a tissue biopsy taken.
After that, your sample goes to a clinical pathology lab to be analysed, in whichever manner the doctor requested. All this is done with the goal of getting to the bottom of the health issue you’re experiencing.
But after all the tests are done, what happens with the leftover sample? In most cases, leftover samples go in the waste bin, destined for incineration. Sometimes though, they may be used again for other purposes, including research.
Kaboompics.com/Pexels Who can use my leftover samples?
The samples we’re talking about here cover the range of samples clinical labs receive in the normal course of their testing work. These include blood and its various components (including plasma and serum), urine, faeces, joint and spinal fluids, swabs (such as from the nose or a wound), and tissue samples from biopsies, among others.
Clinical pathology labs often use leftover samples to practise or check their testing methods and help ensure test accuracy. This type of use is a vital part of the quality assurance processes labs need to perform, and is not considered research.
Leftover samples can also be used by researchers from a range of agencies such as universities, research institutes or private companies.
They may use leftover samples for research activities such as trying out new ideas or conducting small-scale studies (more on this later). Companies that develop new or improved medical diagnostic tests can also use leftover samples to assess the efficacy of their test, generating data needed for regulatory approval.
What about informed consent?
If you’ve ever participated in a medical research project such as a clinical trial, you may be familiar with the concept of informed consent. In this process, you have the opportunity to learn about the study and what your participation involves, before you decide whether or not to participate.
So you may be surprised to learn using leftover samples for research purposes without your consent is permitted in most parts of Australia, and elsewhere. However, it’s only allowed under certain conditions.
In Australia, the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) offers guidance around the use of leftover pathology samples.
One of the conditions for using leftover samples without consent for research is that they were received and retained by an accredited pathology service. This helps ensure the samples were collected safely and properly, for a legitimate clinical reason, and that no additional burdens or risk of harm to the person who provided the sample will be created with their further use.
Another condition is anonymity: the leftover samples must be deidentified, and not easily able to be reidentified. This means they can only be used in research if the identity of the donor is not needed.
Leftover pathology samples are sometimes used in medical research. hedgehog94/Shutterstock The decision to allow a particular research project to use leftover pathology samples is made by an independent human research ethics committee which includes consumers and independent experts. The committee evaluates the project and weighs up the risks and potential benefits before permitting an exemption to the need for informed consent.
Similar frameworks exist in the United States, the United Kingdom, India and elsewhere.
What research might be done on my leftover samples?
You might wonder how useful leftover samples are, particularly when they’re not linked to a person and their medical history. But these samples can still be a valuable resource, particularly for early-stage “discovery” research.
Research using leftover samples has helped our understanding of antibiotic resistance in a bacterium that causes stomach ulcers, Helicobacter pylori. It has helped us understand how malaria parasites, Plasmodium falciparum, damage red blood cells.
Leftover samples are also helping researchers identify better, less invasive ways to detect chronic diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis. And they’re allowing scientists to assess the prevalence of a variant in haemoglobin that can interfere with widely used diagnostic blood tests.
All of this can be done without your permission. The kinds of tests researchers do on leftover samples will not harm the person they were taken from in any way. However, using what would otherwise be discarded allows researchers to test a new method or treatment and avoid burdening people with providing fresh samples specifically for the research.
When considering questions of ethics, it could be argued not using these samples to derive maximum benefit is in fact unethical, because their potential is wasted. Using leftover samples also minimises the cost of preliminary studies, which are often funded by taxpayers.
The use of leftover pathology samples in research has been subject to some debate. Andrey_Popov/Shutterstock Inconsistencies in policy
Despite NHMRC guidance, certain states and territories have their own legislation and guidelines which differ in important ways. For instance, in New South Wales, only pathology services may use leftover specimens for certain types of internal work. In all other cases consent must be obtained.
Ethical standards and their application in research are not static, and they evolve over time. As medical research continues to advance, so too will the frameworks that govern the use of leftover samples. Nonetheless, developing a nationally consistent approach on this issue would be ideal.
Striking a balance between ensuring ethical integrity and fostering scientific discovery is essential. With ongoing dialogue and oversight, leftover pathology samples will continue to play a crucial role in driving innovation and advances in health care, while respecting the privacy and rights of individuals.
Christine Carson, Senior Research Fellow, School of Medicine, The University of Western Australia and Nikolajs Zeps, Professor, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Reinventing Your Life – by Dr. Jeffrey Young & Dr. Janet Klosko
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is quite unlike any other broadly-CBT-focused books we’ve reviewed before. How so, you may wonder?
Rather than focusing on automatic negative thoughts and cognitive distortions with a small-lens focus on an immediate problem, this one zooms out rather and tackles the cause rather than the symptom.
The authors outline eleven “lifetraps” that we can get stuck in:
- Abandonment
- Mistrust & abuse
- Vulnerability
- Dependence
- Emptional deprivation
- Social exclusion
- Defectiveness
- Failure
- Subjugation
- Unrelenting standards
- Entitlement
They then borrow from other areas of psychology, to examine where these things came from, and how they can be addressed, such that we can escape from them.
The style of the book is very reader-friendly pop-psychology, with illustrative (and perhaps apocryphal, but no less useful for it if so) case studies.
The authors then go on to give step-by-step instructions for dealing with each of the 11 lifetraps, per 6 unmet needs we probably had that got us into them, and per 3 likely ways we tried to cope with this using maladaptive coping mechanisms that got us into the lifetrap(s) we ended up in.
Bottom line: if you feel there’s something in your life that’s difficult to escape from (we cannot outrun ourselves, after all, and bring our problems with us), this book could well contain the key that you need to get out of that cycle.
Click here to check out “Reinventing Your Life” and break free from any lifetrap(s) of your own!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: