Fall Asleep In 2 Minutes (Doctor Explains)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Beyond “sleep hygiene”, Dr. Siobhan Deshauer has insights to share:
Rest for your body and mind
First, do still do the basics. That means dimming/filtering lights for an hour before bed, lowering the room temperature a little, ensuring you have nice fresh sheets, not having alcohol or caffeine before bed, and getting out of bed if you’re not asleep within half an hour, to avoid associating being in bed with wakefulness.
Next, the extra tips:
- Progressive relaxation: tense and relax each muscle group from toes to head
- Box breathing: inhale, hold, exhale, and hold for 4 seconds each; helps calm the nervous system (it’s called “box breathing” because of the 4:4:4:4 setup)
- Diaphragmatic breathing: focus on belly breathing, with longer exhalation to activate the parasympathetic nervous system (note that this can, and even ideally should, be done at the same time as the previous)
- Cognitive shuffling: think of words starting with each letter of a chosen word while visualizing them (this is like “counting sheep”, but does the job better—the job in question being preventing your brain from moving to anything more strenuous or stressful)
For more on all of these plus some extra side-along advice, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Non-Sleep Deep Rest: A Neurobiologist’s Take ← a way to get many of the benefits of sleep, while awake
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dogs Paired With Providers at Hospitals Help Ease Staff and Patient Stress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
DENVER — Outside HCA HealthONE Rose medical center, the snow is flying. Inside, on the third floor, there’s a flurry of activity within the labor and delivery unit.
“There’s a lot of action up here. It can be very stressful at times,” said Kristina Fraser, an OB-GYN in blue scrubs.
Nurses wheel a very pregnant mom past.
“We’re going to bring a baby into this world safely,” Fraser said, “and off we go.”
She said she feels ready in part due to a calming moment she had just a few minutes earlier with some canine colleagues.
A pair of dogs, tails wagging, had come by a nearby nursing station, causing about a dozen medical professionals to melt into a collective puddle of affection. A yellow Lab named Peppi showered Fraser in nuzzles and kisses. “I don’t know if a human baby smells as good as that puppy breath!” Fraser had said as her colleagues laughed.
The dogs aren’t visitors. They work here, too, specifically for the benefit of the staff. “I feel like that dog just walks on and everybody takes a big deep breath and gets down on the ground and has a few moments of just decompressing,” Fraser said. “It’s great. It’s amazing.”
Hospital staffers who work with the dogs say there is virtually no bite risk with the carefully trained Labradors, the preferred breed for this work.
The dogs are kept away from allergic patients and washed regularly to prevent germs from spreading, and people must wash their hands before and after petting them.
Doctors and nurses are facing a growing mental health crisis driven by their experiences at work. They and other health care colleagues face high rates of depression, anxiety, stress, suicidal ideation, and burnout. Nearly half of health workers reported often feeling burned out in 2022, an increase from 2018, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. And the percentage of health care workers who reported harassment at work more than doubled over that four-year period. Advocates for the presence of dogs in hospitals see the animals as one thing that can help.
That includes Peppi’s handler, Susan Ryan, an emergency medicine physician at Rose.
Ryan said years working as an emergency room doctor left her with symptoms of PTSD. “I just was messed up and I knew it,” said Ryan, who isolated more at home and didn’t want to engage with friends. “I shoved it all in. I think we all do.”
She said doctors and other providers can be good at hiding their struggles, because they have to compartmentalize. “How else can I go from a patient who had a cardiac arrest, deal with the family members telling them that, and go to a room where another person is mad that they’ve had to wait 45 minutes for their ear pain? And I have to flip that switch.”
To cope with her symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, Ryan started doing therapy with horses. But she couldn’t have a horse in her backyard, so she got a Labrador.
Ryan received training from a national service dog group called Canine Companions, becoming the first doctor trained by the group to have a facility dog in an emergency room. Canine Companions has graduated more than 8,000 service dogs.
The Rose medical center gave Ryan approval to bring a dog to work during her ER shifts. Ryan’s colleagues said they are delighted that a dog is part of their work life.
“When I have a bad day at work and I come to Rose and Peppi is here, my day’s going to be made better,” EMT Jasmine Richardson said. “And if I have a patient who’s having a tough day, Peppi just knows how to light up the room.”
Nursing supervisor Eric Vaillancourt agreed, calling Peppi “joyful.”
Ryan had another dog, Wynn, working with her during the height of the pandemic. She said she thinks Wynn made a huge difference. “It saved people,” she said. “We had new nurses that had never seen death before, and now they’re seeing a covid death. And we were worried sick we were dying.”
She said her hospital system has lost a couple of physicians to suicide in the past two years, which HCA confirmed to KFF Health News and NPR. Ryan hopes the canine connection can help with trauma. “Anything that brings you back to the present time helps ground you again. A dog can be that calming influence,” she said. “You can get down on the ground, pet them, and you just get calm.”
Ryan said research has shown the advantages. For example, one review of dozens of original studies on human-animal interactions found benefits for a variety of conditions including behavioral and mood issues and physical symptoms of stress.
Rose’s president and CEO, Casey Guber, became such a believer in the canine connection he got his own trained dog to bring to the hospital, a black Lab-retriever mix named Ralphie.
She wears a badge: Chief Dog Officer.
Guber said she’s a big morale booster. “Phenomenal,” he said. “It is not uncommon to see a surgeon coming down to our administration office and rolling on the ground with Ralphie, or one of our nurses taking Ralphie out for a walk in the park.”
This article is from a partnership that includes CPR News, NPR, and KFF Health News.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Unleashing My Superpowers – by Dr. Patience Mpofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Patience Mpofu is on a mission to provide women and girls with the inside-information, knowledge, resources, and strategies to break through the glass ceiling. She writes from her experience in STEM, but her lessons are applicable in any field.
Her advices range from the internal (how to deal with imposter syndrome) to the external (how to overcome cultural biases); she also explains and illustrates the importance of both role models and mentors.
While a lot of the book is half instruction manual, half memoir of her incredible life and career (to illustrate her points), and is well-worth reading—and/or perhaps worth gifting to a girl you know with ambitions in STEM?
Share This Post
-
Ageless – by Dr. Andrew Steele
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So, yet another book with “The new science of…” in the title; does this one deliver new science?
Actually, yes, this time! The author was originally a physicist before deciding that aging was the number one problem that needed solving, and switched tracks to computational biology, and pioneered a lot of research, some of the fruits of which can be found in this book, in amongst a more general history of the (very young!) field of biogerontology.
Downside: most of this is not very practical for the lay reader; most of it is explanations of how things happen on a cellular and/or genetic level, and how we learned that. A lot also pertains to what we can learn from animals that either age very slowly, or are biologically immortal (in other words, they can still be killed, but they don’t age and won’t die of anything age-related), or are immune to cancer—and how we might borrow those genes for gene therapy.
However, there are also chapters on such things as “running repairs”, “reprogramming aging”, and “how to live long enough to live even longer”.
The style is conversational pop science; in the prose, he simply states things without reference, but at the back, there are 40 pages of bibliography, indexed in the order in which they occurred and prefaced with the statement that he’s referencing in each case. It’s an odd way to do citations, but it works comfortably enough.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand aging on the cellular level, and how we know what we know and what the likely future possibilities are, then this is a great book; it’s also simply very enjoyable to read, assuming you have an interest in the topic (as this reviewer does).
Click here to check out Ageless, and understand the science of getting older without getting old!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Complete Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Beginners – by Dorothy Calimeris and Lulu Cook
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, about the authors: notwithstanding the names, Calimeris is the cook, and Cook is the nutritionist (and an RDN at that).
As for the book: we get a good primer on the science of inflammation, what it is, why it happens, what things are known to cause/trigger it, and what things are known to fight it. They do also go outside of nutrition a bit for this, speaking briefly on other lifestyle factors too, but the main focus is of course nutrition.
As for the recipes: while distinctly plants-forward (as one might expect of an anti-inflammatory eating book), it’s not outright vegan or even vegetarian, indeed, in the category of main dishes, there are sections for:
- Vegetarian and vegan
- Fish and shellfish
- Poultry and meat
…as well as, before and after those, sections for breakfast and brunch and snacks and sweets. As well as a not-to-be-underestimated section, for sauces, condiments, and dressings. This is important, because those are quite often the most inflammatory parts of an otherwise healthy meal! So being able to make anti-inflammatory versions is a real boon.
The recipes are mostly not illustrated, but the steps are very clearly described and easy to follow.
Bottom line: if inflammation is currently on your to-tackle list, this book will be an excellent companion in the kitchen.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sleep wrinkles are real. Here’s how they leave their mark
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You wake up, stagger to the bathroom and gaze into the mirror. No, you’re not imagining it. You’ve developed face wrinkles overnight. They’re sleep wrinkles.
Sleep wrinkles are temporary. But as your skin loses its elasticity as you age, they can set in.
Here’s what you can do to minimise the chance of them forming in the first place.
How side-sleeping affects your face
Your skin wrinkles for a number of reasons, including ageing, sun damage, smoking, poor hydration, habitual facial expressions (such as grinning, pouting, frowning, squinting) and sleeping positions.
When you sleep on your side or stomach, your face skin is squeezed and crushed a lot more than if you sleep on your back. When you sleep on your side or stomach, gravity presses your face against the pillow. Your face skin is distorted as your skin is stretched, compressed and pulled in all directions as you move about in your sleep.
You can reduce these external forces acting on the face by sleeping on your back or changing positions frequently.
Doctors can tell which side you sleep on by looking at your face
In a young face, sleep wrinkles are transient and disappear after waking.
Temporary sleep wrinkles can become persistent with time and repetition. As we age, our skin loses elasticity (recoil) and extensibility (stretch), creating ideal conditions for sleep wrinkles or lines to set in and last longer.
The time spent in each sleeping position, the magnitude of external forces applied to each area of the face, as well as the surface area of contact with the pillow surface, also affects the pattern and rate of sleep wrinkle formation.
Skin specialists can often recognise this. People who favour sleeping on one side of their body tend to have a flatter face on their sleeping side and more visible sleep lines.
Can a night skincare routine avoid sleep wrinkles?
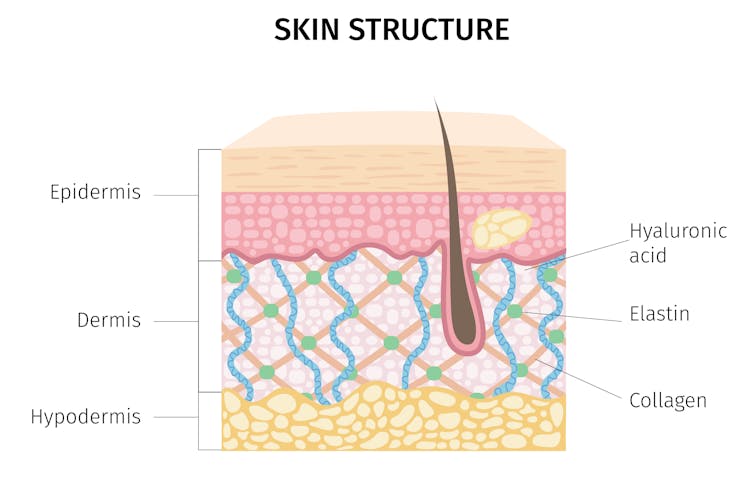
Collagen and elastin are two primary components of the dermis (inner layer) of skin. They form the skin structure and maintain the elasticity of skin.
The dermis is the inner layer of skin. mermaid3/Shutterstock Supplementing collagen through skincare routines to enhance skin elasticity can help reduce wrinkle formation.
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring molecule in human bodies. It holds our skin’s collagen and elastin in a proper configuration, stimulates the production of collagen and adds hydration, which can help slow down wrinkle formation. Hyaluronic acid is one of the most common active ingredients in skincare creams, gels and lotions.
Moisturisers can hydrate the skin in different ways. “Occlusive” substances produce a thin layer of oil on the skin that prevents water loss due to evaporation. “Humectants” attract and hold water in the skin, and they can differ in their capacity to bind with water, which influences the degree of skin hydration.
Do silk pillowcases actually make a difference?
Can they help? New Africa/Shutterstock Silk pillowcases can make a difference in wrinkle formation, if they let your skin glide and move, rather than adding friction and pressure on a single spot. If you can, use silk sheets and silk pillows.
Studies have also shown pillows designed to reduce mechanical stress during sleep can prevent skin deformations. Such a pillow could be useful in slowing down and preventing the formation of certain facial wrinkles.
Sleeping on your back can reduce the risk of sleep lines, as can a nighttime routine of moisturising before sleep.
Otherwise, lifestyle choices and habits, such quitting smoking, drinking plenty of water, a healthy diet (eating enough vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, healthy fats, yogurt and other fermented foods) and regular use of sunscreens can help improve the appearance of the skin on our face.
Yousuf Mohammed, Dermatology researcher, The University of Queensland; Khanh Phan, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Frazer Institute, The University of Queensland, and Vania Rodrigues Leite E. Silva, Honorary Associate Professor, Frazer Institute, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
52 Small Changes – by Brett Blumenthal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We see a lot of books that exhort us to get a six-pack in a month, change our life in 7 days, learn Japanese in 24 hours. The reality is, things take time!
Brett Blumenthal is more realistic while being just as motivational:
The idea is simple… Make one small change per week for 52 weeks, and at the end of the year, you’ll be healthier and happier.
At 10almonds, we’re big fans of small changes that add up (or rather: compound!) to make big differences, so this one’s absolutely our style!
Best of all, she offers us not just “do this” advice, but also “and here’s the information and resources you’ll need to make this change work the best it can for you”
The advices range in topic from nutrition to exercise to sleep to mental wellness to interpersonal stuff and more. The biggest focus is on personal health, though, with small changes to exercise and nutrition making up the lion’s share of the changes.
Bottom line: this is a book you’ll want to grab once a week. Consider setting a reminder on your phone to check in with it each Sunday, for example!
Take the first step and order “52 Small Changes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: