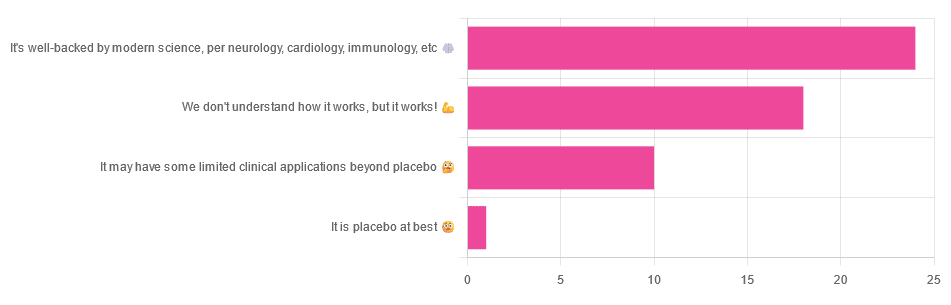Shoe Wear Patterns: What They Mean, Why It Matters, & How To Fix It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you look under your shoes, do you notice how the tread is worn more in some places than others? Specific patterns of shoe wear correspond to how our body applies force, weight, and rotational movement. This reveals how we move, and uneven wear can indicate problematic movement dynamics.
The clues in your shoes
Common shoe wear patterns include:
- Diagonal wear on the outside of the heel: caused by foot angle, leg position, and instability, leading to joint stress.
- Rotational wear at specific points: due to internal or external rotation, often originating from the hip, pelvis, or torso.
- Wear above the big toe: caused by excessive toe lifting, often associated with a “lighter” or kicking leg.
Fixing movement issues to prevent wear involves correcting posture, improving balance, and adjusting how the legs land during walking/running.
Key fixes include:
- Aligning the center of gravity properly to prevent leg overcompensation.
- Ensuring feet land under the hips and not far in front.
- Stabilizing the torso to avoid unnecessary rotation.
- Engaging the glutes effectively to reduce hip flexor dominance and improve leg mechanics.
- Maintaining even weight distribution on both legs to prevent excessive lifting or twisting.
Posture and walking mechanics are vital to reducing uneven wear, but meaningful, lasting change takes time and focused effort, to build new habits.
For more on all this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Support For Long COVID & Chronic Fatigue
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Long COVID and Chronic Fatigue
Getting COVID-19 can be very physically draining, so it’s no surprise that getting Long COVID can (and usually does) result in chronic fatigue.
But, what does this mean and what can we do about it?
What makes Long COVID “long”
Long COVID is generally defined as COVID-19 whose symptoms last longer than 28 days, but in reality the symptoms not only tend to last for much longer than that, but also, they can be quite distinct.
Here’s a large (3,762 participants) study of Long COVID, which looked at 203 symptoms:
Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact
Three symptoms stood at out as most prevalent:
- Chronic fatigue (CFS)
- Cognitive dysfunction
- Post-exertional malaise (PEM)
The latter means “the symptoms get worse following physical or mental exertion”.
CFS, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, is also called Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME).
What can be done about it?
The main “thing that people do about it” is to reduce their workload to what they can do, but this is not viable for everyone. Note that work doesn’t just mean “one’s profession”, but anything that requires physical or mental energy, including:
- Childcare
- Housework
- Errand-running
- Personal hygiene/maintenance
For many, this means having to get someone else to do the things—either with support of family and friends, or by hiring help. For many who don’t have those safety nets available, this means things simply not getting done.
That seems bleak; isn’t there anything more we can do?
Doctors’ recommendations are chiefly “wait it out and hope for the best”, which is not encouraging. Some people do recover from Long COVID; for others, it so far appears it might be lifelong. We just don’t know yet.
Doctors also recommend to journal, not for the usual mental health benefits, but because that is data collection. Patients who journal about their symptoms and then discuss those symptoms with their doctors, are contributing to the “big picture” of what Long COVID and its associated ME/CFS look like.
You may notice that that’s not so much saying what doctors can do for you, so much as what you can do for doctors (and in the big picture, eventually help them help people, which might include you).
So, is there any support for individuals with Long COVID ME/CFS?
Medically, no. Not that we could find.
However! Socially, there are grassroots support networks, that may be able to offer direct assistance, or at least point individuals to useful local resources.
Grassroots initiatives include Long COVID SOS and the Patient-Led Research Collaborative.
The patient-led organization Body Politic also used to have such a group, until it shut down due to lack of funding, but they do still have a good resource list:
Click here to check out the Body Politic resource list (it has eight more specific resources)
Stay strong!
Share This Post
-
Successful Aging – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know about age-related cognitive decline. What if there’s a flipside, though?
Neuroscientist Dr. Daniel Levitin explores the changes that the brain undergoes with age, and notes that it’s not all downhill.
From cumulative improvements in the hippocampi to a dialling-down of the (often overfunctioning) amygdalae, there are benefits too.
The book examines the things that shape our brains from childhood into our eighties and beyond. Many milestones may be behind us, but neuroplasticity means there’s always time for rewiring. Yes, it also covers the “how”.
We learn also about the neurogenesis promoted by such simple acts as taking a different route and/or going somewhere new, and what other things improve the brain’s healthspan.
The writing style is very accessible “pop-science”, and is focused on being of practical use to the reader.
Bottom line: if you want to get the most out of your aging wizening brain, this book is a great how-to manual.
Click here to check out Successful Aging and level up your later years!
Share This Post
-
What You Don’t Know Can Kill You
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Knowledge Is Power!
This is Dr. Simran Malhotra. She’s triple board-certified (in lifestyle medicine, internal medicine, and palliative care), and is also a health and wellness coach.
What does she want us to know?
Three things:
Wellness starts with your mindset
Dr. Malhotra shifted her priorities a lot during the initial and perhaps most chaotic phase of the COVID pandemic:
❝My husband, a critical care physician, was consumed in the trenches of caring for COVID patients in the ICU. I found myself knee-deep in virtual meetings with families whose loved ones were dying of severe COVID-related illnesses. Between the two of us, we saw more trauma, suffering, and death, than we could have imagined.
The COVID-19 pandemic opened my eyes to how quickly life can change our plans and reinforced the importance of being mindful of each day. Harnessing the power to make informed decisions is important, but perhaps even more important is focusing on what is in our control and taking action, even if it is the tiniest step in the direction we want to go!❞
~ Dr. Simran Malhotra
We can only make informed decisions if we have good information. That’s one of the reasons we try to share as much information as we can each day at 10almonds! But a lot will always depend on personalized information.
There are one-off (and sometimes potentially life-saving) things like health genomics:
The Real Benefit Of Genetic Testing
…but also smaller things that are informative on an ongoing basis, such as keeping track of your weight, your blood pressure, your hormones, and other metrics. You can even get fancy:
Track Your Blood Sugars For Better Personalized Health
Lifestyle is medicine
It’s often said that “food is medicine”. But also, movement is medicine. Sleep is medicine. In short, your lifestyle is the most powerful medicine that has ever existed.
Lifestyle encompasses very many things, but fortunately, there’s an “80:20 rule” in play that simplifies it a lot because if you take care of the top few things, the rest will tend to look after themselves:
These Top Few Things Make The Biggest Difference To Overall Health
Gratitude is better than fear
If we receive an unfavorable diagnosis (and let’s face it, most diagnoses are unfavorable), it might not seem like something to be grateful for.
But it is, insofar as it allows us to then take action! The information itself is what gives us our best chance of staying safe. And if that’s not possible e.g. in the worst case scenario, a terminal diagnosis, (bearing in mind that one of Dr. Malhotra’s three board certifications is in palliative care, so she sees this a lot), it at least gives us the information that allows us to make the best use of whatever remains to us.
See also: Managing Your Mortality
Which is very important!
…and/but possibly not the cheeriest note on which to end, so when you’ve read that, let’s finish today’s main feature on a happier kind of gratitude:
How To Get Your Brain On A More Positive Track (Without Toxic Positivity)
Want to hear more from Dr. Malhotra?
Showing how serious she is about how our genes do not determine our destiny and knowledge is power, here she talks about her “previvor’s journey”, as she puts it, with regard to why she decided to have preventative cancer surgery in light of discovering her BRCA1 genetic mutation:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Sun-dried Tomatoes vs Black Olives – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sun-dried tomatoes to black olives, we picked the sun-dried tomatoes.
Why?
These common snack-salad items may seem similar in consistency, but their macros are very different: the tomatoes, being dried, have proportionally a lot more protein, carbs, and fiber. The olives, meanwhile, have more fat (and/but yes, a very healthy blend of fats). Note that these comments are true for the things themselves; be aware that sun-dried tomatoes are often sold in vegetable oil, which would obviously change the macros considerably and be much less healthy. So, for the sake of statistics, we’re assuming you got sun-dried tomatoes that aren’t soaked in oil. All in all, we’re calling this category a win for the tomatoes, but those fats from the olives are very good too.
In terms of vitamins, the sun-dried tomatoes being dried again means that the loss of water weight means the vitamin content is proportionally much higher; the tomatoes are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, and K, while olives are higher only in vitamin E (but in their defence, olives have 165x more vitamin E than sun-dried tomatoes). Still, a win for sun-dried tomatoes here.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a similar story for the same reason; the loss of water weight in the sun-dried tomatoes makes them much more nutritionally dense; they are higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while the olives are higher only in sodium. Note, we’re looking at black olives today; green olives would be even higher in sodium than black ones, as they are “cured” for longer.
Lastly, in terms of polyphenols, they both have a lot of great things to bring, but sun-dried tomatoes are pretty much the richest natural source of lycopene, which itself a very powerful polyphenol even my general polyphenol standards, so we’d call this one a win for the sun-dried tomatoes too.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Powered by Plants – by Ocean Robbins & Nichole Dandrea-Russert
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of the two authors, the former is a professional public speaker, and the latter is a professional dietician. As a result, we get a book that is polished and well-presented, while actually having a core of good solid science (backed up with plenty of references).
There’s an introductory section that’s all about the “notable nutrients”, that will be focused on in the ingredients choices for the recipes in the rest of the book.
The recipes themselves are simple enough to do quickly, yet interesting enough that you’ll want to do them, and certainly they contain all the plant-based nutrient-density you might expect.
Bottom line: if you’d like to expand your plant-based cooking with a focus on nutrition and ease without sacrificing fun, then this is a great cookbook for that.
Click here to check out Powered by Plants, and get powered by plants!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Does One Test Acupuncture Against Placebo Anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture
We asked you for your opinions on acupuncture, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of answers:
- A little under half of all respondents voted for “It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc”
- Slightly fewer respondents voted for “We don’t understand how it works, but it works!”
- A little under a fifth of respondents voted for “It may have some limited clinical applications beyond placebo”
- One (1) respondent voted for for “It’s placebo at best”
When we did a main feature about homeopathy, a couple of subscribers wrote to say that they were confused as to what homeopathy was, so this time, we’ll start with a quick definition first.
First, what is acupuncture? For the convenience of a quick definition so that we can move on to the science, let’s borrow from Wikipedia:
❝Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine in which thin needles are inserted into the body.
Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery.❞
Now, that’s not a promising start, but we will not be deterred! We will instead examine the science itself, rather than relying on tertiary sources like Wikipedia.
It’s worth noting before we move on, however, that there is vigorous debate behind the scenes of that article. The gist of the argument is:
- On one side: “Acupuncture is not pseudoscience/quackery! This has long been disproved and there are peer-reviewed research papers on the subject.”
- On the other: “Yes, but only in disreputable quack journals created specifically for that purpose”
The latter counterclaim is a) potentially a “no true Scotsman” rhetorical ploy b) potentially true regardless
Some counterclaims exhibit specific sinophobia, per “if the source is Chinese, don’t believe it”. That’s not helpful either.
Well, the waters sure are muddy. Where to begin? Let’s start with a relatively easy one:
It may have some clinical applications beyond placebo: True or False?
True! Admittedly, “may” is doing some of the heavy lifting here, but we’ll take what we can get to get us going.
One of the least controversial uses of acupuncture is to alleviate chronic pain. Dr. Vickers et al, in a study published under the auspices of JAMA (a very respectable journal, and based in the US, not China), found:
❝Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic pain and is therefore a reasonable referral option. Significant differences between true and sham acupuncture indicate that acupuncture is more than a placebo.
However, these differences are relatively modest, suggesting that factors in addition to the specific effects of needling are important contributors to the therapeutic effects of acupuncture❞
Source: Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis
If you’re feeling sharp today, you may be wondering how the differences are described as “significant” and “relatively modest” in the same text. That’s because these words have different meanings in academic literature:
- Significant = p<0.05, where p is the probability of the achieved results occurring randomly
- Modest = the differences between the test group and the control group were small
In other words, “significant modest differences” means “the sample sizes were large, and the test group reliably got slightly better results than placebo”
We don’t understand how it works, but it works: True or False
Broadly False. When it works, we generally have an idea how.
Placebo is, of course, the main explanation. And even in examples such as the above, how is placebo acupuncture given?
By inserting acupuncture needles off-target rather than in accord with established meridians and points (the lines and dots that, per Traditional Chinese Medicine, indicate the flow of qi, our body’s vital energy, and welling-points of such).
So, if a patient feels that needles are being inserted randomly, they may no longer have the same confidence that they aren’t in the control group receiving placebo, which could explain the “modest” difference, without there being anything “to” acupuncture beyond placebo. After all, placebo works less well if you believe you are only receiving placebo!
Indeed, a (Korean, for the record) group of researchers wrote about this—and how this confounding factor cuts both ways:
❝Given the current research evidence that sham acupuncture can exert not only the originally expected non-specific effects but also sham acupuncture-specific effects, it would be misleading to simply regard sham acupuncture as the same as placebo.
Therefore, researchers should be cautious when using the term sham acupuncture in clinical investigations.❞
Source: Sham Acupuncture Is Not Just a Placebo
It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc: True or False?
False, for the most part.
While yes, the meridians and points of acupuncture charts broadly correspond to nerves and vasculature, there is no evidence that inserting needles into those points does anything for one’s qi, itself a concept that has not made it into Western science—as a unified concept, anyway…
Note that our bodies are indeed full of energy. Electrical energy in our nerves, chemical energy in every living cell, kinetic energy in all our moving parts. Even, to stretch the point a bit, gravitational potential energy based on our mass.
All of these things could broadly be described as qi, if we so wish. Indeed, the ki in the Japanese martial art of aikido is the latter kinds; kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy based on our mass. Same goes, therefore for the ki in kiatsu, a kind of Japanese massage, while the ki in reiki, a Japanese spiritual healing practice, is rather more mystical.
The qi in Chinese qigong is mostly about oxygen, thus indirectly chemical energy, and the electrical energy of the nerves that are receiving oxygenated blood at higher or lower levels.
On the other hand, the efficacy of the use of acupuncture for various kinds of pain is well-enough evidenced. Indeed, even the UK’s famously thrifty NHS (that certainly would not spend money on something it did not find to work) offers it as a complementary therapy for some kinds of pain:
❝Western medical acupuncture (dry needling) is the use of acupuncture following a medical diagnosis. It involves stimulating sensory nerves under the skin and in the muscles.
This results in the body producing natural substances, such as pain-relieving endorphins. It’s likely that these naturally released substances are responsible for the beneficial effects experienced with acupuncture.❞
Source: NHS | Acupuncture
Meanwhile, the NIH’s National Cancer Institute recommends it… But not as a cancer treatment.
Rather, they recommend it as a complementary therapy for pain management, and also against nausea, for which there is also evidence that it can help.
Frustratingly, while they mention that there is lots of evidence for this, they don’t actually link the studies they’re citing, or give enough information to find them. Instead, they say things like “seven randomized clinical trials found that…” and provide links that look reassuring until one finds, upon clicking on them, that it’s just a link to the definition of “randomized clinical trial”:
Source: NIH | Nactional Cancer Institute | Acupuncture (PDQ®)–Patient Version
However, doing our own searches finds many studies (mostly in specialized, potentially biased, journals such as the Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies) finding significant modest outperformance of [what passes for] placebo.
Sometimes, the existence of papers with promising titles, and statements of how acupuncture might work for things other than relief of pain and nausea, hides the fact that the papers themselves do not, in fact, contain any evidence to support the hypothesis. Here’s an example:
❝The underlying mechanisms behind the benefits of acupuncture may be linked with the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (adrenal) axis and activation of the Wnt/β-catenin and OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathways.
In summary, strong evidence may still come from prospective and well-designed clinical trials to shed light on the potential role of acupuncture in preserving bone loss❞
Source: Acupuncture for Osteoporosis: a Review of Its Clinical and Preclinical Studies
So, here they offered a very sciencey hypothesis, and to support that hypothesis, “strong evidence may still come”.
“We must keep faith” is not usually considered evidence worthy of inclusion in a paper!
PS: the above link is just to the abstract, because the “Full Text” link offered in that abstract leads to a completely unrelated article about HIV/AIDS-related cryptococcosis, in a completely different journal, nothing to do with acupuncture or osteoporosis).
Again, this is not the kind of professionalism we expect from peer-reviewed academic journals.
Bottom line:
Acupuncture reliably performs slightly better than sham acupuncture for the management of pain, and may also help against nausea.
Beyond placebo and the stimulation of endorphin release, there is no consistently reliable evidence that is has any other discernible medical effect by any mechanism known to Western science—though there are plenty of hypotheses.
That said, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, and the logistical difficulty of testing acupuncture against placebo makes for slow research. Maybe one day we’ll know more.
For now:
- If you find it helps you: great! Enjoy
- If you think it might help you: try it! By a licensed professional with a good reputation, please.
- If you are not inclined to having needles put in you unnecessarily: skip it! Extant science suggests that at worst, you’ll be missing out on slight relief of pain/nausea.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: