Zucchini vs Okra – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing zucchini to okra, we picked the okra.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, okra has nearly 2x the protein and more than 3x the fiber (for about 2x the carbs).
In terms of vitamins, things are also quite one-sided; zucchini has a little more vitamin B2, while okra has a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline.
Nor does the mineral situation make any compelling counterargument; zucchini is higher only in sodium, while okra has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium*, selenium, and zinc.
*Actually it’s only a little more potassium. But the rest are with big margins of difference.
Both of these on-the-cusp-of-being-pungent vegetables have beneficial antioxidant polyphenols (especially various forms of quercetin), but okra has more.
In short: enjoy both, of course, but there’s a clear winner here and it’s okra.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy Bitter/Astringent/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Your Eyes Say About Your Health (If You Have A Mirror, You Can Do This Now!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In an age when doctors are increasingly pressed to get you out of their office quickly and not take the time to do thorough tests, having a good basic knowledge of signs and symptoms of disease has become more important than ever for all of us:
The eyes have it:
Dr. Siobhan Deshauer is back, this time working with Dr. Maria Howard, a Canadian optometrist, who advised behind-the-scenes to ensure the best information about these signs and symptoms and what they tell us:
- Color blindness test: Ishihara color test identifies color blindness; in the version in the video, seeing “74” is normal, “12” indicates red-green color blindness, and no numbers suggest complete color blindness due to genetics or retinal/optic nerve issues.
- Yellow sclera (scleral icterus): yellow sclera indicates high bilirubin from excessive red blood cell breakdown, liver damage, bile duct blockage, or Gilbert syndrome.
- Blue sclera: indicates thin collagen in the sclera, which can be linked to osteogenesis imperfecta, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and Marfan syndrome.
- Pink eye: caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or trauma; persistent symptoms or associated pain/vision changes need medical evaluation.
- Physiologic diplopia (double vision): normal test where fingers appear doubled when focusing on different planes; absence may indicate amblyopia.
- Pinhole test (visual acuity): looking through a small pinhole can determine if glasses are needed for clearer vision.
- Nearsighted vs farsighted: nearsightedness risks retinal tears and night vision issues, while farsightedness increases the risk of glaucoma.
- Eye color and health: brown eyes lower cancer risk but higher cataract risk; light eyes higher cancer risk but lower cataract risk; sudden changes may indicate a condition.
- Kayser-Fleischer rings: golden-brown rings around the iris suggest copper buildup from Wilson disease, treatable with chelation therapy.
- Corneal arcus: gray/white ring around the iris indicates cholesterol buildup, normal with aging but concerning in younger individuals, signaling hypercholesterolemia or artery narrowing.
- Limbal rings: dark rings around the iris are generally aesthetic and not health-related.
- Red desaturation test: a difference in red color perception between eyes may indicate optic nerve or retinal issues.
- Eye twitching: often linked to stress, sleep deprivation, or caffeine; persistent twitching or muscle involvement requires medical attention.
- Pupillary reflex: pupil constriction in light; abnormal responses suggest trauma, overdose, or poisoning.
- Cataracts: lens cloudiness due to age, UV exposure, smoking, diabetes, or prednisone; also occurs sometimes in youth due to conditions like diabetes.
- Yellow spots (pinguecula and pterygium): sun damage, wind, and dust exposure cause yellow spots; protect with sunglasses to prevent progression impacting vision.
- Dark spots in the eye: includes freckles, moles (nevi), and melanoma; changes require medical evaluation.
- Hypnotic induction profile: eye roll test assesses susceptibility to hypnosis.
- Floaters: normal clumps in the eye; sudden increases, flashes, or curtain-like effects may signal retinal detachment.
- Retinal detachment: caused by aging-related vitreous shrinkage; treated with lasers, gas bubbles, or retinal buckles.
- Macular degeneration (Amsler grid test): wavy, fuzzy lines or missing vision spots may indicate this condition.
- Giant cell arteritis: no, that’s not a typo: rather it is about blood vessel inflammation that can cause blindness; treated with prednisone, symptoms include headaches and vision changes.
- Near point of convergence: focus test to detect convergence issues common with excessive screen time.
- Blepharitis: eyelid inflammation causing itchiness, burning, or flaky skin; treated with hygiene, antibiotics, or tea tree oil.
- Proptosis (Graves’ disease): bulging eyes due to hyperthyroidism; treatable with medications, radiation, or surgery.
- Ptosis (droopy eyelids): indicates myasthenia gravis, temporarily improved with the ice pack test.
- Night vision issues: caused by retinal problems or high myopia, not typically vitamin A deficiency in developed countries.
- Dry eyes: caused by screen time, smoking, medications, or autoimmune diseases; managed with lubricating drops, reduced screen time, and adjustments.
- Watery eyes: caused by irritation or blocked tear ducts; treated with lubricating drops or surgery.
- Retinoblastoma: rare childhood cancer detectable through flash photography showing one white pupil; early detection enables treatment.
For more on all of these plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
What Your Hands Can Tell You About Your Health
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Dates vs Prunes – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to prunes, we picked the prunes.
Why?
First let’s note: we’re listing the second fruit here as “prunes” rather than “plums”, since prunes are dehydrated plums, and it makes more sense to compare the dried fruit to dates which are invariably dried too. Otherwise, the water weight of plums would unfairly throw out the nutrient proportions per 100g (indeed, upon looking up numbers, dates would overwhelmingly beat plums easily in the category of pretty much every nutrient).
So let’s look at the fairer comparison:
In terms of macros, dates have a little more protein, carbohydrate, and fiber. This is because while both are dried, prunes are usually sold with more water remaining than dates; indeed, per 100g prunes still have 30g water weight to dates’ 20g water weight. This makes everything close, but we are going to call this category a nominal win for dates. Mind you, hydration is still good, but please do not rely on dried fruit for your hydration!
When it comes to vitamins, dates have more of vitamins B5 and B9, while prunes have more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, C, E, K, and choline. A clear win for prunes here.
In the category of minerals, it’s a similar story: dates have more iron, magnesium, and selenium, while prunes have more calcium, copper, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. Another win for prunes.
In short, enjoy either or both, but prunes win on overall nutritional density!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples to Bees, and High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How light tells you when to sleep, focus and poo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is the next article in our ‘Light and health’ series, where we look at how light affects our physical and mental health in sometimes surprising ways. Read other articles in the series.
Exposure to light is crucial for our physical and mental health, as this and future articles in the series will show.
But the timing of that light exposure is also crucial. This tells our body to wake up in the morning, when to poo and the time of day to best focus or be alert. When we’re exposed to light also controls our body temperature, blood pressure and even chemical reactions in our body.
But how does our body know when it’s time to do all this? And what’s light got to do with it?
nymphoenix/Shutterstock What is the body clock, actually?
One of the key roles of light is to re-set our body clock, also known as the circadian clock. This works like an internal oscillator, similar to an actual clock, ticking away as you read this article.
But rather than ticking you can hear, the body clock is a network of genes and proteins that regulate each other. This network sends signals to organs via hormones and the nervous system. These complex loops of interactions and communications have a rhythm of about 24 hours.
In fact, we don’t have one clock, we have trillions of body clocks throughout the body. The central clock is in the hypothalamus region of the brain, and each cell in every organ has its own. These clocks work in concert to help us adapt to the daily cycle of light and dark, aligning our body’s functions with the time of day.
However, our body clock is not precise and works to a rhythm of about 24 hours (24 hours 30 minutes on average). So every morning, the central clock needs to be reset, signalling the start of a new day. This is why light is so important.
The central clock is directly connected to light-sensing cells in our retinas (the back of the eye). This daily re-setting of the body clock with morning light is essential for ensuring our body works well, in sync with our environment.
In parallel, when we eat food also plays a role in re-setting the body clock, but this time the clock in organs other than the brain, such as the liver, kidneys or the gut.
So it’s easy to see how our daily routines are closely linked with our body clocks. And in turn, our body clocks shape how our body works at set times of the day.
What time of day?
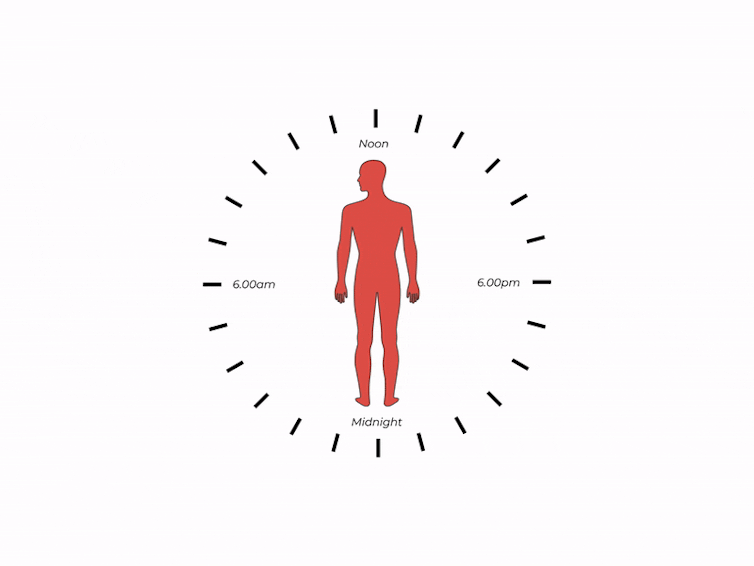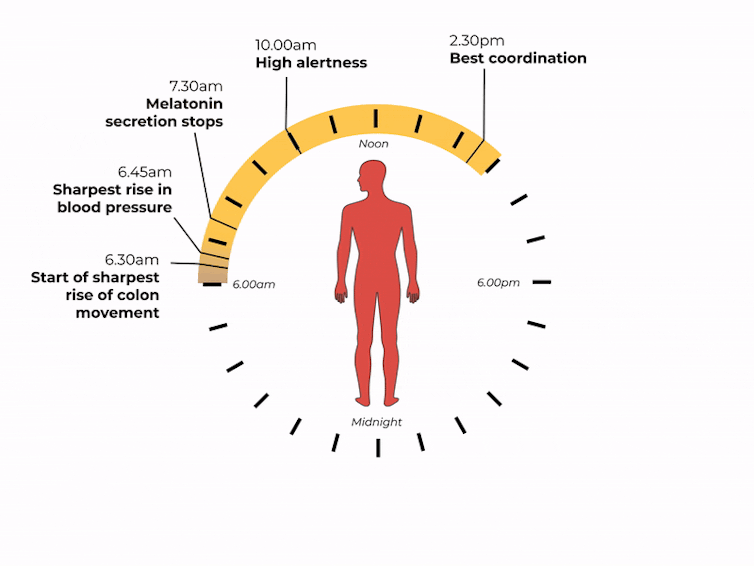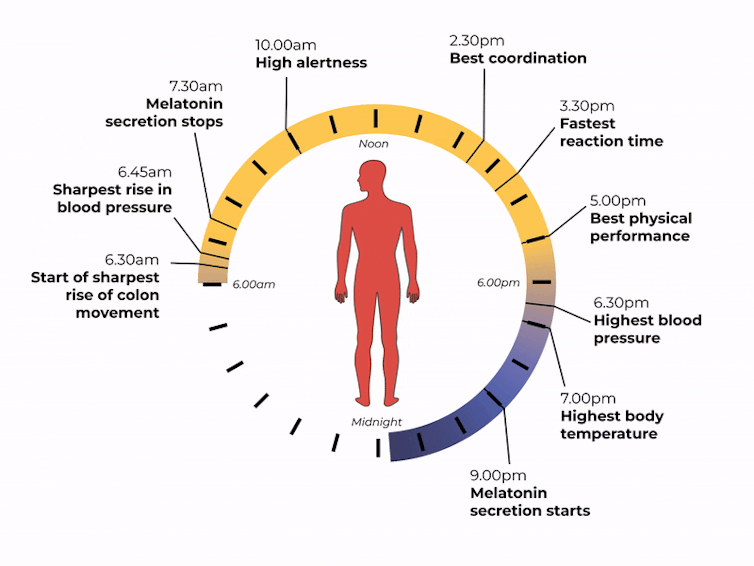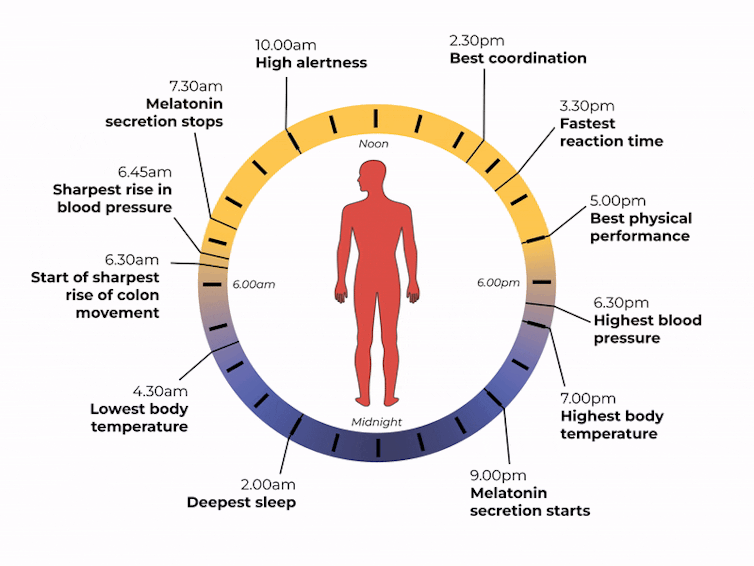
Matt Garrow/The Conversation. Adapted from Delos, CC BY Let’s take a closer look at sleep
The naturally occurring brain hormone melatonin is linked to our central clock and makes us feel sleepy at certain times of day. When it’s light, our body stops making melatonin (its production is inhibited) and we are alert. Closer to bedtime, the hormone is made, then secreted, making us feel drowsy.
Our sleep is also partly controlled by our genes, which are part of our central clock. These genes influence our chronotype – whether we are a “lark” (early riser), “night owl” (late sleeper) or a “dove” (somewhere in between).
But exposure to light at night when we are supposed to be sleeping can have harmful effects. Even dim light from light pollution can impair our heart rate and how we metabolise sugar (glucose), may lead to psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety and bipolar disorder, and increases the overall risk of premature death.
The main reason for these harmful effects is that light “at the wrong time” disturbs the body clock, and these effects are more pronounced for “night owls”.
This “misaligned” exposure to light is also connected to the detrimental health effects we often see in people who work night shifts, such as an increased risk of cancer, diabetes and heart disease.
How about the gut?
Digestion also follows a circadian rhythm. Muscles in the colon that help move waste are more active during the day and slow down at night.
The most significant increase in colon movement starts at 6.30am. This is one of the reasons why most people feel the urge to poo in the early morning rather than at night.
The gut’s day-night rhythm is a direct result of the action of the gut’s own clock and the central clock (which synchronises the gut with the rest of the body). It’s also influenced by when we eat.
At 6.30am, your gut really begins to get going for the day. Rendra Dria Septia Aji/Shutterstock How about focusing?
Our body clock also helps control our attention and alertness levels by changing how our brain functions at certain times of day. Attention and alertness levels improve in the afternoon and evening but dip during the night and early morning.
Those fluctuations impact performance and can lead to decreased productivity and an increased risk of errors and accidents during the less-alert hours.
So it’s important to perform certain tasks that require our attention at certain times of day. That includes driving. In fact, disruption of the circadian clock at the start of daylight savings – when our body hasn’t had a chance to adapt to the clocks changing – increases the risk of a car accident, particularly in the morning.
What else does our body clock control?
Our body clock influences many other aspects of our biology, including:
- physical performance by controlling the activity of our muscles
- blood pressure by controlling the system of hormones involved in regulating our blood volume and blood vessels
- body temperature by controlling our metabolism and our level of physical activity
- how our body handles drugs and toxins by controlling enzymes involved in how the liver and kidneys eliminate these substances from the body.
If you can, avoid driving long distances at night, as you’ll be less alert. trendobjects/Shutterstock Morning light is important
But what does this all mean for us? Exposure to light, especially in the morning, is crucial for synchronising our circadian clock and bodily functions.
As well as setting us up for a good night’s sleep, increased morning light exposure benefits our mental health and reduces the risk of obesity. So boosting our exposure to morning light – for example, by going for a walk, or having breakfast outside – can directly benefit our mental and metabolic health.
However, there are other aspects about which we have less control, including the genes that control our body clock.
Frederic Gachon, Associate Professor, Physiology of Circadian Rhythms, Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland and Benjamin Weger, NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Meditation That You’ll Actually Enjoy
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Meditation That You’ll Actually Enjoy
We previously wrote about…
No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
this is a great primer, by the way, for the science and simplicity of mindfulness, along with the simplest mindfulness meditation to get you going.
Today, we’re going to have some fun with meditation.
First: The Problem
Once the usefulness and health benefits of meditation have been established, often people want to meditate, but complain they don’t have the time.
But that’s not the real reason, though, is it?
Let’s face it, a basic meditation can give benefits within two minutes. Or within two breaths, for that matter. So, it’s not really for a lack of time.
The real reason is because it doesn’t feel productive, and it’s not fun. For us to feel motivated to do a thing, usually we need at least one or the other. And even if we know it really is productive, it not feeling that way will hobble us.
So instead, let us make things a little more fun, with…
Meditation games!
As it turns out, there are good kinds of meditation with which one can have a little fun.
Catch the next thought
A common feature of many meditative practices is the experience of having fewer, or ideally no, thoughts.
But it’s hard to enact a negative, and thoughts keep coming.
So instead, make yourself comfortable, settle in, and lie in wait for thoughts. When one comes along, pounce on it in your mind. And then release it, and wait for the next.
At first, your thoughts may be coming thick and fast, but soon, you’ll find the pauses between them lengthening, and you have moments of contented not-knowing of what the next thought will be before it comes along.
This state of relaxed, ready alertness, calm and receptive, is exactly what we’re hoping to find here. But don’t worry about that while you’re busy lying in wait for the next wild thought to come along
Counting breaths
Many meditative practices involve focus on one’s breath. But it’s easy for attention to wander!
This game is a simple one. Count your breaths, not trying to change your rate of breathing at all, just letting it be, and see how high you can get before you lose count.
Breathing in and out, once, counts as one breath, by the way.
You may find that your rate of breathing naturally slows while you’re doing this. That’s fine; let it. It’ll add to the challenge of the game, because before long there will be lengthy pauses between each number.
If you lose count, just start again, and see if you can beat your high score.
This meditation game is an excellent exercise to build for sustained focus, while also improving the quality of breathing (as a side-effect of merely paying attention to it).
Hot spot, cold spot
The above two meditation games were drawn from Japanese and Chinese meditative practices, zen and qigong respectively; this one’s from an Indian meditative practice, yoga nidra. But for now, just approach it with a sense of playful curiosity, for best results.
Make yourself comfortable, lying on your back, arms by your sides.
Take a moment first to pay attention to each part of your body from head to toe, and release any tension that you may be holding along the way.
First part: mentally scan your body for where it feels warmest, or most active, or most wanting of attention (for example if there is pain, or an itch, or some other sensation); that’s your “hot spot” for the moment.
Second part: mentally scan your body for where it feels coolest, or most inert, or almost like it’s not a part of your body at all; that’s your “cold spot” for the moment.
Now, see if you can flip them. Whether you can or can’t, notice if your “hot spot” or “cold spot” moves, or if you can move them consciously.
This meditation game is a great exercise to strengthen interoception and somatic awareness in general—essential for being able to “listen to your body”!
Closing thoughts
All three practices above have very serious reasons and great benefits, but make sure you don’t skip enjoyment of the fun aspects!
Being “young at heart” is, in part, to do with the ability to enjoy—literally, to take joy in—the little things in life.
With that in mind, all we have left to say here is…
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat To Beat Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Controlling What We Can, To Avoid Cancer
Every time a cell in our body is replaced, there’s a chance it will be cancerous. Exactly what that chance is depends on very many factors. Some of them we can’t control; others, we can.
Diet is a critical, modifiable factor
We can’t choose, for example, our genes. We can, for the most part, choose our diet. Why “for the most part”?
- Some people live in a food desert (the Arctic Circle is a good example where food choices are limited by supply)
- Some people have dietary restrictions (whether by health condition e.g. allergy, intolerance, etc or by personal-but-unwavering choice, e.g. vegetarian, vegan, kosher, halal, etc)
But for most of us, most of the time, we have a good control over our diet, and so that’s an area we can and should focus on.
Choose your animal protein wisely
If you are vegan, you can skip this section. If you are not, then the short version is:
- Fish: almost certainly fine
- Poultry: the jury is out; data is leaning towards fine, though
- Red meat: significantly increased cancer risk
- Processed meat: significantly increased cancer risk
For more details (and a run-down on the science behind the above super-summarized version):
- Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy? ← A mythbuster article that outlines many health properties (good and bad) of animal products
- The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet ← A life-hack article about acting on that information
Skip The Ultra-Processed Foods
Ok, so this one’s probably not a shocker in its simplest form:
❝Studies are showing us is that not only do the ultraprocessed foods increase the risk of cancer, but that after a cancer diagnosis such foods increase the risk of dying❞
Source: Is there a connection between ultraprocessed food and cancer?
There’s an unfortunate implication here! If you took the previous advice to heart and cut out [at least some] meat, and/but then replaced that with ultra-processed synthetic meat, then this was not a great improvement in cancer risk terms.
Ultra-processed meat is worse than unprocessed, regardless of whether it was from an animal or was synthetic.
In other words: if you buy textured soy pieces (a common synthetic meat), it pays to look at the ingredients, because there’s a difference between:
- INGREDIENTS: SOY
- INGREDIENTS: Rehydrated Textured SOY Protein (52%), Water, Rapeseed Oil, SOY Protein Concentrate, Seasoning (SULPHITES) (Dextrose, Flavourings, Salt, Onion Powder, Food Starch Modified, Yeast Extract, Colour: Red Iron Oxide), SOY Leghemoglobin, Fortified WHEAT Flour (WHEAT Flour, Calcium Carbonate, Iron, Niacin, Thiamin), Bamboo Fibre, Methylcellulose, Tomato Purée, Salt, Raising Agent: Ammonium Carbonates
Now, most of those original base ingredients are/were harmless per se (as are/were the grapes in wine—before processing into alcohol), but it has clearly been processed to Hell and back to do all that.
Choose the one that just says “soy”. Or eat soybeans. Or other beans. Or lentils. Really there are a lot of options.
About soy, by the way…
There is (mostly in the US, mostly funded by the animal agriculture industry) a lot of fearmongering about soy. Which is ironic, given the amount of soy that is fed to livestock to be fed to humans, but it does bear addressing:
❝Soy foods are safe for all cancer patients and are an excellent source of plant protein. Studies show soy may improve survival after breast cancer❞
Source: Food risks and cancer: What to avoid
(obviously, if you have a soy allergy then you should not consume soy—for most people, the above advice stands, though)
Advanced Glycation End-Products
These (which are Very Bad™ for very many things, including cancer) occur specifically as a result of processing animal proteins and fats.
Note: not even necessarily ultra-processing, just processing can do it. But ultra-processing is worse. What’s the difference, you wonder?
The difference between “ultra-processed” and just “processed”:
- Your average hotdog has been ultra-processed. It’s not only usually been changed with many artificial additives, it’s also been through a series of processes (physical and chemical) and ends up bearing little relation to the creature it came from.
- Your bacon (that you bought fresh from your local butcher, not a supermarket brand of unknown provenance, and definitely not the kind that might come on the top of frozen supermarket pizza) has been processed. It’s undergone a couple of simple processes on its journey “from farm to table”. Remember also that when you cook it, that too is one more process (and one that results in a lot of AGEs).
Read more: What’s so bad about AGEs?
Note if you really don’t want to cut out certain foods, changing the way you cook them (i.e., the last process your food undergoes before you eat it) can also reduce AGES:
Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Get More Fiber
❝The American Institute for Cancer Research shows that for every 10-gram increase in fiber in the diet, you improve survival after cancer diagnosis by 13%❞
Source: Plant-based diet is encouraged for patients with cancer
Yes, that’s post-diagnosis, but as a general rule of thumb, what is good/bad for cancer when you have it is good/bad for cancer beforehand, too.
If you’re thinking that increasing your fiber intake means having to add bran to everything, happily there are better ways:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Strawberries vs Cherries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing strawberries to cherries, we picked the cherries.
Why?
Both are great, and an argument could be made for either! But here’s our rationale:
In terms of macros, as with most fruits they are both mostly water, and have similar carbs and fiber. Nominally, cherries have the lower glycemic index, so we could call this category nominally a win for cherries, but honestly, they’re both low-GI foods and nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating strawberries, so it’s fairer to consider this category a tie.
Looking at the vitamins, strawberries have more of vitamins C, B9, E, and K, while cherries have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, and choline. Thus, a modest win for cherries here.
When it comes to minerals, strawberries see their day: strawberries have more iron, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus, while cherries have more calcium, copper, and potassium. By the numbers, a win for strawberries.
So far, so tied!
What swings it into cherries’ favor is cherries’ slew of specific phytochemical benefits, including cherry-specific anti-inflammatory properties, sleep-improving abilities, and post-exercise recovery boosts, as well as anti-diabetic benefits above and beyond the normal “this is a fruit” level.
In short, both are very respectable fruits, but cherries have some extra qualities that are just special.
Of course, as ever, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Cherries’ Health Benefits Simply Pop
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: