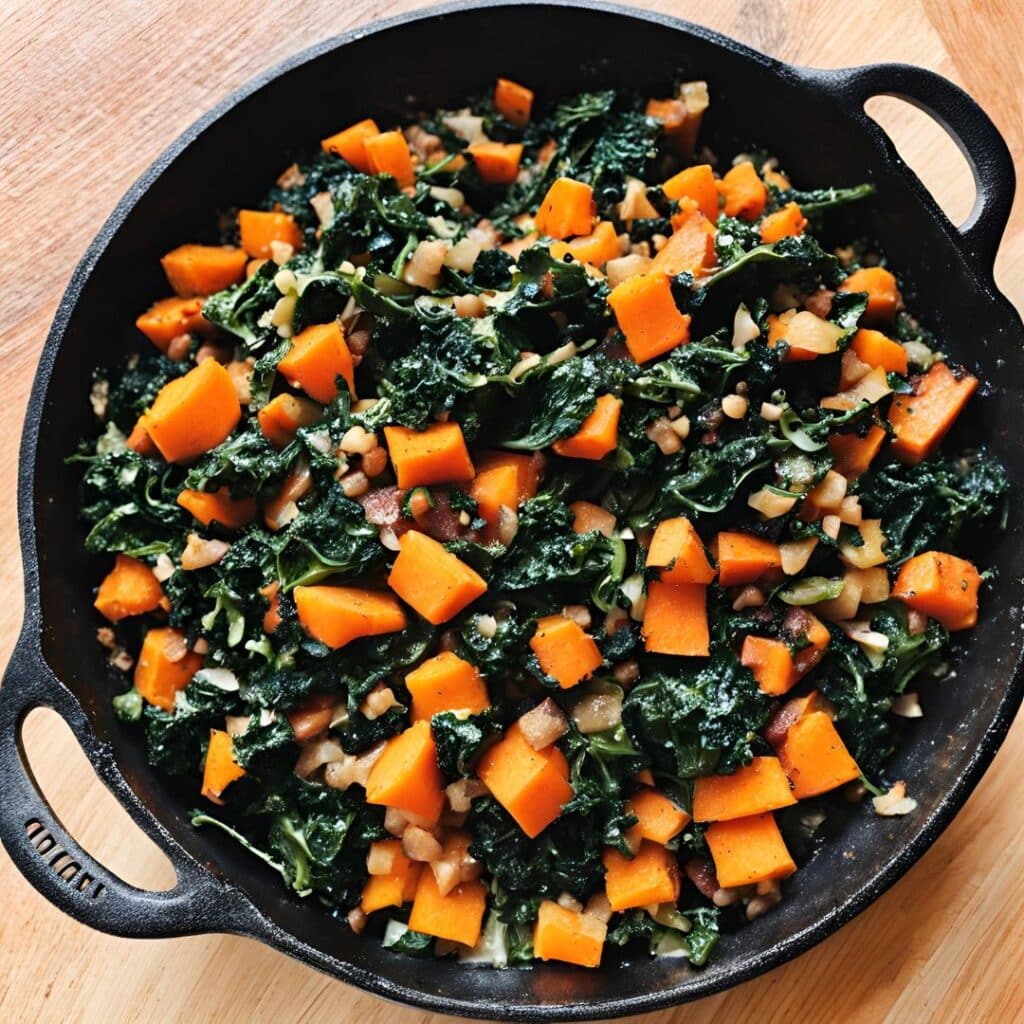
Cavolo Nero & Sweet Potato Hash
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
🎶 Sweet potato hash? It’s a seasonal smash… Catches on in a flash… Let’s do the hash 🎶
You will need
- 6 oz cavolo nero, tough stems removed, chopped
- 1 large sweet potato, diced
- 1 large red onion, finely chopped
- 1 parsnip, grated
- 1 small red pepper, chopped
- 4 oz baby portobello mushrooms, chopped
- ½ cup fresh or thawed peas
- ¼ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp dried rosemary
- 1 tsp dried thyme (dried for convenience; fresh is also fine if you have it)
- 1 tsp red chili flakes (dried for convenience; fresh is also fine if you have it)
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 425℉ / 220℃.
2) Toss the diced sweet potato in 1 tbsp olive oil, as well as the nutritional yeast, ground turmeric, black pepper, and MSG/salt, ensuring an even distribution. Roast in the oven on a lined baking tray, for 30 minutes, turning at least once to get all sides of the potato. When it is done, remove from the oven and set aside.
3) Heat a little oil in a sauté pan or large skillet (either is fine; we’re not adding liquids today), and fry the onion, parsnip, and pepper until softened, which should take about 5 minutes (this is one reason why we grated the parsnip; the other is for the variation in texture).
4) Add the garlic, mushrooms, herbs, and chili flakes, and cook for a further 1 minute, while stirring.
5) Add the cavolo nero and peas, stir until the cavolo nero begins to wilt, and then…
6) Add the roasted sweet potato; cook for about 5 more minutes, pressing down with the spatula here and there to mash the ingredients together.
7) Turn the hash over when it begins to brown on the bottom, to lightly brown the other side too.
8) Serve hot.

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Which Bell Peppers To Pick?
- Ergothioneine: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why do I keep getting urinary tract infections? And why are chronic UTIs so hard to treat?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dealing with chronic urinary tract infections (UTIs) means facing more than the occasional discomfort. It’s like being on a never ending battlefield against an unseen adversary, making simple daily activities a trial.
UTIs happen when bacteria sneak into the urinary system, causing pain and frequent trips to the bathroom.
Chronic UTIs take this to the next level, coming back repeatedly or never fully going away despite treatment. Chronic UTIs are typically diagnosed when a person experiences two or more infections within six months or three or more within a year.
They can happen to anyone, but some are more prone due to their body’s makeup or habits. Women are more likely to get UTIs than men, due to their shorter urethra and hormonal changes during menopause that can decrease the protective lining of the urinary tract. Sexually active people are also at greater risk, as bacteria can be transferred around the area.
Up to 60% of women will have at least one UTI in their lifetime. While effective treatments exist, about 25% of women face recurrent infections within six months. Around 20–30% of UTIs don’t respond to standard antibiotic. The challenge of chronic UTIs lies in bacteria’s ability to shield themselves against treatments.
Why are chronic UTIs so hard to treat?
Once thought of as straightforward infections cured by antibiotics, we now know chronic UTIs are complex. The cunning nature of the bacteria responsible for the condition allows them to hide in bladder walls, out of antibiotics’ reach.
The bacteria form biofilms, a kind of protective barrier that makes them nearly impervious to standard antibiotic treatments.
This ability to evade treatment has led to a troubling increase in antibiotic resistance, a global health concern that renders some of the conventional treatments ineffective.
Some antibiotics no longer work against UTIs.
Michael Ebardt/ShutterstockAntibiotics need to be advanced to keep up with evolving bacteria, in a similar way to the flu vaccine, which is updated annually to combat the latest strains of the flu virus. If we used the same flu vaccine year after year, its effectiveness would wane, just as overused antibiotics lose their power against bacteria that have adapted.
But fighting bacteria that resist antibiotics is much tougher than updating the flu vaccine. Bacteria change in ways that are harder to predict, making it more challenging to create new, effective antibiotics. It’s like a never-ending game where the bacteria are always one step ahead.
Treating chronic UTIs still relies heavily on antibiotics, but doctors are getting crafty, changing up medications or prescribing low doses over a longer time to outwit the bacteria.
Doctors are also placing a greater emphasis on thorough diagnostics to accurately identify chronic UTIs from the outset. By asking detailed questions about the duration and frequency of symptoms, health-care providers can better distinguish between isolated UTI episodes and chronic conditions.
The approach to initial treatment can significantly influence the likelihood of a UTI becoming chronic. Early, targeted therapy, based on the specific bacteria causing the infection and its antibiotic sensitivity, may reduce the risk of recurrence.
For post-menopausal women, estrogen therapy has shown promise in reducing the risk of recurrent UTIs. After menopause, the decrease in estrogen levels can lead to changes in the urinary tract that makes it more susceptible to infections. This treatment restores the balance of the vaginal and urinary tract environments, making it less likely for UTIs to occur.
Lifestyle changes, such as drinking more water and practising good hygiene like washing hands with soap after going to the toilet and the recommended front-to-back wiping for women, also play a big role.
Some swear by cranberry juice or supplements, though researchers are still figuring out how effective these remedies truly are.
What treatments might we see in the future?
Scientists are currently working on new treatments for chronic UTIs. One promising avenue is the development of vaccines aimed at preventing UTIs altogether, much like flu shots prepare our immune system to fend off the flu.
Emerging treatments could help clear chronic UTIs.
guys_who_shoot/ShutterstockAnother new method being looked at is called phage therapy. It uses special viruses called bacteriophages that go after and kill only the bad bacteria causing UTIs, while leaving the good bacteria in our body alone. This way, it doesn’t make the bacteria resistant to treatment, which is a big plus.
Researchers are also exploring the potential of probiotics. Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria into the urinary tract to out-compete harmful pathogens. These good bacteria work by occupying space and resources in the urinary tract, making it harder for harmful pathogens to establish themselves.
Probiotics can also produce substances that inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria and enhance the body’s immune response.
Chronic UTIs represent a stubborn challenge, but with a mix of current treatments and promising research, we’re getting closer to a day when chronic UTIs are a thing of the past.
Iris Lim, Assistant Professor, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Low-Dose Aspirin & Anemia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We recently wrote about…
How To Survive A Heart Attack When You’re Alone
…and one of the items was “if you have aspirin readily available, then after calling an ambulance is the time to take it—but don’t exert yourself trying to find some”.
But what of aspirin as a preventative?
Many people take low-dose aspirin daily as a way to reduce the risk of atherothrombosis specifically (and thus, indirectly, they hope to reduce the risk of heart attacks).
The science of how helpful this is both clear and complicated—that is to say, the stats are not ambiguous*, but there are complicating factors of which many people are unaware.
*it will reduce the overall risk of cardiovascular events, but will not affect CVD mortality; in other words, it may improve your recovery from minor cardiac events, but is not likely to save you from major ones.
And also, it has unwanted side effects that can constitute a more relevant threat for many people. We’ll share more on that at the end of today’s article, but first…
A newly identified threat from daily aspirin use
A large (n=313,508) study of older adults (median age 73) were sorted into those who used low-dose aspirin as a preventative, and those who did not.
The primary outcome was incidence of anemia sufficient to require treatment, and the secondary outcome was major bleeding. And, at least 1 in 5 of those who experienced anemia also experienced bleeding.
The bleeding issue was not “newly identified” and will not surprise many people; after all, the very reason that aspirin is taken as a CVD preventative is for its anti-clotting property of allowing blood to flow more freely.
The anemia, however, has been getting increasing scientific scrutiny lately, after long going unnoticed in the wild. Given that anemia also gives the symptom “dizziness”, this is also a significant threat for increasing the incidence of falls in the older population, too, which can of course lead to serious complications and ultimately death.
Here’s the paper itself:
Want to know more?
As promised, here’s what we wrote previously about some of aspirin’s other risks:
Aspirin, CVD Risk, & Potential Counter-Risks
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How much weight do you actually need to lose? It might be a lot less than you think
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re one of the one in three Australians whose New Year’s resolution involved losing weight, it’s likely you’re now contemplating what weight-loss goal you should actually be working towards.
But type “setting a weight loss goal” into any online search engine and you’ll likely be left with more questions than answers.
Sure, the many weight-loss apps and calculators available will make setting this goal seem easy. They’ll typically use a body mass index (BMI) calculator to confirm a “healthy” weight and provide a goal weight based on this range.
Your screen will fill with trim-looking influencers touting diets that will help you drop ten kilos in a month, or ads for diets, pills and exercise regimens promising to help you effortlessly and rapidly lose weight.
Most sales pitches will suggest you need to lose substantial amounts of weight to be healthy – making weight loss seem an impossible task. But the research shows you don’t need to lose a lot of weight to achieve health benefits.
Using BMI to define our target weight is flawed
We’re a society fixated on numbers. So it’s no surprise we use measurements and equations to score our weight. The most popular is BMI, a measure of our body weight-to-height ratio.
BMI classifies bodies as underweight, normal (healthy) weight, overweight or obese and can be a useful tool for weight and health screening.
But it shouldn’t be used as the single measure of what it means to be a healthy weight when we set our weight-loss goals. This is because it:
- fails to consider two critical factors related to body weight and health – body fat percentage and distribution
- does not account for significant differences in body composition based on gender, ethnicity and age.
How does losing weight benefit our health?
Losing just 5–10% of our body weight – between 6 and 12kg for someone weighing 120kg – can significantly improve our health in four key ways.
1. Reducing cholesterol
Obesity increases the chances of having too much low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol – also known as bad cholesterol – because carrying excess weight changes how our bodies produce and manage lipoproteins and triglycerides, another fat molecule we use for energy.
Having too much bad cholesterol and high triglyceride levels is not good, narrowing our arteries and limiting blood flow, which increases the risk of heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
But research shows improvements in total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels are evident with just 5% weight loss.
2. Lowering blood pressure
Our blood pressure is considered high if it reads more than 140/90 on at least two occasions.
Excess weight is linked to high blood pressure in several ways, including changing how our sympathetic nervous system, blood vessels and hormones regulate our blood pressure.
Essentially, high blood pressure makes our heart and blood vessels work harder and less efficiently, damaging our arteries over time and increasing our risk of heart disease, heart attack and stroke.
Losing weight can lower your blood pressure.
Prostock-studio/ShutterstockLike the improvements in cholesterol, a 5% weight loss improves both systolic blood pressure (the first number in the reading) and diastolic blood pressure (the second number).
A meta-analysis of 25 trials on the influence of weight reduction on blood pressure also found every kilo of weight loss improved blood pressure by one point.
3. Reducing risk for type 2 diabetes
Excess body weight is the primary manageable risk factor for type 2 diabetes, particularly for people carrying a lot of visceral fat around the abdomen (belly fat).
Carrying this excess weight can cause fat cells to release pro-inflammatory chemicals that disrupt how our bodies regulate and use the insulin produced by our pancreas, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious medical conditions if it’s not carefully managed, including damaging our heart, blood vessels, major organs, eyes and nervous system.
Research shows just 7% weight loss reduces risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 58%.
4. Reducing joint pain and the risk of osteoarthritis
Carrying excess weight can cause our joints to become inflamed and damaged, making us more prone to osteoarthritis.
Observational studies show being overweight doubles a person’s risk of developing osteoarthritis, while obesity increases the risk fourfold.
Small amounts of weight loss alleviate this stress on our joints. In one study each kilogram of weight loss resulted in a fourfold decrease in the load exerted on the knee in each step taken during daily activities.
Losing weight eases stress on joints.
Shutterstock/Rostislav_SedlacekFocus on long-term habits
If you’ve ever tried to lose weight but found the kilos return almost as quickly as they left, you’re not alone.
An analysis of 29 long-term weight-loss studies found participants regained more than half of the weight lost within two years. Within five years, they regained more than 80%.
When we lose weight, we take our body out of its comfort zone and trigger its survival response. It then counteracts weight loss, triggering several physiological responses to defend our body weight and “survive” starvation.
Just as the problem is evolutionary, the solution is evolutionary too. Successfully losing weight long-term comes down to:
losing weight in small manageable chunks you can sustain, specifically periods of weight loss, followed by periods of weight maintenance, and so on, until you achieve your goal weight
making gradual changes to your lifestyle to ensure you form habits that last a lifetime.
Setting a goal to reach a healthy weight can feel daunting. But it doesn’t have to be a pre-defined weight according to a “healthy” BMI range. Losing 5–10% of our body weight will result in immediate health benefits.
At the Boden Group, Charles Perkins Centre, we are studying the science of obesity and running clinical trials for weight loss. You can register here to express your interest.
Nick Fuller, Charles Perkins Centre Research Program Leader, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Anise vs Diabetes & Menopause
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What A Daily Gram Of Anise Can Do
Anise, specifically the seed of the plant, also called aniseed, is enjoyed for its licorice taste—as well as its medicinal properties.
Let’s see how well the science lives up to the folk medicine…
What medicinal properties does it claim?
The main contenders are:
- Reduces menopause symptoms
- Reduces blood sugar levels
- Reduces inflammation
Does it reduce menopause symptoms?
At least some of them! Including hot flashes and bone density loss. This seems to be due to the estrogenic-like activity of anethole, the active compound in anise that gives it these effects:
Estrogenic activity of isolated compounds and essential oils of Pimpinella species
1g of anise/day yielded a huge reduction in frequency and severity of hot flashes, compared to placebo*:
*you may be wondering what the placebo is for 1g of a substance that has a very distinctive taste. The researchers used capsules, with 3x330g as the dose, either anise seed or potato starch.
❝In the experimental group, the frequency and severity of hot flashes before the treatment were 4.21% and 56.21% and, after that, were 1.06% and 14.44% at the end of the fourth week respectively. No change was found in the frequency and severity of hot flashes in the control group. The frequency and severity of hot flashes was decreased during 4 weeks of follow up period. P. anisum is effective on the frequency and severity of hot flashes in postmenopausal women. ❞
See for yourself: The Study on the Effects of Pimpinella anisum on Relief and Recurrence of Menopausal Hot Flashes
As for bone mineral density, we couldn’t find a good study for anise, but we did find this one for fennel, which is a plant of the same family and also with the primary active compound anethole:
The Prophylactic Effect of Fennel Essential Oil on Experimental Osteoporosis
That was a rat study, though, so we’d like to see studies done with humans.
Summary on this one: it clearly helps against hot flashes (per the very convincing human study we listed above); it probably helps against bone mineral density loss.
Does it reduce blood sugar levels?
This one got a flurry of attention all so recently, on account of this research review:
Review on Anti-diabetic Research on Two Important Spices: Trachyspermum ammi and Pimpinella anisum
If you read this (and we do recommend reading it! It has a lot more information than we can squeeze in here!) one of the most interesting things about the in vivo anti-diabetic activity of anise was that while it did lower the fasting blood glucose levels, that wasn’t the only effect:
❝Over a course of 60 days, study participants were administered seed powders (5 g/d), which resulted in significant antioxidant, anti-diabetic, and hypolipidemic effects.
Notably, significant reductions in fasting blood glucose levels were observed. This intervention also elicited alterations in the lipid profile, LPO, lipoprotein levels, and the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) level.
Moreover, the serum levels of essential antioxidants, such as beta carotene, vitamin C, vitamin A, and vitamin E, which are typically decreased in diabetic patients, underwent a reversal.❞
That’s just one of the studies cited in that review (the comments lightly edited here for brevity), but it stands out, and you can read that study in its entirety (it’s well worth reading).
Rajeshwari et al, bless them, added a “tl;dr” at the top of their already concise abstract; their “tl;dr” reads:
❝Both the seeds significantly influenced almost all the parameters without any detrimental effects by virtue of a number of phytochemicals, vitamins and minerals present in the seeds having therapeutic effects.❞
Shortest answer: yes, yes it does
Does it fight inflammation?
This one’s quick and simple enough: yes it does; it’s full of antioxidants which thus also have an anti-inflammatory effect:
Review of Pharmacological Properties and Chemical Constituents of Pimpinella anisum
…which can also be used an essential oil, applied topically, to fight both pain and the inflammation that causes it—at least in rats and mice:
❝Indomethacin and etodolac were treated reference drugs for the anti-inflammatory activity. Aspirin and morphine hydrochloride were treated reference drugs for the analgesic activity. The results showed that fixed oil of P. anisum has an anti-inflammatory action more than etodolac and this effect was as strong as indomethacin. P. anisum induces analgesic effect comparable to that of 100 mg/kg Aspirin and 10 mg/kg morphine at 30 th min. of the study❞
Summary of this section:
- Aniseeds are a potent source of antioxidants, which fight inflammation.
- Anise essential oil is probably also useful as a topical anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent, but we’d like to see human tests to know for sure.
Is it safe?
For most people, enjoyed in moderation (e.g., within the dosage parameters described in the above studies), anise is safe. However:
- If you’re allergic to it, it won’t be safe
- Its estrogen-mimicking effects could cause problems if you have (or have a higher risk factor for) breast cancer, ovarian cancer, or endometriosis.
- For most men, the main concern is that it may lower sperm count.
Where to get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, you can buy the seeds in bulk on Amazon, or in case you prefer it, here’s an example of it available as an essential oil.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What does it mean to be transgender?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Transgender media coverage has surged in recent years for a wide range of reasons. While there are more transgender television characters than ever before, hundreds of bills are targeting transgender people’s access to medical care, sports teams, gender-specific public spaces, and other institutions.
Despite the increase in conversation about the transgender community, public confusion around transgender identity remains.
Read on to learn more about what it means to be transgender and understand challenges transgender people may face.
What does it mean to be transgender?
Transgender—or “trans”—is an umbrella term for people whose gender identity or gender expression does not conform to their sex assigned at birth. People can discover they are trans at any age.
Gender identity refers to a person’s inner sense of being a woman, a man, neither, both, or something else entirely. Trans people who don’t feel like women or men might describe themselves as nonbinary, agender, genderqueer, or two-spirit, among other terms.
Gender expression describes the way a person communicates their gender through their appearance—such as their clothing or hairstyle—and behavior.
A person whose gender expression doesn’t conform to the expectations of their assigned sex may not identify as trans. The only way to know for sure if someone is trans is if they tell you.
Cisgender—or “cis”—describes people whose gender identities match the sex they were assigned at birth.
How long have transgender people existed?
Being trans isn’t new. Although the word “transgender” only dates back to the 1960s, people whose identities defy traditional gender expectations have existed across cultures throughout recorded history.
How many people are transgender?
A 2022 Williams Institute study estimates that 1.6 million people over the age of 13 identify as transgender in the United States.
Is being transgender a mental health condition?
No. Conveying and communicating about your gender in a way that feels authentic to you is a normal and necessary part of self-expression.
Social and legal stigma, bullying, discrimination, harassment, negative media messages, and barriers to gender-affirming medical care can cause psychological distress for trans people. This is especially true for trans people of color, who face significantly higher rates of violence, poverty, housing instability, and incarceration—but trans identity itself is not a mental health condition.
What is gender dysphoria?
Gender dysphoria describes a feeling of unease that some trans people experience when their perceived gender doesn’t match their gender identity, or their internal sense of gender. A 2021 study of trans adults pursuing gender-affirming medical care found that most participants started experiencing gender dysphoria by the time they were 7.
When trans people don’t receive the support they need to manage gender dysphoria, they may experience depression, anxiety, social isolation, suicidal ideation, substance use disorder, eating disorders, and self-injury.
How do trans people manage gender dysphoria?
Every trans person’s experience with gender dysphoria is unique. Some trans people may alleviate dysphoria by wearing gender-affirming clothing or by asking others to refer to them by a new name and use pronouns that accurately reflect their gender identity. The 2022 U.S. Trans Survey found that nearly all trans participants who lived as a different gender than the sex they were assigned at birth reported that they were more satisfied with their lives.
Some trans people may also manage dysphoria by pursuing medical transition, which may involve taking hormones and getting gender-affirming surgery.
Access to gender-affirming medical care has been shown to reduce the risk of depression and suicide among trans youth and adults.
To learn more about the trans community, visit resources from the National Center for Transgender Equality, the Trevor Project, PFLAG, and Planned Parenthood.
If you or anyone you know is considering suicide or self-harm or is anxious, depressed, upset, or needs to talk, call the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or text the Crisis Text Line at 741-741. For international resources, here is a good place to begin.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Miss Diagnosis: Anxiety, ADHD, & Women
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Why is ADHD so often misdiagnosed as anxiety in women?❞
A great question! A short and slightly flippant answer could be “it’s the medical misogyny”:
Women and Minorities Bear the Brunt of Medical Misdiagnosis
…and if you’d like to learn more in-depth about this, we recommend this excellent book:
Unwell Women: Misdiagnosis and Myth in a Man-Made World – by Dr. Elinor Cleghorn ← you can read our review here
However, in this case there is more going on too!
Part of this is because ADHD is, like many psychiatric issues, a collection of symptoms that may or may not all always be present. Since clinical definitions are decided by clinicians, rather than some special natural law of the universe, sometimes this results in “several small conditions in a trenchcoat”, and if one symptom is or isn’t present, it can make things look quite different:
What’s The Difference Between ADD and ADHD?
There are two things at hand here: as in the above example, there’s the presence or absence of hyperactivity, but also, that “attention deficit”?
It’s often not really a deficit of attention, so much as the attention is going somewhere else—an example of naming psychiatric disorders for how they affect other people, rather than the person in question.
Sidenote: personality disorders really get the worst of this!
“You have a deep insecurity about never being good enough, and you constantly mess up in your attempt to overcompensate? You may have Evil Bastard Disorder!”
“You have a crippling fear of abandonment and that you are fundamentally unloveable, so you do all you can to try to keep people close? You must have Manipulative Bitch Disorder!”
etc
See also: Why Everyone You Don’t Like Is A Narcissist
In the case of ADHD and anxiety and women, a lot of this comes down to how the redirection of focus is perceived:
❝For some time, it has been held that women with ADHD are more likely to internalize symptoms and become anxious and depressed and to suffer emotional dysregulation❞
This internalization of symptoms, vs the externalization more generally perceived in boys and men, is more likely to be seen as anxiety.
Double standards also abound for social reasons, e.g:
- He is someone who thinks ten steps ahead and covers all bases
- She is anxious and indecisive and unable to settle on one outcome
Here’s a very good overview of how this double-standard makes its way into diagnostic processes, along with other built-in biases:
Miss. Diagnosis: A Systematic Review of ADHD in Adult Women
Want to learn more?
We’ve reviewed quite a few books about ADHD, but if we had to pick one to spotlight, we’d recommend this one:
The Silent Struggle: Taking Charge of ADHD in Adults – by L. William Ross-Child, MLC
Enjoy! And while we have your attention… Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: