Stop Using The Wrong Hairbrush For Your Hair Type
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When you brush your hair, you’re either making it healthier or damaging it, depending on what you’re using and how. To avoid pulling your hair out, and to enjoy healthy hair of whatever kind you have and whatever length suits you, it pays to know a little about different brushes, and the different techniques involved.
Head-to-head
Brush shapes and sizes are designed to achieve different effects in hair, not just for decoration. For example:
- Rat tail combs are excellent for parting and sectioning hair with clean lines. The rat tail part is actually more important than the comb part.
- Regular combs are multipurpose but best for use with flat irons, ensuring straighter hair for a longer time.
- Wide-tooth combs should not be used for detangling as they can cause breakage; instead, use a proper detangling brush. Speaking of detangling…
- Detangling brushes are essential for daily use. Whichever you use, start brushing from the bottom to prevent tangles from stacking and worsening. As for kinds of detangling brush:
- The “Tangle Teaser” is a good beginner option, but it may not detangle well for thicker hair.
- Wet Brush (this is a brand name, and is not about any inherent wetness) is the recommended detangling brush for most people. It can be used on wet or dry hair.
- Mason Pearson brush is a luxury detangling brush (see it here on Amazon) that works slightly more quickly and efficiently, but is expensive and not necessary for most people.
- Teasing brushes are for adding volume by backcombing—but require skill to prevent visible tangles. Best avoided for most people.
- Ceramic round brushes are the best for blow-drying, because they hold tension and help hair dry smoother and shinier.
- Blow-dryer brushes are great for easy blow-drying but should not be used on dry hair, to avoid damage.
- Denman brushes are for people with natural curls, enhancing curls without straightening them like a Wet brush would.
For more on all of these brushes, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cucumber vs Lychee – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cucumber to lychee, we picked the lychee.
Why?
In terms of macros, the lychee has more carbs and more fiber, but both are low glycemic index foods. Functionally a tie, though we could consider it a nominal win for cucumber.
In the category of vitamins, cucumber has more of vitamins A, B1, B5, and K, while lychee has more of vitamins B2, B3, B6, B9, C, E, and choline. In particular, cucumber has a lot more vitamin K and lychee has a lot more vitamin C. Nevertheless, in terms of overall vitamin coverage, lychee is the clear winner here.
Looking at minerals, cucumber has more calcium, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while lychee has more copper (especially rich in this), iron, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. Another clear win for lychee.
Both have an abundance of anti-inflammatory polyphenols, but we could find no strong argument for one being better than the other in this category, just different.
In short, both are fine options, but the more nutritionally dense is the lychee, so that’s our choice!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
It’s OK That You’re Not OK – by Megan Devine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, be aware: this is not a cheerful book. If you’re looking for something to life your mood after a loss, it will not be this.
What, then, will you find? A reminder that grief is also the final translation of love, and not necessarily something to be put aside as quickly as possible—or even ever, if we don’t want to.
Too often, society (and even therapists) will correctly note that no two instances of grief are the same (after all, no two people are, so definitely no two relationships are, so how could two instances of grief be?), but will still expect that if most people can move on quickly from most losses, that you should too, and that if you don’t then there is something pathological at hand that needs fixing.
Part one of the book covers this (and more) in a lot of detail; critics have called it a diatribe against the current status quo in the field of grief.
Part two of the book is about “what to do with your grief”, and addresses the reality of grief, how (and why) to stay alive when not doing so feels like a compelling option, dealing with grief’s physical side effects, and calming your mind in ways that actually work (without trying to sweep your grief under a rug).
Parts three and four are more about community—how to navigate the likely unhelpful efforts a lot of people may make in the early days, and when it comes to those people who can and will actually be a support, how to help them to help you.
In the category of criticism, she also plugs her own (paid, subscription-based) online community, which feels a little mercenary, especially as while community definitely can indeed help, the prospect of being promptly exiled from it if you stop paying, doesn’t.
Bottom line: if you have experienced grief and felt like moving on was the right thing to do, then this book isn’t the one for you. If, on the other hand, your grief feels more like something you will carry just as you carry the love you feel for them, then you’ll find a lot about that here.
Share This Post
-
Anti-Inflammatory Pineapple Fried Rice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fried rice is not most people’s go-to when one thinks of health food, but this one is. It’s packed with plenty of nutrients, many of which are anti-inflammatory, but the real star is the pineapple (with its high bromelain content and thus particularly potent benefits).
You will need
- 2½ cups cooked wholegrain basmati rice (you can use our Tasty Versatile Rice recipe if you don’t already have leftovers to use)
- 1 cup pineapple chunks
- ½ red onion, diced
- 1 red bell pepper, diced
- ½ cup sweetcorn
- ½ peas
- 3 green onions, chopped
- 2 serrano peppers, chopped (omit if you don’t care for heat)
- 2 tbsp coconut oil
- 1 tbsp grated fresh ginger
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Fry the red onion, serrano peppers, and ginger in the coconut oil over a medium heat, stirring frequently, for about 3 minutes.
2) Add the pineapple, bell pepper, sweetcorn, peas, and black pepper, stirring frequently, for about another 3 minutes.
3) Add the rice, stirring gently but thoroughly, until fully reheated and mixed in.
4) Serve, garnishing with the green onions.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Eat To Beat Inflammation
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
Firstly, what is high blood pressure vs normal, and what do those blood pressure readings mean?
Rather than take up undue space here, we’ll just quickly link to…
Blood Pressure Readings Explained (With A Colorful Chart)
More details of specifics, at:
Hypotension | Normal | Elevated | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Danger zone
Keeping Blood Pressure Down
As with most health-related things (and in fact, much of life in general), prevention is better than cure.
People usually know “limit salt” and “manage stress”, but there’s a lot more to it!
Salt isn’t as big a factor as you probably think
That doesn’t mean go crazy on the salt, as it can cause a lot of other problems, including organ failure. But it does mean that you can’t skip the salt and assume your blood pressure will take care of itself.
This paper, for example, considers “high” sodium consumption to be more than 5g per day, and urinary excretion under 3g per day is considered to represent a low sodium dietary intake:
Sodium Intake and Hypertension
Meanwhile, health organizations often recommend to keep sodium intake to under 2g or under 1.5g
Top tip: if you replace your table salt with “reduced sodium” salt, this is usually sodium chloride (regular table salt) cut with potassium chloride, which is almost as “salty” tastewise, but obviously contains less sodium. Not only that, but potassium actually helps the body eliminate sodium, too.
The rest of what you eat is important too
The Mediterranean Diet is as great for this as it is for most health conditions.
If you sometimes see the DASH diet mentioned, that stands for “Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension”, and is basically the Mediterranean Diet with a few tweaks.
What are the tweaks?
- Beans went down a bit in priority
- Red meat got removed entirely instead of “limit to a tiny amount”
- Olive oil was deprioritized, and/but vegetable oil is at the bottom of the list (i.e., use sparingly)
You can check out the details here, with an overview and examples:
DASH Eating Plan—Description, Charts, and Recipes
Don’t drink or smoke
And no, a glass of red a day will not help your heart. Alcohol does make us feel relaxed, but that is because of what it does to our brain, not what it does to our heart.
In reality, even a single drink will increase blood pressure. Yes, really:
And smoking? It’s so bad that even second-hand smoke increases blood pressure:
Get those Zs in
Sleep is a commonly underestimated/forgotten part of health, precisely because in a way, we’re not there for it when it happens. We sleep through it! But it is important, including to protect against hypertension:
Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption
Move your body!
Moving your body often is far more important for your heart than running marathons or bench-pressing your spouse.
Those 150 minutes “moderate exercise” (e.g. walking) per week are important, and can be for example:
- 22 minutes per day, 7 days per week
- 25 minutes per day, 6 days per week
- 30 minutes per day, 5 days per week
- 75 minutes per day, 2 days per week
If you’d like to know more about the science and evidence for this, as well as practical suggestions, you can download the complete second edition of the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans here (it’s free, and no sign-up required!)
If you prefer a bite-size summary, then here’s their own:
Top 10 Things to Know About the Second Edition of the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans
PS: Want a blood pressure monitor? We don’t sell them (or anything else), but for your convenience, here’s a good one you might want to consider.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
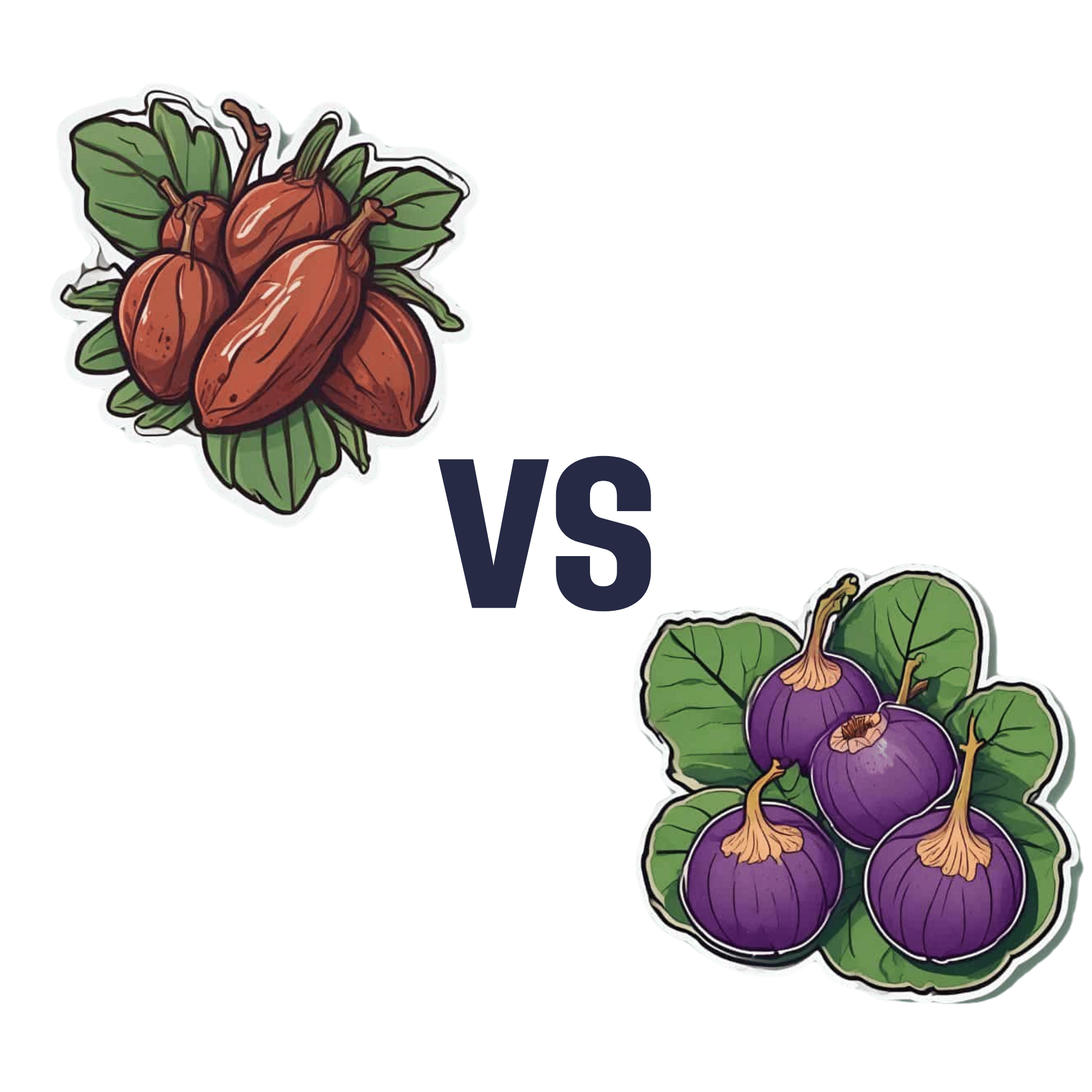
Dates vs Figs – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to figs, we picked the dates.
Why?
Dates are higher in sugar, but also have a lower glycemic index than figs, which makes the sugar content much healthier. On the flipside, figs do have around 3x more fiber.
So far, so balanced.
When it comes to micronutrients though, dates take the prize much more clearly.
Dates have slightly more of most vitamins, and a lot more of most minerals.
In particular, dates are several times higher in copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc.
As for other phytochemical benefits going on:
- both are good against diabetes for reasons beyond the macros
- both have anti-inflammatory properties
- dates have anticancer properties
- dates have kidney-protecting properties
So in this last case, another win for dates.
Both are still great though, so do enjoy both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bird Flu Is Bad for Poultry and Dairy Cows. It’s Not a Dire Threat for Most of Us — Yet.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Headlines are flying after the Department of Agriculture confirmed that the H5N1 bird flu virus has infected dairy cows around the country. Tests have detected the virus among cattle in nine states, mainly in Texas and New Mexico, and most recently in Colorado, said Nirav Shah, principal deputy director at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at a May 1 event held by the Council on Foreign Relations.
A menagerie of other animals have been infected by H5N1, and at least one person in Texas. But what scientists fear most is if the virus were to spread efficiently from person to person. That hasn’t happened and might not. Shah said the CDC considers the H5N1 outbreak “a low risk to the general public at this time.”
Viruses evolve and outbreaks can shift quickly. “As with any major outbreak, this is moving at the speed of a bullet train,” Shah said. “What we’ll be talking about is a snapshot of that fast-moving train.” What he means is that what’s known about the H5N1 bird flu today will undoubtedly change.
With that in mind, KFF Health News explains what you need to know now.
Q: Who gets the bird flu?
Mainly birds. Over the past few years, however, the H5N1 bird flu virus has increasingly jumped from birds into mammals around the world. The growing list of more than 50 species includes seals, goats, skunks, cats, and wild bush dogs at a zoo in the United Kingdom. At least 24,000 sea lions died in outbreaks of H5N1 bird flu in South America last year.
What makes the current outbreak in cattle unusual is that it’s spreading rapidly from cow to cow, whereas the other cases — except for the sea lion infections — appear limited. Researchers know this because genetic sequences of the H5N1 viruses drawn from cattle this year were nearly identical to one another.
The cattle outbreak is also concerning because the country has been caught off guard. Researchers examining the virus’s genomes suggest it originally spilled over from birds into cows late last year in Texas, and has since spread among many more cows than have been tested. “Our analyses show this has been circulating in cows for four months or so, under our noses,” said Michael Worobey, an evolutionary biologist at the University of Arizona in Tucson.
Q: Is this the start of the next pandemic?
Not yet. But it’s a thought worth considering because a bird flu pandemic would be a nightmare. More than half of people infected by older strains of H5N1 bird flu viruses from 2003 to 2016 died. Even if death rates turn out to be less severe for the H5N1 strain currently circulating in cattle, repercussions could involve loads of sick people and hospitals too overwhelmed to handle other medical emergencies.
Although at least one person has been infected with H5N1 this year, the virus can’t lead to a pandemic in its current state. To achieve that horrible status, a pathogen needs to sicken many people on multiple continents. And to do that, the H5N1 virus would need to infect a ton of people. That won’t happen through occasional spillovers of the virus from farm animals into people. Rather, the virus must acquire mutations for it to spread from person to person, like the seasonal flu, as a respiratory infection transmitted largely through the air as people cough, sneeze, and breathe. As we learned in the depths of covid-19, airborne viruses are hard to stop.
That hasn’t happened yet. However, H5N1 viruses now have plenty of chances to evolve as they replicate within thousands of cows. Like all viruses, they mutate as they replicate, and mutations that improve the virus’s survival are passed to the next generation. And because cows are mammals, the viruses could be getting better at thriving within cells that are closer to ours than birds’.
The evolution of a pandemic-ready bird flu virus could be aided by a sort of superpower possessed by many viruses. Namely, they sometimes swap their genes with other strains in a process called reassortment. In a study published in 2009, Worobey and other researchers traced the origin of the H1N1 “swine flu” pandemic to events in which different viruses causing the swine flu, bird flu, and human flu mixed and matched their genes within pigs that they were simultaneously infecting. Pigs need not be involved this time around, Worobey warned.
Q: Will a pandemic start if a person drinks virus-contaminated milk?
Not yet. Cow’s milk, as well as powdered milk and infant formula, sold in stores is considered safe because the law requires all milk sold commercially to be pasteurized. That process of heating milk at high temperatures kills bacteria, viruses, and other teeny organisms. Tests have identified fragments of H5N1 viruses in milk from grocery stores but confirm that the virus bits are dead and, therefore, harmless.
Unpasteurized “raw” milk, however, has been shown to contain living H5N1 viruses, which is why the FDA and other health authorities strongly advise people not to drink it. Doing so could cause a person to become seriously ill or worse. But even then, a pandemic is unlikely to be sparked because the virus — in its current form — does not spread efficiently from person to person, as the seasonal flu does.
Q: What should be done?
A lot! Because of a lack of surveillance, the U.S. Department of Agriculture and other agencies have allowed the H5N1 bird flu to spread under the radar in cattle. To get a handle on the situation, the USDA recently ordered all lactating dairy cattle to be tested before farmers move them to other states, and the outcomes of the tests to be reported.
But just as restricting covid tests to international travelers in early 2020 allowed the coronavirus to spread undetected, testing only cows that move across state lines would miss plenty of cases.
Such limited testing won’t reveal how the virus is spreading among cattle — information desperately needed so farmers can stop it. A leading hypothesis is that viruses are being transferred from one cow to the next through the machines used to milk them.
To boost testing, Fred Gingrich, executive director of a nonprofit organization for farm veterinarians, the American Association of Bovine Practitioners, said the government should offer funds to cattle farmers who report cases so that they have an incentive to test. Barring that, he said, reporting just adds reputational damage atop financial loss.
“These outbreaks have a significant economic impact,” Gingrich said. “Farmers lose about 20% of their milk production in an outbreak because animals quit eating, produce less milk, and some of that milk is abnormal and then can’t be sold.”
The government has made the H5N1 tests free for farmers, Gingrich added, but they haven’t budgeted money for veterinarians who must sample the cows, transport samples, and file paperwork. “Tests are the least expensive part,” he said.
If testing on farms remains elusive, evolutionary virologists can still learn a lot by analyzing genomic sequences from H5N1 viruses sampled from cattle. The differences between sequences tell a story about where and when the current outbreak began, the path it travels, and whether the viruses are acquiring mutations that pose a threat to people. Yet this vital research has been hampered by the USDA’s slow and incomplete posting of genetic data, Worobey said.
The government should also help poultry farmers prevent H5N1 outbreaks since those kill many birds and pose a constant threat of spillover, said Maurice Pitesky, an avian disease specialist at the University of California-Davis.
Waterfowl like ducks and geese are the usual sources of outbreaks on poultry farms, and researchers can detect their proximity using remote sensing and other technologies. By zeroing in on zones of potential spillover, farmers can target their attention. That can mean routine surveillance to detect early signs of infections in poultry, using water cannons to shoo away migrating flocks, relocating farm animals, or temporarily ushering them into barns. “We should be spending on prevention,” Pitesky said.
Q: OK it’s not a pandemic, but what could happen to people who get this year’s H5N1 bird flu?
No one really knows. Only one person in Texas has been diagnosed with the disease this year, in April. This person worked closely with dairy cows, and had a mild case with an eye infection. The CDC found out about them because of its surveillance process. Clinics are supposed to alert state health departments when they diagnose farmworkers with the flu, using tests that detect influenza viruses, broadly. State health departments then confirm the test, and if it’s positive, they send a person’s sample to a CDC laboratory, where it is checked for the H5N1 virus, specifically. “Thus far we have received 23,” Shah said. “All but one of those was negative.”
State health department officials are also monitoring around 150 people, he said, who have spent time around cattle. They’re checking in with these farmworkers via phone calls, text messages, or in-person visits to see if they develop symptoms. And if that happens, they’ll be tested.
Another way to assess farmworkers would be to check their blood for antibodies against the H5N1 bird flu virus; a positive result would indicate they might have been unknowingly infected. But Shah said health officials are not yet doing this work.
“The fact that we’re four months in and haven’t done this isn’t a good sign,” Worobey said. “I’m not super worried about a pandemic at the moment, but we should start acting like we don’t want it to happen.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: