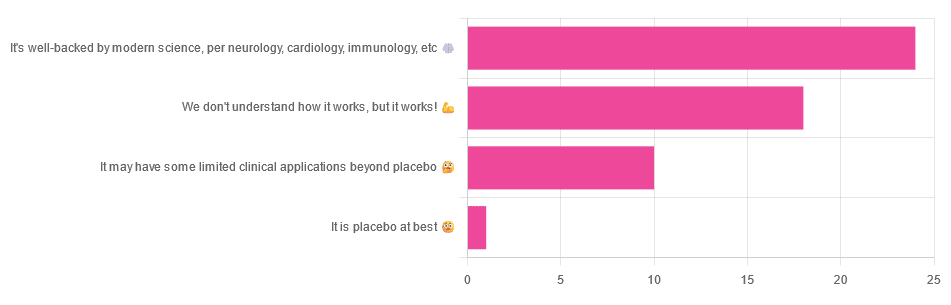
Kumquat vs Persimmon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kumquat to persimmon, we picked the kumquat.
Why?
In terms of macros, kumquats have more protein, though like most fruits, it’s unlike anybody’s eating them for the protein content. More importantly, they have a lot more fiber, for less than half the carbs. It bears mentioning though that (again, like most fruits) persimmon isn’t bad for this either, and both fruits are low glycemic index foods.
When it comes to vitamins, it’s not close: kumquats have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, E, and choline, while persimmon has more vitamin C. It’s worth noting that kumquats are already a very good source of vitamin C though; persimmon just has more.
In the category of minerals, kumquats again lead with more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, and zinc, while persimmon has more iron, phosphorus, and potassium.
In short, enjoy both, and/or whatever fruit you enjoy the most, but if looking for nutritional density, kumquats are bringing it.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Anti-Inflammatory Diet 101 (What to Eat to Fight Inflammation)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic inflammation is a cause and/or exacerbating factor in very many diseases. Arthritis, diabetes, and heart disease are probably top of the list, but there are lots more where they came from. And, it’s good to avoid those things. So, how to eat to avoid inflammation?
Let food be thy medicine
The key things to keep in mind, the “guiding principles” are to prioritize whole, minimally-processed foods, and enjoy foods with plenty of antioxidants. Getting a healthy balance of omega fatty acids is also important, which for most people means getting more omega-3 and less omega-6.
Shopping list (foods to prioritize) includes:
- fruits and vegetables in a variety of colors (e.g. berries, leafy greens, beats)
- whole grains, going for the most fiber-rich options (e.g. quinoa, brown rice, oats)
- healthy fats (e.g. avocados, nuts, seeds)
- fatty fish (e.g. salmon, mackerel, sardines) ← don’t worry about this if you’re vegetarian/vegan though, as the previous category can already cover it
- herbs and spices (e.g. turmeric, garlic, ginger)
Noping list (foods to avoid) includes:
- refined carbohydrates
- highly processed and/or fried foods
- red meats and/or processed meats (yes, that does mean that organic grass-fed farmers’ pinky-promise-certified holistically-raised beef is also off the menu)
- dairy products, especially if unfermented
For more information on each of these, plus advice on transitioning away from an inflammatory diet, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Lacking Motivation? Science Has The Answer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Science Of Motivation (And How To Use It To Your Advantage)
When we do something rewarding, our brain gets a little (or big!) spike of dopamine. Dopamine is popularly associated with pleasure—which is fair— but there’s more to it than this.
Dopamine is also responsible for motivation itself, as a prime mover before we do the thing that we find rewarding. If we eat a banana, and enjoy it, perhaps because our body needed the nutrients from it, our brain gets a hit of dopamine.
(and not because bananas contain dopamine; that dopamine is useful for the body, but can’t pass the blood-brain barrier to have an effect on the brain)
So where does the dopamine in our brain come from? That dopamine is made in the brain itself.
Key Important Fact: the brain produces dopamine when it expects an activity to be rewarding.
If you take nothing else away from today’s newsletter, let it be this!
It makes no difference if the activity is then not rewarding. And, it will keep on motivating you to do something it anticipated being rewarding, no matter how many times the activity disappoints, because it’ll remember the very dopamine that it created, as having been the reward.
To put this into an example:
- How often have you spent time aimlessly scrolling social media, flitting between the same three apps, or sifting through TV channels when “there’s nothing good on to watch”?
- And how often did you think afterwards “that was a good and rewarding use of my time; I’m glad I did that”?
In reality, whatever you felt like you were in search of, you were really in search of dopamine. And you didn’t find it, but your brain did make some, just enough to keep you going.
Don’t try to “dopamine detox”, though.
While taking a break from social media / doomscrolling the news / mindless TV-watching can be a great and healthful idea, you can’t actually “detox” from a substance your body makes inside itself.
Which is fortunate, because if you could, you’d die, horribly and miserably.
If you could “detox” completely from dopamine, you’d lose all motivation, and also other things that dopamine is responsible for, including motor control, language faculties, and critical task analysis (i.e. planning).
This doesn’t just mean that you’d not be able to plan a wedding; it also means:
- you wouldn’t be able to plan how to get a drink of water
- you wouldn’t have any motivation to get water even if you were literally dying of thirst
- you wouldn’t have the motor control to be able to physically drink it anyway
Read: Dopamine and Reward: The Anhedonia Hypothesis 30 years on
(this article is deep and covers a lot of ground, but is a fascinating read if you have time)
Note: if you’re wondering why that article mentions schizophrenia so much, it’s because schizophrenia is in large part a disease of having too much dopamine.
Consequently, antipsychotic drugs (and similar) used in the treatment of schizophrenia are generally dopamine antagonists, and scientists have been working on how to treat schizophrenia without also crippling the patient’s ability to function.
Do be clever about how you get your dopamine fix
Since we are hardwired to crave dopamine, and the only way to outright quash that craving is by inducing anhedonic depression, we have to leverage what we can’t change.
The trick is: question how much your motivation aligns with your goals (or doesn’t).
So if you feel like checking Facebook for the eleventieth time today, ask yourself: “am I really looking for new exciting events that surely happened in the past 60 seconds since I last checked, or am I just looking for dopamine?”
You might then realize: “Hmm, I’m actually just looking for dopamine, and I’m not going to find it there”
Then, pick something else to do that will actually be more rewarding. It helps if you make a sort of dopa-menu in advance, of things to pick from. You can keep this as a list on your phone, or printed and pinned up near your computer.
Examples might be: Working on that passion project of yours, or engaging in your preferred hobby. Or spending quality time with a loved one. Or doing housework (surprisingly not something we’re commonly motivated-by-default to do, but actually is rewarding when done). Or exercising (same deal). Or learning that language on Duolingo (all those bells and whistles the app has are very much intentional dopamine-triggers to make it addictive, but it’s not a terrible outcome to be addicted to learning!).
Basically… Let your brain’s tendency to get led astray work in your favor, by putting things in front of it that will lead you in good directions.
Things for your health and/or education are almost always great things to allow yourself the “ooh, shiny” reaction and pick them up, try something new, etc.
Share This Post
-
Fruit & Veg In The Fridge: Pros & Cons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What effect does refrigeration have on the nutritional value of fruit and vegetables??❞
It’s difficult to give a single definitive answer, because naturally there are a lot of different fruits and vegetables, and a lot of different climates. The answer may be different for tomatoes in Alaska vs bananas in Arizona!
However, we can still generalize at least somewhat
Refrigeration will generally slow down any degradation process, and in the case of fruit and vegetables, that can mean slowing down their “ripening” too, as applicable.
However…
Refrigeration will also impede helpful bioactivity too, and that includes quite a list of things.
Here’s a good study that’s quite illustrative; we’d summarize the conclusions but the rather long title already does that nicely:
So, this really is a case of “there are pros and cons, but probably more cons on balance”.
In practical terms, a good take-away from this can be twofold:
- don’t keep fruit and veg in the fridge unless the ambient temperature really requires it
- if the ambient temperature does require it, it’s best to get the produce in fresh each day if that’s feasible, to minimize time spent in the fridge
An extra thing not included there: often when it comes to the spoilage of fruit and veg, the problem is that it respires and oxidizes; reducing the temperature does lower the rate of those, but often a far better way is to remove the oxygen. So for example, if you get carried away and chop too many carrot batons for your hummus night, then putting them in a sealed container can go a long way to keeping them fresh.
See also: How Does the Nutritional Value of Fruits and Vegetables Change Over Time?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Resistance Beyond Weights
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Resistance, Your Way
We’ve talked before about the importance of resistance training:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
And we’ve even talked about how to make resistance training more effective:
(High Intensity Interval Training, but make it High Intensity Resistance Training)
Which resistance training exercises are best?
There are two reasonable correct answers here:
- The resistance training exercises that you will actually do (because it’s no good knowing the best exercise ever if you’re not going to do it because it is in some way offputting to you)
- The resistance training exercises that will prevent you from getting a broken bone in the event of some accident or incident
This latter is interesting, because when people think resistance training, the usually immediate go-to exercises are often things like the bench press, or the chest machine in the gym.
But ask yourself: how often do we hear about some friend or relative who in their old age has broken their humerus?
It can happen, for sure, but it’s not as often as breaking a hip, a tarsal (ankle bones), or a carpal (wrist bones).
So, how can we train to make those bones strong?
Strong bones grow under strong muscles
When archaeologists dig up a skeleton from a thousand years ago, one of the occupations that’s easy to recognize is an archer. Why?
An archer has an unusual frequent exercise: pushing with their left arm while pulling with their right arm. This will strengthen different muscles on each side, and thus, increase bone density in different places on each arm. The left first metacarpal and right first and second metacarpals and phalanges are also a giveaway.
This is because: one cannot grow strong muscles on weak bones (or else the muscles would just break the bones), so training muscles will force the body to strengthen the relevant bones.
So: if you want strong bones, train the muscles attached to those bones
This answers the question of “how am I supposed to exercise my hips” etc.
Weights, bodyweight, resistance bands
If you go to the gym, there’s a machine for everything, and a member of gym staff will be able to advise which of their machines will strengthen which muscles.
If you train with free weights at home:
- Wrist curls (forearm supported and stationary, lifting a dumbbell in your hand, palm-upwards) will strengthen the wrist
- The farmer’s walk (carrying a heavy weight in each hand) will also strengthen your wrist
- A modified version of this involves holding the weight with just your fingertips, and then raising and lowering it by curling and uncurling your fingers)
- Lateral leg raises (you will need ankle-weights for this) will strengthen your ankles and your hips, as will hip abductions (as in today’s featured video), especially with a weight attached.
- Ankle raises (going up on your tip-toes and down again, repeat) while holding weights in your hands will strengthen your ankles
If you don’t like weights:
- Press-ups will strengthen your wrists
- Fingertip press-ups are even better: to do these, do your press-ups as normal, except that the only parts of your hands in contact with the ground are your fingertips
- This same exercise can be done the other way around, by doing pull-ups
- And that same “even better” works by doing pull-ups, but holding the bar only with one’s fingertips, and curling one’s fingers to raise oneself up
- Lateral leg raises and hip abductions can be done with a resistance band instead of with weights. The great thing about these is that whereas weights are a fixed weight, resistance bands will always provide the right amount of resistance (because if it’s too easy, you just raise your leg further until it becomes difficult again, since the resistance offered is proportional to how much tension the band is under).
Remember, resistance training is still resistance training even if “all” you’re resisting is gravity!
If it fells like work, then it’s working
As for the rest of preparing to get older?
Check out:
Training Mobility Ready For Later Life
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Does One Test Acupuncture Against Placebo Anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pinpointing The Usefulness Of Acupuncture
We asked you for your opinions on acupuncture, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of answers:
- A little under half of all respondents voted for “It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc”
- Slightly fewer respondents voted for “We don’t understand how it works, but it works!”
- A little under a fifth of respondents voted for “It may have some limited clinical applications beyond placebo”
- One (1) respondent voted for for “It’s placebo at best”
When we did a main feature about homeopathy, a couple of subscribers wrote to say that they were confused as to what homeopathy was, so this time, we’ll start with a quick definition first.
First, what is acupuncture? For the convenience of a quick definition so that we can move on to the science, let’s borrow from Wikipedia:
❝Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine in which thin needles are inserted into the body.
Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery.❞
Now, that’s not a promising start, but we will not be deterred! We will instead examine the science itself, rather than relying on tertiary sources like Wikipedia.
It’s worth noting before we move on, however, that there is vigorous debate behind the scenes of that article. The gist of the argument is:
- On one side: “Acupuncture is not pseudoscience/quackery! This has long been disproved and there are peer-reviewed research papers on the subject.”
- On the other: “Yes, but only in disreputable quack journals created specifically for that purpose”
The latter counterclaim is a) potentially a “no true Scotsman” rhetorical ploy b) potentially true regardless
Some counterclaims exhibit specific sinophobia, per “if the source is Chinese, don’t believe it”. That’s not helpful either.
Well, the waters sure are muddy. Where to begin? Let’s start with a relatively easy one:
It may have some clinical applications beyond placebo: True or False?
True! Admittedly, “may” is doing some of the heavy lifting here, but we’ll take what we can get to get us going.
One of the least controversial uses of acupuncture is to alleviate chronic pain. Dr. Vickers et al, in a study published under the auspices of JAMA (a very respectable journal, and based in the US, not China), found:
❝Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic pain and is therefore a reasonable referral option. Significant differences between true and sham acupuncture indicate that acupuncture is more than a placebo.
However, these differences are relatively modest, suggesting that factors in addition to the specific effects of needling are important contributors to the therapeutic effects of acupuncture❞
Source: Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis
If you’re feeling sharp today, you may be wondering how the differences are described as “significant” and “relatively modest” in the same text. That’s because these words have different meanings in academic literature:
- Significant = p<0.05, where p is the probability of the achieved results occurring randomly
- Modest = the differences between the test group and the control group were small
In other words, “significant modest differences” means “the sample sizes were large, and the test group reliably got slightly better results than placebo”
We don’t understand how it works, but it works: True or False
Broadly False. When it works, we generally have an idea how.
Placebo is, of course, the main explanation. And even in examples such as the above, how is placebo acupuncture given?
By inserting acupuncture needles off-target rather than in accord with established meridians and points (the lines and dots that, per Traditional Chinese Medicine, indicate the flow of qi, our body’s vital energy, and welling-points of such).
So, if a patient feels that needles are being inserted randomly, they may no longer have the same confidence that they aren’t in the control group receiving placebo, which could explain the “modest” difference, without there being anything “to” acupuncture beyond placebo. After all, placebo works less well if you believe you are only receiving placebo!
Indeed, a (Korean, for the record) group of researchers wrote about this—and how this confounding factor cuts both ways:
❝Given the current research evidence that sham acupuncture can exert not only the originally expected non-specific effects but also sham acupuncture-specific effects, it would be misleading to simply regard sham acupuncture as the same as placebo.
Therefore, researchers should be cautious when using the term sham acupuncture in clinical investigations.❞
Source: Sham Acupuncture Is Not Just a Placebo
It’s well-backed by modern science, per neurology, cardiology, immunology, etc: True or False?
False, for the most part.
While yes, the meridians and points of acupuncture charts broadly correspond to nerves and vasculature, there is no evidence that inserting needles into those points does anything for one’s qi, itself a concept that has not made it into Western science—as a unified concept, anyway…
Note that our bodies are indeed full of energy. Electrical energy in our nerves, chemical energy in every living cell, kinetic energy in all our moving parts. Even, to stretch the point a bit, gravitational potential energy based on our mass.
All of these things could broadly be described as qi, if we so wish. Indeed, the ki in the Japanese martial art of aikido is the latter kinds; kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy based on our mass. Same goes, therefore for the ki in kiatsu, a kind of Japanese massage, while the ki in reiki, a Japanese spiritual healing practice, is rather more mystical.
The qi in Chinese qigong is mostly about oxygen, thus indirectly chemical energy, and the electrical energy of the nerves that are receiving oxygenated blood at higher or lower levels.
On the other hand, the efficacy of the use of acupuncture for various kinds of pain is well-enough evidenced. Indeed, even the UK’s famously thrifty NHS (that certainly would not spend money on something it did not find to work) offers it as a complementary therapy for some kinds of pain:
❝Western medical acupuncture (dry needling) is the use of acupuncture following a medical diagnosis. It involves stimulating sensory nerves under the skin and in the muscles.
This results in the body producing natural substances, such as pain-relieving endorphins. It’s likely that these naturally released substances are responsible for the beneficial effects experienced with acupuncture.❞
Source: NHS | Acupuncture
Meanwhile, the NIH’s National Cancer Institute recommends it… But not as a cancer treatment.
Rather, they recommend it as a complementary therapy for pain management, and also against nausea, for which there is also evidence that it can help.
Frustratingly, while they mention that there is lots of evidence for this, they don’t actually link the studies they’re citing, or give enough information to find them. Instead, they say things like “seven randomized clinical trials found that…” and provide links that look reassuring until one finds, upon clicking on them, that it’s just a link to the definition of “randomized clinical trial”:
Source: NIH | Nactional Cancer Institute | Acupuncture (PDQ®)–Patient Version
However, doing our own searches finds many studies (mostly in specialized, potentially biased, journals such as the Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies) finding significant modest outperformance of [what passes for] placebo.
Sometimes, the existence of papers with promising titles, and statements of how acupuncture might work for things other than relief of pain and nausea, hides the fact that the papers themselves do not, in fact, contain any evidence to support the hypothesis. Here’s an example:
❝The underlying mechanisms behind the benefits of acupuncture may be linked with the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (adrenal) axis and activation of the Wnt/β-catenin and OPG/RANKL/RANK signaling pathways.
In summary, strong evidence may still come from prospective and well-designed clinical trials to shed light on the potential role of acupuncture in preserving bone loss❞
Source: Acupuncture for Osteoporosis: a Review of Its Clinical and Preclinical Studies
So, here they offered a very sciencey hypothesis, and to support that hypothesis, “strong evidence may still come”.
“We must keep faith” is not usually considered evidence worthy of inclusion in a paper!
PS: the above link is just to the abstract, because the “Full Text” link offered in that abstract leads to a completely unrelated article about HIV/AIDS-related cryptococcosis, in a completely different journal, nothing to do with acupuncture or osteoporosis).
Again, this is not the kind of professionalism we expect from peer-reviewed academic journals.
Bottom line:
Acupuncture reliably performs slightly better than sham acupuncture for the management of pain, and may also help against nausea.
Beyond placebo and the stimulation of endorphin release, there is no consistently reliable evidence that is has any other discernible medical effect by any mechanism known to Western science—though there are plenty of hypotheses.
That said, absence of evidence is not evidence of absence, and the logistical difficulty of testing acupuncture against placebo makes for slow research. Maybe one day we’ll know more.
For now:
- If you find it helps you: great! Enjoy
- If you think it might help you: try it! By a licensed professional with a good reputation, please.
- If you are not inclined to having needles put in you unnecessarily: skip it! Extant science suggests that at worst, you’ll be missing out on slight relief of pain/nausea.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Altered Traits – by Dr. Daniel Goleman & Dr. Richard Davidson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know that meditation helps people to relax, but what more than that?This book explores the available science.
We say “explore the available science”, but it’d be remiss of us not to note that the authors have also expanded the available science, conducting research in their own lab.
From stress tests and EEGs to attention tests and fMRIs, this book looks at the hard science of what different kinds of meditation do to the brain. Not just in terms of brain state, either, but gradual cumulative anatomical changes, too. Powerful stuff!
The style is very pop-science in presentation, easily comprehensible to all. Be aware though that this is an “if this, then that” book of science, not a how-to manual. If you want to learn to meditate, this isn’t the book for that.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand more about how different kinds of meditation affect the brain differently, this is the book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: