Black Bean Burgers With Guacamole
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Once again proving that burgers do not have to be unhealthy, this one’s a nutritional powerhouse full of protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, as well as healthy fats and extra health-giving spices.
You will need
- 1 can black beans, drained and rinsed (or 1 cup same, cooked, drained, and rinsed)
- 3 oz walnuts (if allergic, substitute with pumpkin seeds)
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp flax seeds
- ½ red onion, finely chopped
- 1 small eggplant, diced small (e.g. ½” cubes or smaller)
- 1 small carrot, grated
- 3 tbsp finely chopped cilantro (or if you have the “this tastes like soap” gene, then substitute with parsley)
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 jalapeño pepper, finely chopped (adjust per heat preferences)
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- 1 tsp cayenne pepper (adjust per heat preferences)
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Burger buns (you can use our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe if you like)
For the guacamole:
- 1 large ripe avocado, pitted, skinned, and chopped
- 1 tbsp lime juice
- 1 tomato, finely chopped
- ¼ red onion, finely chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 1 tsp red chili pepper flakes (adjust per heat preferences)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Process the walnuts, chia seeds, and flax seeds in a food processor/blender, until they become a coarse mixture. Set aside.
2) Heat a little oil in a skillet, and fry the red onion, aubergine, and carrot for 5 minutes stirring frequently, then add the garlic and jalapeño and stir for a further 1 minute. Set aside.
3) Combine both mixtures you set aside with the rest of the ingredients from the burger section of the recipe, except the buns, and process them in the food processor on a low setting if possible, until you have a coarse mixture—you still want some texture, not a paste.
4) Shape into patties; this recipe gives for 4 large patties or 8 small ones. When you’ve done this, put them in the fridge for at least 30 minutes, to firm up.
5) While you wait, make the guacamole by mashing the avocado with the lime juice, and then stirring into the onion, tomato, garlic, and pepper.
6) Cook the patties; you can do this on the grill, in a skillet, or in the oven, per your preference. Grilling or frying should take about 5 minutes on each side, give or take the size and shape of the patties. Baking in the oven should take 20–30 minutes at 400℉ / 200℃ turning over halfway through, but keep an eye on them, because again, the size and shape of the patties will affect this. You may be wondering: aren’t they all going to be patty-shaped? And yes, but for example a wide flat patty will cook more quickly than the same volume of burger mixture in a taller less wide patty.
7) Assemble! We recommend the order: bottom bun, guacamole, burger patty, any additional toppings you want to add (e.g. more salad, pickles, etc), top bun:
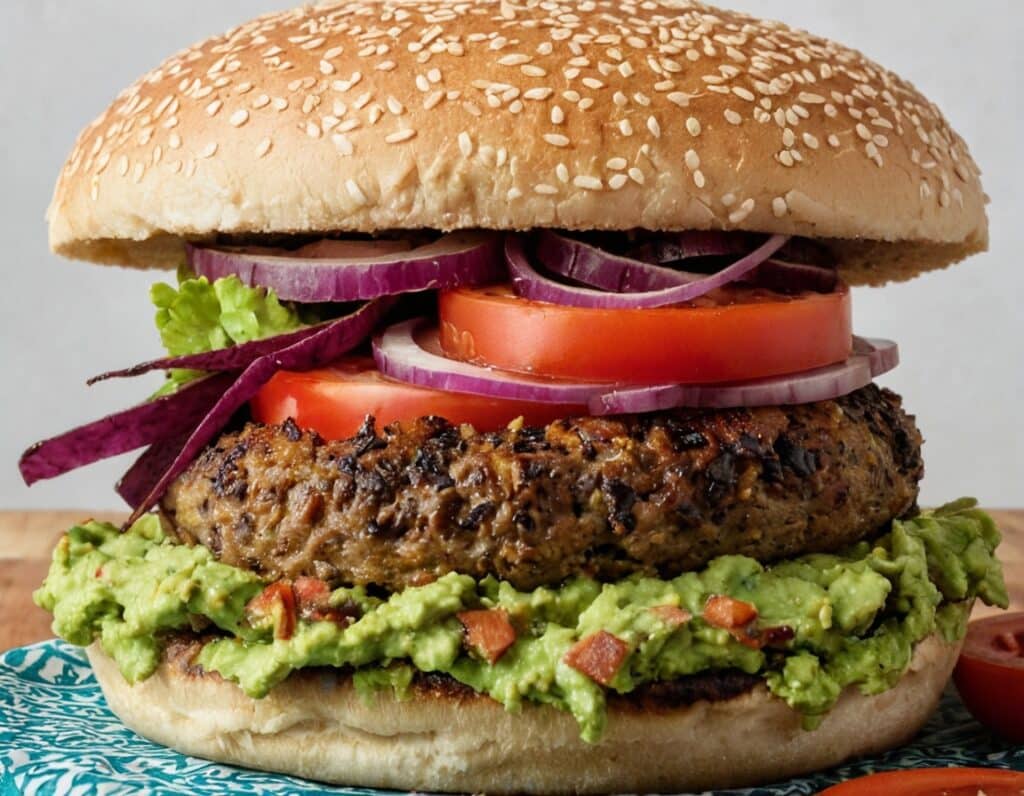

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Chickpeas vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- Kidney Beans or Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Eat to Your Heart’s Content – by Dr. Sat Bains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Making food heart-healthy and tasty is a challenge that vexes many, but it doesn’t have to be so difficult.
Dr. Sat Bains, a professional chef with multiple Michelin stars to his name, is an expert on “tasty”, and after surviving a heart attack himself, he’s become an expert on “heart-healthy” since then.
The book contains not only the recipes (of which there are 68, by the way), but also large sections of explanation of what makes various ingredients or methods heart-healthy or heart-unhealthy.
There’s science in there too, and these sections were written under the guidance of Dr. Neil Williams, a lecturer in physiology and nutrition.
You may be wondering as to why the author himself has a doctorate too; in fact he has three, none of which are relevant:
- Doctor of Arts
- Doctor of Laws
- Doctor of Hospitality (Honorary)
…but we prefix “Dr.” when people are that and he is that. The expertise we’re getting here though is really his culinary skill and extracurricular heart-healthy learning, plus Dr. Williams’ actual professional health guidance.
Bottom line: if you’d like heart-healthy recipes with restaurant-level glamour, this book is a fine choice.
Click here to check out Eat To Your Heart’s Content, and look after yours!
Share This Post
-
Radiant Rebellion – by Karen Walrond
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In health terms, we are often about fighting aging here. But to be more specific, what we’re fighting in those cases is not truly aging itself, so much as age-related decline.
Karen Walrond makes a case that we’ve made from the very start of 10almonds (but she wrote a whole book about it), that there’s merit in looking at what we can and can’t control about aging, doing what we reasonably can, and embracing what we can’t.
And yes, embracing, not merely accepting. This is not a downer of a book; it’s a call to revolution. It asks us to be proud of our grey hairs, to see our smile-lines around our eyes as the sign of a lived-in body, and even to embrace some of the unavoidable “actual decline” things as part of the journey of life. Maybe we’re not as strong as we used to be and now need a grippety-doodah to open jars; not everyone gets to live long enough to experience that! How lucky we are.
Perhaps most importantly, she bids us be the change we want to see in the world, and inspire others with our choices and actions, and shake off ageist biases for good.
Bottom line: if you want to foster a better attitude to aging not only for yourself, but also those around you, then this is a top-tier book for that.
Click here to check out Radiant Rebellion, and reclaim aging!
Share This Post
-
Muir Glen Organic vs First Field Original – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Muir Glen Organic Ketchup to First Field Original Ketchup, we picked the First Field.
Why?
This one was a little unfair to you, as you can’t turn them around to read the ingredients here. But the point we want to share the most today is: you have to turn them around and read the ingredients! You absolutely cannot rely on appearances!
While the Muir Glen Organic may have a very “greenwashed” aesthetic going on and the word “organic” is more eye-catching than any other word on the label, it contains 4x as much sugar and 4x as much sodium.
Side-by-side, they have, per tablespoon:
First Field Original: 1g sugar, 60mg sodium
Muir Glen Organic: 4g sugar, 240mg sodiumBut what about the importance of being organic?
Well, we have one more surprise for you: the First Field ketchup is organic too, non-GMO, and contains no added concentrates either.
This isn’t an ad for First Field (by all means enjoy their products or don’t; we’re not invested), but it is a heartfelt plea to always check the backs of products and read the labels, because fronts of products can’t be relied upon at all.
I’m sure we all get caught out sometimes, but the less often, the better!
PS: we write this, of course, before seeing the results of your voting. Maybe it won’t be a “Muir Glen Organic” sweep in the polls. But either way, it’s a call to vigilance, and a “very good, carry on” to everyone who does this already
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Saffron For The Brain (& More)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Saffron For The Brain (& More)
In yesterday’s edition of 10almonds, one of the items in the “health news from around the world” section was:
Clinical trial finds herbal medicine Sailuotong effective for brain health in older people
But, what is it?
❝SaiLuoTong (SLT) is a modern compound Chinese herbal medicine preparation in capsule form containing standardized extracts of Panax ginseng, Ginkgo biloba, and Crocus sativus L❞
We’ve written previously about ginseng and ginkgo biloba:
So, what’s this about Crocus sativus L.?
That is the plant better known as saffron. And, for all its wide availability (your local supermarket probably has at least a tiny amount in the spice section), there’s a reason we don’t see much of it:
❝Saffron blooms only once a year and should be collected within a very short duration. It is picked during 3–4 weeks in October-November. The method for the cultivation of saffron contributes greatly to its high price. According to some reports, this species is a sterile triploid and so does not produce fertile seeds. Germination can take 1–6 months at 18°C. It takes 3 years for plants to flower from seed.❞
Source: Crocus sativus L.: A comprehensive review
That’s fascinating, but what does it do for us?
Well, in the words of El Midaoui et al. (2022):
❝In the frame of a double-blind-placebo-controlled study, 30 mg per day supplementation with saffron for 16 weeks resulted in improved cognitive function in patients suffering from mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease.
Moreover, the follow-up of this study in which the authors evaluated the effects of saffron (30 mg/day) for 22 weeks showed that saffron was as effective as donepezil in the treatment of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease❞
Read the full review: Saffron (Crocus sativus L.): A Source of Nutrients for Health and for the Treatment of Neuropsychiatric and Age-Related Diseases
Not just that, but it also has powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties beyond the brain (though the brain is where research has been most focused, due to its neuroprotective effects).
(this, too, is a full research review in its own right; we’re getting a lot of “bang for buck” on papers today)
And more?
Yes, and more. Lots more. To bullet-pointify even just the abstract from another research review:
- Saffron has been suggested to be effective in the treatment of a wide range of disorders including coronary artery diseases, hypertension, stomach disorders, dysmenorrhea and learning and memory impairments.
- In addition, different studies have indicated that saffron has anti-inflammatory, anti-atherosclerotic, antigenotoxic and cytotoxic activities. (This is all good; the cytotoxic activities are about killing cancer cells)
- Antitussive effects of stigmas and petals of C. sativus and its components, safranal and crocin have also been demonstrated.
- The anticonvulsant and anti-Alzheimer properties of saffron extract were shown in human and animal studies.
- The efficacy of C. sativus in the treatment of mild to moderate depression was also reported in clinical trial.
- Administration of C. sativus and its constituents increased glutamate and dopamine levels in the brain in a dose-dependent manner.
- It also interacts with the opioid system to reduce withdrawal syndrome.
- C. sativus and its components can be considered as promising agents in the treatment of nervous system disorders.
For more details on any of those items, see:
The effects of Crocus sativus (saffron) and its constituents on nervous system: a review
Is it safe?
The effective dose is 30mg/kg and the LD50 is more than 20g/kg, so yes, it’s very safe. Given the price of it, this also means that if you’re the size of this writer (a little over 70kg, or a little over 150lbs) to poison yourself effectively you’d need to consume about 1.4kg of saffron at a time, which would cost well over $6,000.
Where can I get it?
Your local supermarket probably has a tiny amount in the spice section, or you can get better prices buying it in “bulk” online. Here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dates vs Raisins – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing dates to raisins, we picked the dates.
Why?
There are benefits for each fruit, but we say dates come out on top. See what you think:
In terms of macros, while they’re both dried fruits, dates contain more water (unless you leave them sitting open for a while), which will tend to mathematically lower the relative percentages of other components because they’re being held against water weight too. However, even though this is the case (i.e. dates are being mathematically disadvantaged), dates contain more than twice the fiber that raisins do (8g/100g compared to raisins’ 3.7g/100g).
While we’re talking macros, dates are also lower in total carbs, as well as obviously net carbs, and have a much lower glycemic index than raisins (dates have a glycemic index of 42, considered low, while raisins have a glycemic index of 64, considered medium; their respective glycemic loads are even more telling: 13 for raisins and just 2 for dates!).
About those carbs… For dates, it’s an approximately equal mix of sucrose, glucose, and fructose, while for raisins it’s 49% glucose and 49% fructose. Because sucrose is the only disaccharide here, this (as well as the fiber difference) is one of the reasons for the different glycemic indices and glycemic loads, since glucose and fructose are more quickly absorbed.
That’s more than we usually write about macros, but in this case, both fruits are ones especially often hit with the “aren’t they full of sugar though?” question, so it was important to cover the critical distinctions between the two, because they really are very different.
Summary of macros: dates win easily in every aspect we looked at
In the category of vitamins, raisins get a tally in their favor. Raisins are higher in vitamins B1, B2, C, E, K, and choline, while dates are higher in vitamins A, B3, B5, and B9, giving raisins a 6:4 lead here. In dates’ defense, the difference in vitamin K is marginal, and it’d make it a 5:4 lead if we considered that within the margin of error (because all these figures are of course based on averages), and the vitamins that dates are higher in, the margins are much wider indeed, meaning that both fruits have approximately the same overall levels of vitamins when looked at in total, but still, we’ll call this category a nominal win for raisins.
When it comes to minerals, dates have more magnesium, selenium, and zinc, while raisins have more copper, iron, phosphorus, and potassium. Nominally that’s a 4:3 lead for raisins, but if we consider that raisins also contain more sodium, it’s more like a tie here. If we have to pick one though, this is a very slight win for raisins.
Adding up the sections, we have one huge win for dates (macros) with two very marginal wins for raisins—hence, we say that dates win out.
Still, of course enjoy both; diversity is good for the health.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
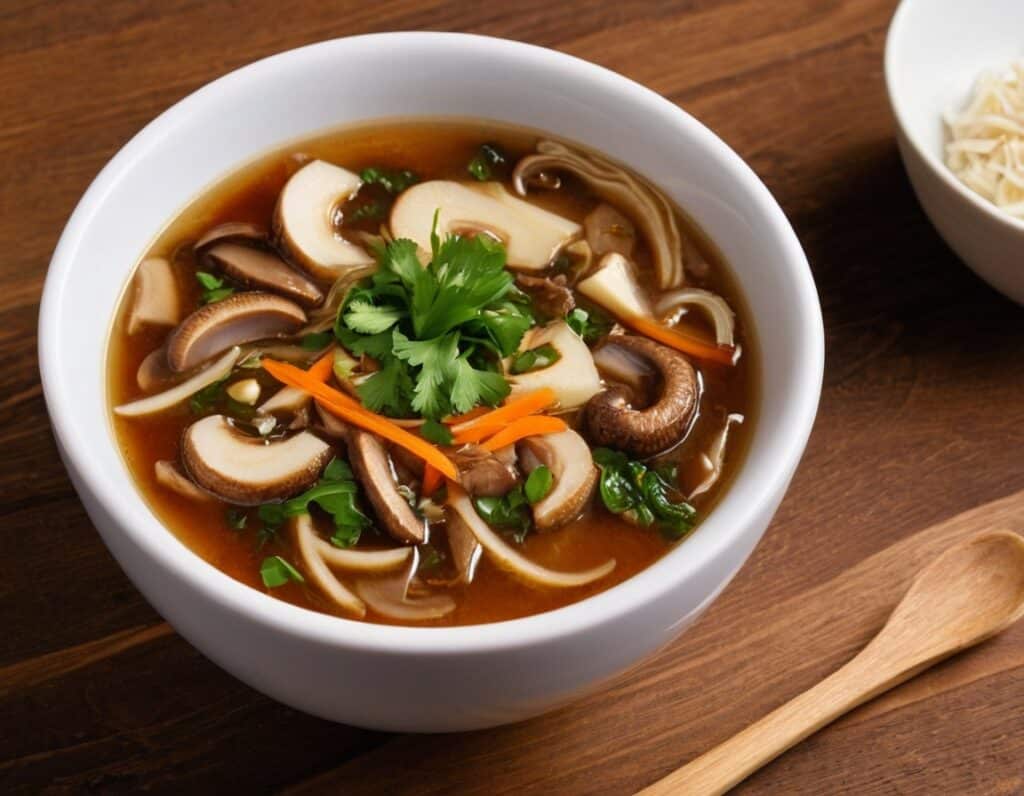
Hot And Sour Shiitake Soup
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a popular, easy, and delicious soup that nonetheless is not found in many western kitchens, despite being enjoyed in restaurants/take-out. Best of all, making it at home means that you know all the ingredients, can account for quality, and also can customize it per your preferences (i.e. how much heat/sourness you like).
You will need
- 3 cups shiitake mushrooms, sliced
- 3 cups bok choy, chopped
- 2 cups cherry tomatoes, quartered
- 1 cup carrot, grated
- 3 spring onions, chopped
- 2 shallots, sliced lengthways
- 2 serrano chilis (or similar), sliced thinly
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tbsp fresh ginger, sliced into 1″ strips
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ bulb garlic, crushed
- 6 cups low-sodium vegetable stock. Ideally you will have made it yourself from vegetable cuttings that you saved in the freezer until you had enough to make stock from, but if that’s not an option, then low-sodium vegetable stock cubes can be purchased and used.
- Garnish: ¼ cup (or 4 tbsp) cilantro, chopped, or if you have the soap gene, then this time we recommend chopped basil as the subsitution
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Put the ginger in a big pot with the stock; cover and simmer for about 20 minutes (otherwise the ginger flavor will remain mostly concentrated in the ginger strips).
2) Bring it to a boil and add the bok choy, mushrooms, shallots, chili peppers, and the carrot; simmer for another 5 minutes
3) Add the remaining ingredients except for the garnish, and simmer for another 5 minutes
4) Serve, adding the garnish
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The (Longevity) Magic of Mushrooms
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- Enjoy Bitter/Hot/Sour/Pungent Foods For Your Heart & Brain
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: