The Worst Cookware Lurking In Your Kitchen (Toxicologist Explains)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Yvonne Burkart gives us a rundown of the worst offenders, and what to use instead:
Hot mess
The very worst offender is non-stick cookware, the kind with materials such as Teflon. These are the most toxic, due to PFAS chemicals.
Non-stick pans release toxic gases, leach chemicals into food, and release microplastic particles, which can accumulate in the body.
One that a lot of people don’t think about, in that category, is the humble air-fryer, which often as not has a non-stick cooking “basket”. These she describes as highly toxic, as they combine plastic, non-stick coatings, and high heat, which can release fumes and other potentially dangerous chemicals into the air and food.
You may be wondering: how bad is it? And the answer is, quite bad. PFAS chemicals are linked to infertility, hypertension in pregnancy, developmental issues in children, cancer, weakened immune systems, hormonal disruption, obesity, and intestinal inflammation.
Dr. Burkart’s top picks for doing better:
- Pure ceramic cookware: top choice for safety, particularly brands like Xtrema, which are tested for heavy metal leaching.
- Carbon steel & cast iron: durable and safe; can leach iron in acidic foods (for most people, this is a plus, but some may need to be aware of it)
- Stainless steel: lightweight and affordable but can leach nickel and chromium in acidic foods at high temperatures. Use only if nothing better is available.
And specifically as alternatives to air-fryers: glass convection ovens or stainless steel ovens are safer than conventional air fryers. The old “combination oven” can often be a good choice here.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
- It’s Not Fantastic To Be Plastic ← for the closely related topic of microplastics and nanoplastics
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cognitive Enhancement Without Drugs
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cognitive Enhancement Without Drugs
This is Elizabeth Ricker. She’s a Harvard-and-MIT-trained neuroscientist and researcher, who now runs the “Citizen Science” DIY-neurohacking organization, NeuroEducate.
Sounds fun! What’s it about?
The philosophy that spurs on her research and practice can be summed up as follows:
❝I’m not going to leave my brain up to my doctor or [anyone else]… My brain is my own responsibility, and I’m going to do the best that I can to optimize it❞
Her goal is not just to optimize her own brain though; she wants to make the science accessible to everyone.
What’s this about Citizen Science?
“Citizen Science” is the idea that while there’s definitely an important role in society for career academics, science itself should be accessible to all. And, not just the conclusions, but the process too.
This can take the form of huge experiments, often facilitated these days by apps where we opt-in to allow our health metrics (for example) to be collated with many thousands of others, for science. It can also involve such things as we talked about recently, getting our own raw genetic data and “running the numbers” at home to get far more comprehensive and direct information than the genetic testing company would ever provide us.
For Ricker, her focus is on the neuroscience side of biohacking, thus, neurohacking.
I’m ready to hack my brain! Do I need a drill?
Happily not! Although… Bone drills for the skull are very convenient instruments that make it quite hard to go wrong even with minimal training. The drill bit has a little step/ledge partway down, which means you can only drill through the thickness of the skull itself, before the bone meeting the wider part of the bit stops you from accidentally drilling into the brain. Still, please don’t do this at home.
What you can do at home is a different kind of self-experimentation…
If you want to consider which things are genuinely resulting in cognitive enhancement and which things are not, you need to approach the matter like a scientist. That means going about it in an organized fashion, and recording results.
There are several ways cognitive enhancement can be measured, including:
- Learning and memory
- Executive function
- Emotional regulation
- Creative intelligence
Let’s look at each of them, and what can be done. We don’t have a lot of room here; we’re a newsletter not a book, but we’ll cover one of Ricker’s approaches for each:
Learning and memory
This one’s easy. We’re going to leverage neuroplasticity (neurons that fire together, wire together!) by simple practice, and introduce an extra element to go alongside your recall. Perhaps a scent, or a certain item of clothing. Tell yourself that clinical studies have shown that this will boost your recall. It’s true, but that’s not what’s important; what’s important is that you believe it, and bring the placebo effect to bear on your endeavors.
You can test your memory with word lists, generated randomly by AI, such as this one:
You’ll soon find your memory improving—but don’t take our word for it!
Executive function
Executive function is the aspect of your brain that tells the other parts how to work, when to work, and when to stop working. If you’ve ever spent 30 minutes thinking “I need to get up” but you were stuck in scrolling social media, that was executive dysfunction.
This can be trained using the Stroop Color and Word Test, which shows you words, specifically the names of colors, which will themselves be colored, but not necessarily in the color the word pertains to. So for example, you might be shown the word “red”, colored green. Your task is to declare either the color of the word only, ignoring the word itself, or the meaning of the word only, ignoring its appearance. It can be quite challenging, but you’ll get better quite quickly:
The Stroop Test: Online Version
Emotional Regulation
This is the ability to not blow up angrily at the person with whom you need to be diplomatic, or to refrain from laughing when you thought of something funny in a sombre situation.
It’s an important part of cognitive function, and success or failure can have quite far-reaching consequences in life. And, it can be trained too.
There’s no online widget for this one, but: when and if you’re in a position to safely* do so, think about something that normally triggers a strong unwanted emotional reaction. It doesn’t have to be something life-shattering, but just something that you feel in some way bad about. Hold this in your mind, sit with it, and practice mindfulness. The idea is to be able to hold the unpleasant idea in your mind, without becoming reactive to it, or escaping to more pleasant distractions. Build this up.
*if you perchance have PTSD, C-PTSD, or an emotional regulation disorder, you might want to talk this one through with a qualified professional first.
Creative Intelligence
Another important cognitive skill, and again, one that can be cultivated and grown.
The trick here is volume. A good, repeatable test is to think of a common object (e.g. a rock, a towel, a banana) and, within a time constraint (such as 15 minutes) list how many uses you can think of for that item.
Writer’s storytime: once upon a time, I was sorting through an inventory of medical equipment with a colleague, and suggested throwing out our old arterial clamps, as we had newer, better ones—in abundance. My colleague didn’t want to part with them, so I challenged him “Give me one use for these, something we could in some possible world use them for that the new clamps don’t do better, and we’ll keep them”. He said “Thumbscrews”, and I threw my hands up in defeat, saying “Fine!”, as he had technically fulfilled my condition.
What’s the hack to improve this one? Just more volume. Creativity, as it turns out, isn’t something we can expend—like a muscle, it grows the more we use it. And because the above test is repeatable (with different objects), you can track your progress.
And if you feel like using your grown creative muscle to write/paint/compose/etc your magnum opus, great! Or if you just want to apply it to the problem-solving of everyday life, also great!
In summary…
Our brain is a wonderful organ with many functions. Society expects us to lose these as we get older, but the simple, scientific truth is that we can not only maintain our cognitive function, but also enhance and grow it as we go.
Want to know more from today’s featured expert?
You might enjoy her book, “Smarter Tomorrow”, which we reviewed back in March
Share This Post
-
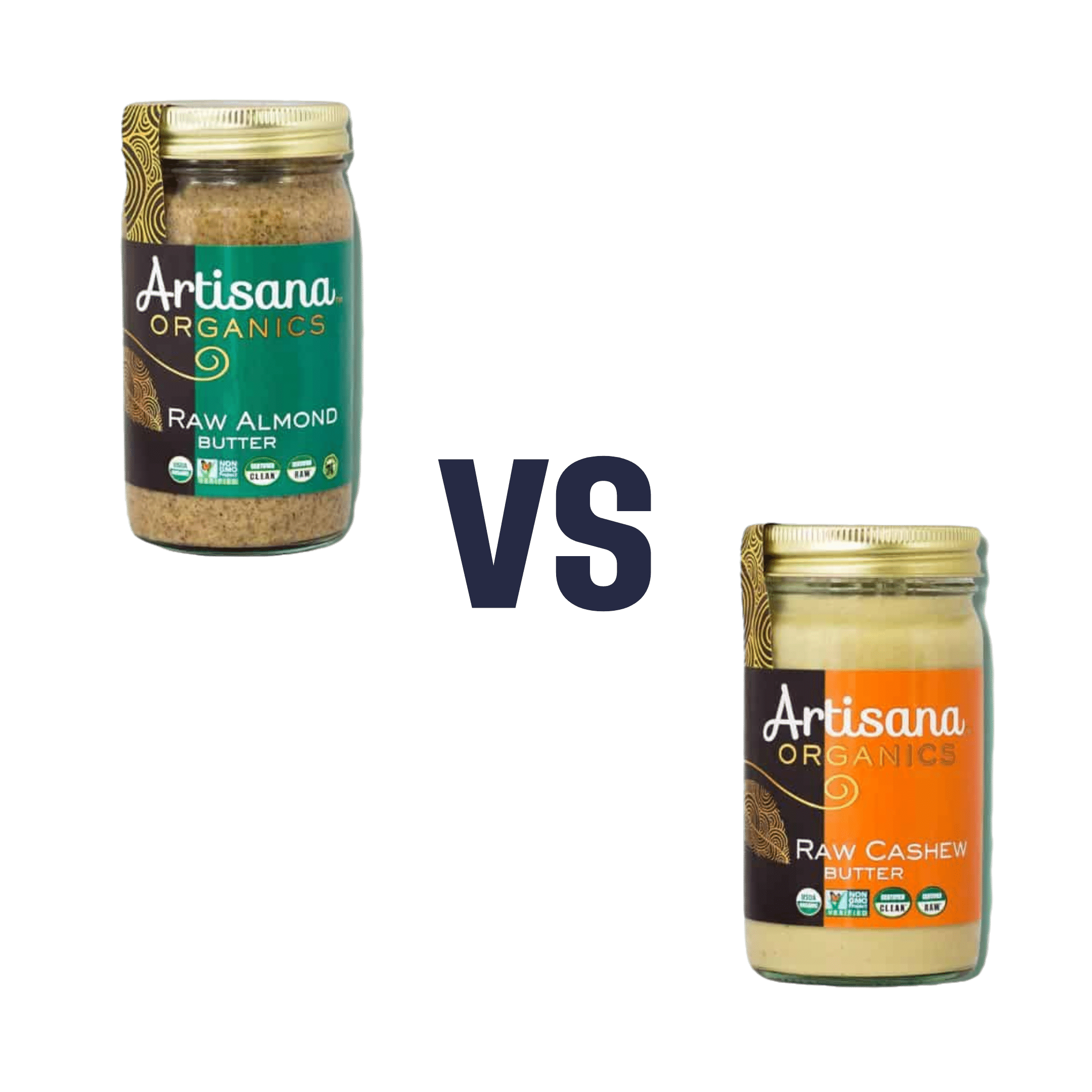
Almond Butter vs Cashew Butter – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almond butter to cashew butter, we picked the almond.
Why?
They’re both good! But, our inherent pro-almond bias notwithstanding, the almond butter does have a slightly better spread of nutrients.
In terms of macros, almond butter has more protein while cashew butter has more carbs, and of their fats, they’re broadly healthy in both cases, but almond butter does have less saturated fat.
In the category of vitamins, both are good sources of vitamin E, but almond butter has about 4x more. The rest of the vitamins they both contain aren’t too dissimilar, aside from some different weightings of various different B-vitamins, that pretty much balance out across the two nut butters. The only noteworthy point in cashew butter’s favor here is that it is a good source of vitamin K, which almond butter doesn’t have.
When it comes to minerals, both are good sources of lots of minerals, but most significantly, almond butter has a lot more calcium and quite a bit more potassium. In contrast, cashew butter has more selenium.
In short, they’re both great, but almond butter has more relative points in its favor than cashew butter.
Here are the two we depicted today, by the way, in case you’d like to try them:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
But First, Inner Peace – by Case Kenny
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Thinking positively and vividly imagining a Ferrari parked in your driveway will not, in fact, cause it to manifest there.
You know what that method does work for, though? Feelings.
This book is essentially a guided thought-and-feeling modelling system that, consisting of 60 chapters to be taken one-per-day, aims to rewire your mind for inner peace.
This is not, however, just a matter of “imagine peacefulness”, or nice-sounding platitudes. Rather, at the end of each chapter there is an exercise and journaling prompts; effectively, work to do along the way.
Weighing in at 438 pages, this is a sizeable book, but part of that is because of the space to write answers to journaling prompts. Still, it’s not exactly a pamphlet, either—there is serious and extensive content here too.
Like any daily reader, you can zip through it all at once if you like, but a benefit to doing the chapter-a-day approach is that it sets a habit of mindful reflection, and gives you a chance to implement each thing, one per day, building up new habits in that regard, too. In contrast, reading it all in one sitting wouldn’t give that.
Bottom line: without inner peace, we don’t have much. Treat yourself—you deserve it.
Click here to check out But First, Inner Peace, and enjoy inner peace!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Hard to Kill – by Dr. Jaime Seeman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about Dr. Seeman’s method for robust health at all ages, focussing on:
- Nutrition
- Movement
- Sleep
- Mindset
- Environment
In this book, she expands on these things far more than we have room to in our little newsletter, including (importantly!) how each interplays with the others. She also follows up with an invitation to take the “Hard to Kill 30-Day Challenge”.
That said, in the category of criticism, it’s only 152 pages, and she takes some of that to advertise her online services in an effort to upsell the reader.
Nevertheless, there’s a lot of worth in the book itself, and the writing style is certainly easy-reading and compelling.
Bottom line: this book is half instructional, half motivational, and covers some very important areas of health.
Click here to check out “Hard to Kill”, and enjoy robust health at every age!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
You can train your nose – and 4 other surprising facts about your sense of smell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Would you give up your sense of smell to keep your hair? What about your phone?
A 2022 US study compared smell to other senses (sight and hearing) and personally prized commodities (including money, a pet or hair) to see what people valued more.
The researchers found smell was viewed as much less important than sight and hearing, and valued less than many commodities. For example, half the women surveyed said they’d choose to keep their hair over sense of smell.
Smell often goes under the radar as one of the least valued senses. But it is one of the first sensory systems vertebrates developed and is linked to your mental health, memory and more.
Here are five fascinating facts about your olfactory system.
DimaBerlin/Shutterstock 1. Smell is linked to memory and emotion
Why can the waft of fresh baking trigger joyful childhood memories? And why might a certain perfume jolt you back to a painful breakup?
Smell is directly linked to both your memory and emotions. This connection was first established by American psychologist Donald Laird in 1935 (although French novelist Marcel Proust had already made it famous in his reverie about the scent of madeleines baking.)
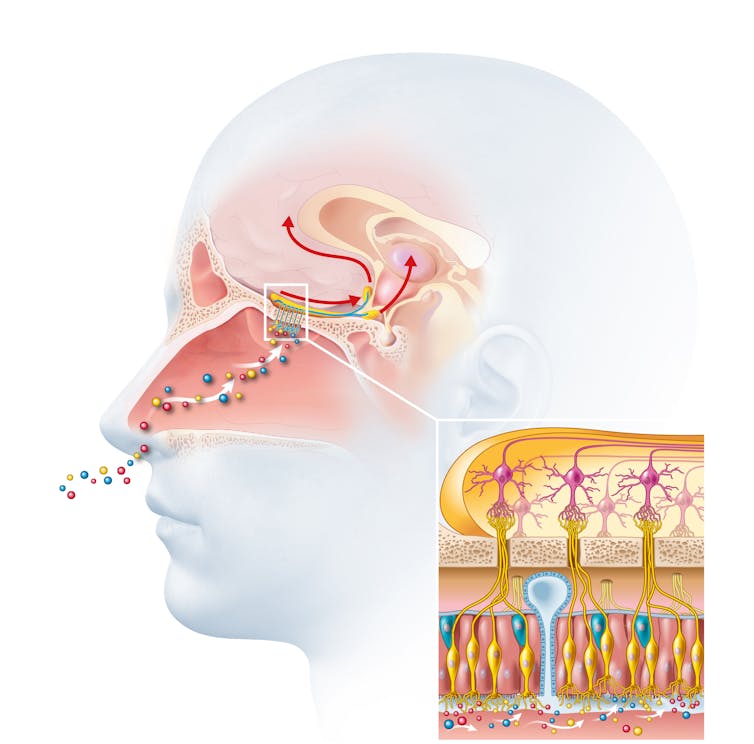
Odours are first captured by special olfactory nerve cells inside your nose. These cells extend upwards from the roof of your nose towards the smell-processing centre of your brain, called the olfactory bulb.
Smells are first detected by nerve cells in the nose. Axel_Kock/Shutterstock From the olfactory bulb they form direct connection with the brain’s limbic system. This includes the amygdala, where emotions are generated, and the hippocampus, where memories are created.
Other senses – such as sight and hearing – aren’t directly connected to the lymbic system.
One 2004 study used functional magnetic resonance imaging to demonstrate odours trigger a much stronger emotional and memory response in the brain than a visual cue.
2. Your sense of smell constantly regenerates
You can lose your ability to smell due to injury or infection – for example during and after a COVID infection. This is known as olfactory dysfunction. In most cases it’s temporary, returning to normal within a few weeks.
This is because every few months your olfactory nerve cells die and are replaced by new cells.
We’re not entirely sure how this occurs, but it likely involves your nose’s stem cells, the olfactory bulb and other cells in the olfactory nerves.
Other areas of your nervous system – including your brain and spinal cord – cannot regenerate and repair after an injury.
Constant regeneration may be a protective mechanism, as the olfactory nerves are vulnerable to damage caused by the external environment, including toxins (such as cigarette smoke), chemicals and pathogens (such as the flu virus).
But following a COVID infection some people might continue to experience a loss of smell. Studies suggest the virus and a long-term immune response damages the cells that allow the olfactory system to regenerate.
3. Smell is linked to mental health
Around 5% of the global population suffer from anosmia – total loss of smell. An estimated 15-20% suffer partial loss, known as hyposmia.
Given smell loss is often a primary and long-term symptom of COVID, these numbers are likely to be higher since the pandemic.
Yet in Australia, the prevalence of olfactory dysfunction remains surprisingly understudied.
Losing your sense of smell is shown to impact your personal and social relationships. For example, it can mean you miss out on shared eating experiences, or cause changes in sexual desire and behaviour.
In older people, declining ability to smell is associated with a higher risk of depression and even death, although we still don’t know why.
Losing your sense of smell can have a major impact on mental health. Halfpoint/Shutterstock 4. Loss of smell can help identify neurodegenerative diseases
Partial or full loss of smell is often an early indicator for a range of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Patients frequently report losing their sense of smell years before any symptoms show in body or brain function. However many people are not aware they are losing their sense of smell.
There are ways you can determine if you have smell loss and to what extent. You may be able to visit a formal smell testing centre or do a self-test at home, which assesses your ability to identify household items like coffee, wine or soap.
5. You can train your nose back into smelling
“Smell training” is emerging as a promising experimental treatment option for olfactory dysfunction. For people experiencing smell loss after COVID, it’s been show to improve the ability to detect and differentiate odours.
Smell training (or “olfactory training”) was first tested in 2009 in a German psychology study. It involves sniffing robust odours — such as floral, citrus, aromatic or fruity scents — at least twice a day for 10—20 seconds at a time, usually over a 3—6 month period.
Participants are asked to focus on the memory of the smell while sniffing and recall information about the odour and its intensity. This is believed to help reorganise the nerve connections in the brain, although the exact mechanism behind it is unclear.
Some studies recommend using a single set of scents, while others recommend switching to a new set of odours after a certain amount of time. However both methods show significant improvement in smelling.
This training has also been shown to alleviate depressive symptoms and improve cognitive decline both in older adults and those suffering from dementia.
Just like physiotherapy after a physical injury, olfactory training is thought to act like rehabilitation for your sense of smell. It retrains the nerves in your nose and the connections it forms within the brain, allowing you to correctly detect, process and interpret odours.
Lynn Nazareth, Research Scientist in Olfactory Biology, CSIRO
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Is it good to eat farm raised fish?❞
We’ll answer this as a purely health-related question (and thus not considering economy, ecology, ethics, or taste).
It’s certainly not as good as wild-caught fish, for several reasons, some more serious than others:
Farmed fish can have quite a different nutritional profile to wild-caught fish, and also contain more contaminants, including heavy metals.
For example, farmed fish tend to have much higher fat content for the same amount of protein, but lower levels of minerals and other nutrients. Here are two side-by-side:
Wild-caught salmon | Farmed salmon
See also:
Quantitative analysis of the benefits and risks of consuming farmed and wild salmon
Additionally, because fish in fish farms tend to be very susceptible to diseases (because of the artificially cramped and overcrowded environment), fish farms tend to make heavy use of antibiotics, which can cause all sorts of problems down the line:
So definitely, “let the buyer beware”!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: