Spiked Acupressure Mat: Trial & Report
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you ready for the least comfortable bed? The reviews are in, and…
Let’s get straight to the point
“Laura Try” tries out health things and reports on her findings. And in this case…
- She noted up front that the claims for this are to improve relaxation, alleviate muscle pain, and improve sleep.
- It also is said to help with myofascial release specifically, which can improve flexibility and mobility (as well as contributing to the alleviation of muscle pain previously mentioned)
- She did not enjoy it at first! Shocking nobody, it was uncomfortable and even somewhat painful. However, after a while, it became less painful and more comfortable—except for trying standing on it, which still hurt (this writer has one too, and I often stand on it at my desk, whenever I feel my feet need a little excitement—it’s probably good for the circulation, but that is just a hypothesis)
- Soon, it became relaxing. Writer’s note: that raised hemicylindrical pillow she’s using? Try putting it under your neck instead, to stimulate the vagus nerve.
- While it is best use on bare skin, the effect can be softened by wearing a thin later of clothing between you and the mat.
- She got hers for £71 GBP (this writer got hers for a fraction of that price from Aldi—and here’s an example product on Amazon, at a more mid-range price)
For more details on all of the above and a blow-by-blow account, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Fascia: Why (And How) You Should Take Care Of Yours
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Exercise Rewires Your Brain for Better Mental Wellbeing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Tracey Marks, psychiatrist, explains what happens immediately, and what happens over the long term:
For now and for later
First of all, a single workout can already alter brain chemistry and protect against stress. In the longer term, exercise promotes neurogenesis, primarily in the hippocampus, improving memory and reversing brain aging. It also strengthens the prefrontal cortex, which is critical for decision-making, focus, and emotional regulation.
In more general terms, exercise boosts brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels, which in turn boost neuron growth and connectivity.
Exercise also promotes angiogenesis (blood vessel construction), improving oxygen and nutrient delivery to the brain.
Timeline of benefits:
- Immediate: increased blood flow and temporary BDNF spike.
- Weeks: new neurons, connections, and blood vessel growth.
- Months: visible brain volume changes and better brain connectivity.
Dr. Marks’ Timing Tips
- Morning: boosts energy and helps regulate the circadian rhythm.
- Midday: resets stress levels (specifically: to low)
- Evening: helps process emotions (but it’s still recommended to avoid high-intensity exercise close to bedtime)
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Wondering what kind of exercise is best?
You might also like to read:
The Neuroscientist In The Gym: Dr. Wendy Suzuki Explains The Exercise That Protects Your Brain
Take care!
Share This Post
-
To Nap Or Not To Nap; That Is The Question
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Is it good to nap in the afternoon, or better to get the famous 7 to 9 hours at night and leave it at that? I’m worried that daytime napping to make up for a shorter night’s sleep will just perpetuate and worsen it in the long run, is there a categorical answer here?❞
Generally considered best is indeed the 7–9 hours at night (yes, including at older ages):
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
…and sleep efficiency does matter too:
Why 7 Hours Sleep Is Not Enough
…which in turn, is influenced by factors other than just length and depth:
The 6 Dimensions Of Sleep (And Why They Matter)
However! Knowing what is best in theory does not help at all if it’s unattainable in practice. So, if you’re not getting a good night’s sleep (and we’ll assume you’re already practising good sleep hygiene; fresh bedding, lights-off by a certain time, no alcohol or caffeine before bed, that kind of thing), then a first port-of-call may be sleep remedies:
Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors
If even those don’t work, then napping is now likely your best back-up option. But, napping done incorrectly can indeed cause as many problems as it solves. There’s a difference between:
- “I napped and now I have energy again” and you continue with your day
- “Darkness took me, and I strayed out of thought and time. Stars wheeled overhead, and every day was as long as the life age of the earth—but it was not the end.” and now you’re not sure whether it’s day or night, whose house you’re in, or whether you’ve been drugged.
These two very common napping experiences are influenced by factors that we can control:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
If you still prefer to not risk napping but do need at least some kind of refreshment that’s actually a refreshment and not just taking stimulants, then you might consider this practice (from yoga nidra) that gives some of the same benefits of sleep, without actually sleeping:
Non-Sleep Deep Rest: A Neurobiologist’s Insights
Take care!
Share This Post
-
How To Avoid Carer Burnout (Without Dropping Care)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Avoid Carer Burnout
Sometimes in life we find ourselves in a caregiving role.
Maybe we chose it. For example, by becoming a professional carer, or even just by being a parent.
Oftentimes we didn’t. Sometimes because our own parents now need care from us, or because a partner becomes disabled.
Philosophical note: an argument could be made for that latter also having been a pre-emptive choice; we probably at some point said words to the effect of “in sickness and in health”, hopefully with free will, and hopefully meant it. And of course, sometimes we enter into a relationship with someone who is already disabled.
But, we are not a philosophy publication, and will henceforth keep to the practicalities.
First: are you the right person?
Sometimes, a caregiving role might fall upon you unasked-for, and it’s worth considering whether you are really up for it. Are you in a position to be that caregiver? Do you want to be that caregiver?
It may be that you do, and would actively fight off anyone or anything that tried to stop you. If so, great, now you only need to make sure that you are actually in a position to provide the care in question.
It may be that you do want to, but your circumstances don’t allow you to do as good a job of it as you’d like, or it means you have to drop other responsibilities, or you need extra help. We’ll cover these things later.
It may be that you don’t want to, but you feel obliged, or “have to”. If that’s the case, it will be better for everyone if you acknowledge that, and find someone else to do it. Nobody wants to feel a burden, and nobody wants someone providing care to be resentful of that. The result of such is two people being miserable; that’s not good for anyone. Better to give the job to someone who actually wants to (a professional, if necessary).
So, be honest (first with yourself, then with whoever may be necessary) about your own preferences and situation, and take steps to ensure you’re only in a caregiving role that you have the means and the will to provide.
Second: are you out of your depth?
Some people have had a life that’s prepared them for being a carer. Maybe they worked in the caring profession, maybe they have always been the family caregiver for one reason or another.
Yet, even if that describes you… Sometimes someone’s care needs may be beyond your abilities. After all, not all care needs are equal, and someone’s condition can (and more often than not, will) deteriorate.
So, learn. Learn about the person’s condition(s), medications, medical equipment, etc. If you can, take courses and such. The more you invest in your own development in this regard, the more easily you will handle the care, and the less it will take out of you.
And, don’t be afraid to ask for help. Maybe the person knows their condition better than you, and certainly there’s a good chance they know their care needs best. And certainly, there are always professionals that can be contacted to ask for advice.
Sometimes, a team effort may be required, and there’s no shame in that either. Whether it means enlisting help from family/friends or professionals, sometimes “many hands make light work”.
Check out: Caregiver Action Network: Organizations Near Me
A very good resource-hub for help, advice, & community
Third: put your own oxygen mask on first
Like the advice to put on one’s own oxygen mask first before helping others (in the event of a cabin depressurization in an airplane), the rationale is the same here. You can’t help others if you are running on empty yourself.
As a carer, sometimes you may have to put someone else’s needs above yours, both in general and in the moment. But, you do have needs too, and cannot neglect them (for long).
One sleepless night looking after someone else is… a small sacrifice for a loved one, perhaps. But several in a row starts to become unsustainable.
Sometimes it will be necessary to do the best you can, and accept that you cannot do everything all the time.
There’s a saying amongst engineers that applies here too: “if you don’t schedule time for maintenance, your equipment will schedule it for you”.
In other words: if you don’t give your body rest, your body will break down and oblige you to rest. Please be aware this goes for mental effort too; your brain is just another organ.
So, plan ahead, schedule breaks, find someone to take over, set up your cared-for-person with the resources to care for themself as well as possible (do this anyway, of course—independence is generally good so far as it’s possible), and make the time/effort to get you what you need for you. Sleep, distraction, a change of scenery, whatever it may be.
Lastly: what if it’s you?
If you’re reading this and you’re the person who has the higher care needs, then firstly:all strength to you. You have the hardest job here; let’s not forget that.
About that independence: well-intentioned people may forget that, so don’t be afraid to remind them when “I would prefer to do that myself”. Maintaining independence is generally good for the health, even if sometimes it is more work for all concerned than someone else doing it for you. The goal, after all, is your wellbeing, so this shouldn’t be cast aside lightly.
On the flipside: you don’t have to be strong all the time; nobody should.
Being disabled can also be quite isolating (this is probably not a revelation to you), so if you can find community with other people with the same or similar condition(s), even if it’s just online, that can go a very, very long way to making things easier. Both practically, in terms of sharing tips, and psychologically, in terms of just not feeling alone.
See also: How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Ketogenic Diet: Burning Fat Or Burning Out?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
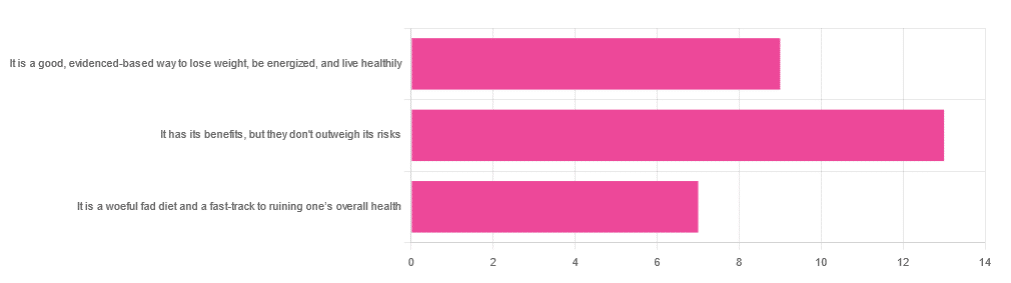
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of the keto diet, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 45% said “It has its benefits, but they don’t outweigh the risks”
- About 31% said “It is a good, evidence-based way to lose weight, be energized, and live healthily”
- About 24% said “It is a woeful fad diet and a fast-track to ruining one’s overall health”
So what does the science say?
First, what is the ketogenic diet?
There are two different stories here:
- Per science, it’s a medical diet designed to help treat refractory epilepsy in children.
- Per popular lore, it’s an energizing weight loss diet for Instagrammers and YouTubers.
Can it be both? The answer is: yes, but with some serious caveats, which we’ll cover over the course of today’s feature.
The ketogenic diet works by forcing the body to burn fat for energy: True or False?
True! This is why it helps for children with refractory epilepsy. By starving the body (including the brain) of glucose, the liver must convert fat into fatty acids and ketones, which latter the brain (and indeed the rest of the body) can now use for energy instead of glucose, thus avoiding one of the the main triggers of refractory epilepsy in children.
See: The Ketogenic Diet: One Decade Later | Pediatrics
Even the pediatric epilepsy studies, however, conclude it does have unwanted side effects, such as kidney stones, constipation, high cholesterol, and acidosis:
Source: Dietary Therapies for Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet is good for weight loss: True or False?
True! Insofar as it does cause weight loss, often rapidly. Of course, so do diarrhea and vomiting, but these are not usually held to be healthy methods of weight loss. As for keto, a team of researchers recently concluded:
❝As obesity rates in the populace keep rising, dietary fads such as the ketogenic diet are gaining traction.
Although they could help with weight loss, this study had a notable observation of severe hypercholesterolemia and increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among the ketogenic diet participants.❞
~ Dr. Shadan Khdher et al.
On which note…
The ketogenic diet is bad for the heart: True or False?
True! As Dr. Joanna Popiolek-Kalisz concluded recently:
❝In terms of cardiovascular mortality, the low-carb pattern is more beneficial than very low-carbohydrate (including the ketogenic diet). There is still scarce evidence comparing ketogenic to the Mediterranean diet.
Other safety concerns in cardiovascular patients such as adverse events related to ketosis, fat-free mass loss, or potential pharmacological interactions should be also taken into consideration in future research.❞
~ Dr. Joanna Popiolek-Kalisz
Read in full: Ketogenic diet and cardiovascular risk: state of the art review
The ketogenic diet is good for short-term weight loss, but not long-term maintenance: True or False?
True! Again, insofar as it works in the short term. It’s not the healthiest way to lose weight and we don’t recommend it, but it did does indeed precipitate short-term weight loss. Those benefits are not typically observed for longer than a short time, though, as the above-linked paper mentions:
❝The ketogenic diet does not fulfill the criteria of a healthy diet. It presents the potential for rapid short-term reduction of body mass, triglycerides level, Hb1Ac, and blood pressure.
Its efficacy for weight loss and the above-mentioned metabolic changes is not significant in long-term observations.❞
~ Ibid.
The ketogenic diet is a good, evidence-based way to lose weight, be energized, and live healthily: True or False?
False, simply, as you may have gathered from the above, but we’ve barely scratched the surface in terms of the risks.
That said, as mentioned, it will induce short-term weight loss, and as for being energized, typically there is a slump-spike-slump in energy:
- At first, the body is running out of glucose, and so naturally feels weak and tired.
- Next, the body enters ketosis, and so feels energized and enlivened ← this is the part where the popular enthusiastic reviews come from
- Then, the body starts experiencing all the longer-term problems associated with lacking carbohydrates and having an overabundance of fat, so becomes gradually more sick and tired.
Because of this, the signs of symptoms of being in ketosis (aside from: measurably increased ketones in blood, breath, and urine) are listed as:
- Bad breath
- Weight loss
- Appetite loss
- Increased focus and energy
- Increased fatigue and irritability
- Digestive issues
- Insomnia
The slump-spike-slump we mentioned is the reason for the seemingly contradictory symptoms of increased energy and increased fatigue—you get one and then the other.
Here’s a small but illustrative study, made clearer by its participants being a demographic whose energy levels are most strongly affected by dietary factors:
The ketogenic diet is a woeful fad diet and a fast-track to ruining one’s overall health: True or False?
True, subjectively in the first part, as it’s a little harsher than we usually go for in tone, though it has been called a fad diet in scientific literature. The latter part (ruining one’s overall health) is observably true.
One major problem is incidental-but-serious, which is that a low-carb diet is typically a de facto low-fiber diet, which is naturally bad for the gut and heart.
Other things are more specific to the keto diet, such as the problems with the kidneys:
However, kidney stones aren’t the worst of the problems:
Is Losing Weight Worth Losing Your Kidney: Keto Diet Resulting in Renal Failure
We’re running out of space and the risks associated with the keto diet are many, but for example even in the short term, it already increases osteoporosis risk:
❝Markers of bone modeling/remodeling were impaired after short-term low-carbohydrate high-fat diet, and only one marker of resorption recovered after acute carbohydrate restoration❞
~ Dr. Ida Heikura et al.
A Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Impairs Markers of Bone Health in Response to Exercise
Want a healthier diet?
We recommend the Mediterranean diet.
See also: Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean
(the above is about keeping to the Mediterranean diet, while tweaking one’s choices within it for a specific extra health focus such as an anti-inflammatory upgrade, a heart-healthy upgrade, a gut-healthy upgrade, and a brain-healthy upgrade)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
A Supplement To Rival St. John’s Wort Against Depression
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do You Feel The SAMe?
S-Adeonsyl-L-Methionone (SAMe) is a chemical found naturally in the body, and/but enjoyed widely as a supplement. The main reasons people take it are:
- Improve mood (antidepressant effect)
- Improve joints (reduce osteoarthritis symptoms)
- Improve liver (detoxifying effect)
Let’s see what the science says for each of those claims…
Does it improve mood?
It seems to perform comparably to St. John’s Wort (which is good; it performs comparably to Prozac).
Best of all, it does this with fewer contraindications (St. John’s Wort has so many contraindications).
Here’s how they stack up:
This looks very promising, though it’d be nice to see a larger body of research, to be sure.
Does it reduce osteoarthritis symptoms?
The good news: it performs comparably to ibuprofen, with fewer side effects!
The bad news: it also performs comparably to placebo!
Read into that what you will about ibuprofen’s usefulness vs OA symptoms.
Read all about it:
S-Adenosylmethionine for osteoarthritis of the knee or hip
If you were hoping for something for OA or similar symptoms, you might like our previous main features:
- Avoiding/Managing Osteoarthritis
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
- (Science-Based) Alternative Pain Relief
Does it help against liver disease?
According to adverts for SAMe: absolutely!
According to science: we don’t know
The science for this is so weak that it’d be unworthy of mention if it weren’t for the fact that SAMe is so widely sold as good against hepatotoxicity.
To be clear: maybe it really is great! Science hasn’t yet disproved its usefulness either.
It is popularly assumed to be beneficial due to there being an association between lower levels of SAMe in the body (remember, it is also produced inside our bodies) and development of liver disease, especially cholestasis.
Here’s an example of what pretty much every study we found was like (inconclusive research based mostly on mice):
S-adenosylmethionine in liver health, injury, and cancer
For other options for liver health, consider:
Is it safe?
Safety trials have been done ranging from 3 months to 2 years, with no serious side effects coming to light. So, it appears quite safe.
That said, as with anything, there are contraindications, such as:
- if you have bipolar disorder, skip this unless directed by your health care provider, because it may worsen the symptoms of mania
- if you are on SSRIs or other serotonergic drugs, it may interact with those
- if you are immunocompromised, you might want to skip it can increase the risk of P. carinii growth in such cases
As always, do speak with your doctor/pharmacist for personalized advice.
Summary
SAMe’s evidence-based qualities seem to stack up as follows:
- Against depression: good
- Against osteoarthritis: weak
- Against liver disease: unknown
As for safety, it has been found quite safe for most people.
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it, but here is an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Millet vs Rye – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing millet to rye, we picked the rye.
Why?
In terms of macros, they’re about equal on protein, and rye has more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which give it the lower glycemic index, so we say rye wins this category.
In the category of vitamins, millet has more of vitamins B1, B2, B6, and B9, while rye has more of vitamins A, B5, E, and K. Notionally, that’s a 4:4 tie, though rye’s margins of difference are an order of magnitude greater, so we say rye takes a marginal victory on this one.
When it comes to minerals, there’s nothing to debate here: millet has more copper, while rye has more calcium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. An easy win for rye on this one.
Adding up the sections gives the overall win to rye, but there is one other thing worth mentioning: millet is naturally gluten-free, but rye is not, so if you are avoiding gluten for any reason, you’ll want to pick the millet in this case.
See also: Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Aside from that, by all means enjoy either or both, in moderation! Diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Grains: Bread Of Life, Or Cereal Killer?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: