Replacing Sugar: Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Sweet Foods
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those with a sweet tooth, it can be challenging to indulge one’s desires while also avoiding inflammation. Happily, Dr. Jia-Yia Lui has scientific insights to share!
Dr. Liu’s Top 10
We’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Grapes
- Goji berries
- Barberries
- Persimmons
- Longans
- Lychees
- Raisins¹
- Applesauce²
- Plums³
- Dates
¹Yes, these are technically also grapes, but there are enough differences that Dr. Liu tackles them separately.
²It makes a difference how it’s made, though.
³And dried plums, in other words, prunes.
For more details on all of these, plus their extra benefits and relevant considerations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
- The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
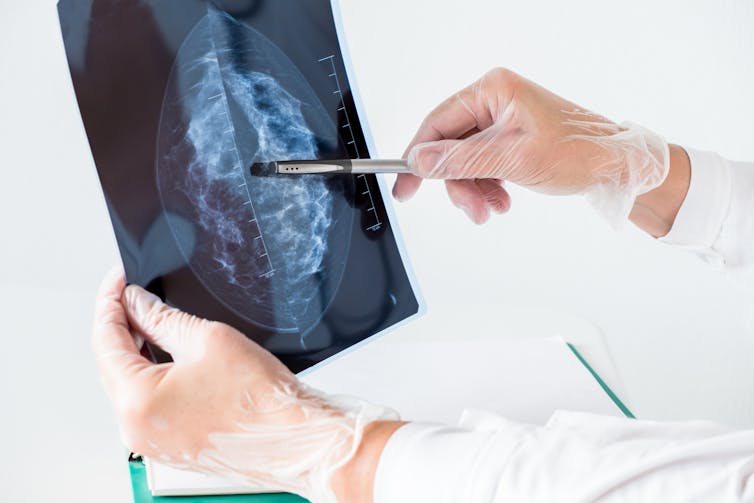
Having dense breasts is linked to cancer. But advice about breast density can depend on where you live
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Having dense breasts is a clear risk factor for breast cancer. It can also make cancers hard to spot on mammograms.
Yet you might not be aware you have dense breasts, even after mammographic screening.
In Australia, advice for women with dense breasts and their health-care professionals can be inconsistent and confusing.
This is because there’s not currently consensus on whether women who have dense breasts, but no symptoms, benefit from further imaging such as ultrasounds. Concerns include potential cost of these tests and the risk they can produce false positives.
Gorodenkoff/Shutterstock What is breast density?
Breasts are made up of fatty tissue and fibroglandular tissue (including glands that make milk, held together by fibrous tissue).
On a mammogram – an x-ray of the breast – fibroglandular tissue appears white and fatty tissue appears dark. The white areas are referred to as breast density.
Fibroglandular tissue shows up white on a mammogram. Nata Sokhrannova/Shutterstock A higher proportion of fibroglandular tissue means your breasts are dense.
There are four categories to classify breast density:
- A: almost entirely fatty
- B: scattered areas of fibroglandular density
- C: heterogeneously or consistently dense
- D: extremely dense.
Breast density is very common. Around 40% of women aged 40–74 are estimated to have “dense breasts”, meaning they fall in category C or D.
What’s the link to cancer?
Breast density is associated with the risk of breast cancer in two ways.
First, breast density usually decreases with age. But if a woman has high breast density for her age, it increases her likelihood of breast cancer.
One study looked at the risk of breast cancer over the age of 50. It found there was a 6.2% risk for the one-third of women with the lowest density. For the 5% with the highest density, the risk was 14.7%.
Second, breast density “masks” cancers if they develop. Both cancers and breast density appear white on a mammogram, making cancers very hard to see.
Breast cancer screening saves lives through early detection and improved treatment options. But we don’t yet know if telling women about their breast density leads to earlier cancer detection, or lives saved.
In Australia, screening mammography is free for all women* aged 40 and older. This is run through BreastScreen Australia, a joint national, state and territory initiative. Those aged 50-74 are invited to have a mammogram, but it’s available for free without a referral from age 40.
However, the messages Australian women currently receive about breast density – and whether it’s recorded – depends on where they live.
What does the advice say?
In 2023, the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists updated its position statement to recommend breast density is recorded during screening and diagnostic tests in Australia and New Zealand.
Meanwhile BreastScreen Australia says it “should not routinely record breast density or provide supplemental testing for women with dense breasts”. However this position statement is from 2020 and is currently under review.
Some state and territory BreastScreen programs, including in Western Australia, South Australia and soon Victoria, notify women if they have dense breasts. Victoria is currently at an early stage of its roll-out.
While the messaging regarding breast density differs by state, none currently recommend further imaging for women with dense breasts without speaking to a doctor about individual risk.
What are the issues?
Providing recommendations for women with dense breasts is difficult.
The European Society of Breast Imaging recommends women with extremely dense breasts aged 50–70 receive an MRI every two to four years, in addition to screening mammography. This is based on a large randomised controlled trial from the Netherlands.
But the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists describes this recommendation as “aspirational”, acknowledging cost, staffing and accessibility as challenges.
That is, it is not feasible to provide a supplemental MRI for everyone in the screening population in category D with extremely dense breasts (around 10%).
Further, there is no consensus on appropriate screening recommendations for women in the category C (heterogeneous density).
We need a national approach to breast density reporting in Australia and to do better at identifying who is most likely to benefit from further testing.
BreastScreen Australia is currently undergoing a review of its policy and funding.
One of its goals is to enable a nationally consistent approach to breast screening practices. Hopefully breast density reporting, including funding to support national implementation, will be a priority.
*This includes those recorded female at birth and who are gender diverse.
Jennifer Stone, Principal Research Fellow, School of Population and Global Health, The University of Western Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Real Self-Care – by Pooja Lakshmin MD
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As the subtitle says, “crystals, cleanses, and bubble baths not included”. So, if it’s not about that sort of self-care, what is it about?
Dr. Lakshmin starts by acknowledging something that many self-help books don’t:
We can do everything correctly and still lose. Not only that, but for many of us, that is the probable outcome. Not because of any fault or weakness of ours, but simply because one way or another the game is rigged against us from the start.
So, should we throw in the towel, throw our hands in the air, and throw the book out of the window?
Nope! Dr. Lakshmin has actually helpful advice, that pertains to:
- creating healthy boundaries and challenging guilt
- treating oneself with compassion
- identifying and aligning oneself with one’s personal values
- asserting one’s personal power to fight for one’s own self-interest
If you’re reading this and thinking “that seems very selfish”, then let’s remember the “challenging guilt” part of that. We’ve all-too-often been conditioned to neglect our own needs and self-sacrifice for others.
And, while selfless service really does have its place, needlessly self-destructive martyrdom does not!
Bottom line: this book delivers a lot of “real talk” on a subject that otherwise often gets removed from reality rather. In short, it’s a great primer for finding the right place to draw the line between being a good-hearted person and being a doormat.
Click here to check out Real Self-Care and “put your own oxygen mask on first”!
Share This Post
-
The Fiber Fueled Cookbook – by Dr. Will Bulsiewicz
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Bulsiewicz’s book “Fiber Fuelled” (which is great), but this one is more than just a cookbook with the previous book in mind. Indeed, this is even a great stand-alone book by itself, since it explains the core principles well enough already, and then adds to it.
It’s also about a lot more than just “please eat more fiber”, though. It looks at FODMAPs, purine, histamine intolerance, celiac disease, altered gallbladder function, acid reflux, and more.
He offers a five-part strategy:
Genesis (what is the etiology of your problem)
- Restrict (cut things out to address that first)
- Observe (keep a food/symptom diary)
- Work things back in (re-add potential triggers one by one, see how it goes)
- Train your gut (your microbiome does not exist in a vacuum, and communication is two-way)
- Holistic healing (beyond the gut itself, looking at other relevant factors and aiming for synergistic support)
As for the recipes themselves, there are more than a hundred of them and they are good, so no more “how can I possibly cook [favorite dish] without [removed ingredient]?”
Bottom line: if you’d like better gut health, this book is a top-tier option for fixing existing complaints, and enjoying plain-sailing henceforth.
Click here to check out The Fiber Fueled Cookbook; your gut will thank you later!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Sometimes, Perfect Isn’t Practical!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝10 AM breakfast is not realistic for most. What’s wrong with 8 AM and Evening me at 6. Don’t quite understand the differentiation.❞
(for reference, this is about our “Breakfasting For Health?” main feature)
It’s not terrible to do it the way you suggest It’s just not optimal, either, that’s all!
Breakfasting at 08:00 and then dining at 18:00 is ten hours apart, so no fasting benefits between those. Let’s say you take half an hour to eat dinner, then eat nothing again until breakfast, that’s 18:30 to 08:00, so that’s 13½ hours fasting. You’ll recall that fasting benefits start at 12 hours into the fast, so that means you’d only get 1½ hours of fasting benefits.
As for breakfasting at 08:00 regardless of intermittent fasting considerations, the reason for the conclusion of around 10:00 being optimal, is based on when our body is geared up to eat breakfast and get the most out of that, which the body can’t do immediately upon waking. So if you wake and get sunlight at 08:30, get a little moderate exercise, then by 10:00 your digestive system will be perfectly primed to get the most out of breakfast.
However! This is entirely based on you waking and getting sunlight at 08:30.
So, iff you wake and get sunlight at 06:30, then in that case, breakfasting at 08:00 would give the same benefits as described above. What’s important is the 1½ hour priming-time.
Writer’s note: our hope here is always to be informational, not prescriptive. Take what works for you; ignore what doesn’t fit your lifestyle.
I personally practice intermittent fasting for about 21hrs/day. I breakfast (often on nuts and perhaps a little salad) around 16:00, and dine at around 18:00ish, giving myself a little wiggleroom. I’m not religious about it and will slide it if necessary.
As you can see: that makes what is nominally my breakfast practically a pre-dinner snack, and I clearly ignore the “best to eat in the morning” rule because that’s not consistent with my desire to have a family dinner together in the evening while still practicing the level of fasting that I prefer.
Science is science, and that’s what we report here. How we apply it, however, is up to us all as individuals!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Garden Cress vs Watercress – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing garden cress to watercress, we picked the garden cress.
Why?
While watercress is (rightly!) popularly viewed as a superfood for its nutritional density, the garden variety actually outperforms it.
In terms of macros first, garden cress has more protein, carbs, and fiber, while also having the lower glycemic index. Not that anyone’s getting blood sugar spikes from eating any kind of cress, but still, by the numbers, this is a clear win on the whole for garden cress in the category of macros.
When it comes to vitamins, garden cress has a lot (tens of times) more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, B7, B9, C, K, and choline, while watercress has (slightly) more of vitamins B1, B5, and E. An easy win for garden cress.
In the category of minerals, garden cress has more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium, while watercress has more calcium. Another clear win for garden cress.
Taking a quick peep at polyphenols in case there’s anything to offset the above, garden cress has 13x more kaempferol (13mg/100g to watercress’s 1mg/100g), and/but watercress, in its favor, has quercetin (at 4mg/100g), which garden cress doesn’t. So, we say this category is also a win for garden cress, but watercress has its merits too.
👆 Let’s clarify: those numbers are all very good, and garden cress’s 13mg/100g kaempferol is absurdly high; most such quotients of most edible plants are orders of magnitude smaller; not to shoehorn in another vegetable, but just to give an example, savoy cabbage, which won on nutritional density vs bok choi recently, has 0.26mg/100g kaempferol and 0.12mg/100g quercetin (which were already very respectable numbers), so you see the difference in cress’s exceptionally generous delivery of these polyphenols!
Adding up the sections makes for an overwhelming win for garden cress!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc ← cress is a great example of this!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Jumping Rope Changes The Human Body
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most popularly enjoyed by professional boxers and six-year-old girls, jumping rope is one of the most metabolism-boosting exercises around:
Just a hop, skip, and a jump away from good health
Maybe you haven’t tried it since your age was in single digits, so, if you do…
What benefits can you expect?
- Improves cardiovascular fitness, equivalent to 30 minutes of running with just 10 minutes of jumping.
- Increases bone density and boosts immunity by aiding the lymphatic system.
- Enhances explosiveness in the lower body, agility, and stamina.
- Improves shoulder endurance, coordination, and spatial awareness.
What kind of rope is best for you?
- Beginner ropes: licorice ropes (nylon/vinyl), beaded ropes for rhythm and durability.
- Advanced ropes: speed ropes (denser, faster materials) for higher speeds and more difficult skills.
- Weighted ropes: build upper body muscles (forearms, shoulders, chest, back).
What length should you get?
- Recommended rope length varies by height (8 ft for 5’0″–5’4″, 9 ft for 5’5″–5’11”, 10 ft for 6’0″ and above).
- Beginners should start with longer ropes for clearance.
What should you learn?
- Initial jump rope skills: start with manageable daily jump totals, gradually increasing as ankles, calves, and feet adapt.
- Further skills: learn the two-foot jump and then the boxer’s skip for efficient, longer sessions and advanced skills. Keep arms close and hands at waist level for a smooth swing.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Do High Intensity Interval Training (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: