Why do I poo in the morning? A gut expert explains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
No, you’re not imagining it. People really are more likely to poo in the morning, shortly after breakfast. Researchers have actually studied this.
But why mornings? What if you tend to poo later in the day? And is it worth training yourself to be a morning pooper?
To understand what makes us poo when we do, we need to consider a range of factors including our body clock, gut muscles and what we have for breakfast.
Here’s what the science says.

So morning poos are real?
In a UK study from the early 1990s, researchers asked nearly 2,000 men and women in Bristol about their bowel habits.
The most common time to poo was in the early morning. The peak time was 7-8am for men and about an hour later for women. The researchers speculated that the earlier time for men was because they woke up earlier for work.
About a decade later, a Chinese study found a similar pattern. Some 77% of the almost 2,500 participants said they did a poo in the morning.
But why the morning?
There are a few reasons. The first involves our circadian rhythm – our 24-hour internal clock that helps regulate bodily processes, such as digestion.
For healthy people, our internal clock means the muscular contractions in our colon follow a distinct rhythm.
There’s minimal activity in the night. The deeper and more restful our sleep, the fewer of these muscle contractions we have. It’s one reason why we don’t tend to poo in our sleep.
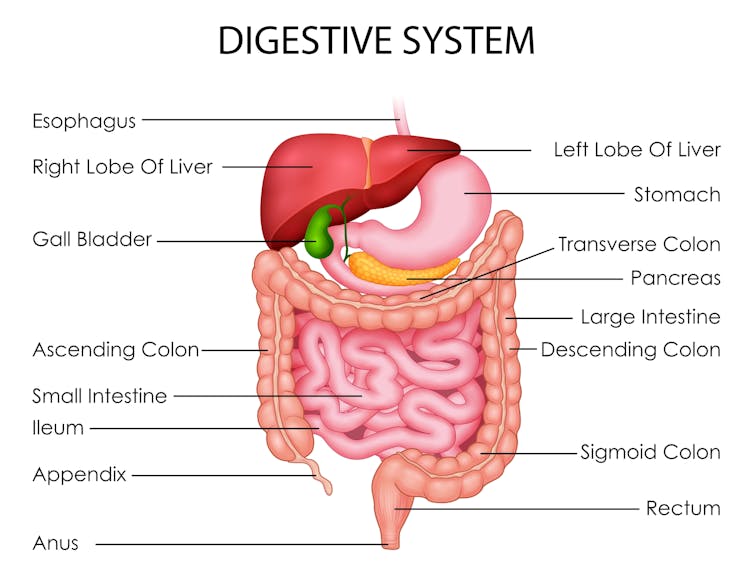
But there’s increasing activity during the day. Contractions in our colon are most active in the morning after waking up and after any meal.
One particular type of colon contraction partly controlled by our internal clock are known as “mass movements”. These are powerful contractions that push poo down to the rectum to prepare for the poo to be expelled from the body, but don’t always result in a bowel movement. In healthy people, these contractions occur a few times a day. They are more frequent in the morning than in the evening, and after meals.
Breakfast is also a trigger for us to poo. When we eat and drink our stomach stretches, which triggers the “gastrocolic reflex”. This reflex stimulates the colon to forcefully contract and can lead you to push existing poo in the colon out of the body. We know the gastrocolic reflex is strongest in the morning. So that explains why breakfast can be such a powerful trigger for a bowel motion.
Then there’s our morning coffee. This is a very powerful stimulant of contractions in the sigmoid colon (the last part of the colon before the rectum) and of the rectum itself. This leads to a bowel motion.
How important are morning poos?
Large international surveys show the vast majority of people will poo between three times a day and three times a week.
This still leaves a lot of people who don’t have regular bowel habits, are regular but poo at different frequencies, or who don’t always poo in the morning.
So if you’re healthy, it’s much more important that your bowel habits are comfortable and regular for you. Bowel motions do not have to occur once a day in the morning.
Morning poos are also not a good thing for everyone. Some people with irritable bowel syndrome feel the urgent need to poo in the morning – often several times after getting up, during and after breakfast. This can be quite distressing. It appears this early-morning rush to poo is due to overstimulation of colon contractions in the morning.
Can you train yourself to be regular?
Yes, for example, to help treat constipation using the gastrocolic reflex. Children and elderly people with constipation can use the toilet immediately after eating breakfast to relieve symptoms. And for adults with constipation, drinking coffee regularly can help stimulate the gut, particularly in the morning.
A disturbed circadian rhythm can also lead to irregular bowel motions and people more likely to poo in the evenings. So better sleep habits can not only help people get a better night’s sleep, it can help them get into a more regular bowel routine.

Regular physical activity and avoiding sitting down a lot are also important in stimulating bowel movements, particularly in people with constipation.
We know stress can contribute to irregular bowel habits. So minimising stress and focusing on relaxation can help bowel habits become more regular.
Fibre from fruits and vegetables also helps make bowel motions more regular.
Finally, ensuring adequate hydration helps minimise the chance of developing constipation, and helps make bowel motions more regular.
Monitoring your bowel habits
Most of us consider pooing in the morning to be regular. But there’s a wide variation in normal so don’t be concerned if your poos don’t follow this pattern. It’s more important your poos are comfortable and regular for you.
If there’s a major change in the regularity of your bowel habits that’s concerning you, see your GP. The reason might be as simple as a change in diet or starting a new medication.
But sometimes this can signify an important change in the health of your gut. So your GP may need to arrange further investigations, which could include blood tests or imaging.
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck – by Mark Manson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may wonder from the title: is this book arguing that we should all be callous heartless monsters? And no, it is not.
Instead, author Mark Manson advocates for cynicism, but less in the manner of Scrooge, and more in the manner of Diogenes:
- That life will involve struggle, so we might as well at least choose our struggles.
- That we will make mistakes, so we might as well accept them as learning experiences.
- That we will love and we will lose, so we might as well do it right while we can.
In short, the book is less about not caring… And more about caring about the right things only.
So, what are “the right things”? Manson bids us decide for ourselves, but certainly has ideas and pointers, with regard to what may or may not be healthy values to pursue.
The style throughout is casual and almost conversational, without being overly padded. It makes for very easy reading.
If the book has a weak point, it’s that when it briefly makes a suprisingly prescriptive turn into recommending we take up Buddhism, it may feel a bit like our friend who wants us to join in the latest MLM scheme. But, he’s soon back on track.
Bottom line: if you ever find yourself stressed with living up to unwanted expectations—your own, other people’s, and society’s—this book can really help streamline things.
Share This Post
-
How much does your phone’s blue light really delay your sleep? Relax, it’s just 2.7 minutes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s one of the most pervasive messages about technology and sleep. We’re told bright, blue light from screens prevents us falling asleep easily. We’re told to avoid scrolling on our phones before bedtime or while in bed. We’re sold glasses to help filter out blue light. We put our phones on “night mode” to minimise exposure to blue light.
But what does the science actually tell us about the impact of bright, blue light and sleep? When our group of sleep experts from Sweden, Australia and Israel compared scientific studies that directly tested this, we found the overall impact was close to meaningless. Sleep was disrupted, on average, by less than three minutes.
We showed the message that blue light from screens stops you from falling asleep is essentially a myth, albeit a very convincing one.
Instead, we found a more nuanced picture about technology and sleep.
Mangostar/Shutterstock What we did
We gathered evidence from 73 independent studies with a total of 113,370 participants of all ages examining various factors that connect technology use and sleep.
We did indeed find a link between technology use and sleep, but not necessarily what you’d think.
We found that sometimes technology use can lead to poor sleep and sometimes poor sleep can lead to more technology use. In other words, the relationship between technology and sleep is complex and can go both ways.
How is technology supposed to harm sleep?
Technology is proposed to harm our sleep in a number of ways. But here’s what we found when we looked at the evidence:
- bright screen light – across 11 experimental studies, people who used a bright screen emitting blue light before bedtime fell asleep an average of only 2.7 minutes later. In some studies, people slept better after using a bright screen. When we were invited to write about this evidence further, we showed there is still no meaningful impact of bright screen light on other sleep characteristics including the total amount or quality of sleep
- arousal is a measure of whether people become more alert depending on what they’re doing on their device. Across seven studies, people who engaged in more alerting or “exciting” content (for example, video games) lost an average of only about 3.5 minutes of sleep compared to those who engaged in something less exciting (for example, TV). This tells us the content of technology alone doesn’t affect sleep as much as we think
- we found sleep disruption at night (for example, being awoken by text messages) and sleep displacement (using technology past the time that we could be sleeping) can lead to sleep loss. So while technology use was linked to less sleep in these instances, this was unrelated to being exposed to bright, blue light from screens before bedtime.
Which factors encourage more technology use?
Research we reviewed suggests people tend to use more technology at bedtime for two main reasons:
- to “fill the time” when they’re not yet sleepy. This is common for teenagers, who have a biological shift in their sleep patterns that leads to later sleep times, independent of technology use.
- to calm down negative emotions and thoughts at bedtime, for apparent stress reduction and to provide comfort.
There are also a few things that might make people more vulnerable to using technology late into the night and losing sleep.
We found people who are risk-takers or who lose track of time easily may turn off devices later and sacrifice sleep. Fear of missing out and social pressures can also encourage young people in particular to stay up later on technology.
What helps us use technology sensibly?
Last of all, we looked at protective factors, ones that can help people use technology more sensibly before bed.
The two main things we found that helped were self-control, which helps resist the short-term rewards of clicking and scrolling, and having a parent or loved one to help set bedtimes.
We found having a parent or loved one to help set bedtimes encourages sensible use of technology. fast-stock/Shutterstock Why do we blame blue light?
The blue light theory involves melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. During the day, we are exposed to bright, natural light that contains a high amount of blue light. This bright, blue light activates certain cells at the back of our eyes, which send signals to our brain that it’s time to be alert. But as light decreases at night, our brain starts to produce melatonin, making us feel sleepy.
It’s logical to think that artificial light from devices could interfere with the production of melatonin and so affect our sleep. But studies show it would require light levels of about 1,000-2,000 lux (a measure of the intensity of light) to have a significant impact.
Device screens emit only about 80-100 lux. At the other end of the scale, natural sunlight on a sunny day provides about 100,000 lux.
What’s the take-home message?
We know that bright light does affect sleep and alertness. However our research indicates the light from devices such as smartphones and laptops is nowhere near bright or blue enough to disrupt sleep.
There are many factors that can affect sleep, and bright, blue screen light likely isn’t one of them.
The take-home message is to understand your own sleep needs and how technology affects you. Maybe reading an e-book or scrolling on socials is fine for you, or maybe you’re too often putting the phone down way too late. Listen to your body and when you feel sleepy, turn off your device.
Chelsea Reynolds, Casual Academic/Clinical Educator and Clinical Psychologist, College of Education, Psychology and Social Work, Flinders University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
“Why Does It Hurt When I Have Sex?” (And What To Do About It)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is one that affects mostly women, with 43% of American women reporting such issues at some point. There’s a distribution curve to this, with higher incidence in younger and older women; younger while first figuring things out, and older with menopause-related body changes. But, it can happen at any time (and often not for obvious reasons!), so here’s what OB/GYN Dr. Jennifer Lincoln advises:
Many possibilities, but easily narrowed down
Common causes include:
- vaginal dryness, which itself can have many causes (half of which are “low estrogen levels” for various different reasons)
- muscular issues, which can be in response to anxiety, pain, and occur as a result of pelvic floor muscle tightening
- vulvar issues, ranging from skin disorders (e.g. lichen sclerosis or lichen planus) to nerve disorders (e.g. vestibulitis or vestibulodynia)
- uterine issues, including endometriosis, fibroids, or scar tissue if you had a surgery
- infections, of the STI variety, but bear in mind that some STIs such as herpes do not necessarily require direct sexual contact per se, and yeast infections definitely don’t. Some STIs are more serious than others, so getting things checked out is a good idea (don’t worry, clinics are discreet about this sort of thing)
- bowel issues, notwithstanding that we have been talking about vaginal sex here, it can’t be happy if its anatomical neighbors aren’t happy—so things like IBS, Crohn’s, or even just constipation, aren’t irrelevant
- trauma, of various kinds, affecting sexual experiences
That’s a lot of possibilities, so if there’s not something standing out as “yes, now that you mention it, it’s obviously that”, Dr. Lincoln recommends a full health evaluation and examination of medical history, as well as a targeted physical exam. That may not be fun, but at least, once it’s done, it’s done.
Treatments vary depending on the cause, of course, and there are many kinds of physical and psychological therapies, as well as surgeries for the uterine issues we mentioned.
Happily, many of the above things can be addressed with simpler and less invasive methods, including learning more about the relevant anatomy and physiology and how to use it (be not ashamed; most people never got meaningful education about this!)*, vulvar skin care (“gentle” is the watchword here), the difference a good lube can make, and estrogen supplementation—which if you’re not up for general HRT, can be a topical estrogen cream that alleviates sexual function issues without raising blood serum estradiol levels.
*10almonds tip: check out the recommended book “Come As You Are” in our links below; it has 400 pages of stuff most people never knew about anatomy and physiology down there; you can thank us later!
Meanwhile, for more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Water-based Lubricant vs Silicon-based Lubricant – Which is Healthier? (counterintuitively, it’s the silicon! But do give it a quick read, because here be science)
- How To Avoid Urinary Tract Infections (may be relevant; always good to know)
- Come As You Are – by Dr. Emily Nagoski (book; if we could only recommend one book on responsible vagina ownership, this would be the one)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Should I get a weighted vest to boost my fitness? And how heavy should it be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Exercise training while wearing a weighted vest is undergoing somewhat of a renaissance. Social media posts and trainers are promoting them as a potential strategy for improving fitness and health.
Exercising with additional weight attached to the body is nothing new. This idea has been used with soldiers for many centuries if not millennia – think long hikes with a heavy pack.
The modern weighted vest comes in a range of designs that are more comfortable and can be adjusted in terms of the weight added. But could one be helpful for you?
ZR10/Shutterstock What the research says
One of the earliest research studies, reported in 1993, followed 36 older people wearing weighted vests during a weekly exercise class and at home over a 20-week period. Wear was associated with improvements in bone health, pain and physical function.
Since then, dozens of papers have evaluated the exercise effects of wearing a weighted vest, reporting a range of benefits.
Not surprisingly, exercise with a weighted vest increases physiological stress – or how hard the body has to work – as shown by increased oxygen uptake, heart rate, carbohydrate utilisation and energy expenditure.
Adding weight equal to 10% of body weight is effective. But it doesn’t appear the body works significantly harder when wearing 5% extra weight compared to body weight alone.
Does more load mean greater injury risk?
A small 2021 study suggested additional weights don’t alter the biomechanics of walking or running. These are important considerations for lower-limb injury risk.
The safety considerations of exercising with weighted vests have also been reported in a biomechanical study of treadmill running with added weight of 1% to 10% of body weight.
While physiological demand (indicated by heart rate) was higher with additional weight and the muscular forces greater, running motion was not negatively affected.
To date no research studies have reported increased injuries due to wearing weighted vests for recreational exercise. However a 2018 clinical study on weight loss in people with obesity found back pain in 25% of those wearing such vests. Whether this can be translated to recreational use in people who don’t have obesity is difficult to say. As always, if pain or discomfort is experienced then you should reduce the weight or stop vest training.
Better for weight loss or bone health?
While wearing a weighted vest increases the energy expenditure of aerobic and resistance exercise, research to show it leads to greater fat loss or retaining muscle mass is somewhat inconclusive.
One older study investigated treadmill walking for 30 minutes, three times a week in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. The researchers found greater fat loss and muscle gain in the participants who wore a weighted vest (at 4–8% body weight). But subsequent research in obese older adults could not show greater fat loss in participants who wore weighted vests for an average of 6.7 hours per day.
There has been considerable interest in the use of weighted vests to improve bone health in older people. One 2003 study reported significant improvements in bone density in a group of older women over 32 weeks of weighted vest walking and strength training compared to a sedentary control group.
But a 2012 study found no difference in bone metabolism between groups of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis walking on a treadmill with or without a weighted vest.
Making progress
As with any exercise, there is a risk of injury if it is not done correctly. But the risk of weighted vest training appears low and can be managed with appropriate exercise progression and technique.
If you are new to training, then the priority should be to simply start exercising and not complicate it with wearing a weighted vest. The use of body weight alone will be sufficient to get you on the path to considerable gains in fitness.
Once you have a good foundation of strength, aerobic fitness and resilience for muscles, joints and bones, using a weighted vest could provide greater loading intensity as well as variation.
It is important to start with a lighter weight (such as 5% bodyweight) and build to no more than 10% body weight for ground impact exercises such as running, jogging or walking.
For resistance training such as squats, push-ups or chin-ups, progression can be achieved by increasing loads and adjusting the number of repetitions for each set to around 10 to 15. So, heavier loads but fewer repetitions, then building up to increase the load over time.
While weighted vests can be used for resistance training, it is probably easier and more convenient to use barbells, dumbbells, kettle bells or weighted bags.
The benefits of added weight can also be achieved by adding repetition or duration. Geert Pieters/Unsplash The bottom line
Weighted vest training is just one tool in an absolute plethora of equipment, techniques and systems. Yes, walking or jogging with around 10% extra body weight increases energy expenditure and intensity. But training for a little bit longer or at a higher intensity can achieve similar results.
There may be benefits for bone health in wearing a weighted vest during ground-based exercise such as walking or jogging. But similar or greater stimulus to bone growth can be achieved by resistance training or even the introduction of impact training such as hopping, skipping or bounding.
Exercising with a weighted vest likely won’t increase your injury risk. But it must be approached intelligently considering fitness level, existing and previous injuries, and appropriate progression for intensity and repetition.
Rob Newton, Professor of Exercise Medicine, Edith Cowan University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
When And Why Do We Pick Up Our Phones?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The School of Life’s Alain de Botton makes the argument that—if we pay attention, if we keep track—there’s an understory to why we pick up our phones:
It’s not about information
Yes, our phones (or rather, the apps therein) are designed to addict us, to draw us back, to keep us scrolling and never let us go. We indeed seek out information like our ancestors once sought out berries; searching, encouraged by a small discovery, looking for more. The neurochemistry is similar.
But when we look at the “when” of picking up our phones, de Botton says, it tells a different story:
We pick them up not to find out what’s going on with the world, but rather specifically to not find out what’s going with ourselves. We pick them up to white out some anxiety we don’t want to examine, a line of thought we don’t want to go down, memories we don’t want to consider, futures we do not want to have to worry about.
And of course, phones do have a great educational potential, are an immensely powerful tool for accessing knowledge of many kinds—if only we can remain truly conscious while using them, and not take them as the new “opiate of the masses”.
De Botton bids us, when next we pick up our phone. ask a brave question:
“If I weren’t allowed to consult my phone right now, what might I need to think about?”
As for where from there? There’s more in the video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Further reading
Making Social Media Work For Your Mental Health
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Hazelnuts vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hazelnuts to cashews, we picked the hazelnuts.
Why?
It’s close! This one’s interesting…
In terms of macros, hazelnuts have more fiber and fats, while cashews have more protein and carbs. All in all, all good stuff all around; maybe a win for one or the other depending on your priorities. We’d pick hazelnuts here, but your preference may vary.
When it comes to vitamins, hazelnuts have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, and E, while cashews have more vitamin K. An easy win for hazelnuts here, and the margins weren’t close.
In the category of minerals, hazelnuts have more calcium, manganese, and potassium, while cashews have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. This is a win for cashews, but it’s worth noting that cup for cup, both of these nuts provide more than the daily requirement of most of those minerals. This means that in practical terms, it doesn’t matter too much that (for example), while cashews provide 732% of the daily requirement for copper, hazelnuts “only” provide 575%. So while this category remains a victory for cashews, it’s something of a “on paper” thing for the most part.
Adding up the sections (ambivalent + clear win for hazelnuts + nominal win for cashews) means that in total today we’re calling it in favour of hazelnuts… But as ever, enjoy both, because both are good and so is diversity!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: