Benefits of Different Tropical Fruits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Would very much like your views of the benefits of different tropical fruits. I do find papaya is excellent for settling the digestion – but keen to know if others have remarkable qualities.❞
Definitely one for a main feature sometime soon! As a bonus while you wait, pineapple has some unique and powerful properties:
❝Its properties include: (1) interference with growth of malignant cells; (2) inhibition of platelet aggregation*; (3) fibrinolytic activity; (4) anti-inflammatory action; (5) skin debridement properties. These biological functions of bromelain, a non-toxic compound, have therapeutic values in modulating: (a) tumor growth; (b) blood coagulation; (c) inflammatory changes; (d) debridement of third degree burns; (e) enhancement of absorption of drugs.❞
*so do be aware of this if you are on blood thinners or otherwise have a bleeding disorder, as you might want to skip the pineapple in those cases!
Source: Bromelain, the enzyme complex of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and its clinical application. An update
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Green Tea Allergies and Capsules
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Hey Sheila – As always, your articles are superb !! So, I have a topic that I’d love you guys to discuss: green tea. I used to try + drink it years ago but I always got an allergic reaction to it. So the question I’d like answered is: Will I still get the same allergic reaction if I take the capsules ? Also, because it’s caffeinated, will taking it interfere with iron pills, other vitamins + meds ? I read that the health benefits of the decaffeinated tea/capsules are not as great as the caffeinated. Any info would be greatly appreciated !! Thanks much !!❞
Hi! I’m not Sheila, but I’ll answer this one in the first person as I’ve had a similar issue:
I found long ago that taking any kind of tea (not herbal infusions, but true teas, e.g. green tea, black tea, red tea, etc) on an empty stomach made me want to throw up. The feeling would subside within about half an hour, but I learned it was far better to circumvent it by just not taking tea on an empty stomach.
However! I take an l-theanine supplement when I wake up, to complement my morning coffee, and have never had a problem with that. Of course, my physiology is not your physiology, and this “shouldn’t” be happening to either of us in the first place, so it’s not something there’s a lot of scientific literature about, and we just have to figure out what works for us.
This last Monday I wrote (inspired in part by your query) about l-theanine supplementation, and how it doesn’t require caffeine to unlock its benefits after all, by the way. So that’s that part in order.
I can’t speak for interactions with your other supplements or medications without knowing what they are, but I’m not aware of any known issue, beyond that l-theanine will tend to give a gentler curve to the expression of some neurotransmitters. So, if for example you’re talking anything that affects that (e.g. antidepressants, antipsychotics, ADHD meds, sleepy/wakefulness meds, etc) then checking with your doctor is best.
Share This Post
-
What Loneliness Does To Your Brain And Body
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Spoiler: it’s nothing good (but it can be addressed!)
Not something to be ignored
Loneliness raises the risk of heart disease by 29% and the risk of stroke by 32%. It also brings about higher susceptibility to illness (flu, COVID, chronic pain, etc), as well as poor sleep quality and cognitive decline, possibly leading to dementia. Not only that, but it also promotes inflammation, and premature death (comparable to smoking).
This is because the lack of meaningful social connections activates the body’s stress response, which in turn increases paranoia, suspicion, and social withdrawal—which makes it harder to seek the social interaction needed to alleviate it.
On a neurological level, cortisol levels become imbalanced, and a faltering dopamine response leads to impulsive behaviors (e.g., drinking, gambling) to try to make up for it. Decreased serotonin, oxytocin, and natural opioids reduce feelings of happiness and negate pain relief.
As for combatting it, the first-line remedy is the obvious one: connecting with others improves emotional and physical wellbeing. However, it is recommended to aim for deep, meaningful connections that make you happy rather than just socializing for its own sake. It’s perfectly possible to be lonely in a crowd, after all.
A second-line remedy is to simply mitigate the harm by means of such things as art therapy and time in nature—they can’t completely replace human connection, but they can at least improve the neurophysiological situation (which in turn, might be enough of a stop-gap solution to enable a return to human connection).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Fitness Walking and Bodyweight Exercises – by Frank S. Ring
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of exercise manuals assume that the reader has a “basic” body (nothing Olympian, but nothing damaged either). As we get older, increasingly few of us fall into the “but nothing damaged either” category!
Here’s where Ring brings to bear his decades of experience as a coach and educator, and also his personal recovery from a serious back injury.
The book covers direct, actionable exercise advice (with all manner of detail), and also offers mental health tips he’s learned along the way.
Ring, like us, is a big fan of keeping things simple, so he focusses on “the core four” of bodyweight exercises:
- Pushups
- Squats
- Lunges
- Planks
These four exercises get a whole chapter devoted to them, though! Because there are ways to make each exercise easier or harder, or have different benefits. For example, adjustments include:
- Body angle
- Points of contact
- Speed
- Pausing
- Range of motion
This, in effect, makes a few square meters of floor (and perhaps a chair or bench) your fully-equipped gym.
As for walking? Ring enjoys and extols the health benefits, and/but also uses his walks a lot for assorted mental exercises, and recommends we try them too.
A fine book for anyone who wants to gain and/or maintain good health, but doesn’t pressingly want to join a gym or start pumping iron!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How to Boost Your Metabolism When Over 50
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Dawn Andalon, a physiotherapist, explains the role of certain kinds of exercise in metabolism; here’s what to keep in mind:
Work with your body
Many people make the mistake of thinking that it is a somehow a battle of wills, and they must simply will their body to pick up the pace. That’s not how it works though, and while that can occasionally get short-term results, at best it’ll quickly result in exhaustion. So, instead:
- Strength training: engage in weight training 2–3 times per week; build muscle and combat bone loss too. Proper guidance from trainers familiar with older adults is recommended. Pilates (Dr. Andalon is a Pilates instructor) can also complement strength training by enhancing core stability and preventing injuries. The “building muscle” thing is important for metabolism, because muscle increases the body’s metabolic base rate.
- Protein intake: Dr. Andalon advises to consume 25–30 grams of lean protein per meal to support muscle growth and repair (again, important for the same reason as mentioned above re exercise). Dr. Andalon’s recommendation is more protein per meal than is usually advised, as it is generally held that the body cannot use more than about 20g at once.
- Sleep quality: prioritize good quality sleep, by practising good sleep hygiene, and also addressing any potential hormonal imbalances affecting sleep. If you do not get good quality sleep, your metabolism will get sluggish in an effort to encourage you to sleep more.
- Exercise to manage stress: regular walking (such as the popular 10,000 steps daily) helps manage stress and improve metabolism. Zone two cardio (low-intensity movement) also supports joint health, blood flow, and recovery—but the main issue about stress here is that if your body experiences unmanaged stress, it will try to save you from whatever is stressing you by reducing your metabolic base rate so that you can out-survive the bad thing. Which is helpful if the stressful thing is that the fruit trees got stripped by giraffes and hunting did not yield a kill, but not so helpful if the stressful thing is the holiday season.
- Hydration: your body cannot function properly without adequate hydration; water is needed (directly or indirectly) for all bodily processes, and your metabolism will also “dry up” without it.
- Antidiabetic & anti-inflammatory diet: minimize sugar intake and reduce processed foods, especially those with inflammatory refined oils (esp. canola & sunflower) and the like. This has very directly to do with your body’s energy metabolism, and as they say in computing, “garbage in; garbage out”.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Scarcity Brain – by Michael Easter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
After a brief overview of theevolutionary psychology underpinnings of the scarcity brain, the author grounds the rest of this book firmly in the present. He explains how the scarcity loop hooks us and why we crave more, and what factors can increase or lessen its hold over us.
As for what things we are wired to consider “potentially scarce any time now” no matter how saturated we are in them, he looks at an array of categories, each with their nuances. From the obvious such as “food” and “stuff“, to understandable “information” and “happiness“, to abstractions like “influence“, he goes to many sources—experts of various kinds from around the world—to explore how we can know “how much is enough”, and—which can be harder—act accordingly.
The key, he argues, is not in simply wanting less, but in understanding why we crave more in the first place, get rid of our worst habits, and use what we already have, better.
Bottom line: if you feel a gnawing sense of needing more “to be on the safe side”, this book can help you to be a little more strategic (and at the same time, less stressed!) about that.
Click here to check out Scarcity Brain, and manage yours more mindfully!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ear Candling: Is It Safe & Does It Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does This Practice Really Hold A Candle To Evidence-Based Medicine?
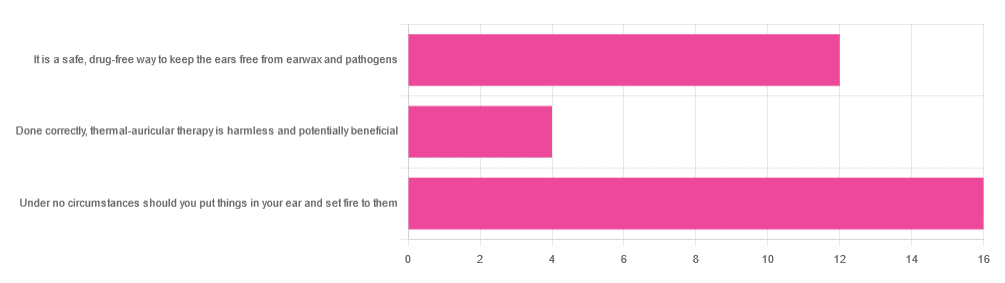
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion of ear candling, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- Exactly 50% said “Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them”
- About 38% said “It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens”
- About 13% said “Done correctly, thermal-auricular therapy is harmless and potentially beneficial”
This means that if we add the two positive-to-candling answers together, it’s a perfect 50:50 split between “do it” and “don’t do it”.
(Yes, 38%+13%=51%, but that’s because we round to the nearest integer in these reports, and more precisely it was 37.5% and 12.5%)
So, with the vote split, what does the science say?
First, a quick bit of background: nobody seems keen to admit to having invented this. One of the major manufacturers of ear candles refers to them as “Hopi” candles, which the actual Hopi tribe has spent a long time asking them not to do, as it is not and never has been used by the Hopi people. Other proposed origins offered by advocates of ear candling include Traditional Chinese Medicine (not used), Ancient Egypt (no evidence of such whatsoever), and Atlantis:
Quackwatch | Why Ear Candling Is Not A Good Idea
It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens: True or False?
False! In a lot of cases of alternative therapy claims, there’s an absence of evidence that doesn’t necessarily disprove the treatment. In this case, however, it’s not even an open matter; its claims have been actively disproven by experimentation:
- It doesn’t remove earwax; on the contrary, experimentation “showed no removal of cerumen from the external auditory canal. Candle wax was actually deposited in some“
- It doesn’t remove pathogens, and the proposed mechanism of action for removing pathogens, that of the “chimney effect”: the idea that the burning candle creates a vacuum that draws wax out of the ear along with debris and bacteria, simply does not work; on the contrary, “Tympanometric measurements in an ear canal model demonstrated that ear candles do not produce negative pressure”.
- It isn’t safe; on the contrary, “Ear candles have no benefit in the management of cerumen and may result in serious injury”
In a medium-sized survey (n=122), the following injuries were reported:
- 13 x burns
- 7 x occlusion of the ear canal
- 6 x temporary hearing loss
- 3 x otitis externa (this also called “swimmer’s ear”, and is an inflammation of the ear, accompanied by pain and swelling)
- 1 x tympanic membrane perforation
Indeed, authors of one paper concluded:
❝Ear candling appears to be popular and is heavily advertised with claims that could seem scientific to lay people. However, its claimed mechanism of action has not been verified, no positive clinical effect has been reliably recorded, and it is associated with considerable risk.
No evidence suggests that ear candling is an effective treatment for any condition. On this basis, we believe it can do more harm than good and we recommend that GPs discourage its use❞
Source: Canadian Family Physician | Ear Candling
Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them: True or False?
True! It’s generally considered good advice to not put objects in general in your ears.
Inserting flaming objects is a definite no-no. Please leave that for the Cirque du Soleil.
You may be thinking, “but I have done this and suffered no ill effects”, which seems reasonable, but is an example of survivorship bias in action—it doesn’t make the thing in question any safer, it just means you were one of the one of the ones who got away unscathed.
If you’re wondering what to do instead… Ear oils can help with the removal of earwax (if you don’t want to go get it sucked out at a clinic—the industry standard is to use a suction device, which actually does what ear candles claim to do). For information on safely getting rid of earwax, see our previous article:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: