What you need to know about xylazine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Xylazine is a non-opioid tranquilizer designed for veterinary use in animals. The sedative is not approved for use in people, yet it’s becoming more prevalent in the illicit drug supply.
Sometimes called “tranq,” it’s often mixed with other drugs, such as fentanyl, a potent opioid responsible for a growing number of overdose deaths. Last year, the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy declared fentanyl mixed with xylazine an “emerging threat.”
Read on to learn more about xylazine: what happens when people take it, what to do if an overdose is suspected, and how harm reduction tools can prevent overdose deaths.
How are people who use drugs exposed to xylazine?
Studies show people are exposed to xylazine—knowingly or unknowingly—when it’s mixed with other drugs like heroin, cocaine, meth, and, most frequently, fentanyl. When combined with opioids or other drugs, it increases the risk of a drug overdose.
What happens if someone takes xylazine?
Taking xylazine can cause drowsiness, amnesia, slow breathing, slow heart rate, dangerously low blood pressure, wounds that can become infected, and death, especially when taken in combination with other drugs.
Why does xylazine increase the risk of overdose?
Xylazine is a central nervous system depressant, which means that it slows down the body’s heart rate and breathing. It can also enhance the effects of other depressants, such as opioids, which may lead to suffocation.
What are the signs of a xylazine-related overdose?
Xylazine-related overdoses look like opioid overdoses. A person who has overdosed may exhibit a slow pulse, slow breathing, blurry vision, disorientation, drowsiness, confusion, blue skin, and loss of consciousness.
How many people die from xylazine-related overdoses in the U.S.?
Xylazine-related overdose deaths in the U.S. rose from 102 deaths in 2018 to 3,468 deaths in 2021. Most occurred in Delaware, the District of Columbia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia. Fentanyl was the most frequently co-occurring drug involved in those deaths.
What should I do if an overdose is suspected?
If you suspect that a person has overdosed on any drug, call 911 and give them naloxone—sometimes sold under the brand name Narcan—a medication that can reverse an opioid overdose. You should also stay with the person who has overdosed until first responders arrive. Most states have Good Samaritan laws, which protect people who have overdosed and those assisting them from certain criminal penalties.
While naloxone cannot reverse the effects of xylazine alone, experts recommend administering naloxone if an overdose is suspected because it’s often mixed with opioids.
You can get naloxone for free from some nonprofit organizations and government-run programs. You can also purchase over-the-counter naloxone at pharmacies, grocery and convenience stores, and other retailers.
Learn how to use naloxone in this short training video from the American Medical Association, or sign up for a free online training.
How can people prevent xylazine-related overdoses?
Harm reduction programs are community programs that prevent drug overdoses, reduce the spread of infectious diseases, and connect people to medical care. These programs provide lifesaving tools like naloxone, as well as fentanyl and xylazine test strips, which can detect the presence of these drugs in a substance and prevent overdoses. Drug test strips can also be ordered online.
However, test strips are considered “drug paraphernalia” in some states and are not legal everywhere. Learn more about state laws around drug checking equipment from the Network for Public Health Law.
Learn more about harm reduction from the CDC.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Neurologists Debunk 11 Brain Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Neuroscientists Dr. Santoshi Billakota and Dr. Brad Kamitaki debunk 11 myths about the brain. How many did you know?
From the top
Without further ado, the myths are…
- “We only use 10% of our brains”: False! We use most parts of our brain at different times, depending on the activity. PET/MRI scans show widespread usage.
- “The bigger the brain, the smarter the creature”: False! While there’s often a correlation, intelligence depends on brain complexity and development of specific regions, not overall size. For this reason get, for example, some corvids that are more intelligent than some dogs.
- “IQ tests are an accurate measure of intelligence”: False! IQ tests measure limited aspects of intelligence and are influenced by external factors like test conditions and education.
- “Video games rot your brain”: False! Video games can improve problem-solving, strategy, and team-building skills when played in moderation.
- “Memory gets worse as you age”: Partly false. While episodic memory may decline, semantic and procedural memory often improve with age.
- “Left-brained people are logical, and right-brained people are creative”: False! Both hemispheres work together, and personality or skills are influenced by environment and experiences, not brain hemispheres.
- “You can’t prevent a stroke”: False! Strokes can often be prevented by managing risk factors like blood pressure, cholesterol, and lifestyle choices.
- “Eating fish makes you smarter”: False! Eating fish, especially those rich in omega-3s, can support brain health but won’t increase intelligence.
- “You can always trust your senses”: False! Senses can be deceptive and influenced by emotions, memories, or neurological conditions.
- “Different sexes have different brains”: False! Structurally, brains are the same regardless of chromosomal sex; differences arise from environmental (including hormonal) and experiential factors—and even there, there’s more than enough overlap that we are far from categorizable as sexually dimorphic.
- “If you have a seizure, you have epilepsy”: False! A seizure can occur from various causes, but epilepsy is defined by recurrent unprovoked seizures and requires specific diagnosis and treatment.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Dopamine Myth ← a bonus 12th myth!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Gut-Positive Pot Noodles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everything we consume either improves our health a little or worsens it. Pot noodles aren’t generally the healthiest foods, but these ones sure are! There’s quite a range of fiber in this, including the soluble fiber of the noodles themselves (which are, in fact, mostly fiber and water). As a bonus, the glucomannan in the noodles promotes feelings of fullness, notwithstanding its negligible carb count. Of course, the protein in the edamame beans also counts for satiety!
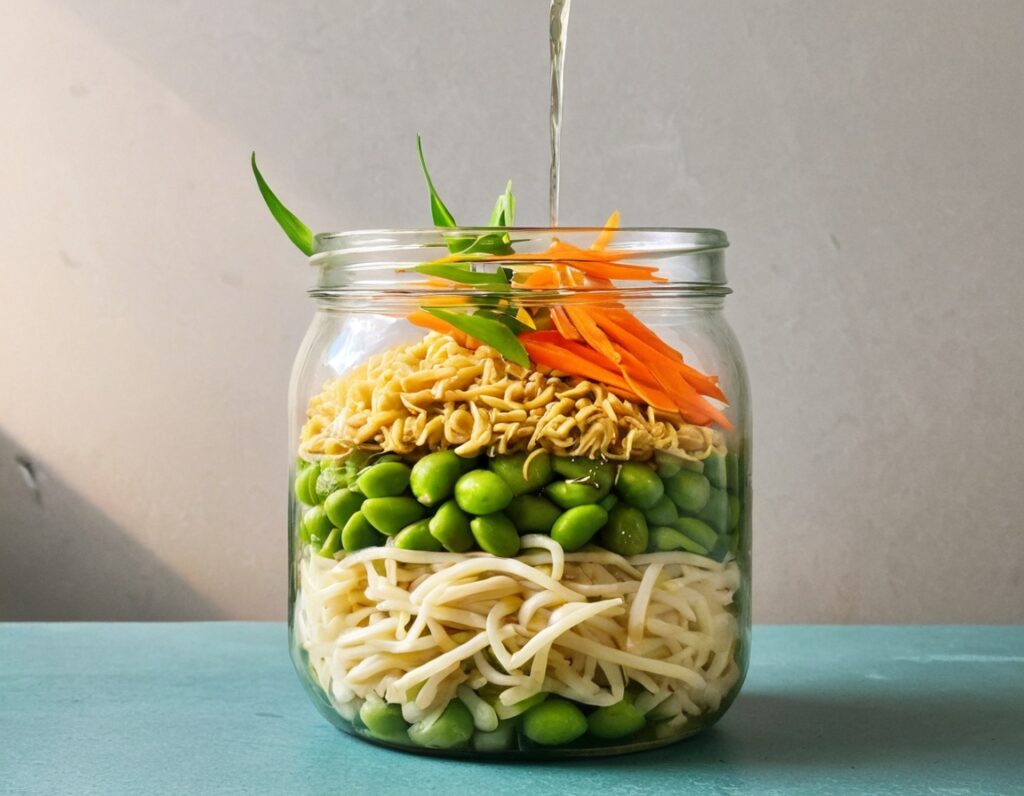
You will need
- ½ cup konjac noodles (also called shirataki), tossed in 1 tsp avocado oil (or sesame oil, if you don’t have avocado)
- 2 oz mangetout, thinly sliced
- 1 oz edamame beans
- ¼ carrot, grated
- 2 baby sweetcorn, cut in half lengthways
- 1 scallion, finely diced
- 1 heaped tsp crunchy peanut butter (omit if allergic)
- 1 tsp miso paste
- 1 tsp chili oil
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp peeled-and-grated ginger
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Layer a heat-resistant jar (mason jars are usually quite resistant to temperature changes) with the noodles and vegetables.
2) Combine the peanut butter, miso paste, and chili oil, black pepper, and ginger in a small bowl. Pour this dressing over the layered vegetables and noodles, and screw the lid on. Refrigerate until needed.
3) Add hot water to the jar and stir, to serve. If you prefer the vegetables to be more cooked, you can microwave (without the lid!) for a minute or two.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars ← today’s recipe makes a perfect high-fiber, low-carb starter, per the hacks here
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Are You Taking PIMs?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Getting Off The Overmedication Train
The older we get, the more likely we are to be on more medications. It’s easy to assume that this is because, much like the ailments they treat, we accumulate them over time. And superficially at least, that’s what happens.
And yet, almost half of people over 65 in Canada are taking “potentially inappropriate medications”, or PIMs—in other words, medications that are not needed and perhaps harmful. This categorization includes medications where the iatrogenic harms (side effects, risks) outweigh the benefits, and/or there’s a safer more effective medication available to do the job.
You may be wondering: what does this mean for the US?
Well, we don’t have the figures for the US because we’re working from Canadian research today, but given the differences between the two country’s healthcare systems (mostly socialized in Canada and mostly private in the US), it seems a fair hypothesis that if it’s almost half in Canada, it’s probably more than half in the US. Socialized healthcare systems are generally quite thrifty and seek to spend less on healthcare, while private healthcare systems are generally keen to upsell to new products/services.
The three top categories of PIMs according to the above study:
- Gabapentinoids (anticonvulsants also used to treat neuropathic pain)
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- Antipsychotics (especially, to people without psychosis)
…but those are just the top of the list; there are many many more.
The list continues: opioids, anticholinergics, sulfonlyurea, NSAIDs, benzodiazepines and related rugs, and cholinesterase inhibitors. That’s where the Canadian study cuts off (although it also includes “others” just before NSAIDs), but still, you guessed it, there are more (we’re willing to bet statins weigh heavily in the “others” section, for a start).
There are two likely main causes of overmedication:
The side effect train
This is where a patient has a condition and is prescribed drug A, which has some undesired side effects, so the patient is prescribed drug B to treat those. However, that drug also has some unwanted side effects of its own, so the patient is prescribed drug C to treat those. And so on.
For a real-life rundown of how this can play out, check out the case study in:
The Hidden Complexities of Statins and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
The convenience factor
No, not convenient for you. Convenient for others. Convenient for the doctor if it gets you out of their office (socialized healthcare) or because it was easy to sell (private healthcare). Convenient for the staff in a hospital or other care facility.
This latter is what happens when, for example, a patient is being too much trouble, so the staff give them promazine “to help them settle down”, notwithstanding that promazine is, besides being a sedative, also an antipsychotic whose common side effects include amenorrhea, arrhythmias, constipation, drowsiness and dizziness, dry mouth, impotence, tiredness, galactorrhoea, gynecomastia, hyperglycemia, insomnia, hypotension, seizures, tremor, vomiting and weight gain.
This kind of thing (and worse) happens more often towards the end of a patient’s life; indeed, sometimes precipitating that end, whether you want it or not:
Mortality, Palliative Care, & Euthanasia
How to avoid it
Good practice is to be “open-mindedly skeptical” about any medication. By this we mean, don’t reject it out of hand, but do ask questions about it.
Ask your prescriber not only what it’s for and what it’ll do, but also what the side effects and risks are, and an important question that many people don’t think to ask, and for which doctors thus don’t often have a well-prepared smooth-selling reply, “what will happen if I don’t take this?”
And look up unbiased neutral information about it, from reliable sources (Drugs.com and The BNF are good reference guides for this—and if it’s important to you, check both, in case of any disagreement, as they function under completely different regulatory bodies, the former being American and the latter being British. So if they both agree, it’s surely accurate, according to best current science).
Also: when you are on a medication, keep a journal of your symptoms, as well as a log of your vitals (heart rate, blood pressure, weight, sleep etc) so you know what the medication seems to be helping or harming, and be sure to have a regular meds review with your doctor to check everything’s still right for you. And don’t be afraid to seek a second opinion if you still have doubts.
Want to know more?
For a more in-depth exploration than we have room for here, check out this book that we reviewed not long back:
To Medicate or Not? That is the Question! – by Dr. Asha Bohannon
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Many Faces Of Cosmetic Surgery
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cosmetic Surgery: What’s The Truth?
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion on elective cosmetic surgeries, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 48% said “Everyone should be able to get what they want, assuming informed consent”
- About 28% said “It can ease discomfort to bring features more in line with normalcy”
- 15% said “They should be available in the case of extreme disfigurement only”
- 10% said “No elective cosmetic surgery should ever be performed; needless danger”
Well, there was a clear gradient of responses there! Not so polarizing as we might have expected, but still enough dissent for discussion
So what does the science say?
The risks of cosmetic surgery outweigh the benefits: True or False?
False, subjectively (but this is important).
You may be wondering: how is science subjective?
And the answer is: the science is not subjective, but people’s cost:worth calculations are. What’s worth it to one person absolutely may not be worth it to another. Which means: for those for whom it wouldn’t be worth it, they are usually the people who will not choose the elective surgery.
Let’s look at some numbers (specifically, regret rates for various surgeries, elective/cosmetic or otherwise):
- Regret rate for elective cosmetic surgery in general: 20%
- Regret rate for knee replacement (i.e., not cosmetic): 17.1%
- Regret rate for hip replacement (i.e., not cosmetic): 4.8%
- Regret rate for gender-affirming surgeries (for transgender patients): 1%
So we can see, elective surgeries have an 80–99% satisfaction rate, depending on what they are. In comparison, the two joint replacements we mentioned have a 82.9–95.2% satisfaction rate. Not too dissimilar, taken in aggregate!
In other words: if a person has studied the risks and benefits of a surgery and decides to go ahead, they’re probably going to be happy with the results, and for them, the benefits will have outweighed the risks.
Sources for the above numbers, by the way:
- What is the regret rate for plastic surgery?
- Decision regret after primary hip and knee replacement surgery
- A systematic review of patient regret after surgery—a common phenomenon in many specialties but rare within gender-affirmation surgery
But it’s just a vanity; therapy is what’s needed instead: True or False?
False, generally. True, sometimes. Whatever the reasons for why someone feels the way they do about their appearance—whether their face got burned in a fire or they just have triple-J cups that they’d like reduced, it’s generally something they’ve already done a lot of thinking about. Nevertheless, it does also sometimes happen that it’s a case of someone hoping it’ll be the magical solution, when in reality something else is also needed.
How to know the difference? One factor is whether the surgery is “type change” or “restorative”, and both have their pros and cons.
- In “type change” (e.g. rhinoplasty), more psychological adjustment is needed, but when it’s all over, the person has a new nose and, statistically speaking, is usually happy with it.
- In “restorative” (e.g. facelift), less psychological adjustment is needed (as it’s just a return to a previous state), so a person will usually be happy quickly, but ultimately it is merely “kicking the can down the road” if the underlying problem is “fear of aging”, for example. In such a case, likely talking therapy would be beneficial—whether in place of, or alongside, cosmetic surgery.
Here’s an interesting paper on that; the sample sizes are small, but the discussion about the ideas at hand is a worthwhile read:
Does cosmetic surgery improve psychosocial wellbeing?
Some people will never be happy no matter how many surgeries they get: True or False?
True! We’re going to refer to the above paper again for this one. In particular, here’s what it said about one group for whom surgeries will not usually be helpful:
❝There is a particular subgroup of people who appear to respond poorly to cosmetic procedures. These are people with the psychiatric disorder known as “body dysmorphic disorder” (BDD). BDD is characterised by a preoccupation with an objectively absent or minimal deformity that causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning.
For several reasons, it is important to recognise BDD in cosmetic surgery settings:
Firstly, it appears that cosmetic procedures are rarely beneficial for these people. Most patients with BDD who have had a cosmetic procedure report that it was unsatisfactory and did not diminish concerns about their appearance.
Secondly, BDD is a treatable disorder. Serotonin-reuptake inhibitors and cognitive behaviour therapy have been shown to be effective in about two-thirds of patients with BDD❞
~ Dr. David Castle et al. (lightly edited for brevity)
Which is a big difference compared to, for example, someone having triple-J breasts that need reducing, or the wrong genitals for their gender, or a face whose features are distinct outliers.
Whether that’s a reason people with BDD shouldn’t be able to get it is an ethical question rather than a scientific one, so we’ll not try to address that with science.
After all, many people (in general) will try to fix their woes with a haircut, a tattoo, or even a new sportscar, and those might sometimes be bad decisions, but they are still the person’s decision to make.
And even so, there can be protectionist laws/regulations that may provide a speed-bump, for example:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Relationships: When To Stick It Out & When To Call It Quits
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Like A Ship Loves An Anchor?
Today’s article may seem a little bit of a downer to start with, but don’t worry, it picks up again too. Simply put, we’ve written before about many of the good parts of relationships, e.g:
Only One Kind Of Relationship Promotes Longevity This Much!
…but what if that’s not what we have?
Note: if you have a very happy, secure, fulfilling, joyous relationship, then, great! Or if you’re single and happy, then, also great! Hopefully you will still find today’s feature of use if you find yourself advising a friend or family member one day. So without further ado, let’s get to it…
You may be familiar with the “sunk cost fallacy”; if not: it’s what happens when a person or group has already invested into a given thing, such that even though the thing is not going at all the way they hoped, they now want to continue trying to make that thing work, lest their previous investment be lost. But the truth is: if it’s not going to work, then the initial investment is already lost, and pouring out extra won’t help—it’ll just lose more.
That “investment” in a given thing could be money, time, energy, or (often the case) a combination of the above.
In the field of romance, the “sunk cost fallacy” keeps a lot of bad relationships going for longer than perhaps they should, and looking back (perhaps after a short adjustment period), the newly-single person says “why did I let that go on?” and vows to not make the same mistake again.
But that prompts the question: how can we know when it’s right to “keep working on it, because relationships do involve work”, as perfectly reasonable relationship advice often goes, and when it’s right to call it quits?
Should I stay or should I go?
Some questions for you (or perhaps a friend you might find yourself advising) to consider:
- What qualities do you consider the most important for a partner to have—and does your partner have them?
- If you described the worst of your relationship to a close friend, would that friend feel bad for you?
- Do you miss your partner when they’re away, or are you glad of the break? When they return, are they still glad to see you?
- If you weren’t already in this relationship, would you seek to enter it now? (This takes away sunk cost and allows a more neutral assessment)
- Do you feel completely safe with your partner (emotionally as well as physically), or must you tread carefully to avoid conflict?
- If your partner decided tomorrow that they didn’t want to be with you anymore and left, would that be just a heartbreak, or an exciting beginning of a new chapter in your life?
- What things would you generally consider dealbreakers in a relationship—and has your partner done any of them?
The last one can be surprising, by the way. We often see or hear of other people’s adverse relationship situations and think “I would never allow…” yet when we are in a relationship and in love, there’s a good chance that we might indeed allow—or rather, excuse, overlook, and forgive.
And, patience and forgiveness certainly aren’t inherently bad traits to have—it’s just good to deploy them consciously, and not merely be a doormat.
Either way, reflect (or advise your friend/family member to reflect, as applicable) on the “score” from the above questions.
- If the score is good, then maybe it really is just a rough patch, and the tools we link at the top and bottom of this article might help.
- If the score is bad, the relationship is bad, and no amount of historic love or miles clocked up together will change that. Sometimes it’s not even anyone’s fault; sometimes a relationship just ran its course, and now it’s time to accept that and turn to a new chapter.
“At my age…”
As we get older, it’s easy for that sunk cost fallacy to loom large. Inertia is heavy, the mutual entanglement of lives is far-reaching, and we might not feel we have the same energy for dating that we did when we were younger.
And there may sometimes be a statistical argument for “sticking it out” at least for a while, depending on where we are in the relationship, per this study (with 165,039 participants aged 20–76), which found:
❝Results on mean levels indicated that relationship satisfaction decreased from age 20 to 40, reached a low point at age 40, then increased until age 65, and plateaued in late adulthood.
As regards the metric of relationship duration, relationship satisfaction decreased during the first 10 years of the relationship, reached a low point at 10 years, increased until 20 years, and then decreased again.❞
Source: Development of Relationship Satisfaction Across the Life Span: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
And yet, when it comes to prospects for a new relationship…
- If our remaining life is growing shorter, then it’s definitely too short to spend in an unhappy relationship
- Maybe we really won’t find romance again… And maybe that’s ok, if w’re comfortable making our peace with that and finding joy in the rest of life (this widowed writer (hi, it’s me) plans to remain single now by preference, and her life is very full of purpose and beauty and joy and yes, even love—for family, friends, etc, plus the memory of my wonderful late beloved)
- Nevertheless, the simple fact is: many people do find what they go on to describe as their best relationship yet, late in life ← this study is with a small sample size, but in this case, even anecdotal evidence seems sufficient to make the claim reasonable; probably you personally know someone who has done so. If they can, so can you, if you so wish.
- Adding on to that last point… Later life relationships can also offer numerous significant advantages unique to such (albeit some different challenges too—but with the right person, those challenges are just a fun thing to tackle together). See for example:
An exploratory investigation into dating among later‐life women
And about those later-life relationships that do work? They look like this:
this one looks like the title says it all, but it really doesn’t, and it’s very much worth at least reading the abstract, if not the entire paper—because it talks a lot about the characteristics that make for happy or unhappy relationships, and the effect that those things have on people. It really is very good, and quite an easy read.
See again: Healthy Relationship, Healthy Life
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Thinking, Fast and Slow – by Dr. Daniel Kahneman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all try to make the best decisions we can with the information available… Don’t we?
Yet, somehow, a survival chance of 90% seems better than a mortality rate of 10%, and as it turns out, we as fallible humans are prey to all manner of dubious heuristics.
Nobel Prize winner Dr. Daniel Kahneman lays out for us two sytems of thought process:
- Fast, intuitive, emotional
- Slow, deliberate, logical
He makes the case for how and why we do need both, but often end up using the wrong one. He notes how the first is required for efficiency, or we would spend all day deciding what socks to wear… The second, meanwhile, is required for high-stakes decisions, but is lazy by nature, and often we don’t engage it when we ought to.
Over the course of many diverse examples, Dr. Kahneman shows how again and again, the second system is slowly cogitating at the back of the class, while the first system is bouncing up and down with its hand in the air saying “I know! I know!”, even when, in fact, it does not know.
For a book largely founded in economics (it’s a massive takedown of the notion of the rational consumer), it is not at all dry, and is very readable in style. It’s engaging throughout, and readers far removed from Wall Street will find plenty of ways it relates to our everyday lives.
Bottom line: if you’d like to avoid making many mistakes in what you’d assumed to be rational decisions, this book is critical reading.
Click here to check out “Thinking, Fast And Slow”, and enjoy the results of better decisions!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: