What is pathological demand avoidance – and how is it different to ‘acting out’?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Charlie” is an eight-year-old child with autism. Her parents are worried because she often responds to requests with insults, aggression and refusal. Simple demands, such as being asked to get dressed, can trigger an intense need to control the situation, fights and meltdowns.
Charlie’s parents find themselves in a constant cycle of conflict, trying to manage her and their own reactions, often unsuccessfully. Their attempts to provide structure and consequences are met with more resistance.
What’s going on? What makes Charlie’s behaviour – that some are calling “pathological demand avoidance” – different to the defiance most children show their parents or carers from time-to-time?
What is pathological demand avoidance?
British developmental psychologist Elizabeth Newson coined the term “pathological demand avoidance” (commonly shortened to PDA) in the 1980s after studying groups of children in her practice.
A 2021 systematic review noted features of PDA include resistance to everyday requests and strong emotional and behavioural reactions.
Children with PDA might show obsessive behaviour, struggle with persistence, and seek to control situations. They may struggle with attention and impulsivity, alongside motor and coordination difficulties, language delay and a tendency to retreat into role play or fantasy worlds.
PDA is also known as “extreme demand avoidance” and is often described as a subtype of autism. Some people prefer the term persistent drive for autonomy or pervasive drive for autonomy.
What does the evidence say?
Every clinician working with children and families recognises the behavioural profile described by PDA. The challenging question is why these behaviours emerge.
PDA is not currently listed in the two diagnostic manuals used in psychiatry and psychology to diagnose mental health and developmental conditions, the current Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and the World Health Organization’s International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11).
Researchers have reported concerns about the science behind PDA. There are no clear theories or explanations of why or how the profile of symptoms develop, and little inclusion of children or adults with lived experience of PDA symptoms in the studies. Environmental, family or other contextual factors that may contribute to behaviour have not been systematically studied.
A major limitation of existing PDA research and case studies is a lack of consideration of overlapping symptoms with other conditions, such as autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder, anxiety disorder, selective mutism and other developmental disorders. Diagnostic labels can have positive and negative consequences and so need to be thoroughly investigated before they are used in practice.
Classifying a “new” condition requires consistency across seven clinical and research aspects: epidemiological data, long-term patient follow-up, family inheritance, laboratory findings, exclusion from other conditions, response to treatment, and distinct predictors of outcome. At this stage, these domains have not been established for PDA. It is not clear whether PDA is different from other formal diagnoses or developmental differences.

Finding the why
Debates over classification don’t relieve distress for a child or those close to them. If a child is “intentionally” engaged in antisocial behaviour, the question is then “why?”
Beneath the behaviour is almost always developmental difference, genuine distress and difficulty coping. A broad and deep understanding of developmental processes is required.
Interestingly, while girls are “under-represented” in autism research, they are equally represented in studies characterising PDA. But if a child’s behaviour is only understood through a “pathologising” or diagnostic lens, there is a risk their agency may be reduced. Underlying experiences of distress, sensory overload, social confusion and feelings of isolation may be missed.
So, what can be done to help?
There are no empirical studies to date regarding PDA treatment strategies or their effectiveness. Clinical advice and case studies suggest strategies that may help include:
- reducing demands
- giving multiple options
- minimising expectations to avoid triggering avoidance
- engaging with interests to support regulation.
Early intervention in the preschool and primary years benefits children with complex developmental differences. Clinical care that involves a range of medical and allied health clinicians and considers the whole person is needed to ensure children and families get the support they need.
It is important to recognise these children often feel as frustrated and helpless as their caregivers. Both find themselves stuck in a repetitive cycle of distress, frustration and lack of progress. A personalised approach can take into account the child’s unique social, sensory and cognitive sensitivities.
In the preschool and early primary years, children have limited ability to manage their impulses or learn techniques for managing their emotions, relationships or environments. Careful watching for potential triggers and then working on timetables and routines, sleep, environments, tasks, and relationships can help.
As children move into later primary school and adolescence, they are more likely to want to influence others and be able to have more self control. As their autonomy and ability to collaborate increases, the problematic behaviours tend to reduce.
Strategies that build self-determination are crucial. They include opportunities for developing confidence, communication and more options to choose from when facing challenges. This therapeutic work with children and families takes time and needs to be revisited at different developmental stages. Support to engage in school and community activities is also needed. Each small step brings more capacity and more effective ways for a child to understand and manage themselves and their worlds.
What about Charlie?
The current scope to explain and manage PDA is limited. Future research must include the voices and views of children and adults with PDA symptoms.
Such emotional and behavioural difficulties are distressing and difficult for children and families. They need compassion and practical help.
For a child like Charlie, this could look like a series of sessions where she and her parents meet with clinicians to explore Charlie’s perspective, experiences and triggers. The family might come to understand that, in addition to autism, Charlie has complex developmental strengths and challenges, anxiety, and some difficulties with adjustment related to stress at home and school. This means Charlie experiences a fight, flight, freeze response that looks like aggression, avoidance or shutting down.
With carefully planned supports at home and school, Charlie’s options can broaden and her distress and avoidance can soften. Outside the clinic room, Charlie and her family can be supported to join an inclusive local community sporting or creative activity. Gradually she can spend more time engaged at home, school and in the community.
Nicole Rinehart, Professor, Child and Adolescent Psychology, Director, Krongold Clinic (Research), Monash University; David Moseley, Senior Research Fellow, Deputy Director (Clinical), Monash Krongold Clinic, Monash University, and Michael Gordon, Associate Professor, Psychiatry, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
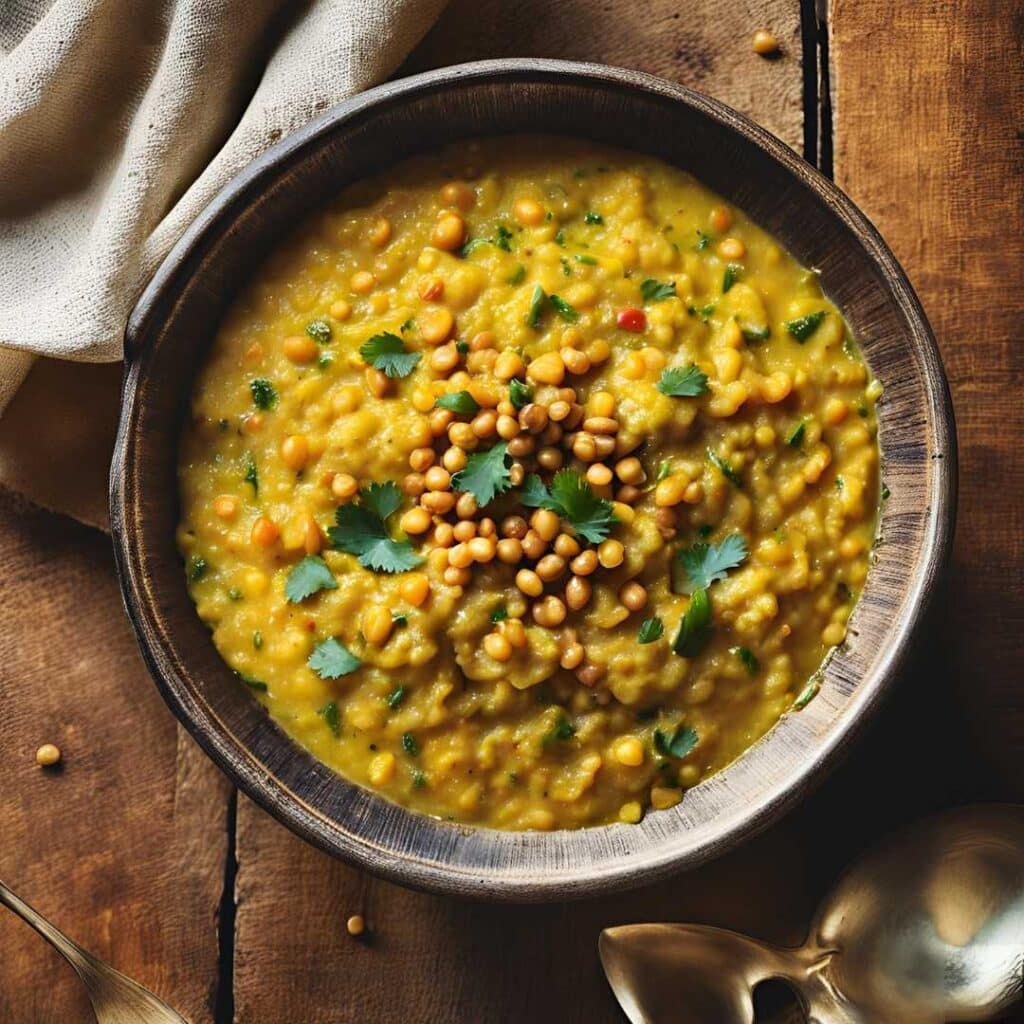
Anti-Inflammatory Khichri & Tadka
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is halfway between a daal and a risotto; it’s delicious and it’s full of protein, fiber, heathy fats, and flavors. And those flavors? Mostly from health-giving phytochemicals of one kind of another.
You will need
For the khichri:
- 1 oz chana dal
- 1 oz red lentils
- 1 oz brown lentils
- 1 oz quinoa
- 4 oz wholegrain basmati rice
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
For the tadka:
- 2 tbsp avocado oil (or other oil suitable for high temperatures—so, not olive oil on this occasion!)
- ¼ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 1 fresh red chili (adjust per heat preferences)
- 1 fresh green chili (adjust per heat preferences)
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 6 curry leaves
- 12 twists of freshly ground black pepper
To serve:
- Optional: flatbreads or poppadoms
- Optional: lemon wedges or lime wedges
- Optional: chopped cilantro or parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Simmer the khichri ingredients in 5 cups of water, stirring occasionally if necessary, until it has a risotto-like consistency; this will probably take about 30–40 minutes. This time can be greatly reduced by using a pressure cooker, but obviously you won’t be able to check or stir, so do that only if you know what you’re doing cooking those grains and pseudograins in there, and what settings/timings to use for your specific device.
2) Make the tadka when the khichri is nearly ready, by heating the 2 tbsp of avocado oil in a skillet until very hot but not smoking, Add the rest of the ingredients from the tadka section, and cook until the garlic is nice and golden.
3) Pour the tadka over the khichri to serve, with any of the optional accompaniments we mentioned.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Diabetes Code – by Dr. Jason Fung
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cure this serious disease with diet!” is often a bold-claim that overreaches scientific rigor, but in this case, it’s well-established as scientifically valid.
Caveat up-front: the only known circumstance in which this won’t work is if you have comorbidities that prevent you from following the advice.
You may be wondering: is this just the Mediterranean diet again? The answer is that the Mediterreanean diet (or similar) is part of it. But there’s a lot more to this book than that.
Dr. Fung explains to us a lot of the physiology of type 2 diabetes; how insulin resistance occurs, how it becomes a vicious cycle that we get locked into, and how to escape it.
- We learn about the role of fructose, and why fruit is very healthful whereas high-fructose corn syrup and similars are very much not.
- We learn about the role of the liver in glycogen metabolism, and how to un-fatty a fatty liver. Good news: the liver has famously strong self-regenerative abilities, if we give it a break to allow it to do so!
- We learn why portion control doesn’t work, and why intermittent fasting does (here be science).
Dr. Fung’s very readable explanations are free from needless jargon while not dumbing down. The writing style is clear and direct: “this happens this way”, “do this, not that”, etc.
Bottom line: if you have type 2 diabetes and would like to not have that (or if you are pre-diabetic and would like to avoid diabetes) this is a book for you. If you are in great metabolic health and would like to stay that way as you get older, then this is a book for you too.
Click here to check out The Diabetes Code, and get/keep your metabolic health in order!
Share This Post
-
What Your Doctor Wants You to Know to Crush Medical Debt – by Dr. Virgie Ellington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First things first: this one’s really only of relevance to people living in the US. That’s most of our readership, but if it’s not you, then apologies, this one won’t be of interest.
For the US Americans, though, Dr. Ellington starts strong with “you got a bill—now get the right bill”, and then gives a step-by-step process for finding the mistakes in your medical bills, fixing them, dealing with insurers who do not want to live up to their part of the bargain, and how to minimize what you need to pay, when you actually arrive at your final bill.
The biggest strength of this book is the wealth of insider knowledge (the author has worked as a primary care physician as well as as a health insurance executive), and while this information won’t stay current forever, its relatively recent publication date (2022) means that little has changed since then, and once you’re up to speed with how things are now, it’ll be easy to roll with whatever changes may come in the future.
Bottom line: if you’re living in the US and would like to not be ripped off as badly as possible when it comes to healthcare costs, this book is a very small, very powerful, investment.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Women are less likely to receive CPR than men. Training on manikins with breasts could help
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If someone’s heart suddenly stops beating, they may only have minutes to live. Doing CPR (cardiopulmonary resusciation) can increase their chances of survival. CPR makes sure blood keeps pumping, providing oxygen to the brain and vital organs until specialist treatment arrives.
But research shows bystanders are less likely to intervene to perform CPR when that person is a woman. A recent Australian study analysed 4,491 cardiac arrests between 2017–19 and found bystanders were more likely to give CPR to men (74%) than women (65%).
Could this partly be because CPR training dummies (known as manikins) don’t have breasts? Our new research looked at manikins available worldwide to train people in performing CPR and found 95% are flat-chested.
Anatomically, breasts don’t change CPR technique. But they may influence whether people attempt it – and hesitation in these crucial moments could mean the difference between life and death.
Pixel-Shot/Shutterstock Heart health disparities
Cardiovascular diseases – including heart disease, stroke and cardiac arrest – are the leading cause of death for women across the world.
But if a woman has a cardiac arrest outside hospital (meaning her heart stops pumping properly), she is 10% less likely to receive CPR than a man. Women are also less likely to survive CPR and more likely to have brain damage following cardiac arrests.
Bystanders are less likely to intervene if a woman needs CPR, compared to a man. doublelee/Shutterstock These are just some of many unequal health outcomes women experience, along with transgender and non-binary people. Compared to men, their symptoms are more likely to be dismissed or misdiagnosed, or it may take longer for them to receive a diagnosis.
Bystander reluctance
There is also increasing evidence women are less likely to receive CPR compared to men.
This may be partly due to bystander concerns they’ll be accused of sexual harassment, worry they might cause damage (in some cases based on a perception women are more “frail”) and discomfort about touching a woman’s breast.
Bystanders may also have trouble recognising a woman is experiencing a cardiac arrest.
Even in simulations of scenarios, researchers have found those who intervened were less likely to remove a woman’s clothing to prepare for resuscitation, compared to men. And women were less likely to receive CPR or defibrillation (an electric charge to restart the heart) – even when the training was an online game that didn’t involve touching anyone.
There is evidence that how people act in resuscitation training scenarios mirrors what they do in real emergencies. This means it’s vital to train people to recognise a cardiac arrest and be prepared to intervene, across genders and body types.
Skewed to male bodies
Most CPR training resources feature male bodies, or don’t specify a sex. If the bodies don’t have breasts, it implies a male default.
For example, a 2022 study looking at CPR training across North, Central and South America, found most manikins available were white (88%), male (94%) and lean (99%).
It’s extremely rare for a manikin to have breasts or a larger body. M Isolation photo/Shutterstock These studies reflect what we see in our own work, training other health practitioners to do CPR. We have noticed all the manikins available to for training are flat-chested. One of us (Rebecca) found it difficult to find any training manikins with breasts.
A single manikin with breasts
Our new research investigated what CPR manikins are available and how diverse they are. We identified 20 CPR manikins on the global market in 2023. Manikins are usually a torso with a head and no arms.
Of the 20 available, five (25%) were sold as “female” – but only one of these had breasts. That means 95% of available CPR training manikins were flat-chested.
We also looked at other features of diversity, including skin tone and larger bodies. We found 65% had more than one skin tone available, but just one was a larger size body. More research is needed on how these aspects affect bystanders in giving CPR.
Breasts don’t change CPR technique
CPR technique doesn’t change when someone has breasts. The barriers are cultural. And while you might feel uncomfortable, starting CPR as soon as possible could save a life.
Signs someone might need CPR include not breathing properly or at all, or not responding to you.
To perform effective CPR, you should:
- put the heel of your hand on the middle of their chest
- put your other hand on the top of the first hand, and interlock fingers (keep your arms straight)
- press down hard, to a depth of about 5cm before releasing
- push the chest at a rate of 100-120 beats per minute (you can sing a song) in your head to help keep time!)
https://www.youtube.com/embed/Plse2FOkV4Q?wmode=transparent&start=94 An example of how to do CPR – with a flat-chested manikin.
What about a defibrillator?
You don’t need to remove someone’s bra to perform CPR. But you may need to if a defibrillator is required.
A defibrillator is a device that applies an electric charge to restore the heartbeat. A bra with an underwire could cause a slight burn to the skin when the debrillator’s pads apply the electric charge. But if you can’t remove the bra, don’t let it delay care.
What should change?
Our research highlights the need for a range of CPR training manikins with breasts, as well as different body sizes.
Training resources need to better prepare people to intervene and perform CPR on people with breasts. We also need greater education about women’s risk of getting and dying from heart-related diseases.
Jessica Stokes-Parish, Assistant Professor in Medicine, Bond University and Rebecca A. Szabo, Honorary Senior Lecturer in Critical Care and Obstetrics, Gynaecology and Newborn Health, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
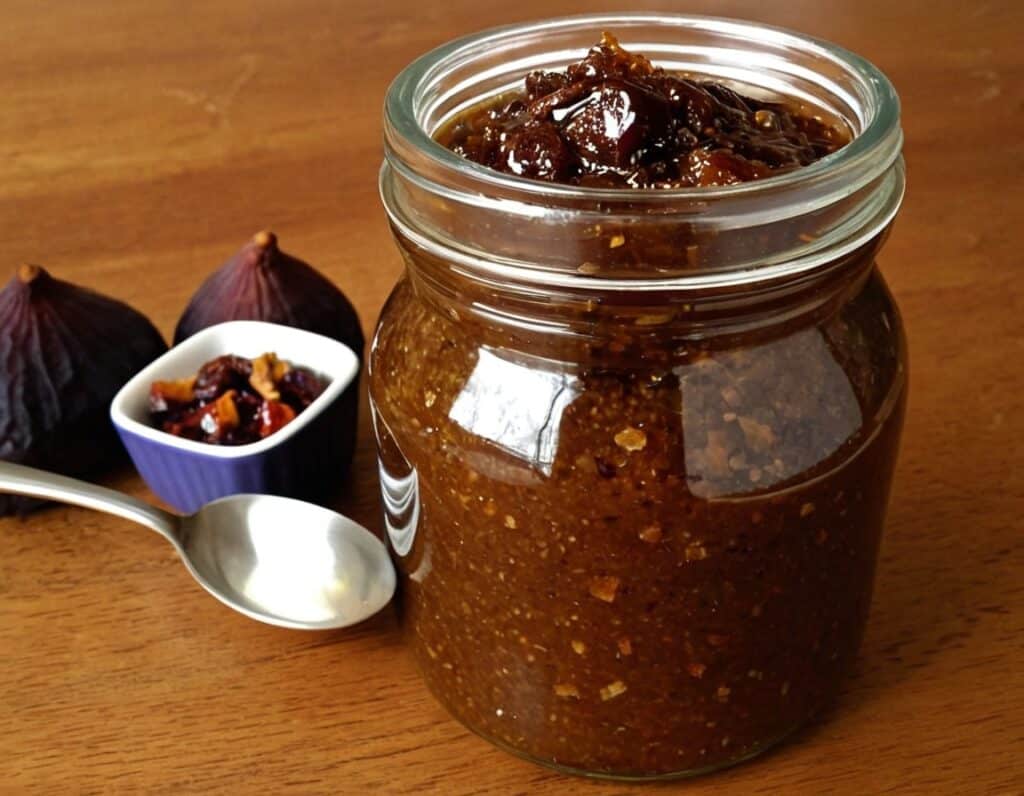
Spiced Fruit & Nut Chutney
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
‘Tis the season to make the chutney that will then be aged chutney when you want it later! And unlike supermarket varieties with their ingredients list that goes “Sugar, spirit vinegar, inverted glucose-fructose syrup,” this one has an array of health-giving fruits and nuts (just omit the nuts if you or someone you may want to give this to has an allergy), and really nothing bad in here at all. And of course, tasty healthful spices!
You will need
- 2 red onions, chopped
- 1½ cups dried apricots, chopped
- 1½ cups dried figs, chopped
- 1 cup raisins
- ½ cup apple cider vinegar
- ½ cup slivered almonds
- ½ lime, chopped and deseeded
- ¼ bulb garlic, chopped
- 1 hot pepper, chopped (your choice what kind; omit if you don’t like heat at all; multiply if you want more heat)
- 2 tablespoons honey or maple syrup (omit for a less sweet chutney; there is sweetness in the dried fruits already, after all)
- 1 tbsp freshly grated ginger
- 2 tsp sweet cinnamon
- 1 tsp nutmeg
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ teaspoon allspice
- ½ MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Heat some oil in a heavy-based pan that will be large enough for all ingredients to go into eventually. Fry the onions on a gentle heat for around 15 minutes. We don’t need to caramelize them yet (this will happen with time), but we do want them soft and sweet already.
2) Add the ginger, garlic, and chili, and stir in well.
3) When the onions start to brown, add the fruit and stir well to mix thoroughly.
4) Add the honey or maple syrup (if using), and the vinegar; add the remaining spices/seasonings, so everything is in there now except the almonds.
5) Cook gently for another 30 minutes while stirring. At some point it’ll become thick and sticky; add a little water as necessary. You don’t want to drown it, but you do want it to stay moist. It’ll probably take only a few tablespoons of added water in total, but add them one at a time and stir in before judging whether more is needed. By the end of the 30 minutes, it should be more solid, to the point it can stand up by itself.
6) Add the almonds, stir to combine, and leave to cool. Put it in jars until you need it (or perhaps give it as gifts).
Alternative method: if you don’t want to be standing at a stove stirring for about an hour in total, you can use a slow cooker / crock pot instead. Put the same ingredients in the same order, but don’t stir them, just leave them in layers (this is because of the pattern of heat distribution; it’ll be hotter at the bottom, so the things that need to be more cooked should be there, and the design means they won’t burn) for about two hours, then stir well to mix thoroughly, and leave it for another hour or two, before turning it off to let it cool. Put it in jars until you need it (or perhaps give it as gifts).
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← figs and apricots appear here
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess
- Almonds vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier? ← almonds won, but walnuts were close and would also work in this recipe
- Pistachios vs Almonds – Which is Healthier? ← almonds won, but pistachios were close and would also work in this recipe
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored 4/5 today!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Women and Minorities Bear the Brunt of Medical Misdiagnosis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Charity Watkins sensed something was deeply wrong when she experienced exhaustion after her daughter was born.
At times, Watkins, then 30, had to stop on the stairway to catch her breath. Her obstetrician said postpartum depression likely caused the weakness and fatigue. When Watkins, who is Black, complained of a cough, her doctor blamed the flu.
About eight weeks after delivery, Watkins thought she was having a heart attack, and her husband took her to the emergency room. After a 5½-hour wait in a North Carolina hospital, she returned home to nurse her baby without seeing a doctor.
When a physician finally examined Watkins three days later, he immediately noticed her legs and stomach were swollen, a sign that her body was retaining fluid. After a chest X-ray, the doctor diagnosed her with heart failure, a serious condition in which the heart becomes too weak to adequately pump oxygen-rich blood to organs throughout the body. Watkins spent two weeks in intensive care.
She said a cardiologist later told her, “We almost lost you.”
Watkins is among 12 million adults misdiagnosed every year in the U.S.
In a study published Jan. 8 in JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers found that nearly 1 in 4 hospital patients who died or were transferred to intensive care had experienced a diagnostic error. Nearly 18% of misdiagnosed patients were harmed or died.
In all, an estimated 795,000 patients a year die or are permanently disabled because of misdiagnosis, according to a study published in July in the BMJ Quality & Safety periodical.
Some patients are at higher risk than others.
Women and racial and ethnic minorities are 20% to 30% more likely than white men to experience a misdiagnosis, said David Newman-Toker, a professor of neurology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and the lead author of the BMJ study. “That’s significant and inexcusable,” he said.
Researchers call misdiagnosis an urgent public health problem. The study found that rates of misdiagnosis range from 1.5% of heart attacks to 17.5% of strokes and 22.5% of lung cancers.
Weakening of the heart muscle — which led to Watkins’ heart failure — is the most common cause of maternal death one week to one year after delivery, and is more common among Black women.
Heart failure “should have been No. 1 on the list of possible causes” for Watkins’ symptoms, said Ronald Wyatt, chief science and chief medical officer at the Society to Improve Diagnosis in Medicine, a nonprofit research and advocacy group.
Maternal mortality for Black mothers has increased dramatically in recent years. The United States has the highest maternal mortality rate among developed countries. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, non-Hispanic Black mothers are 2.6 times as likely to die as non-Hispanic white moms. More than half of these deaths take place within a year after delivery.
Research shows that Black women with childbirth-related heart failure are typically diagnosed later than white women, said Jennifer Lewey, co-director of the pregnancy and heart disease program at Penn Medicine. That can allow patients to further deteriorate, making Black women less likely to fully recover and more likely to suffer from weakened hearts for the rest of their lives.
Watkins said the diagnosis changed her life. Doctors advised her “not to have another baby, or I might need a heart transplant,” she said. Being deprived of the chance to have another child, she said, “was devastating.”
Racial and gender disparities are widespread.
Women and minority patients suffering from heart attacks are more likely than others to be discharged without diagnosis or treatment.
Black people with depression are more likely than others to be misdiagnosed with schizophrenia.
Minorities are less likely than whites to be diagnosed early with dementia, depriving them of the opportunities to receive treatments that work best in the early stages of the disease.
Misdiagnosis isn’t new. Doctors have used autopsy studies to estimate the percentage of patients who died with undiagnosed diseases for more than a century. Although those studies show some improvement over time, life-threatening mistakes remain all too common, despite an array of sophisticated diagnostic tools, said Hardeep Singh, a professor at Baylor College of Medicine who studies ways to improve diagnosis.
“The vast majority of diagnoses can be made by getting to know the patient’s story really well, asking follow-up questions, examining the patient, and ordering basic tests,” said Singh, who is also a researcher at Houston’s Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center. When talking to people who’ve been misdiagnosed, “one of the things we hear over and over is, ‘The doctor didn’t listen to me.’”
Racial disparities in misdiagnosis are sometimes explained by noting that minority patients are less likely to be insured than white patients and often lack access to high-quality hospitals. But the picture is more complicated, said Monika Goyal, an emergency physician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington, D.C., who has documented racial bias in children’s health care.
In a 2020 study, Goyal and her colleagues found that Black kids with appendicitis were less likely than their white peers to be correctly diagnosed, even when both groups of patients visited the same hospital.
Although few doctors deliberately discriminate against women or minorities, Goyal said, many are biased without realizing it.
“Racial bias is baked into our culture,” Goyal said. “It’s important for all of us to start recognizing that.”
Demanding schedules, which prevent doctors from spending as much time with patients as they’d like, can contribute to diagnostic errors, said Karen Lutfey Spencer, a professor of health and behavioral sciences at the University of Colorado-Denver. “Doctors are more likely to make biased decisions when they are busy and overworked,” Spencer said. “There are some really smart, well-intentioned providers who are getting chewed up in a system that’s very unforgiving.”
Doctors make better treatment decisions when they’re more confident of a diagnosis, Spencer said.
In an experiment, researchers asked doctors to view videos of actors pretending to be patients with heart disease or depression, make a diagnosis, and recommend follow-up actions. Doctors felt far more certain diagnosing white men than Black patients or younger women.
“If they were less certain, they were less likely to take action, such as ordering tests,” Spencer said. “If they were less certain, they might just wait to prescribe treatment.”
It’s easy to see why doctors are more confident when diagnosing white men, Spencer said. For more than a century, medical textbooks have illustrated diseases with stereotypical images of white men. Only 4.5% of images in general medical textbooks feature patients with dark skin.
That may help explain why patients with darker complexions are less likely to receive a timely diagnosis with conditions that affect the skin, from cancer to Lyme disease, which causes a red or pink rash in the earliest stage of infection. Black patients with Lyme disease are more likely to be diagnosed with more advanced disease, which can cause arthritis and damage the heart. Black people with melanoma are about three times as likely as whites to die within five years.
The covid-19 pandemic helped raise awareness that pulse oximeters — the fingertip devices used to measure a patient’s pulse and oxygen levels — are less accurate for people with dark skin. The devices work by shining light through the skin; their failures have delayed critical care for many Black patients.
Seven years after her misdiagnosis, Watkins is an assistant professor of social work at North Carolina Central University in Durham, where she studies the psychosocial effects experienced by Black mothers who survive severe childbirth complications.
“Sharing my story is part of my healing,” said Watkins, who speaks to medical groups to help doctors improve their care. “It has helped me reclaim power in my life, just to be able to help others.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: