Red Light, Go!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Casting Yourself In A Healthier Light
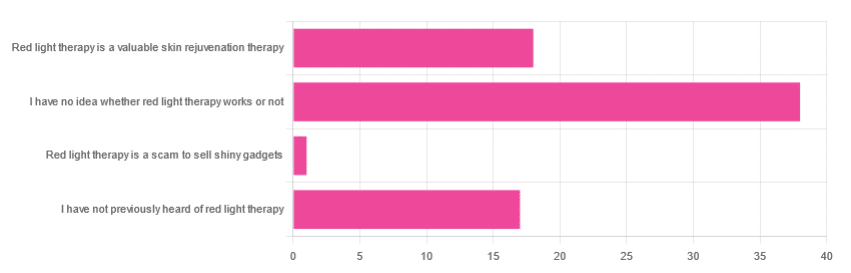
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of red light therapy (henceforth: RLT), and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 51% said “I have no idea whether light therapy works or not”
- About 24% said “Red light therapy is a valuable skin rejuvenation therapy”
- About 23% said “I have not previously heard of red light therapy”
- One (1) person said: “Red light therapy is a scam to sell shiny gadgets”
A number of subscribers wrote with personal anecdotes of using red light therapy to beneficial effect, for example:
❝My husband used red light therapy after surgery on his hand. It did seem to speed healing of the incision and there is very minimal scarring. I would like to know if the red light really helped or if he was just lucky❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
And one wrote to report having observed mixed results amongst friends, per:
❝Some people it works, others I’ve seen it breaks them out❞
~ 10almonds subscriber
So, what does the science say?
RLT rejuvenates skin, insofar as it reduces wrinkles and fine lines: True or False?
True! This one’s pretty clear-cut, so we’ll just give one example study of many, which found:
❝The treated subjects experienced significantly improved skin complexion and skin feeling, profilometrically assessed skin roughness, and ultrasonographically measured collagen density.
The blinded clinical evaluation of photographs confirmed significant improvement in the intervention groups compared with the control❞
~ Dr. Alexander Wunsch & Dr. Karsten Matuschka
RLT helps speed up healing of wounds: True or False?
True! There is less science for this than the above claim, but the studies that have been done are quite compelling, for example this NASA technology study found that…
❝LED produced improvement of greater than 40% in musculoskeletal training injuries in Navy SEAL team members, and decreased wound healing time in crew members aboard a U.S. Naval submarine.❞
Read more: Effect of NASA light-emitting diode irradiation on wound healing
RLT’s benefits are only skin-deep: True or False?
False, probably, but we’d love to see more science for this, to be sure.
However, it does look like wavelengths in the near-infrared spectrum reduce the abnormal tau protein and neurofibrillary tangles associated with Alzheimer’s disease, resulting in increased blood flow to the brain, and a decrease in neuroinflammation:
Therapeutic Potential of Photobiomodulation In Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Would you like to try RLT for yourself?
There are some contraindications, for example:
- if you have photosensitivity (for obvious reasons)
- if you have Lupus (mostly because of the above)
- if you have hyperthyroidism (because if you use RLT to your neck as well as face, it may help stimulate thyroid function, which in your case is not what you want)
As ever, please check with your own doctor if you’re not completely sure; we can’t cover all bases here, and cannot speak for your individual circumstances.
For most people though, it’s very safe, and if you’d like to try it, here’s an example product on Amazon, and by all means do read reviews and shop around for the ideal device for you
Take care! 😎
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Much Alcohol Does It Take To Increase Cancer Risk?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Alcohol is, of course, unhealthy. Not even the famous “small glass of red” is recommended:
Alcohol also increases all-cause mortality at any dose (even “low-risk drinking”):
Alcohol Consumption Patterns and Mortality Among Older Adults
…and the World Health Organization has declared that the only safe amount of alcohol is zero:
WHO: No level of alcohol consumption is safe for our health
But what of alcohol and cancer? According to the American Association of Cancer Research’s latest report, more than half of Americans do not know that alcohol increases the risk of cancer:
Source: AACR Cancer Progress Report
Why/how does alcohol increase the risk of cancer?
There’s an obvious aspect and a less obvious but very important aspect:
- The obvious: alcohol damages almost every system in the body, and so it’s little surprise if that includes systems whose job it is to keep us safe from cancer.
- The less obvious: alcohol is largely metabolized by certain enzymes that have an impact on DNA repair, such as alcohol dehydrogenases and aldehyde dehydrogenases, amongst others, and noteworthily, acetaldehyde (the main metabolite of alcohol) is itself genotoxic.
Read more: Alcohol & Cancer
This is important, because it means alcohol also increases the risk of cancers other than the obvious head/neck, laryngeal, esophageal, liver, and colorectal cancers.
However, those cancers are of course the most well-represented of alcohol-related cancers, along with breast cancer (this has to do with alcohol’s effect on estrogen metabolism).
If you’re curious about the numbers, and the changes in risk if one reduces/quits/reprises drinking:
❝The increased alcohol-related cancer incidence was associated with dose; those who changed from nondrinking to mild (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.03; 95% CI, 1.00-1.06), moderate (aHR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.02-1.18), or heavy (aHR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.23-1.45) drinking levels had an associated higher risk than those who did not drink.
Those with mild drinking levels who quit drinking had a lower risk of alcohol-related cancer (aHR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.92-0.99) than those who sustained their drinking levels.
Those with moderate (aHR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.03-1.12) or heavy (aHR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02-1.12) drinking levels who quit drinking had a higher all cancer incidence than those who sustained their levels, but when quitting was sustained, this increase in risk disappeared.
Results of this study showed that increased alcohol consumption was associated with higher risks for alcohol-related and all cancers, whereas sustained quitting and reduced drinking were associated with lower risks of alcohol-related and all cancers.
Alcohol cessation and reduction should be reinforced for the prevention of cancer.❞
Source: Association Between Changes in Alcohol Consumption and Cancer Risk
Worried it’s too late?
If you’re reading this (and thus, evidently, still alive), it isn’t. It’s never too late (nor too early) to reduce, or ideally stop, drinking. Even if you already have cancer, drinking more alcohol will only exacerbate things, and abstaining from alcohol will improve your chances of recovery.
For a reassuring timeline of recovery from alcohol-related damage, see:
What Happens To Your Body When You Stop Drinking Alcohol
Want to stop, but have tried before and find it daunting?
There are a few ways to make it a lot easier:
Rethinking Drinking: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Don’t Do *This* If You’re Over 50 (And Want Better Sleep)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michael Breus, sleep specialist, explains:
Don’t make these mistakes
Dr. Breus recommends avoiding…
- Misusing magnesium: magnesium is a helpful sleep aid but must be carefully monitored. Recommended doses are 250mg for women and 300–350 mg for men, with slight adjustments for hot climates or active lifestyles. Overdosing can cause stomach issues, diarrhea, and dehydration, disrupting sleep. He recommends starting with magnesium glycinate for fewer stomach issues, and later mix with magnesium citrate. Always check supplements to avoid excessive magnesium intake.
- Misusing melatonin: melatonin production declines after age 55–60, making low-dose supplementation (0.5–1 mg) beneficial. He recommends, however, avoiding high doses (3–10mg), and he recommends to take it 90 minutes before bedtime. Melatonin interacts with some medications (including some meds for blood pressure or depression), so consult a pharmacist before use to avoid risks like serotonin syndrome.
- Going to bed too early: going to bed too early disrupts circadian rhythms and reduces sleep drive, causing earlier waking. Now, being an “early bird” is a generally healthy thing, but if you’re already getting up at 5am, say, you probably want your schedule to not continue to creep further forwards until you become nocturnal. Set a consistent wake-up time and count 7.5 hours backward (plus a set time to fall asleep, e.g. 20 minutes, but you’ll know what it is for you) to determine bedtime.
- Excessive caffeine consumption: from the heading, it may seem like a no-brainer, but older adults metabolize caffeine 33% slower on average, prolonging its effects. Dr. Breus recommends to reduce intake with “caffeine fading,” switching to half-caffeinated coffee for a while and then considering transitioning to decaf. He also suggests enjoying increasingly lower-caffeine teas, like black tea in the morning, matcha in the afternoon, and herbal tea at night to reduce caffeine’s impact on sleep.
- Falling foul of serotonin: avoid taking 5-HTP supplements with SSRI antidepressants like Prozac or Zoloft due to the risk of serotonin syndrome.
- Consider checking for physical problems: if you regularly wake up tired and/or groggy (despite having ostensibly had enough sleep, and there not being a pharmaceutical explanation for your grogginess), consider screening for sleep apnea. Home sleep tests are a convenient way to identify and treat this common but often undiagnosed condition.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
How to Fall Asleep Faster: CBT-Insomnia Treatment
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Sweetener That Interferes With Hunger/Satiety Signals
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Non-sugar sweeteners came under fire from the World Health Organization a couple of years ago:
The Problem With Sweeteners ← this is mostly about how they prompt cravings of increasingly sweeter foods/drinks, but there are other considerations discussed too
And sucralose (which is technically a sugar, but isn’t processed by the body as sugar, so it “doesn’t count” as such; the body treats it as a dietary fiber instead) got some bad press of its own:
The Sucralose News: Scaremongering Or Serious? ← the answer is both, by the way, but there’s nuance here, so do read the article!
And now, there’s more news about how sucralose specifically interferes with the brain’s hunger/satiety signals:
The study
A medium-sized (n=75) study of adults looked at the brain’s responses to, varyingly,
- Water
- Sucralose in water
- Sucrose in water (matched to be the same sweetness as the sucralose)
…using MRI, focusing on hunger-related regions like the hypothalamus.
Additionally, blood samples were taken to measure glucose, insulin, and satiety hormone (GLP-1) levels.
As for what they found:
- Sucralose kept hunger signals active in the brain for up to 35 minutes, unlike sucrose, which reduced hunger activity quickly.
- There was increased hypothalamic blood flow after sucralose intake, which meant heightened hunger signaling.
- Participants felt hungrier after consuming sucralose compared to sugar
- Sugar intake increased blood glucose (obviously), suppressing hunger, whereas sucralose had no such effect (again, reasonable, though it was worth checking, because if sucralose had an effect on insulin response, that would indirectly affect blood sugar levels one way or the other, depending on the effect on insulin levels—but that didn’t happen, so for now we may assume sucralose doesn’t affect insulin or insulin signalling).
- Women exhibited twice the hypothalamic response to sucralose compared to men, reinforcing sex-based differences in appetite control. Specifically, it was most likely hormonal differences that drove this, since the study’s participants were young adults (ages 18–35); it’s possible that if older adults had been included, untreated menopause could have changed these stats. But that latter’s just a hypothesis for now.
- Sucralose enhanced brain connectivity between the hypothalamus and motivation/reward-processing areas, potentially increasing cravings.
You can read the paper itself here:
The practical takeaway? Sucralose interferes with the brain’s “full” signals, keeping you hungrier for longer, which will (all else being equal) incline you to eat more than you would otherwise.
So, it might be worth skipping sucralose, unless you specifically want to increase how much you eat.
Want to learn more?
You might want to check out:
Carbonated Water: For Weight Loss, Satiety, Or Just Gas?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
52 Small Changes – by Brett Blumenthal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We see a lot of books that exhort us to get a six-pack in a month, change our life in 7 days, learn Japanese in 24 hours. The reality is, things take time!
Brett Blumenthal is more realistic while being just as motivational:
The idea is simple… Make one small change per week for 52 weeks, and at the end of the year, you’ll be healthier and happier.
At 10almonds, we’re big fans of small changes that add up (or rather: compound!) to make big differences, so this one’s absolutely our style!
Best of all, she offers us not just “do this” advice, but also “and here’s the information and resources you’ll need to make this change work the best it can for you”
The advices range in topic from nutrition to exercise to sleep to mental wellness to interpersonal stuff and more. The biggest focus is on personal health, though, with small changes to exercise and nutrition making up the lion’s share of the changes.
Bottom line: this is a book you’ll want to grab once a week. Consider setting a reminder on your phone to check in with it each Sunday, for example!
Take the first step and order “52 Small Changes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sleep wrinkles are real. Here’s how they leave their mark
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You wake up, stagger to the bathroom and gaze into the mirror. No, you’re not imagining it. You’ve developed face wrinkles overnight. They’re sleep wrinkles.
Sleep wrinkles are temporary. But as your skin loses its elasticity as you age, they can set in.
Here’s what you can do to minimise the chance of them forming in the first place.
How side-sleeping affects your face
Your skin wrinkles for a number of reasons, including ageing, sun damage, smoking, poor hydration, habitual facial expressions (such as grinning, pouting, frowning, squinting) and sleeping positions.
When you sleep on your side or stomach, your face skin is squeezed and crushed a lot more than if you sleep on your back. When you sleep on your side or stomach, gravity presses your face against the pillow. Your face skin is distorted as your skin is stretched, compressed and pulled in all directions as you move about in your sleep.
You can reduce these external forces acting on the face by sleeping on your back or changing positions frequently.
Doctors can tell which side you sleep on by looking at your face
In a young face, sleep wrinkles are transient and disappear after waking.
Temporary sleep wrinkles can become persistent with time and repetition. As we age, our skin loses elasticity (recoil) and extensibility (stretch), creating ideal conditions for sleep wrinkles or lines to set in and last longer.
The time spent in each sleeping position, the magnitude of external forces applied to each area of the face, as well as the surface area of contact with the pillow surface, also affects the pattern and rate of sleep wrinkle formation.
Skin specialists can often recognise this. People who favour sleeping on one side of their body tend to have a flatter face on their sleeping side and more visible sleep lines.
Can a night skincare routine avoid sleep wrinkles?
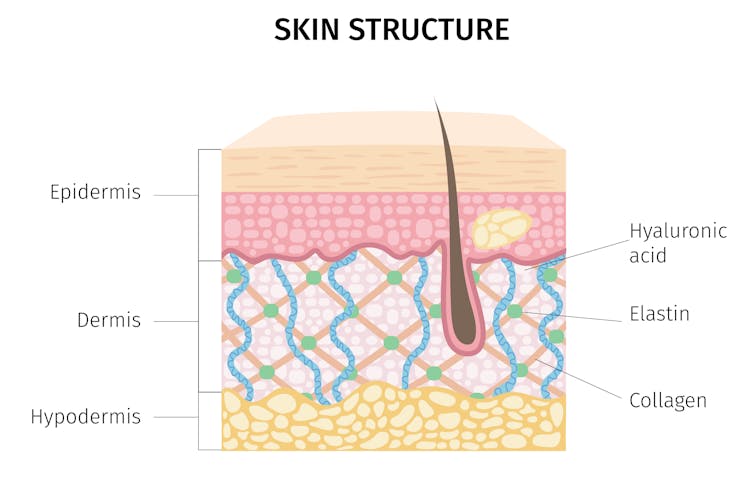
Collagen and elastin are two primary components of the dermis (inner layer) of skin. They form the skin structure and maintain the elasticity of skin.
The dermis is the inner layer of skin. mermaid3/Shutterstock Supplementing collagen through skincare routines to enhance skin elasticity can help reduce wrinkle formation.
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring molecule in human bodies. It holds our skin’s collagen and elastin in a proper configuration, stimulates the production of collagen and adds hydration, which can help slow down wrinkle formation. Hyaluronic acid is one of the most common active ingredients in skincare creams, gels and lotions.
Moisturisers can hydrate the skin in different ways. “Occlusive” substances produce a thin layer of oil on the skin that prevents water loss due to evaporation. “Humectants” attract and hold water in the skin, and they can differ in their capacity to bind with water, which influences the degree of skin hydration.
Do silk pillowcases actually make a difference?
Can they help? New Africa/Shutterstock Silk pillowcases can make a difference in wrinkle formation, if they let your skin glide and move, rather than adding friction and pressure on a single spot. If you can, use silk sheets and silk pillows.
Studies have also shown pillows designed to reduce mechanical stress during sleep can prevent skin deformations. Such a pillow could be useful in slowing down and preventing the formation of certain facial wrinkles.
Sleeping on your back can reduce the risk of sleep lines, as can a nighttime routine of moisturising before sleep.
Otherwise, lifestyle choices and habits, such quitting smoking, drinking plenty of water, a healthy diet (eating enough vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, healthy fats, yogurt and other fermented foods) and regular use of sunscreens can help improve the appearance of the skin on our face.
Yousuf Mohammed, Dermatology researcher, The University of Queensland; Khanh Phan, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Frazer Institute, The University of Queensland, and Vania Rodrigues Leite E. Silva, Honorary Associate Professor, Frazer Institute, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
3 Health Things A Lot Of People Are Getting Wrong (Don’t Make These Mistakes)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s time for our weekly health news roundup, and this week we’re putting the spotlight on…
Don’t Dabble In dubious diabetes Drugs
Diabetes drugs are in hot demand, both for actual diabetics and also for people who want to lose weight and/or generally improve their metabolic health. However, there are a lot of claims out there for products that simply do not work and/or are outright fakes, as well as claims for supplements that are known to have a real hypoglycemic effect (such as berberine) but the supplements in question are not regulated, so it can be hard to control for quality, to ensure you are really getting what it says on the label.
As for the prescription drugs specifically (such as metformin, or GLP-1 RAs): there are online black market and gray market pharmacies who offer to sell you prescription drugs either…
- no questions asked (black market), or
- basic questions asked (e.g. “are you diabetic?”), and a doctor with flexible morals will rubber-stamp the prescription on the basis of your answers (gray market).
The problem with these is that once again they may be fakes and there is practically no accountability (these sorts of online pharmacies come and go as quickly as street vendors). Furthermore, even if they are real, self-medicating in this fashion without the requisite expert knowledge can result in messing up dosages, which can cause all sorts of issues, not least of all, death.
Read in full: The dangers of fraudulent diabetes products and how to avoid them
Related: Metformin For Weight-Loss & More
There is no “just the flu”
It’s easy, and very socially normal, to dismiss flu—which has killed millions—as “just the flu”.
However, flu deaths have surpassed COVID deaths all so recently this year (you are mindful that COVID is still out and killing people, yes? Governments declaring the crisis over doesn’t make the virus pack up and retire), and because it’s peaking a little late (it had seemed to be peaking just after new year, which would be normal, but it’s enjoying a second larger surge now), people are letting their guard down more.
Thus, getting the current flu vaccination is good, if available (we know it’s not fun, but neither is being hospitalized by flu), and either way, taking care of all the usual disease-avoidance and immune-boosting strategies (see our “related” link for those).
Read in full: Report indicates this flu season is the worst in a decade
Related: Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
The hospital washbasins that give you extra bugs
First they came for the hand-dryer machines, and we did not speak up because those things are so noisy.
But more seriously: just like hand-dryer machines are now fairly well-known to incubate and spread germs at impressive rates, washbasins have come under scrutiny because the process goes:
- Person A has germs on their hands, and washes them (yay)
- The germs are now in the washbasin (soap causes them to slide off, but doesn’t usually kill them)
- Person B has germs on their hands, and washes them
- The splashback from the water hitting the washbasin distributes person A’s germs onto person B
- Not just their hands, which would be less of a problem (they are getting washed right now, after all), but also their face, because yes, even with flow restrictors, the splashback produces respirable-sized bioaerosols that travel far and easily
In other words: it’s not just the visible/tangible splashback you need to be aware of, but also, that which you can’t see or feel, too.
Read in full: Researchers warn about germ splashback from washbasins
Related: The Truth About Handwashing
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: