Women’s Strength Training Anatomy Workouts – by Frédéric Delavier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed another book of Delavier’s, “Women’s Strength Training Anatomy“, which itself is great. This book adds a lot of practical advice to that one’s more informational format, but to gain full benefit of this one does not require having read that one.
A common reason that many women avoid strength-training is because they do not want to look muscular. Largely this is based on a faulty assumption, since you will never look like a bodybuilder unless you also eat like a bodybuilder, for example.
However, for those for whom the concern remains, today’s book is an excellent guide to strength-training with aesthetics in mind as well as functionality.
The exercises are divided into sections, thus: round your glutes / tone your quadriceps / shape your hamstrings / trim your calves / flatten your abs / curve your shoulders / develop a pain-free upper back / protect your lower back / enhance your chest / firm up your arms.
As you can see, a lot of these are mindful of aesthetics, but there’s nothing here that’s antithetical to function, and some (especially for example “develop a pain-free upper back” and “protect your lower back“) are very functional indeed.
Bottom line: Delavier’s anatomy and exercise books are top-tier, and this one is no exception. If you are a woman and would like to strength-train (or perhaps you already do, and would like to refine your training), then this book is an excellent choice.
Click here to check out Women’s Strength Training Anatomy Workouts, and have the body you want!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
ADHD… As An Adult?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
ADHD—not just for kids!
Consider the following:
- If a kid has consistent problems paying attention, it’s easy and common to say “Aha, ADHD!”
- If a young adult has consistent problems paying attention, it’s easy and common to say “Aha, a disinterested ne’er-do-well!”
- If an older adult has consistent problems paying attention, it’s easy and common to say “Aha, a senior moment!”
Yet, if we recognize that ADHD is fundamentally a brain difference in children (and we do; there are physiological characteristics that we can test), and we can recognize that as people get older our brains typically have less neuroplasticity (ability to change) than when we are younger rather than less, then… Surely, there are just as many adults with ADHD as kids!
After all, that rather goes with the linear nature of time and the progressive nature of getting older.
So why do kids get diagnoses so much more often than adults?
Parents—and schools—can find children’s ADHD challenging, and it’s their problem, so they look for an explanation, and ADHD isn’t too difficult to find as a diagnosis.
Meanwhile, adults with ADHD have usually developed coping mechanisms, have learned to mask and/or compensate for their symptoms, and we expect adults to manage their own problems, so nobody’s rushing to find an explanation on their behalf.
Additionally, the stigma of neurodivergence—especially something popularly associated with children—isn’t something that many adults will want for themselves.
But, if you have an ADHD brain, then recognizing that (even if just privately to yourself) can open the door to much better management of your symptoms… and your life.
So what does ADHD look like in adults?
ADHD involves a spread of symptoms, and not everyone will have them all, or have them in the same magnitude. However, very commonly most noticeable traits include:
- Lack of focus (ease of distraction)
- Conversely: high focus (on the wrong things)
- To illustrate: someone with ADHD might set out to quickly tidy the sock drawer, and end up Marie Kondo-ing their entire wardrobe… when they were supposed to doing something else
- Conversely: high focus (on the wrong things)
- Poor time management (especially: tendency to procrastinate)
- Forgetfulness (of various kinds—for example, forgetting information, and forgetting to do things)
Want To Take A Quick Test? Click Here ← this one is reputable, and free. No sign in required; the test is right there.
Wait, where’s the hyperactivity in this Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder?
It’s often not there. ADHD is simply badly-named. This stems from how a lot of mental health issues are considered by society in terms of how much they affect (and are observable by) other people. Since ADHD was originally noticed in children (in fact being originally called “Hyperkinetic Reaction of Childhood”), it ended up being something like:
“Oh, your brain has an inconvenient relationship with dopamine and you are driven to try to correct that by shifting attention from boring things to stimulating things? You might have trouble-sitting-still disorder”
Hmm, this sounds like me (or my loved one); what to do now at the age of __?
Some things to consider:
- If you don’t want medication (there are pros and cons, beyond the scope of today’s article), you might consider an official diagnosis not worth pursuing. That’s fine if so, because…
- More important than whether or not you meet certain diagnostic criteria, is whether or not the strategies recommended for it might help you.
- Whether or not you talk to other people about it is entirely up to you. Maybe it’s a stigma you’d rather avoid… Or maybe it’ll help those around you to better understand and support you.
- Either way, you might want to learn more about ADHD in adults. Today’s article was about recognizing it—we’ll write more about managing it another time!
In the meantime… We recommended a great book about this a couple of weeks ago; you might want to check it out:
Click here to see our review of “The Silent Struggle: Taking Charge of ADHD in Adults”!
Note: the review is at the bottom of that page. You’ll need to scroll past the video (which is also about ADHD) without getting distracted by it and forgetting you were there to see about the book. So:
- Click the above link
- Scroll straight to the review!
Share This Post
-
Marathons in Mid- and Later-Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
We had several requests pertaining to veganism, meatless mondays, and substitutions in recipes—so we’re going to cover those on a different day!
As for questions we’re answering today…
Q: Is there any data on immediate and long term effects of running marathons in one’s forties?
An interesting and very specific question! We didn’t find an overabundance of studies specifically for the short- and long-term effects of marathon-running in one’s 40s, but we did find a couple of relevant ones:
The first looked at marathon-runners of various ages, and found that…
- there are virtually no relevant running time differences (p<0.01) per age in marathon finishers from 20 to 55 years
- the majority of middle-aged and elderly athletes have training histories of less than seven years of running
From which they concluded:
❝The present findings strengthen the concept that considers aging as a biological process that can be considerably speeded up or slowed down by multiple lifestyle related factors.❞
See the study: Performance, training and lifestyle parameters of marathon runners aged 20–80 years: results of the PACE-study
The other looked specifically at the impact of running on cartilage, controlled for age (45 and under vs 46 and older) and activity level (marathon-runners vs sedentary people).
The study had the people, of various ages and habitual activity levels, run for 30 minutes, and measured their knee cartilage thickness (using MRI) before and after running.
They found that regardless of age or habitual activity level, running compressed the cartilage tissue to a similar extent. From this, it can be concluded that neither age nor marathon-running result in long-term changes to cartilage response to running.
Or in lay terms: there’s no reason that marathon-running at 40 should ruin your knees (unless you are doing something wrong).
That may or may not have been a concern you have, but it’s what the study looked at, so hey, it’s information.
Here’s the study: Functional cartilage MRI T2 mapping: evaluating the effect of age and training on knee cartilage response to running
Q: Information on [e-word] dysfunction for those who have negative reactions to [the most common medications]?
When it comes to that particular issue, one or more of these three factors are often involved:
- Hormones
- Circulation
- Psychology
The most common drugs (that we can’t name here) work on the circulation side of things—specifically, by increasing the localized blood pressure. The exact mechanism of this drug action is interesting, albeit beyond the scope of a quick answer here today. On the other hand, the way that they work can cause adverse blood-pressure-related side effects for some people; perhaps you’re one of them.
To take matters into your own hands, so to speak, you can address each of those three things we just mentioned:
Hormones
Ask your doctor (or a reputable phlebotomy service) for a hormone test. If your free/serum testosterone levels are low (which becomes increasingly common in men over the age of 45), they may prescribe something—such as testosterone shots—specifically for that.
This way, it treats the underlying cause, rather than offering a workaround like those common pills whose names we can’t mention here.
Circulation
Look after your heart health; eat for your heart health, and exercise regularly!
Cold showers/baths also work wonders for vascular tone—which is precisely what you need in this matter. By rapidly changing temperatures (such as by turning off the hot water for the last couple of minutes of your shower, or by plunging into a cold bath), your blood vessels will get practice at constricting and maintaining that constriction as necessary.
Psychology
[E-word] dysfunction can also have a psychological basis. Unfortunately, this can also then be self-reinforcing, if recalling previous difficulties causes you to get distracted/insecure and lose the moment. One of the best things you can do to get out of this catch-22 situation is to not worry about it in the moment. Depending on what you and your partner(s) like to do in bed, there are plenty of other equally respectable options, so just switch track!
Having a conversation about this in advance will probably be helpful, so that everyone’s on the same page of the script in that eventuality, and it becomes “no big deal”. Without that conversation, misunderstandings and insecurities could arise for your partner(s) as well as yourself (“aren’t I desirable enough?” etc).
So, to recap, we recommend:
- Have your hormones checked
- Look after your circulation
- Make the decision to have fun!
Share This Post
-
Our blood-brain barrier stops bugs and toxins getting to our brain. Here’s how it works
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our brain is an extremely complex and delicate organ. Our body fiercely protects it by holding onto things that help it and keeping harmful things out, such as bugs that can cause infection and toxins.
It does that though a protective layer called the blood-brain barrier. Here’s how it works, and what it means for drug design.
The Conversation, Rattiya Thongdumhyu/Shutterstock, Petr Ganaj/Pexels First, let’s look at the circulatory system
Adults have roughly 30 trillion cells in their body. Every cell needs a variety of nutrients and oxygen, and they produce waste, which needs to be taken away.
Our circulatory system provides this service, delivering nutrients and removing waste.
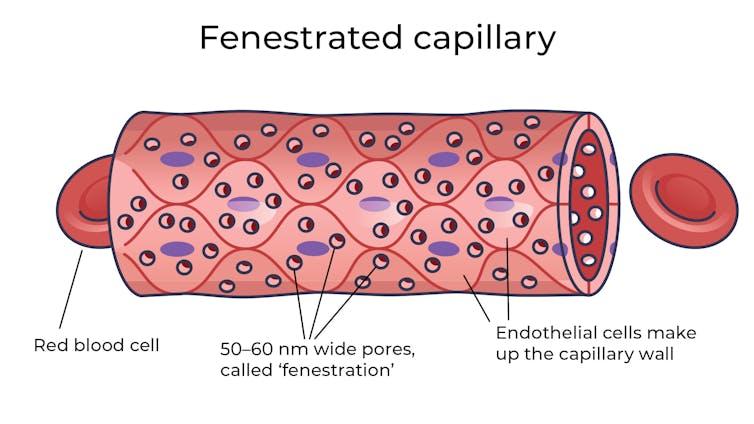
Fenestrated capillaries let nutrients and waste pass through. Vectormine/Shutterstock Where the circulatory system meets your cells, it branches down to tiny tubes called capillaries. These tiny tubes, about one-tenth the width of a human hair, are also made of cells.
But in most capillaries, there are some special features (known as fenestrations) that allow relatively free exchange of nutrients and waste between the blood and the cells of your tissues.
It’s kind of like pizza delivery
One way to think about the way the circulation works is like a pizza delivery person in a big city. On the really big roads (vessels) there are walls and you can’t walk up to the door of the house and pass someone the pizza.
But once you get down to the little suburban streets (capillaries), the design of the streets means you can stop, get off your scooter and walk up to the door to deliver the pizza (nutrients).
We often think of the brain as a spongy mass without much blood in it. In reality, the average brain has about 600 kilometres of blood vessels.
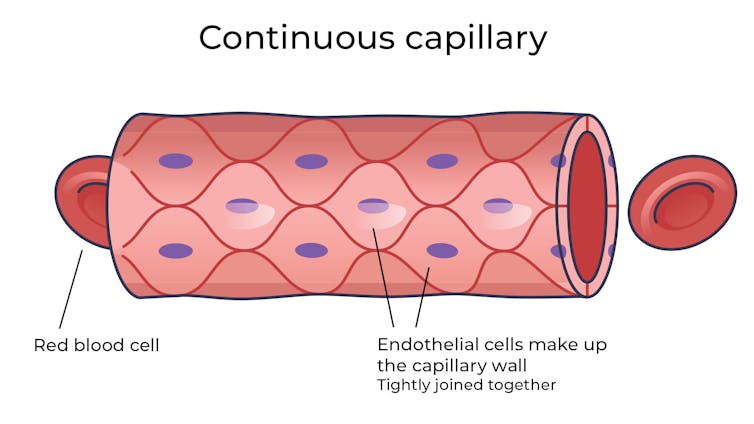
The difference between the capillaries in most of the brain and those elsewhere is that these capillaries are made of specialised cells that are very tightly joined together and limit the free exchange of anything dissolved in your blood. These are sometimes called continuous capillaries.
Continuous capillaries limit the free exchange of anything dissolved in your blood. Vectormine/Shutterstock This is the blood brain barrier. It’s not so much a bag around your brain stopping things from getting in and out but more like walls on all the streets, even the very small ones.
The only way pizza can get in is through special slots and these are just the right shape for the pizza box.
The blood brain barrier is set up so there are specialised transporters (like pizza box slots) for all the required nutrients. So mostly, the only things that can get in are things that there are transporters for or things that look very similar (on a molecular scale).
The analogy does fall down a little bit because the pizza box slot applies to nutrients that dissolve in water. Things that are highly soluble in fat can often bypass the slots in the wall.
Why do we have a blood-brain barrier?
The blood brain barrier is thought to exist for a few reasons.
First, it protects the brain from toxins you might eat (think chemicals that plants make) and viruses that often can infect the rest of your body but usually don’t make it to your brain.
It also provides protection by tightly regulating the movement of nutrients and waste in and out, providing a more stable environment than in the rest of the body.
Lastly, it serves to regulate passage of immune cells, preventing unnecessary inflammation which could damage cells in the brain.
What it means for medicines
One consequence of this tight regulation across the blood brain barrier is that if you want a medicine that gets to the brain, you need to consider how it will get in.
There are a few approaches. Highly fat-soluble molecules can often pass into the brain, so you might design your drug so it is a bit greasy.
The blood-brain barrier stops many medicines getting into the brain. Ron Lach/Pexels Another option is to link your medicine to another molecule that is normally taken up into the brain so it can hitch a ride, or a “pro-drug”, which looks like a molecule that is normally transported.
Using it to our advantage
You can also take advantage of the blood brain barrier.
Opioids used for pain relief often cause constipation. They do this because their target (opioid receptors) are also present in the nervous system of the intestines, where they act to slow movement of the intestinal contents.
Imodium (Loperamide), which is used to treat diarrhoea, is actually an opioid, but it has been specifically designed so it can’t cross the blood brain barrier.
This design means it can act on opioid receptors in the gastrointestinal tract, slowing down the movement of contents, but does not act on brain opioid receptors.
In contrast to Imodium, Ozempic and Victoza (originally designed for type 2 diabetes, but now popular for weight-loss) both have a long fat attached, to improve the length of time they stay in the body.
A consequence of having this long fat attached is that they can cross the blood-brain barrier, where they act to suppress appetite. This is part of the reason they are so effective as weight-loss drugs.
So while the blood brain barrier is important for protecting the brain it presents both a challenge and an opportunity for development of new medicines.
Sebastian Furness, ARC Future Fellow, School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Holistic Approach To Resculpting A Face Affected By Hypothyroidism, PCOS, Or Menopause
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mila Magnani has PCOS and hypothyroidism, but the principles are the same for menopause because both menopause and PCOS are a case of a hormone imbalance resulting in androgenic effects, so there’s a large amount of overlap.
Obviously, a portion of the difference in the thumbnail is a matter of angle and make-up, but as you can see in the video itself, there’s also a lot of genuine change underneath, too:
Stress-free method
Firstly, she bids us get lab tests and work with a knowledgeable doctor to address potential thyroid, hormonal, or nutrient imbalances. Perhaps we already know at least part of what is causing our problems, but even if so, it doesn’t hurt to take steps to rule the others out. Imagine spending ages unsuccessfully battling PCOS or menopause, only to discover it was a thyroid issue, and you were fighting the wrong battle!
Magnani used a natural route to manage her PCOS and hypothyroidism, while acknowledging that medication is fine too; it’s usually cheaper and more convenient—and there’s a lot more standardization for medications than there is for supplements, which makes it a lot easier to navigate, find what works, and keep getting the exact same thing once it does work.
Other things she recommends include:
- Lymphatic drainage: addressing the lymphatic system to reduce puffiness. Techniques include lymphatic drainage massage, stretching, rebounding (trampoline), and dry brushing. She emphasizes that for facial de-puffing, it’s important to treat the whole upper body, not just the face.
- Low-impact exercise: she switched from high-intensity workouts to low-impact exercises like nature walking and gentle stretching to reduce stress and improve health.
- Nervous system regulation: she worked on nervous system regulation by means of journaling, breathwork, and stimulating the vagus nerve, which improved sleep and reduced stress and anxiety. These things, of course, have knock-on benefits for almost every part of health.
- Diet: she adopted a low-glycemic diet, reduced salt intake, and cooked at home to avoid water retention caused by high sodium in restaurant meals.
- Natural diuretics: she uses teas like hibiscus and chamomile to reduce puffiness after consuming high-sodium foods.
- Sauna and sweating: consider a sauna mat or hot baths to detox and reduce swelling; that’s what she uses in lieu of a convenient sauna.
You may be wondering how quickly you can expect results: it took 3–6 months of daily effort to see significant changes, and she now maintains the routine less frequently (every 2–3 days, instead of daily).
For more on all this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
- 7-Minute Face Fitness For Lymphatic Drainage & Youthful Jawline
- Saunas: Health Benefits (& Caveats)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why are people on TikTok talking about going for a ‘fart walk’? A gastroenterologist weighs in
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Fart walks” have become a cultural phenomenon, after a woman named Mairlyn Smith posted online a now-viral video about how she and her husband go on walks about 60 minutes after dinner and release their gas.
Smith, known on TikTok as @mairlynthequeenoffibre and @mairlynsmith on Instagram, has since appeared on myriad TV and press interviews extolling the benefits of a fart walk. Countless TikTok and Instagram users and have now shared their own experiences of feeling better after taking up the #fartwalk habit.
So what’s the evidence behind the fart walk? And what’s the best way to do it?
CandyBox Images/Shutterstock Exercise can help get the gas out
We know exercise can help relieve bloating by getting gas moving and out of our bodies.
Researchers from Barcelona, Spain in 2006 asked eight patients complaining of bloating, seven of whom had irritable bowel syndrome, to avoid “gassy” foods such as beans for two days and to fast for eight hours before their study.
Each patient was asked to sit in an armchair, in order to avoid any effects of body position on the movement of gas. Gas was pumped directly into their small bowel via a thin plastic tube that went down their mouth, and the gas expelled from the body was collected into a bag via a tube placed in the rectum. This way, the researchers could determine how much gas was retained in the gut.
The patients were then asked to pedal on a modified exercise bike while remaining seated in their armchairs.
The researchers found that much less gas was retained in the patients’ gut when they exercised. They determined exercise probably helped the movement and release of intestinal gas.
Walking may have another bonus; it may trigger a nerve reflex that helps propel foods and gas contents through the gut.
Walking can also increase internal abdominal pressure as you use your abdominal muscles to stay upright and balance as you walk. This pressure on the colon helps to push intestinal gas out.
Proper fart walk technique
One study from Iran studied the effects of walking in 94 individuals with bloating.
They asked participants to carry out ten to 15 minutes of slow walking (about 1,000 steps) after eating lunch and dinner. They filled out gut symptom questionnaires before starting the program and again at the end of the four week program.
The researchers found walking after meals resulted in improvements to gut symptoms such as belching, farting, bloating and abdominal discomfort.
Now for the crucial part: in the Iranian study, there was a particular way in which participants were advised to walk. They were asked to clasp hands together behind their back and to flex their neck forward.
The clasped hands posture leads to more internal abdominal pressure and therefore more gentle squeezing out of gas from the colon. The flexed neck posture decreases the swallowing of air during walking.
This therefore is the proper fart walk technique, based on science.
Could walking with your hands behind your back yield better or more farts? candy candy/Shutterstock What about constipation?
A fart walk can help with constipation.
One study involved middle aged inactive patients with chronic constipation, who did a 12 week program of brisk walking at least 30 minutes a day – combined with 11 minutes of strength and flexibility exercises.
This program, the researchers found, improved constipation symptoms through reduced straining, less hard stools and more complete evacuation.
It also appears that the more you walk the better the benefits for gut symptoms.
In patients with irritable bowel syndrome, one study increasing the daily step count to 9,500 steps from 4,000 steps led to a 50% reduction in the severity of their symptoms.
And just 30 minutes of a fart walk has been shown to improve blood sugar levels after eating.
Walking after eating can help keep your blood sugar levels under control. IndianFaces/Shutterstock What if I can’t get outside the house?
If getting outside the house after dinner is impossible, could you try walking slowly on a treadmill or around the house for 1,000 steps?
If not, perhaps you could borrow an idea from the Barcelona research: sit back in an armchair and pedal using a modified exercise bike. Any type of exercise is better than none.
Whatever you do, don’t be a couch potato! Research has found more leisure screen time is linked to a greater risk of developing gut diseases.
We also know physical inactivity during leisure time and eating irregular meals are linked to a higher risk of abdominal pain, bloating and altered bowel motions.
Try the fart walk today
It may not be for everyone but this simple physical activity does have good evidence behind it. A fart walk can improve common symptoms such as bloating, abdominal discomfort and constipation.
It can even help lower blood sugar levels after eating.
Will you be trying a fart walk today?
Vincent Ho, Associate Professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
‘I can’t quite shut it off’: Prevalence of insomnia a growing concern for women
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tasha Werner, 43, gets up at 3:30 a.m. twice a week for her part-time job at a fitness centre in Calgary. After a five-hour shift, she is back home by 9 a.m. to homeschool her two children, aged 9 and 12. The hardest part of her position – stay-at-home mom, homeschool teacher and part-time worker – is the downtime “lost from my life,” says Werner.
A study by Howard M. Kravitz, a psychiatrist in Chicago, showed that up to 60 per cent of women experience sleep disorders due to hormonal changes linked to menopause. But there is an increasing prevalence of insomnia symptoms in women that may be attributed, in part, to societal changes.
“We live in a world that didn’t exist a generation ago. Now everyone is trying to figure it out,” says Michael Grandner, director of the Sleep and Health Research Program at the University of Arizona.
While women are no longer expected to stay at home, many who are employed outside the home also have the primary responsibility for family matters. And women aged 40 to 60 commonly fall within the “sandwich generation,” caring for both children and parents.
As women juggle their responsibilities, these duties can take a toll, both emotionally and practically.
Both Werner and her husband were raised in traditional homes; their mothers stayed at home to oversee childcare, cooking, grocery shopping and household duties. Initially, Werner and her husband followed a similar path, mirroring their parents’ lives as homemakers. “I think we just fell into what we were used to,” says Werner.
However, a notable shift in their family dynamics occurred once she started working outside the home.
Her children’s physical needs and illnesses have had major consequences on her sleep. If one of the children is sick with the flu, that’s “a week of not a lot of sleep during the night,” she says, “because that’s my job.” Many nights, she finds herself waking up between 1 a.m. and 3 a.m., worrying about how the kids are doing academically or behaviourally.
“We face a specific set of anxieties and a different set of pressures than men,” says Emma Kobil, who has been a therapist in Denver, Colo., for 15 years and is now an insomnia coach. There is so much pressure to be everything as a woman – to be an amazing homemaker and worker while maintaining a hot-rocking body and having a cool personality, to “be the cool mom but also the CEO, to follow your dreams and be the boss b****,” says Kobil.
And there’s an appeal to that concept. Daughters grow up viewing their moms as superwomen juggling responsibilities. But what isn’t always obvious are the challenges women face while managing their lives and the health issues they may encounter.
A study revealed that women are 41 per cent more at risk of insomnia than men.
A thorough study revealed that women are 41 per cent more at risk of insomnia than men. Beyond menopausal hormonal shifts, societal pressures, maternal concerns and the challenge of balancing multiple roles contribute to women’s increased susceptibility to insomnia.
Cyndi Aarrestad, 57, lives on a farm in Saskatchewan with her husband, Denis. Now an empty nester, Aarrestad fills her time working on the farm, keeping house, volunteering at her church and managing her small woodworking business. And she struggles with sleep.
Despite implementing some remedies, including stretching, drinking calming teas and rubbing her feet before bed, Aarrestad says achieving restful sleep has remained elusive for the past decade.
Two primary factors contribute to her sleep challenges — her inability to quiet her mind and hormonal hot flashes due to menopause. Faced with family and outside commitments, Aarrestad finds it challenging to escape night time’s mental chatter. “It’s a mom thing for me … I can’t quite shut it off.” Even as her children transitioned to young adulthood and moved out, the worries persisted, highlighting the lasting concerns moms have about their kids’ jobs, relationships and overall well-being.
Therapist Kobil says that every woman she’s ever worked with experiences this pressure to do everything, to be perfect. These women feel like they’re not measuring up. They’re encouraged to take on other people’s burdens; to be the confidante and the saviour in many ways; to sacrifice themselves. Sleep disruptions simply reflect the consequences of this pressure.
“They’re trying to fit 20 hours in a 24-hour day, and it doesn’t work,” says Grandner, the sleep specialist.
Grandner says that consistently sleeping six hours or less as an adult makes one 55 per cent more likely to become obese, 20 per cent more likely to develop high blood pressure, and 30 per cent more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes if you didn’t have it already. This lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch the flu. It makes vaccines less effective, and it increases your likelihood of developing depression and anxiety.
When is the time to change? Yesterday. Grandner warns that the sleep sacrifices made at a young age impact health later. But it’s never too late to make changes, he says, and “you do the best with what you’ve got.”
Kobil suggests a practical approach for women struggling with sleep. She emphasizes understanding that sleeplessness isn’t a threat and encourages a shift in mindset about being awake. Instead of fighting sleeplessness, she advises treating oneself kindly, recognizing the difficulty.
Kobil recommends creating a simple playbook with comforting activities for awake moments during the night. Just as you would comfort a child who’s afraid, she suggests being gentle with yourself, gradually changing the perception of wakefulness into a positive experience.
This article is republished from HealthyDebate under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: