Nasal Hair; How Far To Go?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
t’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝As a man in his sixties I find I need to trim my nasal hair quite frequently, otherwise it sticks out in an unsightly manner. But I’m never sure how severely I should cut the hairs back, or even how best to do it. Please advise.❞
As you might know, those hairs are really important for our health, so let’s start by mentioning that yes, trimming is the way, not plucking!
In an ideal world, we’d not trim them further back than the entrance to our nostrils, but given the constant nature of hair-growing, that could become a Sisyphean task.
A good compromise, if you’re not up for trimming when you get up and having visible hairs by evening, is to put the scissors away (if you haven’t already) and use a nasal hair trimmer; these are good at a) trimming nasal hairs b) abstaining from trimming them too far back.
By all means shop around, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience!
- Note 1: despite the product description, please do not stick this in your ear (or any other orifice that’s not your nose, for the love of all that is holey)
- Note 2: we chose that one for a reason; the shape of the head prevents overtrimming.
- In contrast, we do not recommend this cheaper one that has a different shape head for a closer trim, which in this case, is not what we want.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Your Doctor May Not Tell You About Fibromyalgia – by Dr. R. Paul St Amand
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The core claim of the book is that guaifenesin, an over-the-counter expectorant (with a good safety profile) usually taken to treat a chesty cough, is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and is rapidly metabolized and excreted into the urine—and on the way, it lowers uric acid levels, which is a big deal for fibromyalgia sufferers.
He goes on to explain how the guaifenesin, by a similar biochemical mechanism, additionally facilitates the removal of other excess secretions that are associated with fibromyalgia.
The science for all this is… Compelling and logical, while not being nearly so well-established yet as his confidence would have us believe.
In other words, he could be completely wrong, because adequate testing has not yet been done. However, he also could be right; scientific knowledge is, by the very reality of scientific method, always a step behind hypothesis and theory (in that order).
Meanwhile, there are certainly many glowing testimonials from fibromyalgia sufferers, saying that this helped a lot.
Bottom line: if you have fibromyalgia and do not mind trying a relatively clinically untested (yet logical and anecdotally successful) protocol to lessen then symptoms (allegedly, to zero), then this book will guide you through that and tell you everything to watch out for.
Share This Post
-
Tourette’s Syndrome Treatment Options
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Is there anything special that might help someone with Tourette’s syndrome?❞
There are of course a lot of different manifestations of Tourette’s syndrome, and some people’s tics may be far more problematic to themselves and/or others, while some may be quite mild and just something to work around.
It’s an interesting topic for sure, so we’ll perhaps do a main feature (probably also covering the related-and-sometimes-overlapping OCD umbrella rather than making it hyperspecific to Tourette’s), but meanwhile, you might consider some of these options:
Share This Post
-
A Planet of Viruses – by Carl Zimmer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed numerous books on the immune system before, and this one’s mostly not about that.
Instead, this one focuses on the viruses themselves, and the part they play in our world, for good and for ill. Popular awareness tends to focus on the ill, of course.
But, there’s a lot that viruses do for us too, including:
- Weak/harmless viruses that keep our immune systems on their toes and ready
- Bacteriophage viruses that kill and consume pathogens that, left unchecked, would do the same to us
- Endogenous retroviruses that have become symbiotic with the human organism, without which our species would quickly go extinct
He also talks about biological warfare, and how we cannot bury our heads in the sand by avoiding research on those grounds, because someone will always do it anyway, so (as the motto of the immune system itself might say), best to be prepared.
The author is a science journalist, by the way, and has no PhD, but does have a flock of Fellowships and assorted scientific awards and honors, so he appears to be doing good work so far as the scientific community is concerned.
Bottom line: if you’d like to know more about viruses than “they’re very small and can cause harm”, then this book will open a whole new world.
Click here to check out A Planet of Viruses, and upgrade your knowledge!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Can you get sunburnt or UV skin damage through car or home windows?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When you’re in a car, train or bus, do you choose a seat to avoid being in the sun or do you like the sunny side?
You can definitely feel the sun’s heat through a window. But can you get sunburn or skin damage when in your car or inside with the windows closed?
Let’s look at how much UV (ultraviolet) radiation passes through different types of glass, how tinting can help block UV, and whether we need sunscreen when driving or indoors.
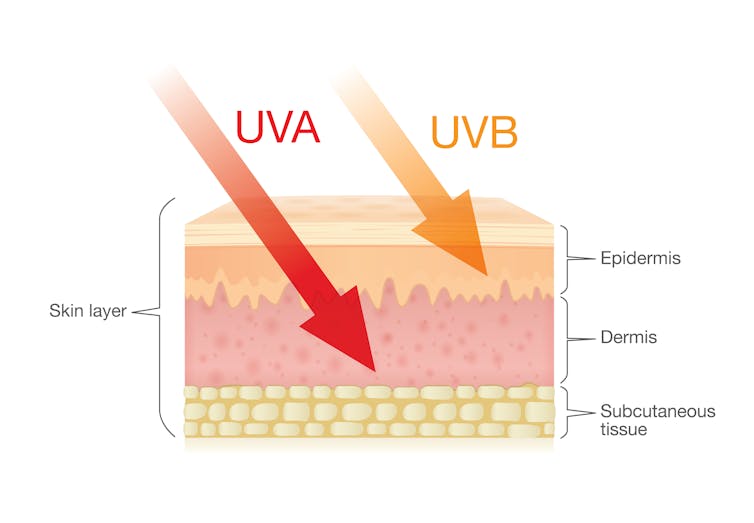
Zac Harris/Unsplash What’s the difference between UVA and UVB?
Of the total UV radiation that reaches Earth, about 95% is UVA and 5% is UVB.
UVB only reaches the upper layers of our skin but is the major cause of sunburn, cataracts and skin cancer.
UVA penetrates deeper into our skin and causes cell damage that leads to skin cancer.
UVA penetrates deeper than UVB. Shutterstock/solar22 Glass blocks UVA and UVB radiation differently
All glass used in house, office and car windows completely blocks UVB from passing through.
But only laminated glass can completely block UVA. UVA can pass through other glass used in car, house and office windows and cause skin damage, increasing the risk of cancer.
Car windscreens block UVA, but the side and rear windows don’t
A car’s front windscreen lets in lots of sunshine and light. Luckily it blocks 98% of UVA radiation because it is made of two layers of laminated glass.
But the side and rear car windows are made of tempered glass, which doesn’t completely block UVA. A study of 29 cars found a range from 4% to almost 56% of UVA passed through the side and rear windows.
The UVA protection was not related to the car’s age or cost, but to the type of glass, its colour and whether it has been tinted or coated in a protective film. Grey or bronze coloured glass, and window tinting, all increase UVA protection. Window tinting blocks around 95% of UVA radiation.
In a separate study from Saudi Arabia, researchers fitted drivers with a wearable radiation monitor. They found drivers were exposed to UV index ratings up to 3.5. (In Australia, sun protection is generally recommended when the UV index is 3 or above – at this level it takes pale skin about 20 minutes to burn.)
So if you have your windows tinted, you should not have to wear sunscreen in the car. But without tinted windows, you can accumulate skin damage.
UV exposure while driving increases skin cancer risk
Many people spend a lot of time in the car – for work, commuting, holiday travel and general transport. Repeated UVA radiation exposure through car side windows might go unnoticed, but it can affect our skin.
Indeed, skin cancer is more common on the driver’s side of the body. A study in the United States (where drivers sit on the left side) found more skin cancers on the left than the right side for the face, scalp, arm and leg, including 20 times more for the arm.
Another US study found this effect was higher in men. For melanoma in situ, an early form of melanoma, 74% of these cancers were on the on the left versus 26% on the right.
Earlier Australian studies reported more skin damage and more skin cancer on the right side.
Cataracts and other eye damage are also more common on the driver’s side of the body.
What about UV exposure through home or office windows?
We see UV damage from sunlight through our home windows in faded materials, furniture or plastics.
Most glass used in residential windows lets a lot of UVA pass through, between 45 and 75%.
Residential windows can let varied amounts of UVA through. Sherman Trotz/Pexels Single-pane glass lets through the most UVA, while thicker, tinted or coated glass blocks more UVA.
The best options are laminated glass, or double-glazed, tinted windows that allow less than 1% of UVA through.
Skylights are made from laminated glass, which completely stops UVA from passing through.
Most office and commercial window glass has better UVA protection than residential windows, allowing less than 25% of UVA transmission. These windows are usually double-glazed and tinted, with reflective properties or UV-absorbent chemicals.
Some smart windows that reduce heat using chemical treatments to darken the glass can also block UVA.
So when should you wear sunscreen and sunglasses?
The biggest risk with skin damage while driving is having the windows down or your arm out the window in direct sun. Even untinted windows will reduce UVA exposure to some extent, so it’s better to have the car window up.
For home windows, window films or tint can increase UVA protection of single pane glass. UVA blocking by glass is similar to protection by sunscreen.
When you need to use sunscreen depends on your skin type, latitude and time of the year. In a car without tinted windows, you could burn after one hour in the middle of the day in summer, and two hours in the middle of a winter’s day.
But in the middle of the day next to a home window that allows more UVA to pass through, it could take only 30 minutes to burn in summer and one hour in winter.
When the UV index is above three, it is recommended you wear protective sunglasses while driving or next to a sunny window to avoid eye damage.
Theresa Larkin, Associate Professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sesame Chocolate Fudge
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’d like a sweet treat without skyrocketing your blood sugars with, well, rocket fuel… Today’s recipe can help you enjoy a taste of decadence that’s not bad for your blood sugars, and good for your heart and brain.
You will need
- ½ cup sesame seeds
- ¼ cup cocoa powder
- 3 tbsp maple syrup
- 1 tbsp coconut oil (plus a little extra for the pan)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Lightly toast the sesame seeds in a pan until golden brown. Remove from the heat and allow to cool.
2) Put them in a food processor, and blend on full speed until they start to form a dough-like mixture. This may take a few minutes, so be patient. We recommend doing it in 30-second sessions with a 30-second rest between them, to avoiding overheating the motor.
3) Add the rest of the ingredients and blend to combine thoroughly—this should go easily now and only take 10 seconds or so, but judge it by eye.
4) Grease an 8″ square baking tin with a little coconut oil, and add the mixture, patting it down to fill the tin, making sure it is well-compressed.
5) Allow to chill in the fridge for 6 hours, until firm.
6) Turn the fudge out onto a chopping board, and cut into the size squares you want. Serve, or store in the fridge until ready to serve.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tasty Polyphenols For Your Heart & Brain
- Cacao vs Carob – Which is Healthier?
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
War in Ukraine affected wellbeing worldwide, but people’s speed of recovery depended on their personality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The war in Ukraine has had impacts around the world. Supply chains have been disrupted, the cost of living has soared and we’ve seen the fastest-growing refugee crisis since World War II. All of these are in addition to the devastating humanitarian and economic impacts within Ukraine.
Our international team was conducting a global study on wellbeing in the lead up to and after the Russian invasion. This provided a unique opportunity to examine the psychological impact of the outbreak of war.
As we explain in a new study published in Nature Communications, we learned the toll on people’s wellbeing was evident across nations, not just in Ukraine. These effects appear to have been temporary – at least for the average person.
But people with certain psychological vulnerabilities struggled to recover from the shock of the war.
Tracking wellbeing during the outbreak of war
People who took part in our study completed a rigorous “experience-sampling” protocol. Specifically, we asked them to report their momentary wellbeing four times per day for a whole month.
Data collection began in October 2021 and continued throughout 2022. So we had been tracking wellbeing around the world during the weeks surrounding the outbreak of war in February 2022.
We also collected measures of personality, along with various sociodemographic variables (including age, gender, political views). This enabled us to assess whether different people responded differently to the crisis. We could also compare these effects across countries.
Our analyses focused primarily on 1,341 participants living in 17 European countries, excluding Ukraine itself (44,894 experience-sampling reports in total). We also expanded these analyses to capture the experiences of 1,735 people living in 43 countries around the world (54,851 experience-sampling reports) – including in Australia.
A global dip in wellbeing
On February 24 2022, the day Russia invaded Ukraine, there was a sharp decline in wellbeing around the world. There was no decline in the month leading up to the outbreak of war, suggesting the change in wellbeing was not already occurring for some other reason.
However, there was a gradual increase in wellbeing during the month after the Russian invasion, suggestive of a “return to baseline” effect. Such effects are commonly reported in psychological research: situations and events that impact our wellbeing often (though not always) do so temporarily.
Unsurprisingly, people in Europe experienced a sharper dip in wellbeing compared to people living elsewhere around the world. Presumably the war was much more salient for those closest to the conflict, compared to those living on an entirely different continent.
Interestingly, day-to-day fluctuations in wellbeing mirrored the salience of the war on social media as events unfolded. Specifically, wellbeing was lower on days when there were more tweets mentioning Ukraine on Twitter/X.
Our results indicate that, on average, it took around two months for people to return to their baseline levels of wellbeing after the invasion.
Different people, different recoveries
There are strong links between our wellbeing and our individual personalities.
However, the dip in wellbeing following the Russian invasion was fairly uniform across individuals. None of the individual factors assessed in our study, including personality and sociodemographic factors, predicted people’s response to the outbreak of war.
On the other hand, personality did play a role in how quickly people recovered. Individual differences in people’s recovery were linked to a personality trait called “stability”. Stability is a broad dimension of personality that combines low neuroticism with high agreeableness and conscientiousness (three traits from the Big Five personality framework).
Stability is so named because it reflects the stability of one’s overall psychological functioning. This can be illustrated by breaking stability down into its three components:
- low neuroticism describes emotional stability. People low in this trait experience less intense negative emotions such as anxiety, fear or anger, in response to negative events
- high agreeableness describes social stability. People high in this trait are generally more cooperative, kind, and motivated to maintain social harmony
- high conscientiousness describes motivational stability. People high in this trait show more effective patterns of goal-directed self-regulation.
So, our data show that people with less stable personalities fared worse in terms of recovering from the impact the war in Ukraine had on wellbeing.
In a supplementary analysis, we found the effect of stability was driven specifically by neuroticism and agreeableness. The fact that people higher in neuroticism recovered more slowly accords with a wealth of research linking this trait with coping difficulties and poor mental health.
These effects of personality on recovery were stronger than those of sociodemographic factors, such as age, gender or political views, which were not statistically significant.
Overall, our findings suggest that people with certain psychological vulnerabilities will often struggle to recover from the shock of global events such as the outbreak of war in Ukraine.
Luke Smillie, Professor in Personality Psychology, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: