What is Ryeqo, the recently approved medicine for endometriosis?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For women diagnosed with endometriosis it is often a long sentence of chronic pain and cramping that impacts their daily life. It is a condition that is both difficult to diagnose and treat, with many women needing either surgery or regular medication.
A medicine called Ryeqo has just been approved for marketing specifically for endometriosis, although it was already available in Australia to treat a different condition.
Women who want the drug will need to consult their local doctor and, as it is not yet on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, they will need to pay the full cost of the script.
What does Ryeqo do?
Endometriosis affects 14% of women of reproductive age. While we don’t have a full understanding of the cause, the evidence suggests it’s due to body tissue that is similar to the lining of the uterus (called the endometrium) growing outside the uterus. This causes pain and inflammation, which reduces quality of life and can also affect fertility.
Ryeqo is a tablet containing three different active ingredients: relugolix, estradiol and norethisterone.
Relugolix is a drug that blocks a particular peptide from releasing other hormones. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Estradiol is a naturally occurring oestrogen hormone in women that helps regulate the menstrual cycle and is used in menopausal hormone therapy. Norethisterone is a synthetic hormone commonly used in birth control medications and to delay menstruation and help with heavy menstrual bleeding.
All three components work together to regulate the levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body that contribute to endometriosis, alleviating its symptoms.
Relugolix reduces the overall levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body. The estradiol compensates for the loss of oestrogen because low oestrogen levels can cause hot flushes (also called hot flashes) and bone density loss. And norethisterone blocks the effects of estradiol on the uterus (where too much tissue growth is unwanted).
Is it really new?
The maker of Ryeqo claims it is the first new drug for endometriosis in Australia in 13 years.
But individually, all three active ingredients in Ryeqo have been in use since 2019 or earlier.
Ryeqo has been available in Australia since 2022, but until now was not specifically indicated for endometriosis. It was originally approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids, which share some common symptoms with endometriosis and have related causes.
In addition to Ryeqo, current medical guidance lists other drugs that are suitable for endometriosis and some reformulations of these have also only been recently approved.
The oral medicine Dienogest was approved in 2021, and there have been a number of injectable drugs for endometriosis recently approved, such as Sayana Press which was approved in a smaller dose form for self-injection in 2023.
Shutterstock
How to take it and what not to do
Ryeqo is a once-a-day tablet. You can take it with, or without food, but it should be taken about the same time each day.
It is recommended you start taking Ryeqo within the first five days after the start of your next period. If you start at another time during your period, you may experience initial irregular or heavier bleeding.
Because it contains both synthetic and natural hormones, you can’t use the contraceptive pill and Ryeqo together. However, because Ryeqo does contain norethisterone it can be used as your contraception, although it will take at least one month of use to be effective. So, if you are on Ryeqo, you should use a non-hormonal contraceptive – such as condoms – for a month when starting the medicine.
Ryeqo may be incompatible with other medicines. It might not be suitable for you if you take medicines for epilepsy, HIV and AIDS, hepatitis C, fungal or bacterial infections, high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, angina (chest pain), or organ rejection. You should also not take Ryeqo if you have a liver tumour or liver disease.
The possible side effects of Ryeqo are similar to those of oral contraceptives. Blood clots are a risk with any medicine that contains an oestrogen or a progestogen, which Ryeqo does. Other potential side effects include bone loss, a reduction in menstrual blood loss or loss of your period.
It’s costly for now
Ryeqo can now be prescribed in Australia, so you should discuss whether Ryeqo is right for you with the doctor you usually consult for your endometriosis.
While the maker has made a submission to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee, it is not yet subsidised by the Australian government. This means that rather than paying the normal PBS price of up to A$31.60, it has been reported it may cost as much as $135 for a one-month supply. The committee will make a decision on whether to subsidise Ryeqo at its meeting next month.
Correction: this article has been updated to clarify the recent approval of specific formulations of drugs for endometriosis.
Nial Wheate, Associate Professor of the School of Pharmacy, University of Sydney and Jasmine Lee, Pharmacist and PhD Candidate, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fennel vs Onion – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing fennel to onion, we picked the fennel.
Why?
First note, in case you didn’t see the picture: we are talking about white onions here (also called brown onions, by virtue of their attire).
Looking at the macros, fennel has nearly 2x the fiber and a little more protein, while onion has more carbs. An easy win in this category for the fennel.
In the category of vitamins, fennel has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B9, C, E, K, and choline (most of them by generous margins and some by especially large margins, we are talking, for example, 480x the vitamin A, 29x the vitamin E, and 157x the vitamin K), while onions have more of vitmains B1 and B6. Another clear win for fennel.
When it comes to minerals, fennel has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while onion is not higher in any minerals. No prizes for guessing: fennel wins this category too.
You may be curious as to how they add up on the polyphenol front, and the answer is, they don’t, much. Wonderful as these two vegetables are, an abundance of polyphenols is not amongst their strengths; fennel has some lignans and onion has some flavonols, but we’re talking tiny numbers here (in contrast, red onion would have aced it with 120mg/100g quercetin, amongst others, but red onion wasn’t on trial today).
Adding up the sections makes a clear win for fennel today.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Put Your Feet Up! (Against A Wall, For 20 Minutes)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Feel free to browse our articles while you do
Here are 10 good reasons to give it a try; there are another 10 in the short (3:18) video:
- Improves blood circulation
- Improves blood pressure
- Relaxes the body as a whole
- Alleviates lower back tension
- Eases headaches and migraines
- Reduces knee pain
- Relieves swelling in feet and ankles
- Improves lymphatic flow
- Stretches the hamstrings (and hip flexors, if you do it wide)
- Helps quiet the mind
As for the rest…
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
PS: about that circulation… As a general rule of thumb, anything that slightly confuses the heart (anatomically, not romantically) will tend to have a beneficial effect, in moderation. This goes for being upside-down (as is partly the case here), and also for high-intensity interval training (HIIT):
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Genetic Risk Factors For Long COVID
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people, after getting COVID, go on to have Long COVID. There are various contributing factors to this, including:
- Lifestyle factors that impact general disease-proneness
- Immune-specific factors such as being immunocompromised already
- Genetic factors
We looked at some modifiable factors to improve one’s disease-resistance, yesterday:
And we’ve taken a more big-picture look previously:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
Along with some more systemic issues:
Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
But, for when the “don’t get COVID” ship has sailed, one of the big remaining deciding factors with regard to whether one gets Long COVID or not, is genetic
The Long COVID Genes
For those with their 23andMe genetic data to hand…
❝Study findings revealed that three specific genetic loci, HLA-DQA1–HLA-DQB1, ABO, and BPTF–KPAN2–C17orf58, and three phenotypes were at significantly heightened risk, highlighting high-priority populations for interventions against this poorly understood disease.❞
For those who don’t, then first: you might consider getting that! Here’s why:
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
But also, all is not lost meanwhile:
The same study also found that individuals with genetic predispositions to chronic fatigue, depression, and fibromyalgia, as well as other phenotypes such as autoimmune conditions and cardiometabolic conditions, are at significantly higher risk of long-COVID than individuals without these conditions.
Good news, bad news
Another finding was that women and non-smokers were more likely to get Long COVID, than men and smokers, respectively.
Does that mean that those things are protective against Long COVID, which would be very counterintuitive in the case of smoking?
Well, yes and no; it depends on whether you count “less likely to get Long COVID because of being more likely to just die” as protective against Long COVID.
(Incidentally, estrogen is moderately immune-enhancing, while testosterone is moderately immune-suppressing, so the sex thing was not too surprising. It’s also at least contributory to why women get more autoimmune disorders, while men get more respiratory infections such as colds and the like)
Want to know more?
You can read the paper itself, here:
*GWAS = Genome-Wide Association Study
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Some women’s breasts can’t make enough milk, and the effects can be devastating
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many new mothers worry about their milk supply. For some, support from a breastfeeding counsellor or lactation consultant helps.
Others cannot make enough milk no matter how hard they try. These are women whose breasts are not physically capable of producing enough milk.
Our recently published research gives us clues about breast features that might make it difficult for some women to produce enough milk. Another of our studies shows the devastating consequences for women who dream of breastfeeding but find they cannot.
Some breasts just don’t develop
Unlike other organs, breasts are not fully developed at birth. There are key developmental stages as an embryo, then again during puberty and pregnancy.
At birth, the breast consists of a simple network of ducts. Usually during puberty, the glandular (milk-making) tissue part of the breast begins to develop and the ductal network expands. Then typically, further growth of the ductal network and glandular tissue during pregnancy prepares the breast for lactation.
But our online survey of women who report low milk supply gives us clues to anomalies in how some women’s breasts develop.
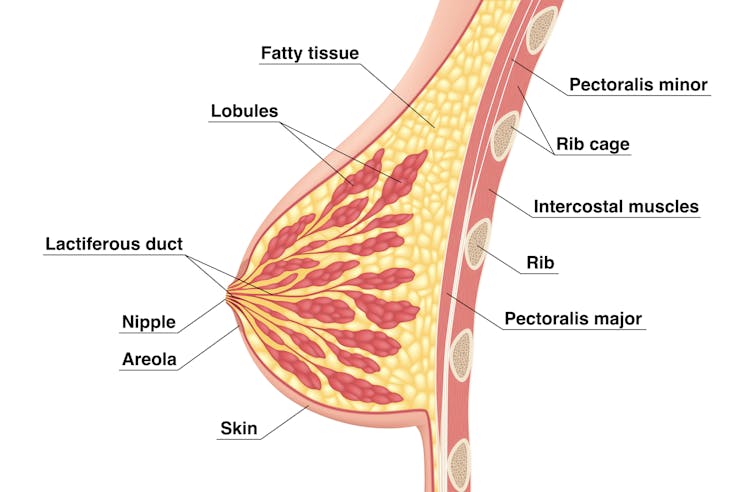
We’re not talking about women with small breasts, but women whose glandular tissue (shown in this diagram as “lobules”) is underdeveloped and have a condition called breast hypoplasia.
Sometimes not enough glandular tissue, shown here as lobules, develop.
Tsuyna/ShutterstockWe don’t know how common this is. But it has been linked with lower rates of exclusive breastfeeding.
We also don’t know what causes it, with much of the research conducted in animals and not humans.
However, certain health conditions have been associated with it, including polycystic ovary syndrome and other endocrine (hormonal) conditions. A high body-mass index around the time of puberty may be another indicator.
Could I have breast hypoplasia?
Our survey and other research give clues about who may have breast hypoplasia.
But it’s important to note these characteristics are indicators and do not mean women exhibiting them will definitely be unable to exclusively breastfeed.
Indicators include:
- a wider than usual gap between the breasts
- tubular-shaped (rather than round) breasts
- asymmetric breasts (where the breasts are different sizes or shapes)
- lack of breast growth in pregnancy
- a delay in or absence of breast fullness in the days after giving birth
In our survey, 72% of women with low milk supply had breasts that did not change appearance during pregnancy, and about 70% reported at least one irregular-shaped breast.
The effects
Mothers with low milk supply – whether or not they have breast hyoplasia or some other condition that limits their ability to produce enough milk – report a range of emotions.
Research, including our own, shows this ranges from frustration, confusion and surprise to intense or profound feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair.
Some mothers describe “breastfeeding grief” – a prolonged sense of loss or failure, due to being unable to connect with and nourish their baby through breastfeeding in the way they had hoped.
These feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair can trigger symptoms of anxiety and depression for some women.
Feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair were common.
Bricolage/ShutterstockOne woman told us:
[I became] so angry and upset with my body for not being able to produce enough milk.
Many women’s emotions intensified when they discovered that despite all their hard work, they were still unable to breastfeed their babies as planned. A few women described reaching their “breaking point”, and their experience felt “like death”, “the worst day of [my] life” or “hell”.
One participant told us:
I finally learned that ‘all women make enough milk’ was a lie. No amount of education or determination would make my breasts work. I felt deceived and let down by all my medical providers. How dare they have no answers for me when I desperately just wanted to feed my child naturally.
Others told us how they learned to accept their situation. Some women said they were relieved their infant was “finally satisfied” when they began supplementing with formula. One resolved to:
prioritise time with [my] baby over pumping for such little amounts.
Where to go for help
If you are struggling with low milk supply, it can help to see a lactation consultant for support and to determine the possible cause.
This will involve helping you try different strategies, such as optimising positioning and attachment during breastfeeding, or breastfeeding/expressing more frequently. You may need to consider taking a medication, such as domperidone, to see if your supply increases.
If these strategies do not help, there may be an underlying reason why you can’t make enough milk, such as insufficient glandular tissue (a confirmed inability to make a full supply due to breast hypoplasia).
Even if you have breast hypoplasia, you can still breastfeed by giving your baby extra milk (donor milk or formula) via a bottle or using a supplementer (which involves delivering milk at the breast via a tube linked to a bottle).
More resources
The following websites offer further information and support:
- Australian Breastfeeding Association
- Lactation Consultants of Australia and New Zealand
- Royal Women’s Hospital, Melbourne
- Supply Line Breastfeeders Support Group of Australia Facebook support group
- IGT And Low Milk Supply Support Group Facebook support group
- Breastfeeding Medicine Network Australia/New Zealand
- Supporting breastfeeding grief (a collection of resources).
Shannon Bennetts, a research fellow at La Trobe University, contributed to this article.
Renee Kam, PhD candidate and research officer, La Trobe University and Lisa Amir, Professor in Breastfeeding Research, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Carrots vs Broccoli – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing carrots to broccoli, we picked the broccoli.
Why?
These are both excellent candidates that should be in everyone’s diet, but there’s a clear winner:
In terms of macros, carrots have 50% more carbs for the same fiber (giving carrots the relatively higher glycemic index, though really, nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating carrots, which are a low-GI food already), while broccoli has more protein. By the numbers, it’s a nominal win for broccoli here, but really, both are great.
In the category of vitamins, carrots have more of vitamins A and B3, while broccoli has more of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline. An easy win for broccoli. We’d like to emphasize, though, that this doesn’t mean carrots don’t have lots of vitamins—they do—it’s just that broccoli has even more!
When it comes to minerals, carrots are genuinely great, and/but not higher in any minerals than broccoli, while broccoli has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. So again, a clear win for broccoli, despite carrots’ fortitude.
All in all, an overwhelming win for broccoli, though once again, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What Do The Different Kinds Of Fiber Do? 30 Foods That Rank Highest
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Working Smarter < Working Brighter!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to working smarter, not harder, there’s plenty of advice and honestly, it’s mostly quite sensible. For example:
(Nice to see they featured a method we talked about last week—great minds!)
But, as standards of productivity rise, the goalposts get moved too, and the treadmill just keeps on going…
- 49% of entrepreneurs say they’ve struggled with some kind of mental illness
- Millennial women are one of the workforce groups at the highest risk of anxiety
- About 7 in 10 millennials experience burnout at work
Not that these things are confined to Millennials, by any stretch, but Millennials make up a huge portion of working people. Ideally, this age group should be able to bring the best of both worlds to the workplace by combining years of experience with youthful energy.
So clearly something is going wrong; the question is: what can be done about it?
Workers of the World, Unwind
A knee-jerk response might be “work to rule”—a tactic long-used by disgruntled exploited workers to do no more than the absolute minimum required to not get fired. And it’s arguably better for them than breaking themselves at work, but that’s not exactly enriching, is it?
This is Brittany Berger, founder of “Work Brighter”.
She’s a content marketing consultant, mental health advocate, and (in her words) a highly ridiculous human who always has a pop culture reference at the ready.
What, besides pop culture references, is she bringing to the table? What is Working Brighter?
❝Working brighter means going beyond generic “work smarter” advice on the internet and personalizing it to work FOR YOU. It means creating your own routines for work, productivity, and self-care.❞
Brittany Berger
Examples of working brighter include…
Asking:
- What would your work involve, if it were more fun?
- How can you make your work more comfortable for you?
- What changes could you make that would make your work more sustainable (i.e., to avoid burnout)?
Remembering:
- Mental health is just health
- Self-care is a “soft skill”
- Rest is work when it’s needed
This is not one of those “what workers really want is not more pay, it’s beanbags” things, by the way (but if you want a beanbag, then by all means, get yourself a beanbag).
It’s about making time to rest, it’s about having the things that make you feel good while you’re working, and making sure you can enjoy working. You’re going to spend a lot of your life doing it; you might as well enjoy it.
❝Nobody goes to their deathbed wishing they’d spent more time at the office❞
Anon
On the contrary, having worked too hard is one of the top reported regrets of the dying!
Article: The Top Five Regrets Of The Dying
And no, they don’t wish they’d “worked smarter, not harder”. They wish (also in the above list, in fact) that they’d had the courage to live a life more true to themselves.
You can do that in your work. Whatever your work is. And if your work doesn’t permit that (be it the evil boss trope, or even that you are the boss and your line of work just doesn’t work that way), time to change that up. Stop focusing on what you can’t do, and look for what you can do.
Spoiler: you can have a blast just trying things out!
That doesn’t mean you should quit your job, or replace your PC with a Playstation, or whatever.
It just means that you deserve comfort and happiness while working, and around your work!
Need a helping hand getting started?
- Create your own self-care plan to avoid burnout
- ⏳ Complete your first “time audit”
- ❣️ Zip through to self-awareness with bullet-journalling
Like A Boss
And pssst, if you’re a business-owner who is thinking “but I have quotas to meet”, your customers are going to love your staff being happier, and will enjoy their interactions with your company much more. Or if your staff aren’t customer-facing, then still, they’ll work better when they enjoy doing it. This isn’t rocket science, but all too many companies give a cursory nod to it before proceeding to ignore it for the rest of the life of the company.
So where do you start, if you’re in those particular shoes?
Read on…
*straightens tie because this is the serious bit* —just kidding, I’m wearing my comfiest dress and fluffy-lined slipper-socks. But that makes this absolutely no less serious:
The Institute for Health and Productivity Management (IHPM) and WorkPlace Wellness Alliance (WPWA) might be a good place to get you on the right track!
❝IHPM/WPWA is a global nonprofit enterprise devoted to establishing the full economic value of employee health as a business asset—a neglected investment in the increased productivity of human capital.
IHPM helps employers identify the full economic cost impact of employee health issues on business performance, design and implement the best programs to reduce this impact by improving functional health and productivity, and measure the success of their efforts in financial terms.❞
The Institute for Health and Productivity Management
They offer courses and consultations, but they also have free downloadables and videos, which are awesome and in many cases may already be enough to seriously improve things for your business already:
Check Out IHPM’s Resources Here!
What can you do to make your working life better for you? We’d love to hear about any changes you make inspired by Brittany’s work—you can always just hit reply, and we’re always glad to hear from you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: