How can I stop overthinking everything? A clinical psychologist offers solutions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As a clinical psychologist, I often have clients say they are having trouble with thoughts “on a loop” in their head, which they find difficult to manage.
While rumination and overthinking are often considered the same thing, they are slightly different (though linked). Rumination is having thoughts on repeat in our minds. This can lead to overthinking – analysing those thoughts without finding solutions or solving the problem.
It’s like a vinyl record playing the same part of the song over and over. With a record, this is usually because of a scratch. Why we overthink is a little more complicated.
We’re on the lookout for threats
Our brains are hardwired to look for threats, to make a plan to address those threats and keep us safe. Those perceived threats may be based on past experiences, or may be the “what ifs” we imagine could happen in the future.
Our “what ifs” are usually negative outcomes. These are what we call “hot thoughts” – they bring up a lot of emotion (particularly sadness, worry or anger), which means we can easily get stuck on those thoughts and keep going over them.
However, because they are about things that have either already happened or might happen in the future (but are not happening now), we cannot fix the problem, so we keep going over the same thoughts.
Who overthinks?
Most people find themselves in situations at one time or another when they overthink.
Some people are more likely to ruminate. People who have had prior challenges or experienced trauma may have come to expect threats and look for them more than people who have not had adversities.
Deep thinkers, people who are prone to anxiety or low mood, and those who are sensitive or feel emotions deeply are also more likely to ruminate and overthink.

BĀBI/Unsplash
Also, when we are stressed, our emotions tend to be stronger and last longer, and our thoughts can be less accurate, which means we can get stuck on thoughts more than we would usually.
Being run down or physically unwell can also mean our thoughts are harder to tackle and manage.
Acknowledge your feelings
When thoughts go on repeat, it is helpful to use both emotion-focused and problem-focused strategies.
Being emotion-focused means figuring out how we feel about something and addressing those feelings. For example, we might feel regret, anger or sadness about something that has happened, or worry about something that might happen.
Acknowledging those emotions, using self-care techniques and accessing social support to talk about and manage your feelings will be helpful.
The second part is being problem-focused. Looking at what you would do differently (if the thoughts are about something from your past) and making a plan for dealing with future possibilities your thoughts are raising.
But it is difficult to plan for all eventualities, so this strategy has limited usefulness.
What is more helpful is to make a plan for one or two of the more likely possibilities and accept there may be things that happen you haven’t thought of.
Think about why these thoughts are showing up
Our feelings and experiences are information; it is important to ask what this information is telling you and why these thoughts are showing up now.
For example, university has just started again. Parents of high school leavers might be lying awake at night (which is when rumination and overthinking is common) worrying about their young person.

TheVisualsYouNeed/Shutterstock
Knowing how you would respond to some more likely possibilities (such as they will need money, they might be lonely or homesick) might be helpful.
But overthinking is also a sign of a new stage in both your lives, and needing to accept less control over your child’s choices and lives, while wanting the best for them. Recognising this means you can also talk about those feelings with others.
Let the thoughts go
A useful way to manage rumination or overthinking is “change, accept, and let go”.
Challenge and change aspects of your thoughts where you can. For example, the chance that your young person will run out of money and have no food and starve (overthinking tends to lead to your brain coming up with catastrophic outcomes!) is not likely.
You could plan to check in with your child regularly about how they are coping financially and encourage them to access budgeting support from university services.
Your thoughts are just ideas. They are not necessarily true or accurate, but when we overthink and have them on repeat, they can start to feel true because they become familiar. Coming up with a more realistic thought can help stop the loop of the unhelpful thought.
Accepting your emotions and finding ways to manage those (good self-care, social support, communication with those close to you) will also be helpful. As will accepting that life inevitably involves a lack of complete control over outcomes and possibilities life may throw at us. What we do have control over is our reactions and behaviours.
Remember, you have a 100% success rate of getting through challenges up until this point. You might have wanted to do things differently (and can plan to do that) but nevertheless, you coped and got through.
So, the last part is letting go of the need to know exactly how things will turn out, and believing in your ability (and sometimes others’) to cope.
What else can you do?
A stressed out and tired brain will be more likely to overthink, leading to more stress and creating a cycle that can affect your wellbeing.
So it’s important to manage your stress levels by eating and sleeping well, moving your body, doing things you enjoy, seeing people you care about, and doing things that fuel your soul and spirit.

antoniodiaz/Shutterstock
Distraction – with pleasurable activities and people who bring you joy – can also get your thoughts off repeat.
If you do find overthinking is affecting your life, and your levels of anxiety are rising or your mood is dropping (your sleep, appetite and enjoyment of life and people is being negatively affected), it might be time to talk to someone and get some strategies to manage.
When things become too difficult to manage yourself (or with the help of those close to you), a therapist can provide tools that have been proven to be helpful. Some helpful tools to manage worry and your thoughts can also be found here.
When you find yourself overthinking, think about why you are having “hot thoughts”, acknowledge your feelings and do some future-focused problem solving. But also accept life can be unpredictable and focus on having faith in your ability to cope.
Kirsty Ross, Associate Professor and Senior Clinical Psychologist, Massey University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Think you’re good at multi-tasking? Here’s how your brain compensates – and how this changes with age
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re all time-poor, so multi-tasking is seen as a necessity of modern living. We answer work emails while watching TV, make shopping lists in meetings and listen to podcasts when doing the dishes. We attempt to split our attention countless times a day when juggling both mundane and important tasks.
But doing two things at the same time isn’t always as productive or safe as focusing on one thing at a time.
The dilemma with multi-tasking is that when tasks become complex or energy-demanding, like driving a car while talking on the phone, our performance often drops on one or both.
Here’s why – and how our ability to multi-task changes as we age.
Doing more things, but less effectively
The issue with multi-tasking at a brain level, is that two tasks performed at the same time often compete for common neural pathways – like two intersecting streams of traffic on a road.
In particular, the brain’s planning centres in the frontal cortex (and connections to parieto-cerebellar system, among others) are needed for both motor and cognitive tasks. The more tasks rely on the same sensory system, like vision, the greater the interference.
This is why multi-tasking, such as talking on the phone, while driving can be risky. It takes longer to react to critical events, such as a car braking suddenly, and you have a higher risk of missing critical signals, such as a red light.
The more involved the phone conversation, the higher the accident risk, even when talking “hands-free”.
Generally, the more skilled you are on a primary motor task, the better able you are to juggle another task at the same time. Skilled surgeons, for example, can multitask more effectively than residents, which is reassuring in a busy operating suite.
Highly automated skills and efficient brain processes mean greater flexibility when multi-tasking.
Adults are better at multi-tasking than kids
Both brain capacity and experience endow adults with a greater capacity for multi-tasking compared with children.
You may have noticed that when you start thinking about a problem, you walk more slowly, and sometimes to a standstill if deep in thought. The ability to walk and think at the same time gets better over childhood and adolescence, as do other types of multi-tasking.
When children do these two things at once, their walking speed and smoothness both wane, particularly when also doing a memory task (like recalling a sequence of numbers), verbal fluency task (like naming animals) or a fine-motor task (like buttoning up a shirt). Alternately, outside the lab, the cognitive task might fall by wayside as the motor goal takes precedence.
Brain maturation has a lot to do with these age differences. A larger prefrontal cortex helps share cognitive resources between tasks, thereby reducing the costs. This means better capacity to maintain performance at or near single-task levels.
The white matter tract that connects our two hemispheres (the corpus callosum) also takes a long time to fully mature, placing limits on how well children can walk around and do manual tasks (like texting on a phone) together.
For a child or adult with motor skill difficulties, or developmental coordination disorder, multi-tastking errors are more common. Simply standing still while solving a visual task (like judging which of two lines is longer) is hard. When walking, it takes much longer to complete a path if it also involves cognitive effort along the way. So you can imagine how difficult walking to school could be.
What about as we approach older age?
Older adults are more prone to multi-tasking errors. When walking, for example, adding another task generally means older adults walk much slower and with less fluid movement than younger adults.
These age differences are even more pronounced when obstacles must be avoided or the path is winding or uneven.
Older adults tend to enlist more of their prefrontal cortex when walking and, especially, when multi-tasking. This creates more interference when the same brain networks are also enlisted to perform a cognitive task.
These age differences in performance of multi-tasking might be more “compensatory” than anything else, allowing older adults more time and safety when negotiating events around them.
Older people can practise and improve
Testing multi-tasking capabilities can tell clinicians about an older patient’s risk of future falls better than an assessment of walking alone, even for healthy people living in the community.
Testing can be as simple as asking someone to walk a path while either mentally subtracting by sevens, carrying a cup and saucer, or balancing a ball on a tray.
Patients can then practise and improve these abilities by, for example, pedalling an exercise bike or walking on a treadmill while composing a poem, making a shopping list, or playing a word game.
The goal is for patients to be able to divide their attention more efficiently across two tasks and to ignore distractions, improving speed and balance.
There are times when we do think better when moving
Let’s not forget that a good walk can help unclutter our mind and promote creative thought. And, some research shows walking can improve our ability to search and respond to visual events in the environment.
But often, it’s better to focus on one thing at a time
We often overlook the emotional and energy costs of multi-tasking when time-pressured. In many areas of life – home, work and school – we think it will save us time and energy. But the reality can be different.
Multi-tasking can sometimes sap our reserves and create stress, raising our cortisol levels, especially when we’re time-pressured. If such performance is sustained over long periods, it can leave you feeling fatigued or just plain empty.
Deep thinking is energy demanding by itself and so caution is sometimes warranted when acting at the same time – such as being immersed in deep thought while crossing a busy road, descending steep stairs, using power tools, or climbing a ladder.
So, pick a good time to ask someone a vexed question – perhaps not while they’re cutting vegetables with a sharp knife. Sometimes, it’s better to focus on one thing at a time.
Peter Wilson, Professor of Developmental Psychology, Australian Catholic University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Gut Health 2.0
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gene Expression & Gut Health
This is Dr. Tim Spector. After training in medicine and becoming a consultant rheumatologist, he’s turned his attention to medical research, and is these days a specialist in twin studies, genetics, epigenetics, microbiome, and diet.
What does he want us to know?
For one thing: epigenetics are for more than just getting your grandparents’ trauma.
More usefully: there are things we can do to improve epigenetic factors in our body
DNA is often seen as the script by which our body does whatever it’s going to do, but it’s only part of the story. Thinking of DNA as some kind of “magical immutable law of reality” overlooks (to labor the metaphor) script revisions, notes made in the margins, directorial choices, and ad-lib improvizations, as well as the quality of the audience’s hearing and comprehension.
Hence the premise of one of Dr. Spector’s older books, “Identically Different: Why We Can Change Our Genes”
(*in fact, it was his first, from all the way back in 2013, when he’d only been a doctor for 34 years)
Gene expression will trump genes every time, and gene expression is something that can often be changed without getting in there with CRISPR / a big pair of scissors and some craft glue.
How this happens on the micro level is beyond the scope of today’s article; part of it has to do with enzymes that get involved in the DNA transcription process, and those enzymes in turn are despatched or not depending on hormonal messaging—in the broadest sense of “hormonal”; all the body’s hormonal chemical messengers, not just the ones people think of as hormones.
However, hormonal messaging (of many kinds) is strongly influenced by something we can control relatively easily with a little good (science-based) knowledge: the gut.
The gut, the SAD, and the easy
In broad strokes: we know what is good for the gut. We’ve written about it before at 10almonds:
Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
This is very much in contrast with what in scientific literature is often abbreviated “SAD”, the Standard American Diet, which is very bad for the gut.
However, Dr. Spector (while fully encouraging everyone to enjoy an evidence-based gut-healthy diet) wanted to do one better than just a sweeping one-size-fits-all advice, so he set up a big study with 15,000 identical twins; you can read about it here: TwinsUK
The information that came out of that was about a lot more than just gene expression and gut health, but it did provide the foundation for Dr. Spector’s next project, ZOE.
ZOE crowdsources huge amounts of data including individual metabolic responses to standardized meals in order to predict personalized food responses based on individual biology and unique microbiome profile.
In other words, it takes the guesswork out of a) knowing what your genes mean for your food responses b) tailoring your food choices with your genetic expression in mind, and c) ultimately creating a positive feedback loop to much better health on all levels.
Now, this is not an ad for ZOE, but if you so wish, you can…
- Get the free ZOE gut health guide (this is good, but generic, gut health information)
- Take the ZOE home gut health test (quiz followed by offers of lab tests)
- Browse the ZOE Health Academy, its education wing
Want to know more?
Dr. Spector has a bunch of books out, including some that we’ve reviewed previously:
- Spoon-Fed: Why Almost Everything We’ve Been Told About Food Is Wrong
- The Diet Myth: The Real Science Behind What We Eat
- Food for Life: The New Science of Eating Well
You can also check out our own previous main feature, which wasn’t about Dr. Spector’s work but was very adjacent:
The Brain-Gut Highway: A Two-Way Street
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
What’s the difference between wholemeal and wholegrain bread? Not a whole lot
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you head to the shops to buy bread, you’ll face a variety of different options.
But it can be hard to work out the difference between all the types on sale.
For instance, you might have a vague idea that wholemeal or wholegrain bread is healthy. But what’s the difference?
Here’s what we know and what this means for shoppers in Australia and New Zealand.
Phish Photography/Shutterstock Let’s start with wholemeal bread
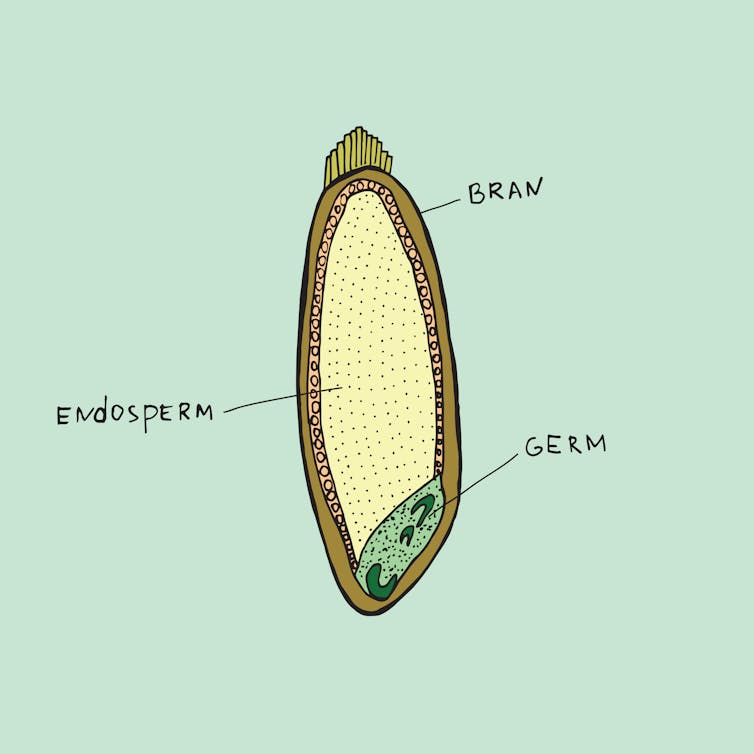
According to Australian and New Zealand food standards, wholemeal bread is made from flour containing all parts of the original grain (endosperm, germ and bran) in their original proportions.
Because it contains all parts of the grain, wholemeal bread is typically darker in colour and slightly more brown than white bread, which is made using only the endosperm.
Wholemeal flour is made from all parts of the grain. Rerikh/Shutterstock How about wholegrain bread?
Australian and New Zealand food standards define wholegrain bread as something that contains either the intact grain (for instance, visible grains) or is made from processed grains (flour) where all the parts of the grain are present in their original proportions.
That last part may sound familiar. That’s because wholegrain is an umbrella term that encompasses both bread made with intact grains and bread made with wholemeal flour. In other words, wholemeal bread is a type of wholegrain bread, just like an apple is a type of fruit.
Don’t be confused by labels such as “with added grains”, “grainy” or “multigrain”. Australian and New Zealand food standards don’t define these so manufacturers can legally add a small amount of intact grains to white bread to make the product appear healthier. This doesn’t necessarily make these products wholegrain breads.
So unless a product is specifically called wholegrain bread, wholemeal bread or indicates it “contains whole grain”, it is likely to be made from more refined ingredients.
Which one’s healthier?
So when thinking about which bread to choose, both wholemeal and wholegrain breads are rich in beneficial compounds including nutrients and fibre, more so than breads made from further-refined flour, such as white bread.
The presence of these compounds is what makes eating wholegrains (including wholemeal bread) beneficial for our overall health. Research has also shown eating wholegrains helps reduce the risk of common chronic diseases, such as heart disease.
The table below gives us a closer look at the nutritional composition of these breads, and shows some slight differences.
Wholegrain bread is slightly higher in fibre, protein, niacin (vitamin B3), iron, zinc, phosphorus and magnesium than wholemeal bread. But wholegrain bread is lower in carbohydrates, thiamin (vitamin B1) and folate (vitamin B9).
However the differences are relatively small when considering how these contribute to your overall dietary intake.
Which one should I buy?
Next time you’re shopping, look for a wholegrain bread (one made from wholemeal flour that has intact grains and seeds throughout) as your number one choice for fibre and protein, and to support overall health.
If you can’t find wholegrain bread, wholemeal bread comes in a very close second.
Wholegrain and wholemeal bread tend to cost the same, but both tend to be more expensive than white bread.
Margaret Murray, Senior Lecturer, Nutrition, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Replacing Sugar: Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Sweet Foods
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those with a sweet tooth, it can be challenging to indulge one’s desires while also avoiding inflammation. Happily, Dr. Jia-Yia Lui has scientific insights to share!
Dr. Liu’s Top 10
We’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Grapes
- Goji berries
- Barberries
- Persimmons
- Longans
- Lychees
- Raisins¹
- Applesauce²
- Plums³
- Dates
¹Yes, these are technically also grapes, but there are enough differences that Dr. Liu tackles them separately.
²It makes a difference how it’s made, though.
³And dried plums, in other words, prunes.For more details on all of these, plus their extra benefits and relevant considerations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
- The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Loaded Mocha Chocolate Parfait
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Packed with nutrients, including a healthy dose of protein and fiber, these parfait pots can be a healthy dessert, snack, or even breakfast!
You will need (for 4 servings)
For the mocha cream:
- ½ cup almond milk
- ½ cup raw cashews
- ⅓ cup espresso
- 2 tbsp maple syrup
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
For the chocolate sauce:
- 4 tbsp coconut oil, melted
- 2 tbsp unsweetened cocoa powder
- 1 tbsp maple syrup
- 1 tsp vanilla extract
For the other layers:
- 1 banana, sliced
- 1 cup granola, no added sugar
Garnish (optional): 3 coffee beans per serving
Note about the maple syrup: since its viscosity is similar to the overall viscosity of the mocha cream and chocolate sauce, you can adjust this per your tastes, without affecting the composition of the dish much besides sweetness (and sugar content). If you don’t like sweetness, the maple syrup be reduced or even omitted entirely (your writer here is known for her enjoyment of very strong bitter flavors and rarely wants anything sweeter than a banana); if you prefer more sweetness than the recipe called for, that’s your choice too.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend all the mocha cream ingredients. If you have time, doing this in advance and keeping it in the fridge for a few hours (or even up to a week) will make the flavor richer. But if you don’t have time, that’s fine too.
2) Stir all the chocolate sauce ingredients together in a small bowl, and set it aside. This one should definitely not be refrigerated, or else the coconut oil will solidify and separate itself.
3) Gently swirl the the mocha cream and chocolate sauce together. You want a marble effect, not a full mixing. Omit this step if you want clearer layers.
4) Assemble in dessert glasses, alternating layers of banana, mocha chocolate marble mixture (or the two parts, if you didn’t swirl them together), and granola.
5) Add the coffee-bean garnish, if using, and serve!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (Or Is It?)
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Toxic Gas That Sterilizes Medical Devices Prompts Safety Rule Update
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Over the past two years, Madeline Beal has heard frustration and even bewilderment during public meetings about ethylene oxide, a cancer-causing gas that is used to sterilize half of the medical devices in the U.S.
Beal, senior risk communication adviser for the Environmental Protection Agency, has fielded questions about why the agency took so long to alert people who live near facilities that emit the chemical about unusually high amounts of the carcinogenic gas in their neighborhoods. Residents asked why the EPA couldn’t close those facilities, and they wanted to know how many people had developed cancer from their exposure.
“If you’re upset by the information you’re hearing tonight, if you’re angry, if it scares you to think about risk to your family, those are totally reasonable responses,” Beal told an audience in Laredo, Texas, in September 2022. “We think the risk levels near this facility are too high.”
There are about 90 sterilizing plants in the U.S. that use ethylene oxide, and for decades companies used the chemical to sterilize medical products without drawing much attention. Many medical device-makers send their products to the plants to be sterilized before they are shipped, typically to medical distribution companies.
But people living around these facilities have been jolted in recent years by a succession of warnings about cancer risk from the federal government and media reports, an awareness that has also spawned protests and lawsuits alleging medical harm.
The EPA is expected to meet a March 1 court-ordered deadline to finalize tighter safety rules around how the toxic gas is used. The proposed changes come in the wake of a 2016 agency report that found that long-term exposure to ethylene oxide is more dangerous than was previously thought.
But the anticipated final rules — the agency’s first regulatory update on ethylene oxide emissions in more than a decade — are expected to face pushback. Medical device-makers worry stricter regulation will increase costs and may put patients at higher risk of infection from devices, ranging from surgical kits to catheters, due to deficient sterilization. The new rules are also not likely to satisfy the concerns of environmentalists or members of the public, who already have expressed frustration about how long it took the federal government to sound the alarm.
“We have been breathing this air for 40 years,” said Connie Waller, 70, who lives with her husband, David, 75, within two miles of such a sterilizing plant in Covington, Georgia, east of Atlanta. “The only way to stop these chemicals is to hit them in their pocketbook, to get their attention.”
The EPA says data shows that long-term exposure to ethylene oxide can increase the risk of breast cancer and cancers of the white blood cells, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma, myeloma, and lymphocytic leukemia. It can irritate the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs, and has been linked to damage to the brain and nervous and reproductive systems. Children are potentially more vulnerable, as are workers routinely exposed to the chemical, EPA officials say. The agency calculates the risk based on how much of the gas is in the air or near the sterilizing facility, the distance a person is from the plant, and how long the person is exposed.
Waller said she was diagnosed with breast cancer in 2004 and that her husband was found to have non-Hodgkin lymphoma eight years later.
A 2022 study of communities living near a sterilization facility in Laredo found the rates of acute lymphocytic leukemia and breast cancer were greater than expected based on statewide rates, a difference that was statistically significant.
Beal, the EPA risk adviser, who regularly meets with community members, acknowledges the public’s concerns. “We don’t think it’s OK for you to be at increased risk from something that you have no control over, that’s near your house,” she said. “We are working as fast as we can to get that risk reduced with the powers that we have available to us.”
In the meantime, local and state governments and industry groups have scrambled to defuse public outcry.
Hundreds of personal injury cases have been filed in communities near sterilizing plants. In 2020, New Mexico’s then-attorney general filed a lawsuit against a plant in Santa Teresa, and that case is ongoing. In a case that settled last year in suburban Atlanta, a company agreed to pay $35 million to 79 people who alleged ethylene oxide used at the plant caused cancer and other injuries.
In Cook County, Illinois, a jury in 2022 awarded $363 million to a woman who alleged exposure to ethylene oxide gas led to her breast cancer diagnosis. But, in another Illinois case, a jury ruled that the sterilizing company was not liable for a woman’s blood cancer claim.
Greg Crist, chief advocacy officer for the Advanced Medical Technology Association, a medical device trade group that says ethylene oxide is an effective and reliable sterilant, attributes the spate of lawsuits to the litigious nature of trial attorneys.
“If they smell blood in the water, they’ll go after it,” Crist said.
Most states have at least one sterilizing plant. According to the EPA, a handful, like California and North Carolina, have gone further than the agency and the federal Clean Air Act to regulate ethylene oxide emissions. After a media and political firestorm raised awareness about the metro Atlanta facilities, Georgia started requiring sterilizing plants that use the gas to report all leaks.
The proposed rules the EPA is set to finalize would set lower emissions limits for chemical plants and commercial sterilizers and increase some safety requirements for workers within these facilities. The agency is expected to set an 18-month deadline for commercial sterilizers to come into compliance with the emissions rules.
That would help at facilities that “cut corners,” with lax pollution controls that allow emissions of the gas into nearby communities, said Richard Peltier, a professor of environmental health sciences at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst. Stronger regulation also prevents the plants from remaining under the radar. “One of the dirty secrets is that a lot of it is self-regulated or self-policed,” Peltier added.
But the proposed rules did not include protections for workers at off-site warehouses that store sterilized products, which can continue to emit ethylene oxide. They also did not require air testing around the facilities, prompting debate about how effective they would be in protecting the health of nearby residents.
Industry officials also don’t expect an alternative that is as broadly effective as ethylene oxide to be developed anytime soon, though they support researching other methods. Current alternatives include steam, radiation, and hydrogen peroxide vapor.
Increasing the use of alternatives can reduce industry dependence on “the crutch of ethylene oxide,” said Darya Minovi, senior analyst with the Union of Concerned Scientists, an advocacy group.
But meeting the new guidelines will be disruptive to the industry, Crist said. He estimates companies will spend upward of $500 million to comply with the new EPA rules and could struggle to meet the agency’s 18-month timetable. Sterilization companies will also have difficulty adjusting to new rules on how workers handle the gas without a dip in efficiency, Crist said.
The Food and Drug Administration, which regulates drugs and medical devices, is also watching the regulatory moves closely and worries the updated emissions rule could “present some unique challenges” if implemented as proposed, said Audra Harrison, an FDA spokesperson. “The FDA is concerned about the rule’s effects on the availability of medical devices,” she added.
Other groups, like the American Chemistry Council and the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, the state’s environmental agency, assert that ethylene oxide use isn’t as dangerous as the EPA says. The EPA’s toxicity assessment has “severe flaws” and is “overly conservative,” the council said in an emailed statement. Texas, which has several sterilizing plants, has said ethylene oxide isn’t as high a cancer risk as the agency claims, an assessment that the EPA has rejected.
Tracey Woodruff, a researcher at the University of California-San Francisco who previously worked at the EPA, said it can be hard for the agency to keep up with regulating chemicals like ethylene oxide because of constrained resources, the technical complications of rulemaking, and industry lobbying.
But she’s hopeful the EPA can strike a balance between its desire to reduce exposure and the desire of the FDA not to disrupt medical device sterilization. And scrutiny can also help the device sterilization industry think outside the box.
“We continue to discover these chemicals that we’ve already been exposed to were toxic, and we have high exposures,” she said. “Regulation is an innovation forcer.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: