What Happens To Your Body When You Do Squats Every Day-Not Just For Legs!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Squat Every Day? Yes, Please!
It’s back to basics with this video (below). Passion for Health’s video, “What Happens To Your Body When You Do Squats Every Day-Not Just For Legs!” really brings home how squats aren’t just a one-trick pony for your legs.
The humble bodyweight squat is shown to contribute to everything from bolstering all-around lower body strength to bettering bone density and increasing metabolism.
Indeed, squats are so powerful that we reviewed a whole book that focuses just on the topic of squatting. Other, broader books on exercise also focus on the positive impacts that squatting can make.
A proper squat goes beyond your legs, engaging your core, enhancing joint health, and, some argue, can lead to improved balance and circulation.
(Plus, they’re easy to execute, given they can be done anywhere, without any equipment).
This is probably why Luigi Fontana and Dr Rangan Chatterjee have spoken about the benefits of squatting.
How Should We Start?
The video goes beyond the ‘why’ and delves into the ‘how’, offering step-by-step squatting techniques.
It answers the burning question: should you really be doing squats every day?
(Hint: the answer is most likely “yes”).
Of course, some of us may not be able to squat, and for those, we’ll feature alternatives in a future article.
For beginners, the advice is to start slow, aiming for 10 repetitions. You can gradually increase that count as you feel your muscles strengthen. Experienced gym-goers might push for 20 or more reps, adding variations like jump squats for an extra challenge.
The key takeaway is to listen to your body and ensure rest days for muscle recovery.
At the end of the day, Passion for Health’s video is a treasure trove for squat lovers, from novices to the seasoned, and insists on the importance of form, frequency, and listening to one’s body.
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Engage Your Whole Brain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Stroke Of Insight That Nobody Wants
This is Dr. Jill Bolte Taylor. She’s a neuroanatomist, who, at the age of 37 (when she was a post-doctoral fellow at Harvard Medical School), had what she refers to as her “stroke of insight”.
That is to say, she had a massive stroke, and after a major brain surgery to remove a clot the size of a golf ball, she spent the next 8 years re-learning to do everything.
Whereas previously she’d been busy mapping the brain to determine how cells communicate with each other, now she was busy mapping whether socks or shoes should go on first. Needless to say, she got an insight into neuroplasticity that few people would hope for.
What does she want us to know?
Dr. Taylor (now once again a successful scientist, lecturer, and author) advocates for “whole brain living”, which involves not taking parts of our brain for granted.
About those parts…
Dr. Taylor wants us to pay attention to all the parts regardless of size, ranging from the two hemispheres, all the way down to the billions of brain cells, and yet even further, to the “trillions of molecular geniuses”—because each brain cell is itself reliant on countless molecules of the many neurochemicals that make up our brain.
For a quick refresher on some of the key players in that latter category, see our Neurotransmitter Cheatsheet 😎
When it comes to the hemispheres, there has historically been a popular belief that these re divided into:
- The right brain: emotional, imaginative, creative, fluid feeling
- The left brain: intellectual, analytical, calculating, crystal thinking
…which is not true, anatomically speaking, because there are cells on both sides doing their part of both of these broad categories of brain processes.
However, Dr. Taylor found, while one hemisphere of her brain was much more damaged than the other, that nevertheless she could recover some functions more quickly than others, which, once she was able to resume her career, inspired her model of four distinct ways of cogitating that can be switched-between and played with or against each other:
Meet The Four Characters Inside Your Brain
Why this matters
As she was re-learning everything, the way forward was not quick or easy, and she also didn’t know where she was going, because for obvious reasons, she couldn’t remember, much less plan.
Looking backwards after her eventual full recovery, she noted a lot of things that she needed during that recovery, some of which she got and some of which she didn’t.
Most notably for her, she needed the right kind of support that would allow all four of the above “characters” as she puts it, to thrive and grow. And, when we say “grow” here we mean that literally, because of growing new brain cells to replace the lost ones (as well as the simple ongoing process of slowly replacing brain cells).
For more on growing new brain cells, by the way, see:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
In order to achieve this in all of the required brain areas (i.e., and all of the required brain functions), she also wants us to know… drumroll please…
When to STFU
Specifically, the ability to silence parts of our brain that while useful in general, aren’t necessarily being useful right now. Since it’s very difficult to actively achieve a negative when it comes to brain-stuff (don’t think of an elephant), this means scheduling time for other parts of our brain to be louder. And that includes:
- scheduling time to feel (emotionally)
- scheduling time to feel (gut feelings)
- scheduling time to feel (kinesthetically)
…amongst others.
Note: those three are presented in that order, from least basic to most basic. And why? Because, clever beings that we are, we typically start from a position that’s not remotely basic, such as “overthinking”, for example. So, there’s a wind-down through thinking just the right amount, thinking through simpler concepts, feeling, noticing one’s feelings, noticing noticing one’s feelings, all the way down to what, kinesthetically, are we actually physically feeling.
❝It is interesting to note that although our limbic system fucntions throughout our lifetime, it does not mature. As a result, when our emotional “buttons” are pushed, we retain the ability to react to incoming stimulation as though we were a two-year-old, even when we are adults.❞
~ Dr. Jill Taylor
Of course, sometimes the above is not useful, which is why the ability to switch between brain modes is a very important and useful skill to develop.
And how do we do that? By practising. Which is something that it’s necessary to take up consciously, and pursue consistently. When children are at school, there are (hopefully, ideally) curricula set out to ensure they engage and train all parts of their brain. As adults, this does not tend to get the same amount of focus.
“Children’s brains are still developing”—indeed, and so are adult brains:
The Brain As A Work-In-Progress
Dr. Taylor had the uncommon experience of having to, in many ways, neurologically speaking, redo childhood. And having had a second run at it, she developed an appreciation of the process that most of us didn’t necessarily get when doing childhood just the once.
In other words: take the time to feel stuff; take the time to quiet down your chatty mind, take the time engage your senses, and take it seriously! Really notice, as though for the first time, what the texture of your carpet is like. Really notice, as though for the first time, what it feels like to swallow some water. Really notice, as though for the first time, what it feels like to experience joy—or sadness, or comfort, or anger, or peace. Exercise your imagination. Make some art (it doesn’t have to win awards; it just has to light up your brain!). Make music (again, it’s about wiring your brain in your body, not about outdoing Mozart in composition and/or performance). Make changes! Make your brain work in the ways it’s not in the habit of doing.
If you need a little help switching off parts of your brain that are being too active, so that you can better exercise other parts of your brain that might otherwise have been neglected, you might want to try:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
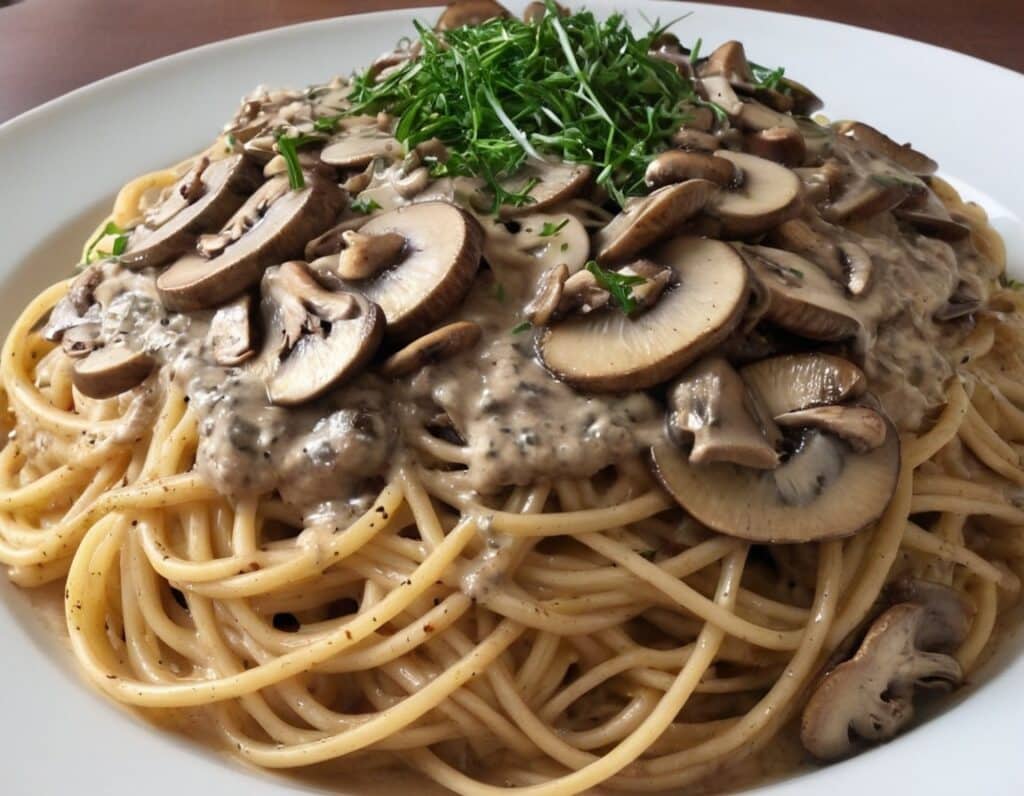
Omega-3 Mushroom Spaghetti
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The omega-3 is not the only healthy fat in here; we’re also going to have medium-chain triglycerides, as well as monounsaturates. Add in the ergothioneine from the mushrooms and a stack of polyphenols from, well, most of the ingredients, not to mention the fiber, and this comes together as a very healthy dish. There’s also about 64g protein in the entire recipe, so you do the math for how much that is per serving, depending on how big you want the servings to be.
You will need
- 1lb wholewheat spaghetti (or gluten-free equivalent, such as a legume-based pasta, if avoiding gluten/wheat)
- 12oz mushrooms, sliced (any non-poisonous edible variety)
- ½ cup coconut milk
- ½ onion, finely chopped
- ¼ cup chia seeds
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced (or more, if you like)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tbsp lime juice
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the spaghetti according to packet instructions, or your own good sense, aiming for al dente. When it’s done, drain it, and lastly rinse it (with cold water), and set it aside.
2) Heat the olive oil in a skillet and add the onion, cooking for 5 minutes
3) Add the garlic, mushrooms, and black pepper, cooking for another 8 minutes.
4) Add the coconut milk, lime juice, and chia seeds, stirring well and cooking for a further two minutes
5) Reheat the spaghetti by passing boiling water through it in a colander (the time it spent cold was good for it; it lowered the glycemic index)
6) Serve, adding the mushroom sauce to the spaghetti:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Magic of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- The Many Health Benefits of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Are Brain Chips Safe?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ready For Cyborgization?
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your views on Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs), such as the Utah Array and Neuralink’s chips on/in brains that allow direct communication between brains and computers, so that (for example) a paralysed person can use a device to communicate, or manipulate a prosthetic limb or two.
We didn’t get as many votes as usual; it’s possible that yesterday’s newsletter ended up in a lot of spam filters due to repeated use of a word in “extra ______ olive oil” in its main feature!
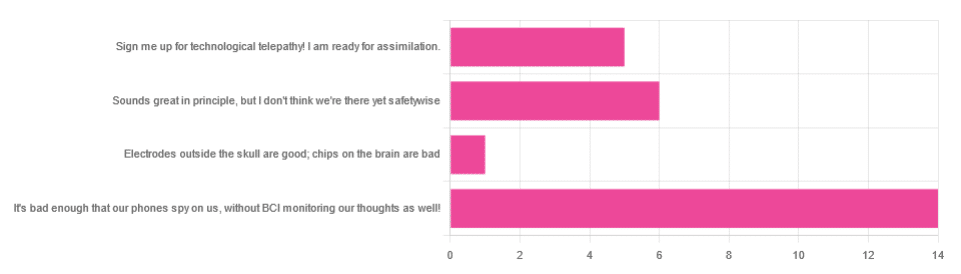
However, of the answers we did get…
- About 54% said “It’s bad enough that our phones spy on us, without BCI monitoring our thoughts as well!”
- About 23% said “Sounds great in principle, but I don’t think we’re there yet safetywise”
- About 19% said “Sign me up for technological telepathy! I am ready for assimilation”
- One (1) person said “Electrode outside the skull are good; chips on the brain are bad”
But what does the science say?
We’re not there yet safetywise: True or False?
True, in our opinion, when it comes to the latest implants, anyway. While it’s very difficult to prove a negative (it could be that everything goes perfectly in human trials), “extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence”, and so far this seems to be lacking.
The stage before human trials is usually animal trials, starting with small creatures and working up to non-human primates if appropriate, before finally humans.
- Good news: the latest hot-topic BCI device (Neuralink) was tested on animals!
- Bad news: to say it did not go well would be an understatement
The Gruesome Story of How Neuralink’s Monkeys Actually Died
The above is a Wired article, and we tend to go for more objective sources, however we chose this one because it links to very many objective sources, including an open letter from the Physicians’ Committee for Responsible Medicine, which basically confirms everything in the Wired article. There are lots of links to primary (medical and legal) sources, too.
Electrodes outside the skull are good; chips on/in the brain are bad: True or False?
True or False depending on how they’re done. The Utah Array (an older BCI implant, now 20 years old, though it’s been updated many times since) has had a good safety record, after being used by a few dozen people with paralysis to control devices:
How the Utah Array is advancing BCI science
The Utah Array works on the same general principle as Neuralink, but the mechanics of its implementation are very different:
- The Utah Array involves a tiny bundle of microelectrodes (held together by a rigid structure that looks a bit like a nanoscale hairbrush) put in place by a brain surgeon, and that’s that.
- The Neuralink has a dynamic web of electrodes, implanted by a little robot that acts like a tiny sewing machine to implant many polymer threads, each containing its own a bunch of electrodes.
In theory, the latter is much more advanced. In practice, so far, the former has a much better safety record.
I am right to be a little worried about giving companies access to my brain: True or False?
True or False, depending on the nature of your concern.
For privacy: current BCI devices have quite simple switches operated consciously by the user. So while technically any such device that then runs its data through Bluetooth or WiFi could be hacked, this risk is no greater than using a wireless mouse and/or keyboard, because it has access to about the same amount of information.
For safety: yes, probably there is cause to be worried. Likely the first waves of commercial users of any given BCI device will be severely disabled people who are more likely to waive their rights in the hope of a life-changing assistance device, and likely some of those will suffer if things go wrong.
Which on the one hand, is their gamble to make. And on the other hand, makes rushing to human trials, for companies that do that, a little more predatory.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Can kimchi really help you lose weight? Hold your pickle. The evidence isn’t looking great
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fermented foods have become popular in recent years, partly due to their perceived health benefits.
For instance, there is some evidence eating or drinking fermented foods can improve blood glucose control in people with diabetes. They can lower blood lipid (fats) levels and blood pressure in people with diabetes or obesity. Fermented foods can also improve diarrhoea symptoms.
But can they help you lose weight, as a recent study suggests? Let’s look at the evidence.
Remind me, what are fermented foods?
Fermented foods are ones prepared when microbes (bacteria and/or yeast) ferment (or digest) food components to form new foods. Examples include yoghurt, cheese, kefir, kombucha, wine, beer, sauerkraut and kimchi.
As a result of fermentation, the food becomes acidic, extending its shelf life (food-spoilage microbes are less likely to grow under these conditions). This makes fermentation one of the earliest forms of food processing.
Fermentation also leads to new nutrients being made. Beneficial microbes (probiotics) digest nutrients and components in the food to produce new bioactive components (postbiotics). These postbiotics are thought to contribute to the health benefits of the fermented foods, alongside the health benefits of the bacteria themselves.
What does the evidence say?
A study published last week has provided some preliminary evidence eating kimchi – the popular Korean fermented food – is associated with a lower risk of obesity in some instances. But there were mixed results.
The South Korean study involved 115,726 men and women aged 40-69 who reported how much kimchi they’d eaten over the previous year. The study was funded by the World Institute of Kimchi, which specialises in researching the country’s national dish.
Eating one to three servings of any type of kimchi a day was associated with a lower risk of obesity in men.
Men who ate more than three serves a day of cabbage kimchi (baechu) were less likely to have obesity and abdominal obesity (excess fat deposits around their middle). And women who ate two to three serves a day of baechu were less likely to have obesity and abdominal obesity.
Eating more radish kimchi (kkakdugi) was associated with less abdominal obesity in both men and women.
However, people who ate five or more serves of any type of kimchi weighed more, had a larger waist sizes and were more likely to be obese.
The study had limitations. The authors acknowledged the questionnaire they used may make it difficult to say exactly how much kimchi people actually ate.
The study also relied on people to report past eating habits. This may make it hard for them to accurately recall what they ate.
This study design can also only tell us if something is linked (kimchi and obesity), not if one thing causes another (if kimchi causes weight loss). So it is important to look at experimental studies where researchers make changes to people’s diets then look at the results.
How about evidence from experimental trials?
There have been several experimental studies looking at how much weight people lose after eating various types of fermented foods. Other studies looked at markers or measures of appetite, but not weight loss.
One study showed the stomach of men who drank 1.4 litres of fermented milk during a meal took longer to empty (compared to those who drank the same quantity of whole milk). This is related to feeling fuller for longer, potentially having less appetite for more food.
Another study showed drinking 200 millilitres of kefir (a small glass) reduced participants’ appetite after the meal, but only when the meal contained quickly-digested foods likely to make blood glucose levels rise rapidly. This study did not measure changes in weight.
Kefir, a fermented milk drink, reduced people’s appetite.
Ildi Papp/ShutterstockAnother study looked at Indonesian young women with obesity. Eating tempeh (a fermented soybean product) led to changes in an appetite hormone. But this did not impact their appetite or whether they felt full. Weight was not measured in this study.
A study in South Korea asked people to eat about 70g a day of chungkookjang (fermented soybean). There were improvements in some measures of obesity, including percentage body fat, lean body mass, waist-to-hip ratio and waist circumference in women. However there were no changes in weight for men or women.
A systematic review of all studies that looked at the impact of fermented foods on satiety (feeling full) showed no effect.
What should I do?
The evidence so far is very weak to support or recommend fermented foods for weight loss. These experimental studies have been short in length, and many did not report weight changes.
To date, most of the studies have used different fermented foods, so it is difficult to generalise across them all.
Nevertheless, fermented foods are still useful as part of a healthy, varied and balanced diet, particularly if you enjoy them. They are rich in healthy bacteria, and nutrients.
Are there downsides?
Some fermented foods, such as kimchi and sauerkraut, have added salt. The latest kimchi study said the average amount of kimchi South Koreans eat provides about 490mg of salt a day. For an Australian, this would represent about 50% of the suggested dietary target for optimal health.
Eating too much salt increases your risk of high blood pressure, heart disease and stroke.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healing Trauma – by Dr. Peter Levine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Levine’s better-selling book about trauma, Waking The Tiger, laid the foundations for this one, but the reason we’re skipping straight into Healing Trauma, is that while the former book is more about the ideas that led him to what he currently believes is the best approach to healing trauma, this book is the one that explains how to actually do it.
The core thesis is that trauma is a natural, transient response, and is not inherently pathological, but that it can become so if not allowed to do its thing.
This book outlines exercises, trademarked as “somatic experiencing”, which allow the body to go through the physiological processes it needs to, to facilitate healing. If you buy the physical book, there is also an audio CD, which this reviewer has not listened to and cannot comment on, but the exercises are clearly described in the book in any case.
The physical aspects of the exercises are similar to the principles of progressive relaxation, while the mental aspects of the exercises are about re-experiencing trauma in a safer fashion, in small doses.
Any kind of dealing with trauma is not going to be comfortable, so this book is not an enjoyable read.
As for how useful the exercises are, your mileage may vary. Like many books about trauma, the expectation is that once upon a time you were in a situation that was unsafe, and now you are safe. If that describes your trauma, you will get the most out of this. However, if your trauma is unrelated to your personal safety, or if it is about your personal safety but the threat still remains extant, then a lot of this may not help and may even make things worse.
In terms of discussing sexual trauma specifically, it was probably not a good choice to favorably quote Woody Allen, and little things like that may be quite jarring for a lot of readers.
Bottom line: if your trauma is PTSD of the kind “you faced an existential threat and now it is gone”, then chances are that this book can help you a lot. If your trauma is different, then your mileage may vary widely on this one.
Click here to check out Healing Trauma, if it seems right for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Hormones And How To Hack Them
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Healthy Hormones And How To Hack Them!
Hormones are vital for far more than they tend to get credit for. Even the hormones that people think of first—testosterone and estrogen—do a lot more than just build/maintain sexual characteristics and sexual function. Without them, we’d lack energy, we’d be depressed, and we’d soon miss the general smooth-running of our bodies that we take for granted.
And that’s without getting to the many less-talked-about hormones that play a secondary sexual role or are in the same general system…
How are your prolactin levels, for example?
Unless you’re ill, taking certain medications, recently gave birth, or picked a really interesting time to read this newsletter, they’re probably normal, by the way.
But, prolactin can explain “la petite mort”, the downturn in energy and the somewhat depressed mood that many men experience after orgasm.
Otherwise, if you have too much prolactin in general, you will be sleepy and depressed.
Prolactin’s primary role? In women, it stimulates milk production when needed. In men, it plays a role in regulating mood and metabolism.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: