Thriving Beyond Fifty – by Will Harlow
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve featured this author sometimes in our video section; he’s an over-50s specialist physiotherapist with a lot of very functional advice to offer.
In this book, Harlow focusses heavily on three things: mobility, strength, endurance.
You may not want to be a gymnast, powerlifter, or marathon-runner, but these things are important for us all to maintain to at least a fair degree:
- Mobility can be the difference between tweaking one’s shoulder getting something from a high shelf, or not
- Strength can be the difference between being able to get back up, or not
- Endurance can be the difference between coming back from a long day on your feet and thinking “that was a good day; I’m looking forward to tomorrow now”, or not
One of the greatest strengths of this book is its comprehensive troubleshooting aspect; if you have a weak spot, chances are this book has the remedy.
As for the style, it’s quite casual/conversational in tone, but without skimping on science and detail. It’s clear, explanatory, and helpful throughout.
Bottom line: if you’d like to maintain/improve mobility, strength, and endurance, then this book is a very recommendable resource.
Click here to check out Thriving Beyond Fifty, and keep thriving at every age!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wakefulness, Cognitive Enhancement, AND Improved Mood?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Old Drug, New Tricks?
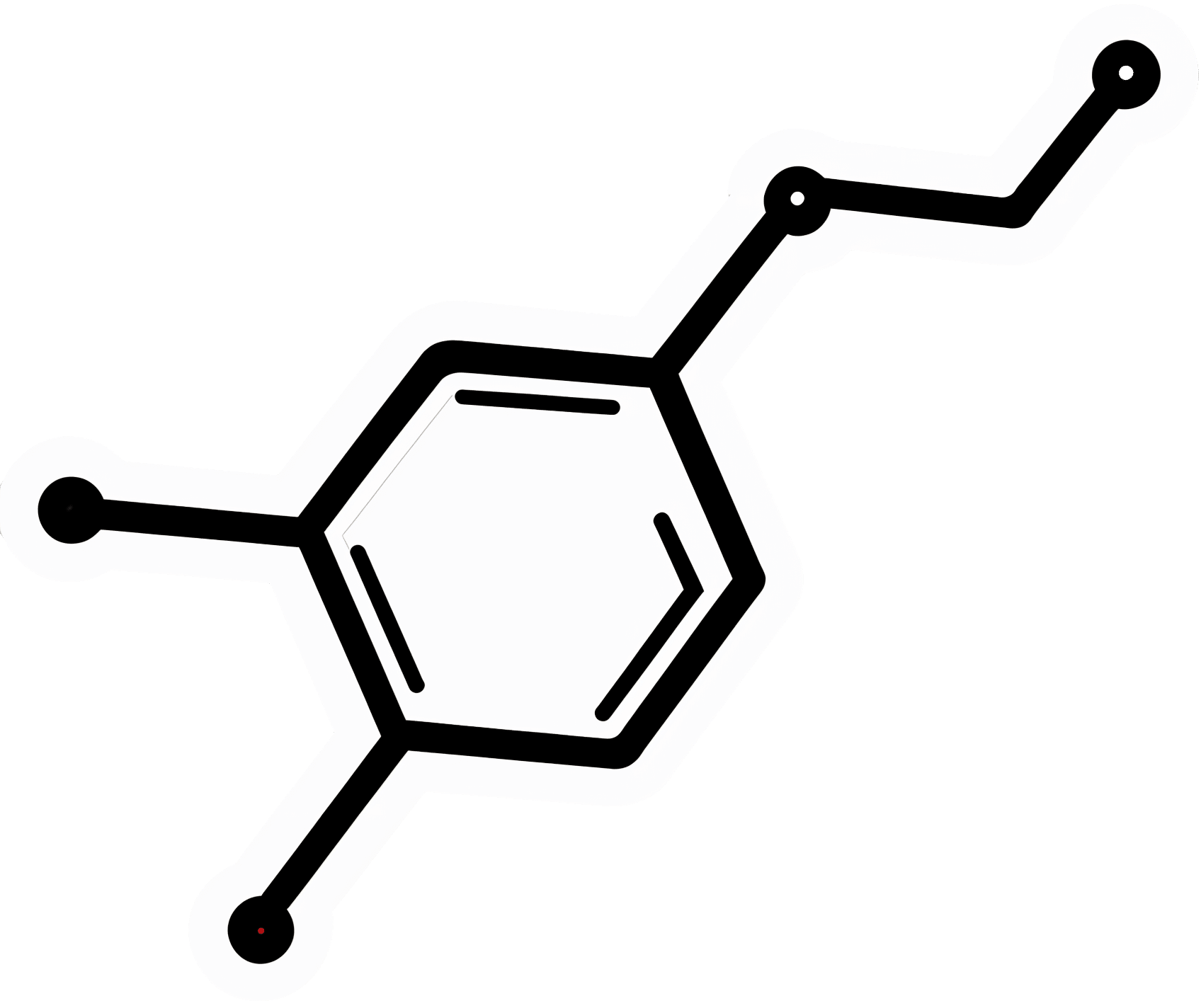
Modafinil (also known by brand names including Modalert and Provigil) is a dopamine uptake inhibitor.
What does that mean? It means it won’t put any extra dopamine in your brain, but it will slow down the rate at which your brain removes naturally-occuring dopamine.
The result is that your brain will get to make more use of the dopamine it does have.
(dopamine is a neutrotransmitter that allows you to feel wakeful and happy, and perform complex cognitive tasks)
Modafinil is prescribed for treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness. Often that’s caused by shift work sleep disorder, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or narcolepsy.
Read: Overview of the Clinical Uses, Pharmacology, and Safety of Modafinil
Many studies done on humans (rather than rats) have been military experiments to reduce the effects of sleep deprivation:
Click Here To See A Military Study On Modafinil!
They’ve found modafinil to be helpful, and more effective and more long-lasting than caffeine, without the same “crash” later. This is for two reasons:
1) while caffeine works by blocking adenosine (so you don’t feel how tired you are) and by constricting blood vessels (so you feel more ready-for-action), modafinil works by allowing your brain to accumulate more dopamine (so you’re genuinely more wakeful, and you get to keep the dopamine)
2) the biological half-life of modafinil is 12–15 hours, as opposed to 4–8 hours* for caffeine.
*Note: a lot of sources quote 5–6 hours for caffeine, but this average is misleading. In reality, we are each genetically predetermined to be either a fast caffeine metabolizer (nearer 4 hours) or a slow caffeine metabolizer (nearer 8 hours).
What’s a biological half-life (also called: elimination half-life)?
A substance’s biological half-life is the time it takes for the amount in the body to be reduced by exactly half.
For example: Let’s say you’re a fast caffeine metabolizer and you have a double-espresso (containing 100mg caffeine) at 8am.
By midday, you’ll have 50mg of caffeine left in your body. So far, so simple.
By 4pm you might expect it to be gone, but instead you have 25mg remaining (because the amount halves every four hours).
By 8pm, you have 12.5mg remaining.
When midnight comes and you’re tucking yourself into bed, you still have 6.25mg of caffeine remaining from your morning coffee!
Use as a nootropic
Many healthy people who are not sleep-deprived use modafinil “off-label” as a nootropic (i.e., a cognitive enhancer).
Read: Modafinil for cognitive neuroenhancement in healthy non-sleep-deprived subjects: A systematic review
Important Note: modafinil is prescription-controlled, and only FDA-approved for sleep disorders.
To get around this, a lot of perfectly healthy biohackers describe the symptoms of sleep pattern disorder to their doctor, to get a prescription.
We do not recommend lying to your healthcare provider, and nor do we recommend turning to the online “grey market”.
Such websites often use anonymized private doctors to prescribe on an “informed consent” basis, rather than making a full examination. Those websites then dispense the prescribed medicines directly to the patient with no further questions asked (i.e. very questionable practices).
Caveat emptor!
A new mood-brightener?
Modafinil was recently tested head-to-head against Citalapram for the treatment of depression, and scored well:
See its head-to-head scores here!
How does it work? Modafinil does for dopamine what a lot of anti-depressants do for serotonin. Both dopamine and serotonin promote happiness and wakefulness.
This is very promising, especially as modafinil (in most people, at least) has fewer unwanted side-effects than a lot of common anti-depressant medications.
Share This Post
-
Feel Great, Lose Weight – by Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that losing weight sustainably tends to be harder than simply losing weight. We know that weight loss needs to come with lifestyle change. But how to get there?
One of the biggest problems that we might face while trying to lose weight is that our “metabolic thermostat” has got stuck at the wrong place. Trying to move it just makes our bodies think we are starving, and everything gets even worse. We can’t even “mind over matter” our way through it with willpower, because our bodies will do impressive things on a cellular level in an attempt to save us… Things that are as extraordinary as they are extraordinarily unhelpful.
Dr. Rangan Chatterjee is here to help us cut through that.
In this book, he covers how our metabolic thermostat got stuck in the wrong place, and how to gently tease it back into a better position.
Some advices won’t be big surprises—go for a whole foods diet, avoiding processed food, for example. Probably not a shocker.
Others are counterintuitive, but he explains how they work—exercising less while moving more, for instance. Sounds crazy, but we assure you there’s a metabolic explanation for it that’s beyond the scope of this review. And there’s plenty more where that came from, too.
Bottom line: if your weight has been either slowly rising, or else very stable but at a higher point than you’d like, Dr. Chatterjee can help you move the bar back to where you want it—and keep it there.
Share This Post
-
Voluntary assisted dying is different to suicide. But federal laws conflate them and restrict access to telehealth
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Voluntary assisted dying is now lawful in every Australian state and will soon begin in the Australian Capital Territory.
However, it’s illegal to discuss it via telehealth. That means people who live in rural and remote areas, or those who can’t physically go to see a doctor, may not be able to access the scheme.
A federal private members bill, introduced to parliament last week, aims to change this. So what’s proposed and why is it needed?
What’s wrong with the current laws?
Voluntary assisted dying doesn’t meet the definition of suicide under state laws.
But the Commonwealth Criminal Code prohibits the discussion or dissemination of suicide-related material electronically.
This opens doctors to the risk of criminal prosecution if they discuss voluntary assisted dying via telehealth.
Successive Commonwealth attorneys-general have failed to address the conflict between federal and state laws, despite persistent calls from state attorneys-general for necessary clarity.
This eventually led to voluntary assistant dying doctor Nicholas Carr calling on the Federal Court of Australia to resolve this conflict. Carr sought a declaration to exclude voluntary assisted dying from the definition of suicide under the Criminal Code.
In November, the court declared voluntary assisted dying was considered suicide for the purpose of the Criminal Code. This meant doctors across Australia were prohibited from using telehealth services for voluntary assisted dying consultations.
Last week, independent federal MP Kate Chaney introduced a private members bill to create an exemption for voluntary assisted dying by excluding it as suicide for the purpose of the Criminal Code. Here’s why it’s needed.
Not all patients can physically see a doctor
Defining voluntary assisted dying as suicide in the Criminal Code disproportionately impacts people living in regional and remote areas. People in the country rely on the use of “carriage services”, such as phone and video consultations, to avoid travelling long distances to consult their doctor.
Other people with terminal illnesses, whether in regional or urban areas, may be suffering intolerably and unable to physically attend appointments with doctors.
The prohibition against telehealth goes against the principles of voluntary assisted dying, which are to minimise suffering, maximise quality of life and promote autonomy.
Some people aren’t able to attend doctors’ appointments in person.
Jeffrey M Levine/ShutterstockDoctors don’t want to be involved in ‘suicide’
Equating voluntary assisted dying with suicide has a direct impact on doctors, who fear criminal prosecution due to the prohibition against using telehealth.
Some doctors may decide not to help patients who choose voluntary assisted dying, leaving patients in a state of limbo.
The number of doctors actively participating in voluntary assisted dying is already low. The majority of doctors are located in metropolitan areas or major regional centres, leaving some locations with very few doctors participating in voluntary assisted dying.
It misclassifies deaths
In state law, people dying under voluntary assisted dying have the cause of their death registered as “the disease, illness or medical condition that was the grounds for a person to access voluntary assisted dying”, while the manner of dying is recorded as voluntary assisted dying.
In contrast, only coroners in each state and territory can make a finding of suicide as a cause of death.
In 2017, voluntary assisted dying was defined in the Coroners Act 2008 (Vic) as not a reportable death, and thus not suicide.
The language of suicide is inappropriate for explaining how people make a decision to die with dignity under the lawful practice of voluntary assisted dying.
There is ongoing taboo and stigma attached to suicide. People who opt for and are lawfully eligible to access voluntary assisted dying should not be tainted with the taboo that currently surrounds suicide.
So what is the solution?
The only way to remedy this problem is for the federal government to create an exemption in the Criminal Code to allow telehealth appointments to discuss voluntary assisted dying.
Chaney’s private member’s bill is yet to be debated in federal parliament.
If it’s unsuccessful, the Commonwealth attorney-general should pass regulations to exempt voluntary assisted dying as suicide.
A cooperative approach to resolve this conflict of laws is necessary to ensure doctors don’t risk prosecution for assisting eligible people to access voluntary assisted dying, regional and remote patients have access to voluntary assisted dying, families don’t suffer consequences for the erroneous classification of voluntary assisted dying as suicide, and people accessing voluntary assisted dying are not shrouded with the taboo of suicide when accessing a lawful practice to die with dignity.
Failure to change this will cause unnecessary suffering for patients and doctors alike.
Michaela Estelle Okninski, Lecturer of Law, University of Adelaide; Marc Trabsky, Associate professor, La Trobe University, and Neera Bhatia, Associate Professor in Law, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Whole – by Dr. T. Colin Campbell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us have at least a broad idea of what we’re supposed to be eating, what nutrients we should be getting. Many of us look at labels, and try to get our daily dose of this and that and the other.
And what we don’t get from food? There are supplements.
Dr. Campbell thinks we can do better:
Perhaps most critical in this book, where it stands out from others (we may already know, for example, that we should try to eat diverse plants and whole foods) is its treatment of why many supplements aren’t helpful.
We tend to hear “supplements are a waste of money” and sometimes they are, sometimes they aren’t. How to know the difference?
Key: things directly made from whole food sources will tend to be better. Seems reasonable, but… why? The answer lies in what else those foods contain. An apple may contain a small amount of vitamin C, less than a vitamin C tablet, but also contains a whole host of other things—tiny phytonutrients, whose machinations are mostly still mysteries to us—that go with that vitamin C and help it work much better. Lab-made supplements won’t have those.
There’s a lot more to the book… A chunk of which is a damning critique of the US healthcare system (the author argues it would be better named a sicknesscare system). We also learn about getting a good balance of macro- and micronutrients from our diet rather than having to supplement so much.
The style is conversational, while not skimping on the science. The author has had more than 150 papers published in peer-reviewed journals, and is no stranger to the relevant academia. Here, however, he focuses on making things easily comprehensible to the lay reader.
In short: if you’ve ever wondered how you’re doing at getting a good nutritional profile, and how you could do better, this is definitely the book for you.
Click here to check out “Whole” on Amazon today, and level up your daily diet!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Primary Care Is Being Disrupted: A Video Primer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How patients are seeing their doctor is changing, and that could shape access to and quality of care for decades to come.
More than 100 million Americans don’t have regular access to primary care, a number that has nearly doubled since 2014. Yet demand for primary care is up, spurred partly by record enrollment in Affordable Care Act plans. Under pressure from increased demand, consolidation, and changing patient expectations, the model of care no longer means visiting the same doctor for decades.
KFF Health News senior correspondent Julie Appleby breaks down what is happening — and what it means for patients.
More From This Investigation
Primary Care Disrupted
Known as the “front door” to the health system, primary care is changing. Under pressure from increased demand, consolidation, and changing patient expectations, the model of care no longer means visiting the same doctor for decades. KFF Health News looks at what this means for patients.
Credits
Hannah Norman Video producer and animator Oona Tempest Illustrator and creative director KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fruit & Veg In The Fridge: Pros & Cons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What effect does refrigeration have on the nutritional value of fruit and vegetables??❞
It’s difficult to give a single definitive answer, because naturally there are a lot of different fruits and vegetables, and a lot of different climates. The answer may be different for tomatoes in Alaska vs bananas in Arizona!
However, we can still generalize at least somewhat
Refrigeration will generally slow down any degradation process, and in the case of fruit and vegetables, that can mean slowing down their “ripening” too, as applicable.
However…
Refrigeration will also impede helpful bioactivity too, and that includes quite a list of things.
Here’s a good study that’s quite illustrative; we’d summarize the conclusions but the rather long title already does that nicely:
So, this really is a case of “there are pros and cons, but probably more cons on balance”.
In practical terms, a good take-away from this can be twofold:
- don’t keep fruit and veg in the fridge unless the ambient temperature really requires it
- if the ambient temperature does require it, it’s best to get the produce in fresh each day if that’s feasible, to minimize time spent in the fridge
An extra thing not included there: often when it comes to the spoilage of fruit and veg, the problem is that it respires and oxidizes; reducing the temperature does lower the rate of those, but often a far better way is to remove the oxygen. So for example, if you get carried away and chop too many carrot batons for your hummus night, then putting them in a sealed container can go a long way to keeping them fresh.
See also: How Does the Nutritional Value of Fruits and Vegetables Change Over Time?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: