Eat To Beat Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Controlling What We Can, To Avoid Cancer
Every time a cell in our body is replaced, there’s a chance it will be cancerous. Exactly what that chance is depends on very many factors. Some of them we can’t control; others, we can.
Diet is a critical, modifiable factor
We can’t choose, for example, our genes. We can, for the most part, choose our diet. Why “for the most part”?
- Some people live in a food desert (the Arctic Circle is a good example where food choices are limited by supply)
- Some people have dietary restrictions (whether by health condition e.g. allergy, intolerance, etc or by personal-but-unwavering choice, e.g. vegetarian, vegan, kosher, halal, etc)
But for most of us, most of the time, we have a good control over our diet, and so that’s an area we can and should focus on.
Choose your animal protein wisely
If you are vegan, you can skip this section. If you are not, then the short version is:
- Fish: almost certainly fine
- Poultry: the jury is out; data is leaning towards fine, though
- Red meat: significantly increased cancer risk
- Processed meat: significantly increased cancer risk
For more details (and a run-down on the science behind the above super-summarized version):
- Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy? ← A mythbuster article that outlines many health properties (good and bad) of animal products
- The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet ← A life-hack article about acting on that information
Skip The Ultra-Processed Foods
Ok, so this one’s probably not a shocker in its simplest form:
❝Studies are showing us is that not only do the ultraprocessed foods increase the risk of cancer, but that after a cancer diagnosis such foods increase the risk of dying❞
Source: Is there a connection between ultraprocessed food and cancer?
There’s an unfortunate implication here! If you took the previous advice to heart and cut out [at least some] meat, and/but then replaced that with ultra-processed synthetic meat, then this was not a great improvement in cancer risk terms.
Ultra-processed meat is worse than unprocessed, regardless of whether it was from an animal or was synthetic.
In other words: if you buy textured soy pieces (a common synthetic meat), it pays to look at the ingredients, because there’s a difference between:
- INGREDIENTS: SOY
- INGREDIENTS: Rehydrated Textured SOY Protein (52%), Water, Rapeseed Oil, SOY Protein Concentrate, Seasoning (SULPHITES) (Dextrose, Flavourings, Salt, Onion Powder, Food Starch Modified, Yeast Extract, Colour: Red Iron Oxide), SOY Leghemoglobin, Fortified WHEAT Flour (WHEAT Flour, Calcium Carbonate, Iron, Niacin, Thiamin), Bamboo Fibre, Methylcellulose, Tomato Purée, Salt, Raising Agent: Ammonium Carbonates
Now, most of those original base ingredients are/were harmless per se (as are/were the grapes in wine—before processing into alcohol), but it has clearly been processed to Hell and back to do all that.
Choose the one that just says “soy”. Or eat soybeans. Or other beans. Or lentils. Really there are a lot of options.
About soy, by the way…
There is (mostly in the US, mostly funded by the animal agriculture industry) a lot of fearmongering about soy. Which is ironic, given the amount of soy that is fed to livestock to be fed to humans, but it does bear addressing:
❝Soy foods are safe for all cancer patients and are an excellent source of plant protein. Studies show soy may improve survival after breast cancer❞
Source: Food risks and cancer: What to avoid
(obviously, if you have a soy allergy then you should not consume soy—for most people, the above advice stands, though)
Advanced Glycation End-Products
These (which are Very Bad™ for very many things, including cancer) occur specifically as a result of processing animal proteins and fats.
Note: not even necessarily ultra-processing, just processing can do it. But ultra-processing is worse. What’s the difference, you wonder?
The difference between “ultra-processed” and just “processed”:
- Your average hotdog has been ultra-processed. It’s not only usually been changed with many artificial additives, it’s also been through a series of processes (physical and chemical) and ends up bearing little relation to the creature it came from.
- Your bacon (that you bought fresh from your local butcher, not a supermarket brand of unknown provenance, and definitely not the kind that might come on the top of frozen supermarket pizza) has been processed. It’s undergone a couple of simple processes on its journey “from farm to table”. Remember also that when you cook it, that too is one more process (and one that results in a lot of AGEs).
Read more: What’s so bad about AGEs?
Note if you really don’t want to cut out certain foods, changing the way you cook them (i.e., the last process your food undergoes before you eat it) can also reduce AGES:
Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Get More Fiber
❝The American Institute for Cancer Research shows that for every 10-gram increase in fiber in the diet, you improve survival after cancer diagnosis by 13%❞
Source: Plant-based diet is encouraged for patients with cancer
Yes, that’s post-diagnosis, but as a general rule of thumb, what is good/bad for cancer when you have it is good/bad for cancer beforehand, too.
If you’re thinking that increasing your fiber intake means having to add bran to everything, happily there are better ways:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are plant-based burgers really bad for your heart? Here’s what’s behind the scary headlines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re hearing a lot about ultra-processed foods and the health effects of eating too many. And we know plant-based foods are popular for health or other reasons.
So it’s not surprising new research out this week including the health effects of ultra-processed, plant-based foods is going to attract global attention.
And the headlines can be scary if that research and the publicity surrounding it suggests eating these foods increases your risk of heart disease, stroke or dying early.
Here’s how some media outlets interpreted the research. The Daily Mail ran with:
Vegan fake meats are linked to increase in heart deaths, study suggests: Experts say plant-based diets can boost health – but NOT if they are ultra-processed
The New York Post’s headline was:
Vegan fake meats linked to heart disease, early death: study
But when we look at the study itself, it seems the media coverage has focused on a tiny aspect of the research, and is misleading.
So does eating supermarket plant-based burgers and other plant-based, ultra-processed foods really put you at greater risk of heart disease, stroke and premature death?
Here’s what prompted the research and what the study actually found.
Nina Firsova/Shutterstock Remind me, what are ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods undergo processing and reformulation with additives to enhance flavour, shelf-life and appeal. These include everything from packet macaroni cheese and pork sausages, to supermarket pastries and plant-based mince.
There is now strong and extensive evidence showing ultra-processed foods are linked with an increased risk of many physical and mental chronic health conditions.
Although researchers question which foods should be counted as ultra-processed, or if all of them are linked to poorer health, the consensus is that, generally, we should be eating less of them.
We also know plant-based diets are popular. These are linked with a reduced risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease and stroke, cancer and diabetes. And supermarkets are stocking more plant-based, ultra-processed food options.
How about the new study?
The study looked for any health differences between eating plant-based, ultra-processed foods compared to eating non-plant based, ultra-processed foods. The researchers focused on the risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease and stroke) and deaths from it.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods in this study included mass-produced packaged bread, pastries, buns, cakes, biscuits, cereals and meat alternatives (fake meats). Ultra-processed foods that were not plant-based included milk-based drinks and desserts, sausages, nuggets and other reconstituted meat products.
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank. This is a large biomedical database that contains de-identified genetic, lifestyle (diet and exercise) and health information and biological samples from half a million UK participants. This databank allows researchers to determine links between this data and a wide range of diseases, including heart disease and stroke.
They used data from nearly 127,000 people who provided details of their diet between 2009 and 2012. The researchers linked this to their hospital records and death records. On average, the researchers followed each participant’s diet and health for nine years.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods included in this study included packaged supermarket bread. doublelee/Shutterstock What did the study find?
With every 10% increase of total energy from plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods there was an associated 5% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or stroke) and a 12% higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
But for every 10% increase in plant-sourced, non-ultra-processed foods consumed there was an associated 7% lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 13% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
The researchers found no evidence for an association between all plant-sourced foods (whether or not they were ultra-processed) and either an increased or decreased risk of cardiovascular disease or dying from it.
This was an observational study, where people recalled their diet using questionnaires. When coupled with other data, this can only tell us if someone’s diet is associated with a particular risk of a health outcome. So we cannot say that, in this case, the ultra-processed foods caused the heart disease and deaths from it.
Why has media coverage focused on fake meats?
Much of the media coverage has focused on the apparent health risks associated with eating fake meats, such as sausages, burgers, nuggets and even steaks.
These are considered ultra-processed foods. They are made by deconstructing whole plant foods such as pea, soy, wheat protein, nuts and mushrooms, and extracting the protein. They are then reformulated with additives to make the products look, taste and feel like traditional red and white meats.
However this was only one type of plant-based, ultra-processed food analysed in this study. This only accounted for an average 0.2% of the dietary energy intake of all the participants.
Compare this to bread, pastries, buns, cakes and biscuits, which are other types of plant-based, ultra-processed foods. These accounted for 20.7% of total energy intake in the study.
This image was at the top of the media release. Screenshot/Imperial It’s hard to say why the media focused on fake meat. But there is one clue in the media release issued to promote the research.
Although the media release did not mention the words “fake meat”, an image of plant-based burgers, sausages and meat balls or rissoles featured prominently.
The introduction of the study itself also mentions plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods, such as sausages, nuggets and burgers.
So it’s no wonder people can be confused.
Does this mean fake meats are fine?
Not necessarily. This study analysed the total intake of plant-based, ultra-processed foods, which included fake meats, albeit a very small proportion of people’s diets.
From this study alone we cannot tell if there would be a different outcome if someone ate large amounts of fake meats.
In fact, a recent review of fake meats found there was not enough evidence to determine their impact on health.
We also need more recent data to reflect current eating patterns of fake meats. This study used dietary data collected from 2009 to 2012, and fake meats have become more popular since.
What if I really like fake meat?
We have known for a while that ultra-processed foods can harm our health. This study tells us that regardless if an ultra-processed food is plant-based or not, it may still be harmful.
We know fake meat can contain large amounts of saturated fats (from coconut or palm oil), salt and sugar.
So like other ultra-processed foods, they should be eaten infrequently. The Australian Dietary Guidelines currently recommends people should only consume foods like this sometimes and in small amounts.
Are some fake meats healthier than others?
Check the labels and nutrition information panels. Look for those lowest in fat and salt. Burgers and sausages that are a “pressed cake” of minced ingredients such as nuts, beans and vegetables will be preferable to reformulated products that look identical to meat.
You can also eat whole plant-based protein foods such as legumes. These include beans, lentils, chickpeas and soy beans. As well as being high in protein and fibre, they also provide essential nutrients such as iron and zinc. Using spices and mushrooms alongside these in your recipes can replicate some of the umami taste associated with meat.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
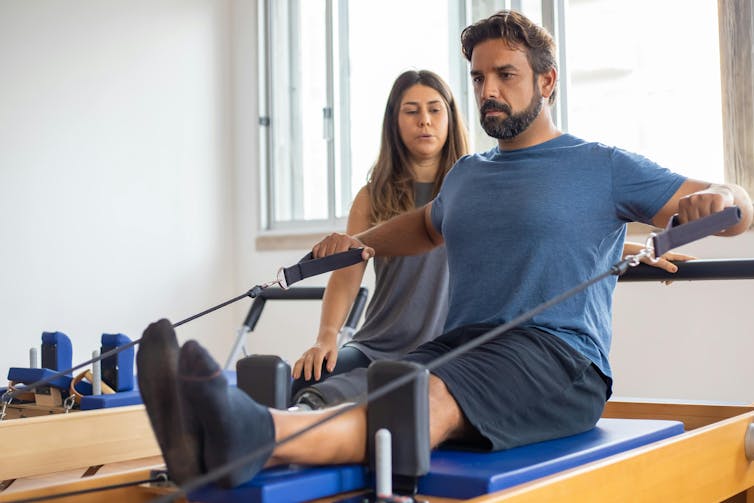
What is reformer pilates? And is it worth the cost?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Reformer pilates is steadily growing in popularity, with new studios opening regularly in major cities all over the world.
But what exactly is reformer pilates? And how does it compare with regular pilates and other types of exercise?
Classes aren’t cheap so let’s look at the potential benefits and drawbacks to help you decide if it’s right for you.
Ahmet Kurt/Unsplash Pilates with special equipment
Pilates is a mode of exercise that focuses on core stability and flexibility, while also addressing muscular strength and endurance, balance and general fitness. At first glance, it might look a bit like yoga, with some more traditional weight training components thrown in.
Reformer pilates uses a piece of equipment called a “reformer”. This looks like a narrow bed that slides along a carriage, has straps to hold onto, and has adjustable springs that add resistance to movement. You perform pilates on the reformer to target specific muscle groups and movement patterns.
The reformer was first designed to help people recover from injuries. However, it has now become common for general fitness and even sports performance.
Unlike normal pilates, also known as “mat pilates”, which only uses your body weight, the reformer adds resistance, meaning you can change the difficulty according to your current level of fitness.
This not only provides a way to overload your muscles, but can make the exercise session more aerobically demanding, which has been proposed to improve cardiovascular fitness.
Mat pilates uses your body weight. Kampus Productions/Pexels What are the benefits of reformer pilates?
Despite being around for decades, there is surprisingly little research looking at the benefits of reformer pilates. However, what we have seen so far suggests it has a similar effect to other modes of exercise.
Reformer pilates has been shown to help with weight loss, cause some small increases in muscle mass, and enhance cognitive function. All of these benefits are commonly seen when combining weight training and cardio into the same routine.
Similarly, among older adults, it has been shown to improve strength, enhance flexibility and may even reduce the risk of falling.
From a rehabilitation perspective, there is some evidence indicating reformer pilates can improve shoulder health and function, reduce lower back pain and increase flexibility.
Finally, there is some evidence suggesting a single session of reformer pilates can improve two key markers of cardiovascular health, being flow-mediated dilation and pulse wave velocity, while also improving cholesterol and insulin levels. This suggests reformer pilates could lead to long-term improvements in heart and metabolic health, although more research is needed to confirm this.
Reformer pilates was first designed to help people recover from injuries. Kampus Productions/Pexels However, there are some key things to consider when discussing these benefits. Most of this research is quite exploratory and comes from a very small number of studies. So we do not know whether these findings will apply to everyone.
Very few studies compared reformer pilates to other types of exercise. Therefore, while it can improve most aspects of health and function, it’s unlikely reformer pilates provides the optimal mode of exercise for each individual component of physical fitness.
Traditional weight training, for example, will likely cause larger improvements in strength than reformer pilates. Similarly, stretching will probably make you more flexible. And running or cycling will make you fitter.
However, if you want a type of exercise that gives you broad overall health benefits, it could be a good option.
What are the downsides of reformer pilates
Reformer pilates is not for everyone.
First and foremost, classes can be expensive compared to other fitness options. You need to be doing at least two to three sessions per week of any type of exercise to maximise the benefits. So even if you can find a class for A$20 or $30, paying for two or three classes a week (or buying a weekly or monthly subscription) is a significant outlay.
Second, it’s not as accessible as other exercise. Even if you can afford it, not every town or suburb has a reformer pilates studio.
Cost and access are major barriers. Or you might get better results with specific modes of exercises. Karolina Grabowska/Pexels Third, the effectiveness of your workout is likely to be impacted by how competent your instructor is. There are a host of different pilates qualifications you can get in Australia, and some take much less time than others. With this in mind, it might be best to look for accredited pilates instructors, although this will further reduce the number of options you have available.
Finally, there is a learning curve. While you will get better over time, the exercise will likely be less effective during those first few weeks (or months) when you are getting used to the machine and the movements.
Is it right for you?
Reformer pilates can be a great addition to your fitness routine, especially if you’re looking for a low-impact way to build strength and flexibility.
But if you have more specific goals, you might need a more specific mode of exercise. For example, if you need to get stronger to improve your ability to manage your daily life, then strength training is probably your best bet. Likewise, if your goal is to run a marathon, you will get more specific benefits from running.
The cost and availability of reformer pilates make it less accessible for some people. With this in mind, if you are after similar benefits at a lower price point, mat pilates might be a better option. Not only does it have evidence suggesting it can improve strength and fitness, but it is something you can do at home if you find a good resource (YouTube could be a good starting point here).
Hunter Bennett, Lecturer in Exercise Science, University of South Australia; Jacinta Brinsley, Exercise Physiologist and Postdoctoral Researcher in the Alliance for Research in Nutrition, Exercise and Activity, University of South Australia, and Lewis Ingram, Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The AFib Cure – by Dr. John Day & Dr. Jared Bunch
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The authors—cardiologists and AFib specialists—make the case that if you have atrial fibrillation, you do in fact have more options than “take these pills and suffer”.
To be clear: they’re not anti-medication per se and they also acknowledge that for some people the meds may still have their place (safety first, and all), but they do fall on the side of “it would be nice to not have to, if possible, so let’s see what we can do”.
Rather, they recommend lifestyle adjustments (no surprises there), and certain biomarker optimizations (this is where it gets more in-depth), which have a good record of reducing symptoms to the point of remission and freedom from medications.
The book is first a primer on the topic of AFib, and then a how-to manual of fixing the problems that you now understand, by biomarker monitoring, lifestyle optimization, and if those things don’t work, ablative therapy which they argue is safer, easier, and more successful than you might think.
The style is clear and easy to understand, with frequent scholarly citations throughout. On the downside, the tone can sometimes be a little on the pushy side for this reviewer’s tastes, but if one overlooks that, it doesn’t detract from the useful content.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one have AFib and would like more treatment/management options than have hitherto been presented, this book will give you that.
Click here to check out The AFib Cure, and look after your heart!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
ADHD For Smart Ass Women – by Tracy Otsuka
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed books about ADHD in adults before, what makes this one different? It’s the wholly female focus. Which is not to say some things won’t apply to men too, they will.
But while most books assume a male default unless it’s “bikini zone” health issues, this one is written by a woman for women focusing on the (biological and social) differences in ADHD for us.
A strength of the book is that it neither seeks to:
- over-medicalize things in a way that any deviation from the norm is inherently bad and must be fixed, nor
- pretend that everything’s a bonus, that we are superpowered and beautiful and perfect and capable and have no faults that might ever need addressing actually
…instead, it gives a good explanation of the ins and outs of ADHD in women, the strengths and weaknesses that this brings, and good solid advice on how to play to the strengths and reduce (or at least work around) the weaknesses.
Bottom line: this book has been described as “ADHD 2.0 (a very popular book that we’ve reviewed previously), but for women”, and it deserves that.
Click here to check out ADHD for Smart Ass Women, and fall in love with your neurodivergent brain!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Rose Hips vs Blueberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing rose hips to blueberries, we picked the rose hips.
Why?
Both of these fruits are abundant sources of antioxidants and other polyphenols, but one of them stands out for overall nutritional density:
In terms of macros, rose hips have about 2x the carbohydrates, and/but about 10x the fiber. That’s an easy calculation and a clear win for rose hips.
When it comes to vitamins, rose hips have a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B6, C, E, K, and choline. On the other hand, blueberries boast more of vitamins B1 and B9. That’s a 9:2 lead for rose hips, even before we consider rose hips’ much greater margins of difference (kicking off with 80x the vitamin A, for instance, and many multiples of many of the others).
In the category of minerals, rose hips have a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. Meanwhile, blueberries are not higher in any minerals.
In short: as ever, enjoy both, but if you’re looking for nutritional density, there’s a clear winner here and it’s rose hips.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
It’s In The Hips: Rosehip’s Benefits, Inside & Out
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cabbage vs Cauliflower – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cabbage to cauliflower, we picked the cauliflower.
Why?
First, let’s note: these are two different cultivars of the same species (Brassica oleracea) and/but as usual (we say, as there are a lot of cultivars of Brassica oleracea, and we’ve done a fair few pairings of them before) there are still nutritional differences to consider, such as…
In terms of macros, cabbage has very slightly more carbs and fiber, while cauliflower has very slightly more protein. However, the numbers are all so close (and the glycemic index equal), such that we’re going to call the macros category a tie.
In the category of vitamins, cabbage has more of vitamins A, B1, E, and K, while cauliflower has more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline. Superficially, this is a clear 8:4 win for cauliflower; it’s worth noting though that the differences in amounts are mostly small, so this isn’t as big a win as it looks like. Still a win for cauliflower, though.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a similar story: cabbage has a little more calcium, iron, and manganese, while cauliflower has a little more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc. This time a 6:3 win for cauliflower, and again, the margins are small so there’s really not as much between them as it looks like. Still a win for cauliflower, though.
In short: enjoy either or both (diversity is good), but the most nutritionally dense is cauliflower, even if cabbage isn’t far behind it.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: