Your Simplest Life – by Lisa Turner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We probably know how to declutter, and perhaps even do a “unnecessary financial expenditures” audit. So, what does this offer beyond that?
A large portion of this book focuses on keeping our general life in a state of “flow”, and strategies include:
- How to make sure you’re doing the right part of the 80:20 split on a daily basis
- Knowing when to switch tasks, and when not to
- Knowing how to plan time for tasks
- No more reckless optimism, but also without falling foul of Parkinson’s Law (i.e. work expands to fill the time allotted to it)
- Decluttering your head, too!
When it comes to managing life responsibilities in general, Turner is very attuned to generational differences… Including the different challenges faced by each generation, what’s more often expected of us, what we’re used to, and how we probably initially learned to do it (or not).
To this end, a lot of strategies are tailored with variations for each age group. Not often does an author take the time to address each part of their readership like that, and it’s really helpful that she does!
All in all, a great book for simplifying your daily life.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
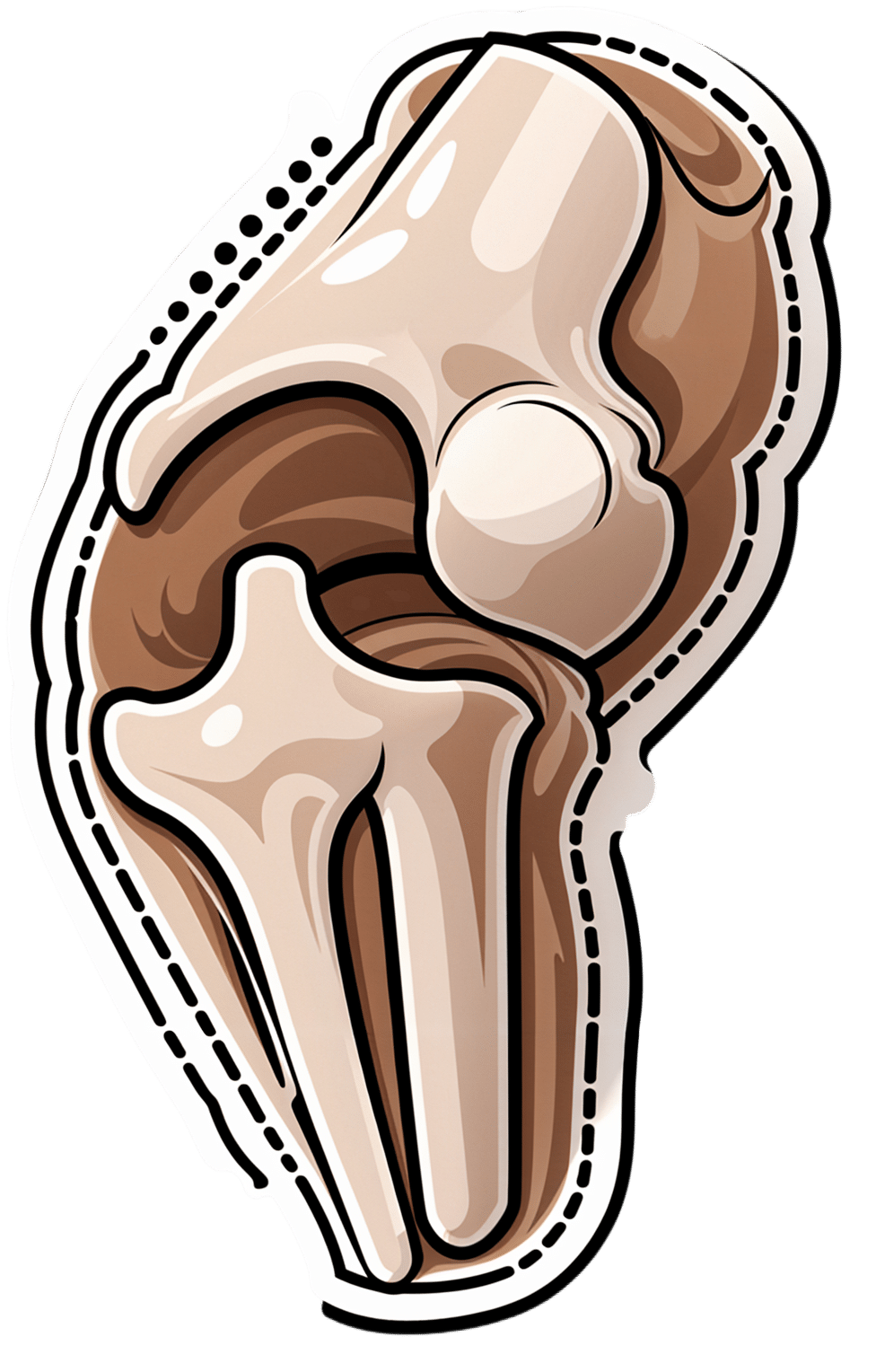
Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Very informative thank you. And made me think. I am a 72 yr old whitewoman, have never used ( or even been offered) HRT since menopause ~15 yrs ago. Now I’m wondering if it would have delayed the onset of osteoarthritis ( knee) and give me more energy in general. And is it wise to start taking hrt after being without those hormones for so long?❞
(this was in response to our article about menopausal HRT)
Thanks for writing! To answer your first question, obviously we can never know for sure now, but it certainly is possible, per for example a large-ish (n=1003) study of women aged 45–64, in which:
- Those with HRT were significantly less likely to have knee arthritis than those without
- However, to enjoy this benefit depended on continued use (those who used it for a bit and then stopped did not enjoy the same results)
- While it made a big difference to knee arthritis, it made only a small (but still beneficial) difference to wrist/hand arthritis.
We could hypothesize that this is because the mechanism of action is more about strengthening the bones (proofing against osteoporosis is one of the main reasons many people take HRT) and cartilage than it is against inflammation directly.
Since the knee is load-bearing and the hand/wrist joints usually are not, this would mean the HRT strengthening the bones makes a big difference to the “wear and tear” aspect of potential osteoarthritis of the knee, but not the same level of benefit for the hand/wrist, which is less about wear and tear and more about inflammatory factors. But that latter, about it being load-bearing, is just this writer’s hypothesis as to why the big difference.
The researchers do mention:
❝In OA the mechanisms by which HRT might act are highly speculative, but could entail changes in cartilage repair or bone turnover, perhaps with cytokines such as interleukin 6, for example.❞
What is clear though, is that it does indeed appear to have a protective effect against osteoarthritis of the knee.
With regard to the timing, the researchers do note:
❝Why as little as three years of HRT should have a demonstrable effect is unclear. Given the difficulty in ascertaining when the disease starts, it is hard to be sure of the importance of the timing of HRT, and whether early or subclinical disease was present.
These results taken together suggest that HRT has a metabolic action that is only effective if given continuously, perhaps by preventing disease initiation; once HRT is stopped there might be a ‘rebound’ effect, explaining the rapid return to normal risk❞
~ Ibid.
You can read the study here:
On whether it is worth it now…
Again, do speak with an endocrinologist because your situation may vary, but:
- hormones are simply messengers, and your body categorically will respond to those messages regardless of age, or time elapsed without having received such a message. Whether it will repair all damage done is another matter entirely, but it would take a biological miracle for it to have no effect at all.
- anecdotally, many women do enjoy life-changing benefits upon starting HRT at your age and older!
(We don’t like to rely on “anecdotally”, but we couldn’t find studies isolating according to “length of time since menopause”—we’ll keep an eye out and if we find something in the future, we’ll mention it!)
Meanwhile, take care!
Share This Post
-
The GLP-1 Lifestyle – by Dr. Joshua Hackett
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
While GLP-1 receptor agonists (i.e. semaglutide drugs such as Ozempic and Wegovy) have enjoyed the spotlight as a miracle cure (with some drawbacks), this book argues very reasonably that we should see them as a tool that we can use (or not) as part of a holistic approach to manage our metabolism.
Unusually, Dr. Hackett doesn’t argue strongly for one way or another, when it comes to using GLP-1 RAs. Rather, he makes the case that they indeed have pros and cons, and we should not only be aware of those pros and cons before making a decision either way, but also, we must understand the process of what goes on.
In contrast to the “inject it and forget it” marketing, he explains how if we actually understand what’s happening in our metabolism, we can improve things for ourselves and, at the very least, avoid sabotaging ourselves. Again, this knowledge is applicable with or without the drugs.
Much of the book is spent covering the physiological underpinnings and how things work for people of various different sizes and metabolic rates, as well as everything you’d expect about dosing, side effects, and whatnot—as well as things you might not have considered closely related, such gut health, and the question of “is there any way to retain the slimmer figure after stopping?”.
The style is methodical and clear, and not at all sensationalized. It’s very much a “read it cover to cover” book rather than a “dip in” book, so be ready for that, though.
Bottom line: if you and/or a loved one are on GLP1-RAs—or on the fence about them—this is a very even-minded and helpfully explanatory book.
Click here to check out The GLP-1 Lifestyle, and transform your metabolism!
Share This Post
-
Healthy Recipes When There Are A Lot Of Restrictions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I need to cook for a family event and the combined dietary restrictions are: vegetarian, no lactose, no gluten, no nuts, including peanuts and coconuts, no discernible carbs, including lentils and chickpeas, no garlic or onions, no cabbage, no soup, and it can’t be remotely spicy. The nut allergy is of course absolute and we are vegetarian, the other things may be slightly negotiable but I’d like a stress-free dinner. Ideas?❞
That is indeed quite restrictive! But a challenge is (almost) always fun.
To answer generally first: one approach is to do buffet-style dining, with many small dishes. While nuts will still need to be absent, because of the nature of nut allergies, the rest can just be skipped on a per-person basis.
But, let’s see what we can do with a one-dish-fits-all approach!
The biggest challenge seems to be getting protein and flavor. Protein options are more limited without meat, lactose, or legumes, and flavor requires some attention without being able to rely on spices.
To give a sample à la carte menu… With these things in mind, we’ve selected three of our recipes from the recipes section of our site, that will require only minor modifications:
1) Invigorating Sabzi Khordan: skip the walnuts and either partition or omit the scallions, and ensure the cheese is lactose-free (most supermarkets stock lactose-free cheeses, nowadays).
With regard to the flatbreads, you can either skip, or use our gluten-free Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe, though it does use chickpea flour and quinoa flour, so the “no discernible carbs” person(s) might still want to skip them. If it’s not an issue on the carbs front, then you might also consider, in lieu of one of the more traditional cheeses, using our High-Protein Paneer recipe which, being vegan, is naturally lactose-free. Also, which is not traditional but would work fine, you might want to add cold hard-boiled halved eggs, since the next course will be light on protein:
2) Speedy Easy Ratatouille: skip the red chili and garlic; that’s all for this one!
3) Black Forest Chia Pudding: the glycemic index of this should hopefully be sufficient to placate the “no discernible carbs” person(s), but if it’s not, we probably don’t have a keto-friendlier dessert than this. And obviously, when it comes to the garnish of “a few almonds, and/or berries, and/or cherries and/or cacao nibs”, don’t choose the almonds.
Want to know more?
For any who might be curious:
Gluten: What’s The Truth? ← this also discusses the differences between an allergy/intolerance/sensitivity—it’s more than just a matter of severity!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Seven Sins Of Memory – by Dr. Daniel Schacter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As we get older, we often become more forgetful—despite remembering many things clearly from decades past. Why?
Dr. Daniel Shacter takes us on a tour of the brain, and also through evolution, to show how memory is not just one thing, but many. And furthermore, it’s not just our vast memory that’s an evolutionary adaptation, but also, our capacity to forget.
He does also discusses disease that affect memory, including Alzheimer’s, and explores the biological aspects of memory too.
The “seven sins” of the title are seven ways our (undiseased, regular) memory “lets us down”, and why, and how that actually benefits us as individuals and as a species, and/but also how we can modify that if we so choose.
The book’s main strength is in how it separates—or bids us separate for ourselves—what is important to us and our lives and what is not. How and why memory and information processing are often at odds with each other (and what that means for us). And, on a practical note, how we can tip the scales for or against certain kinds of memory.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand human memory in all its glorious paradoxes, and put into place practical measures to make it work for you the way you want, this is a fine book for you.
Click here to check out The Seven Sins of Memory, and get managing yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Plant-Based Athlete – by Matt Frazier and Robert Cheeke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you’re already a seasoned plant-based athlete yourself, you can probably skip this book; the 60 recipes at the end would still provide value, but there is the “No Meat Athlete Cookbook” that you could hop straight to, in any case.
For most readers, there will be plenty of value from start to finish. We get a quick ground-up tour of nutrition basics, before getting into restructuring diet to optimize it for performance.
There is less in the way of “Vegans struggle with…” and more in the way of “People think vegans struggle with…” and explanations of what vegan athletes actually eat. The book does include science, but isn’t too science-heavy, and relies more on modelling what plant-based superathletes enjoy on a daily basis.
To that end,if the book has a weak point, it’s perhaps that it could have stood to include more science. The book comes recommended by Dr. Michael Greger, whose nutritional approach is incredibly science-heavy and well-referenced, and this book is obviously compatible with that (so they could have!), but in this case Frazier and Cheeke leave us to take their word for it.
Nevertheless, the science is good whether they cite it or not, and this book is quite a comprehensive primer of plant-based athleticism.
Bottom line: if you’re wondering how to optimize the two goals of “eating plants” and “being a powerful athlete”, then this one’s the book for you.
Click here to check out The Plant-Based Athlete and upgrade your health and athletic performance!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
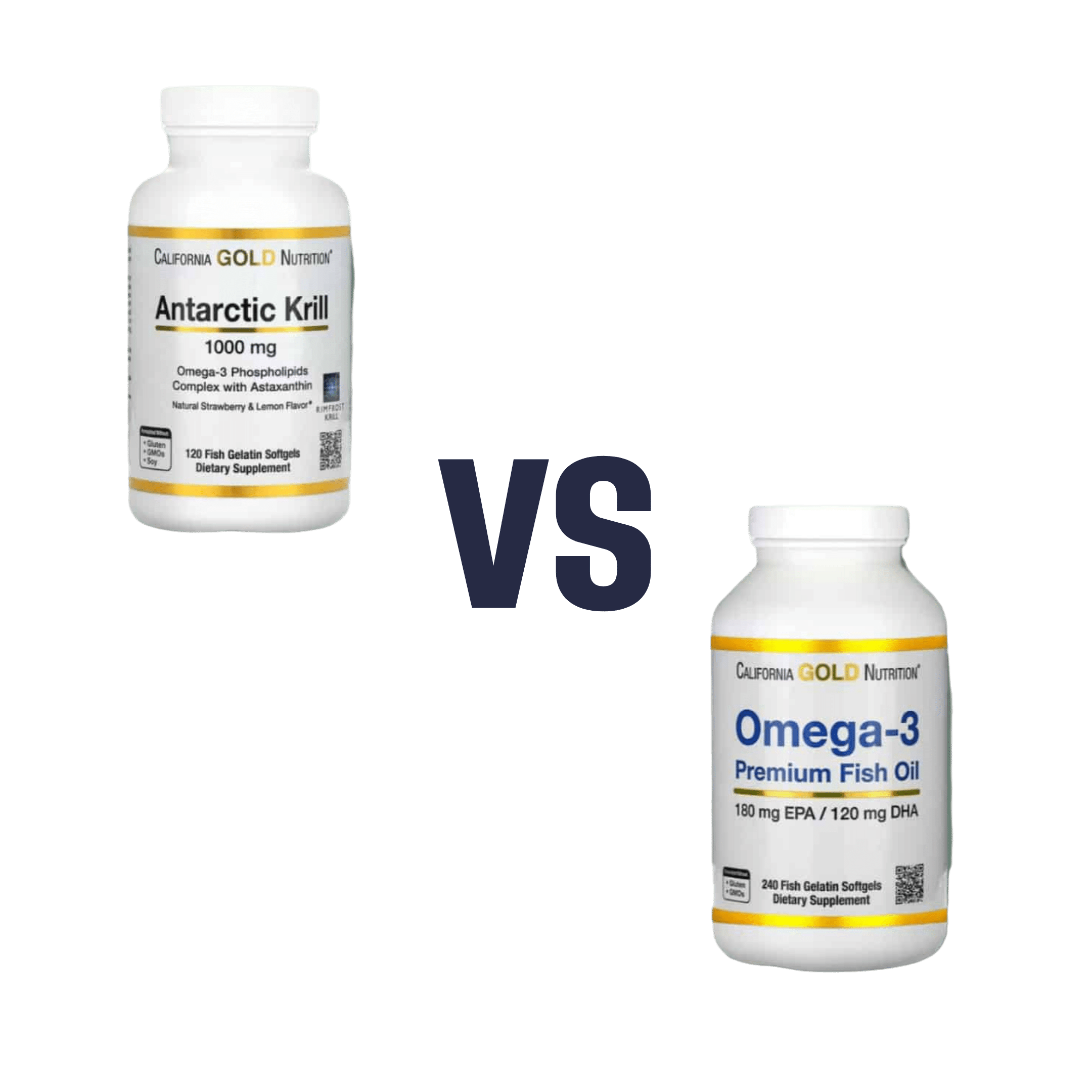
Krill Oil vs Fish Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing krill oil to fish oil, we picked the krill oil.
Why?
Both of these products are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, and for the specific brand depicted above, in both cases 2 softgels will give you the recommended daily amount (which is generally held to be 250–500mg combined omega-3s per day).
This brand’s fish oil gives more (640mg combined omega-3s per 2 softgels, to the same brand’s krill oil’s 480mg per 2 softgels), but since the krill oil is already in the high end of RDA territory, the excess beyond the RDA is not helpful, and not a huge factor. More quantity is not always better, when the body can only process so much at a time.
However, the krill oil gives some extra things that the fish oil doesn’t:
- Astaxanthin, a “super-antioxidant”
- and neuroprotectant, heart-healthy phospholipids
Additional considerations
We have declared “the winner” based on health considerations only. That’s a sticking point for us in all our writings; we’ll occasionally look at and mention other factors, but we know that health is what you’re here for, so that’s what we’ll always treat as most critical.
However, in case these factors may interest you and/or influence you to one or the other:
• The fish oil is about 30% cheaper financially
• The krill oil is a lot more sustainable environmentallyBack to the health science…
Read more:
• What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
• Astaxanthin: Super-Antioxidant & NeuroprotectantWant some? Here for your convenience are some example products on Amazon:
(brands available will vary per region, but now you know what to look out for on the labels!)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: