Women take more antidepressants after divorce than men but that doesn’t mean they’re more depressed
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Research out today from Finland suggests women may find it harder to adjust to later-life divorce and break-ups than men.
The study used population data from 229,000 Finns aged 50 to 70 who had undergone divorce, relationship break-up or bereavement and tracked their use of antidepressants before and after their relationship ended.
They found antidepressant use increased in the four years leading to the relationship dissolution in both genders, with women experiencing a more significant increase.
But it’s too simplistic to say women experience poorer mental health or tend to be less happy after divorce than men.
Remind me, how common is divorce?
Just under 50,000 divorces are granted each year in Australia. This has slowly declined since the 1990s.
More couple are choosing to co-habitate, instead of marry, and the majority of couples live together prior to marriage. Divorce statistics don’t include separations of cohabiting couples, even though they are more likely than married couples to separate.
Those who divorce are doing so later in life, often after their children grow up. The median age of divorce increased from 45.9 in 2021 to 46.7 in 2022 for men and from 43.0 to 43.7 for women.
The trend of late divorces also reflects people deciding to marry later in life. The median duration from marriage to divorce in 2022 was around 12.8 years and has remained fairly constant over the past decade.
Why do couples get divorced?
Changes in social attitudes towards marriage and relationships mean divorce is now more accepted. People are opting not to be in unhappy marriages, even if there are children involved.
Instead, they’re turning the focus on marriage quality. This is particularly true for women who have established a career and are financially autonomous.
Similarly, my research shows it’s particularly important for people to feel their relationship expectations can be fulfilled long term. In addition to relationship quality, participants reported needing trust, open communication, safety and acceptance from their partners.
“Grey divorce” (divorce at age 50 and older) is becoming increasingly common in Western countries, particularly among high-income populations. While factors such as an empty nest, retirement, or poor health are commonly cited predictors of later-in-life divorce, research shows older couples divorce for the same reasons as younger couples.
What did the new study find?
The study tracked antidepressant use in Finns aged 50 to 70 for four years before their relationship breakdown and four years after.
They found antidepressant use increased in the four years leading to the relationship break-up in both genders. The proportion of women taking antidepressants in the lead up to divorce increased by 7%, compared with 5% for men. For de facto separation antidepressant use increased by 6% for women and 3.2% for men.
Within a year of the break-up, antidepressant use fell back to the level it was 12 months before the break-up. It subsequently remained at that level among the men.
But it was a different story for women. Their use tailed off only slightly immediately after the relationship breakdown but increased again from the first year onwards.

sk/Unsplash
The researchers also looked at antidepressant use after re-partnering. There was a decline in the use of antidepressants for men and women after starting a new relationship. But this decline was short-lived for women.
But there’s more to the story
Although this data alone suggest women may find it harder to adjust to later-life divorce and break-ups than men, it’s important to note some nuances in the interpretation of this data.
For instance, data suggesting women experience depression more often than men is generally based on the rate of diagnoses and antidepressant use, which does not account for undiagnosed and unmedicated people.
Women are generally more likely to access medical services and thus receive treatment. This is also the case in Australia, where in 2020–2022, 21.6% of women saw a health professional for their mental health, compared with only 12.9% of men.
Why women might struggle more after separating
Nevertheless, relationship dissolution can have a significant impact on people’s mental health. This is particularly the case for women with young children and older women.
So what factors might explain why women might experience greater difficulties after divorce later in life?
Research investigating the financial consequences of grey divorce in men and women showed women experienced a 45% decline in their standard of living (measured by an income-to-needs ratio), whereas men’s dropped by just 21%. These declines persisted over time for men, and only reversed for women following re-partnering.
Another qualitative study investigating the lived experiences of heterosexual couples post-grey divorce identified financial worries as a common theme between female participants.
A female research participant (age 68) said:
[I am most worried about] the money, [and] what I’m going to do when the little bit of money I have runs out […] I have just enough money to live. And, that’s it, [and if] anything happens I’m up a creek. And Medicare is incredibly expensive […] My biggest expense is medicine.
Another factor was loneliness. One male research participant (age 54) described he preferred living with his ex-wife, despite not getting along with her, than being by himself:
It was still [good] knowing that [the] person was there, and now that’s gone.
Other major complications of later-life divorce are possible issues with inheritance rights and next-of-kin relationships for medical decision-making.
Separation can be positive
For some people, divorce or separation can lead to increased happiness and feeling more independent.
And the mental health impact and emotional distress of a relationship dissolution is something that can be counterattacked with resilience. Resilience to dramatic events built from life experience means older adults often do respond better to emotional distress and might be able to adjust better to divorce than their younger counterparts.
Raquel Peel, Adjunct Senior Lecturer, University of Southern Queensland and Senior Lecturer, RMIT University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Lost for words? Research shows art therapy brings benefits for mental health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Creating art for healing purposes dates back tens of thousands of years, to the practices of First Nations people around the world. Art therapy uses creative processes, primarily visual art such as painting, drawing or sculpture, with a view to improving physical health and emotional wellbeing.
When people face significant physical or mental ill-health, it can be challenging to put their experiences into words. Art therapists support people to explore and process overwhelming thoughts, feelings and experiences through a reflective art-making process. This is distinct from art classes, which often focus on technical aspects of the artwork, or the aesthetics of the final product.
Art therapy can be used to support treatment for a wide range of physical and mental health conditions. It has been linked to benefits including improved self-awareness, social connection and emotional regulation, while lowering levels of distress, anxiety and even pain scores.
In a study published this week in the Journal of Mental Health, we found art therapy was associated with positive outcomes for children and adolescents in a hospital-based mental health unit.
An option for those who can’t find the words
While a person’s engagement in talk therapies may sometimes be affected by the nature of their illness, verbal reflection is optional in art therapy.
Where possible, after finishing an artwork, a person can explore the meaning of their work with the art therapist, translating unspoken symbolic material into verbal reflection.
However, as the talking component is less central to the therapeutic process, art therapy is an accessible option for people who may not be able to find the words to describe their experiences.
Art therapy has supported improved mental health outcomes for people who have experienced trauma, people with eating disorders, schizophrenia and dementia, as well as children with autism.
Art therapy has also been linked to improved outcomes for people with a range of physical health conditions. These include lower levels of anxiety, depression and fatigue among people with cancer, enhanced psychological stability for patients with heart disease, and improved social connection among people who have experienced a traumatic brain injury.
Art therapy has been associated with improved mood and anxiety levels for patients in hospital, and lower pain, tiredness and depression among palliative care patients.
Studies suggest art therapy could support people with a range of health conditions. mojo cp/Shutterstock Our research
Mental ill-health, including among children and young people, presents a major challenge for our society. While most care takes place in the community, a small proportion of young people require care in hospital to ensure their safety.
In this environment, practices that place even greater restriction, such as seclusion or physical restraint, may be used briefly as a last resort to ensure immediate physical safety. However, these “restrictive practices” are associated with negative effects such as post-traumatic stress for patients and health professionals.
Worryingly, staff report a lack of alternatives to keep patients safe. However, the elimination of restrictive practices is a major aim of mental health services in Australia and internationally.
Our research looked at more than six years of data from a child and adolescent mental health hospital ward in Australia. We sought to determine whether there was a reduction in restrictive practices during the periods when art therapy was offered on the unit, compared to times when it was absent.
We found a clear association between the provision of art therapy and reduced frequency of seclusion, physical restraint and injection of sedatives on the unit.
We don’t know the precise reason for this. However, art therapy may have lessened levels of severe distress among patients, thereby reducing the risk they would harm themselves or others, and the likelihood of staff using restrictive practices to prevent this.
This artwork was described by the young person who made it as a dead tree with new growth, representing a sense of hope emerging as they started to move towards their recovery. Author provided That said, hospital admission involves multiple therapeutic interventions including talk-based therapies and medications. Confirming the effect of a therapeutic intervention requires controlled clinical trials where people are randomly assigned one treatment or another.
Although ours was an observational study, randomised controlled trials support the benefits of art therapy in youth mental health services. For instance, a 2011 hospital-based study showed reduced symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder among adolescents randomised to trauma-focussed art therapy compared to a “control” arts and crafts group.
Artwork made by a young person during an art therapy session in an in-patient mental health unit. Author provided What do young people think?
In previous research we found art therapy was considered by adolescents in hospital-based mental health care to be the most helpful group therapy intervention compared to other talk-based therapy groups and creative activities.
In research not yet published, we’re speaking with young people to better understand their experiences of art therapy, and why it might reduce distress. One young person accessing art therapy in an acute mental health service shared:
[Art therapy] is a way of sort of letting out your emotions in a way that doesn’t involve being judged […] It let me release a lot of stuff that was bottling up and stuff that I couldn’t explain through words.
A promising area
The burgeoning research showing the benefits of art therapy for both physical and especially mental health highlights the value of creative and innovative approaches to treatment in health care.
There are opportunities to expand art therapy services in a range of health-care settings. Doing so would enable greater access to art therapy for people with a variety of physical and mental health conditions.
Sarah Versitano, Academic, Master of Art Therapy Program, Western Sydney University and Iain Perkes, Senior Lecturer, Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How stigma perpetuates substance use
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In 2022, 54.6 million people 12 and older in the United States needed substance use disorder (SUD) treatment. Of those, only 24 percent received treatment, according to the most recent National Survey on Drug Use and Health.
SUD is a treatable, chronic medical condition that causes people to have difficulty controlling their use of legal or illegal substances, such as alcohol, tobacco, prescription opioids, heroin, methamphetamine, or cocaine. Using these substances may impact people’s health and ability to function in their daily life.
While help is available for people with SUD, the stigma they face—negative attitudes, stereotypes, and discrimination—often leads to shame, worsens their condition, and keeps them from seeking help.
Read on to find out more about how stigma perpetuates substance use.
Stigma can keep people from seeking treatment
Suzan M. Walters, assistant professor at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine, has seen this firsthand in her research on stigma and health disparities.
She explains that people with SUD may be treated differently at a hospital or another health care setting because of their drug use, appearance (including track marks on their arms), or housing situation, which may discourage them from seeking care.
“And this is not just one case; this is a trend that I’m seeing with people who use drugs,” Walters tells PGN. “Someone said, ‘If I overdose, I’m not even going to the [emergency room] to get help because of this, because of the way I’m treated. Because I know I’m going to be treated differently.’”
People experience stigma not only because of their addiction, but also because of other aspects of their identities, Walters says, including “immigration or race and ethnicity. Hispanic folks, brown folks, Black folks [are] being treated differently and experiencing different outcomes.”
And despite the effective harm reduction tools and treatment options available for SUD, research has shown that stigma creates barriers to access.
Syringe services programs, for example, provide infectious disease testing, Narcan, and fentanyl test strips. These programs have been proven to save lives and reduce the spread of HIV and hepatitis C. SSPs don’t increase crime, but they’re often mistakenly “viewed by communities as potential settings of drug-related crime;” this myth persists despite decades of research proving that SSPs make communities safer.
To improve this bias, Walters says it’s helpful for people to take a step back and recognize how we use substances, like alcohol, in our own lives, while also humanizing those with addiction. She says, “There’s a lack of understanding that these are human beings and people … [who] are living lives, and many times very functional lives.”
Misconceptions lead to stigma
SUD results from changes in the brain that make it difficult for a person to stop using a substance. But research has shown that a big misconception that leads to stigma is that addiction is a choice and reflects a person’s willpower.
Michelle Maloney, executive clinical director of mental health and addiction recovery services for Rogers Behavioral Health, tells PGN that statements such as “you should be able to stop” can keep a patient from seeking treatment. This belief goes back to the 1980s and the War on Drugs, she adds.
“We think about public service announcements that occurred during that time: ‘Just say no to drugs,’” Maloney says. “People who have struggled, whether that be with nicotine, alcohol, or opioids, [know] it’s not as easy as just saying no.”
Stigma can worsen addiction
Stigma can also lead people with SUD to feel guilt and shame and blame themselves for their medical condition. These feelings, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, may “reinforce drug-seeking behavior.”
In a 2020 article, Dr. Nora D. Volkow, the director of NIDA, said that “when internalized, stigma and the painful isolation it produces encourage further drug taking, directly exacerbating the disease.”
Overall, research agrees that stigma harms people experiencing addiction and can make the condition worse. Experts also agree that debunking myths about the condition and using non-stigmatizing language (like saying someone is a person with a substance use disorder, not an addict) can go a long way toward reducing stigma.
Resources to mitigate stigma:
- CDC: Stigma Reduction
- National Harm Reduction Coalition: Respect To Connect: Undoing Stigma
- NIDA:
- Shatterproof: Addiction language guide (Disclosure: The Public Good Projects, PGN’s parent company, is a Shatterproof partner)
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Avocado, Coconut & Lime Crumble Pots
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one’s a refreshing snack or dessert, whose ingredients come together to make a very good essential fatty acid supplement. Coconut is a good source of MCTs, avocados are rich in omega 3, 6, and 9, while chia seeds are a great ALA omega 3 food, topping up the healthy balance.
You will need
- flesh of 2 large ripe avocados
- grated zest and juice of 2 limes
- 3 tbsp coconut oil
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 2 tsp honey (omit if you prefer a less sweet dish)
- 1 tsp desiccated coconut
- 4 low-sugar oat biscuits
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the avocado, lime juice, coconut oil, honey, and half the desiccated coconut, in a food processor.
2) Scoop the mixture into 4 ramekins (or equivalent-sized glasses), making sure to leave a ½” gap at the top. Refrigerate for at least 2–4 hours (longer is fine if you’re not ready to serve yet).
3) Assemble, by crumbling the oat biscuits and sprinkling on top of each serving, along with the other half of the desiccated coconut, the lime zest, and the chia seeds.
4) Serve immediately:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Make Your Coffee Heart-Healthier!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Health-Hack Your Coffee
We have previously written about the general health considerations (benefits and potential problems) of coffee:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Today, we will broadly assume that you are drinking coffee (in general, not necessarily right now, though if you are, same!) and would like to continue to do so. We also assume you’d like to do so as healthily as possible.
Not all coffees are created equal
If you order a coffee in France or Italy without specifying what kind, the coffee you receive will be short, dark,
and handsomeand without sugar. Healthwise, this is not a bad starting point. However…- It will usually be espresso
- Or it may be what in N. America is called a French press (in Europe it’s just called a cafetière)
Both of these kinds of coffee mean that cafestol, a compound found in the oily part of coffee and which is known to raise LDL (“bad” cholesterol”), stays in the drink.
Read: Cafestol and Kahweol: A Review on Their Bioactivities and Pharmacological Properties
Also: Cafestol extraction yield from different coffee brew mechanisms
If you’re reading that second one and wondering what a mocha pot or a Turkish coffee is, they are these things:
- Mocha pot: a stovetop device used for making espresso without an espresso machine
- Turkish coffee pot: also a stovetop device; this thing makes some of the strongest coffee you have ever encountered. Turks usually add sugar (this writer doesn’t; but my taste in coffee been described as “coffee like a punch in the face”)
So, wonderful as they are for those of us who love strong coffee, they also produce the highest in-drink levels of cafestol. If you’d like to cut the cafestol (for example, if you are keeping an eye on your LDL), we recommend…
The humble filter coffee
Whether by your favorite filter coffee machine or a pour-over low-tech coffee setup of the kind you could use even without an electricity supply, the filter keeps more than just the coffee grinds out; it keeps the cafestol out too; most of it, anyway, depending on what kind of filter you use, and the grind of the coffee:
Physical characteristics of the paper filter and low cafestol content filter coffee brews
What about instant coffee?
It has very little cafestol in it. It’s up to you whether that’s sufficient reason to choose it over any other form of coffee (this coffee-lover could never)
Want to make any coffee healthier?
This one isn’t about the cafestol, but…
If you take l-theanine (see here for our previous main feature about l-theanine), the l-theanine acts as a moderator and modulator of the caffeine, amongst other benefits:
The Cognitive-Enhancing Outcomes of Caffeine and L-theanine: A Systematic Review
As to where to get that, we don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fast Burn – by Dr. Ian K. Smith
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Intermittent fasting seems simple enough: how complicated can “stop eating for a bit” be? Well, there are nuances and tweaks and hacks and “if you do this bit wrong it will sabotage your benefits” things to know about, too.
Dr. Smith takes us through the basic essentials first, and covers each of the main kinds of intermittent fasting, for example:
- Time-restricted eating; 12:12, 16:8, etc, with those being hours fasting vs hours eating
- Caloric restriction models; for example 5:2, where one eats “normally” for 5 days a week, and on two non-consecutive days, eats only 500 calories
- Day off models and more; for example, “no eating on Sundays” that can, depending on your schedule, be anything from a 24-hour fast to 36 hours or more.
…and, most notably, what they each do metabolically.
Then, the real meat of the book is his program. Taking into account the benefits of each form of fasting, he weaves together a 9-week program to first ease us gently into intermittent fasting, and then enjoy the maximum benefits with minimum self-sabotage.
Which is the biggest stumbling-block for many trying intermittent fasting for the first time, so it’s a huge help that he takes care of this here.
He also includes meal plans and recipes; readers can use those or not; the fasting plan stands on its own two feet without them too.
Bottom line: if you’ve been thinking of trying intermittent fasting but have been put off by all the kinds or have had trouble sticking to it, this book may be just what you need.
Click here to check out Fast Burn on Amazon and see what you can achieve!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
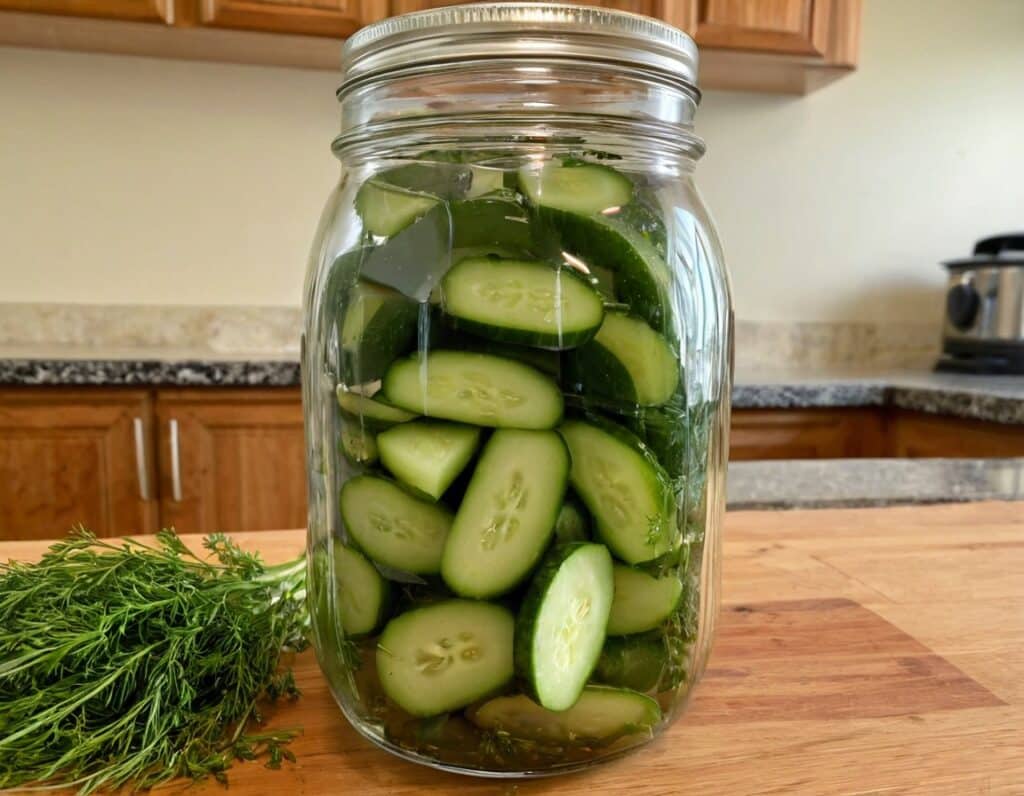
Fast-Pickled Cucumbers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pickled vegetables are great for the gut, and homemade is invariably better than store-bought. But if you don’t have pickling jars big enough for cucumbers, and don’t want to wait a couple of weeks for the results, here’s a great way to do it quickly and easily.
You will need
- 1 large cucumber, sliced
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 1½ tbsp salt (do not omit or substitute)
- 3 cloves garlic, whole, peeled
- 3 large sprigs fresh dill
- 2 tsp whole black peppercorns
- ½ tsp crushed red pepper flakes
- 1 bay leaf
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Mix the vinegar and salt with 1½ cups of water in a bowl.
2) Assemble the rest of the ingredients, except the cucumber, into a quart-size glass jar with an airtight lid.
3) Add the cucumber slices into the jar.
4) Add the pickling brine that you made, leaving ½” space at the top.
5) Close the lid, and shake well.
6) Refrigerate for 2 days, after which, serve at your leisure:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← 3/5 of these spices are in this recipe!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: