Do We Need Sunscreen In Winter, Really?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝I keep seeing advice that we shoudl wear sunscreen out in winter even if it’s not hot or sunny, but is there actually any real benefit to this?❞
Short answer: yes (but it’s indeed not as critical as it is during summer’s hot/sunny days)
Longer answer: first, let’s examine the physics of summer vs winter when it comes to the sun…
In summer (assuming we live far enough from the equator to have this kind of seasonal variation), the part of the planet where we live is tilted more towards the sun. This makes it closer, and more importantly, it’s more directly overhead during the day. The difference in distance through space isn’t as big a deal as the difference in distance through the atmosphere. When the sun is more directly overhead, its rays have a shorter path through our atmosphere, and thus less chance of being blocked by cloud cover / refracted elsewhere / bounced back off into space before it even gets that far.
In winter, the opposite of all that is true.
Morning/evening also somewhat replicate this compared to midday, because the sun being lower in the sky has a similar effect to seasonal variation causing it to be less directly overhead.
For this reason, even though visually the sun may be just as bright on a winter morning as it is on a summer midday, the rays have been filtered very differently by the time they get to us.
This is one reason why you’re much less likely to get sunburned in the winter, compared to the summer (others include the actual temperature difference, your likely better hydration, and your likely more modest attire protecting you).
However…
The reason it is advisable to wear sunscreen in winter is not generally about sunburn, and is rather more about long-term cumulative skin damage (ranging from accelerated aging to cancer) caused by the UV rays—specifically, mostly UVA rays, since UVB rays (with their higher energy but shorter wavelength) have nearly all been blocked by the atmosphere.
Here’s a good explainer of that from the American Cancer Society:
UV (Ultraviolet) Radiation and Cancer Risk
👆 this may seem like a no-brainer, but there’s a lot explained here that demystifies a lot of things, covering ionizing vs non-ionizing radiation, x-rays and gamma-rays, the very different kinds of cancer caused by different things, and what things are dangerous vs which there’s no need to worry about (so far as best current science can say, at least).
Consequently: yes, if you value your skin health and avoidance of cancer, wearing sunscreen when out even in the winter is a good idea. Especially if your phone’s weather app says the UV index is “moderate” or above, but even if it’s “low”, it doesn’t hurt to include it as part of your skincare routine.
But what if sunscreens are dangerous?
Firstly, not all sunscreens are created equal:
Learn more: Who Screens The Sunscreens?
Secondly: consider putting on a protective layer of moisturizer first, and then the sunscreen on top. Bear in mind, this is winter we’re talking about, so you’re probably not going out in a bikini, so this is likely a face-neck-hands job and you’re done.
What about vitamin D?
Humans evolved to have more or less melanin in our skin depending on where we lived, and white people evolved to wring the most vitamin D possible out of the meagre sun far from the equator. Black people’s greater melanin, on the other hand, offers some initial protection against the sun (but any resultant skin cancer is then more dangerous than it would be for white people if it does occur, so please do use sunscreen whatever your skintone).
Nowadays many people live in many places which may or may not be the places we evolved for, and so we have to take that into account when it comes to sun exposure.
Here’s a deeper dive into that, for those who want to learn:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Alpha, beta, theta: what are brain states and brain waves? And can we control them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There’s no shortage of apps and technology that claim to shift the brain into a “theta” state – said to help with relaxation, inward focus and sleep.
But what exactly does it mean to change one’s “mental state”? And is that even possible? For now, the evidence remains murky. But our understanding of the brain is growing exponentially as our methods of investigation improve.
Brain-measuring tech is evolving
Currently, no single approach to imaging or measuring brain activity gives us the whole picture. What we “see” in the brain depends on which tool we use to “look”. There are myriad ways to do this, but each one comes with trade-offs.
We learnt a lot about brain activity in the 1980s thanks to the advent of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Eventually we invented “functional MRI”, which allows us to link brain activity with certain functions or behaviours in real time by measuring the brain’s use of oxygenated blood during a task.
We can also measure electrical activity using EEG (electroencephalography). This can accurately measure the timing of brain waves as they occur, but isn’t very accurate at identifying which specific areas of the brain they occur in.
Alternatively, we can measure the brain’s response to magnetic stimulation. This is very accurate in terms of area and timing, but only as long as it’s close to the surface.
What are brain states?
All of our simple and complex behaviours, as well as our cognition (thoughts) have a foundation in brain activity, or “neural activity”. Neurons – the brain’s nerve cells – communicate by a sequence of electrical impulses and chemical signals called “neurotransmitters”.
Neurons are very greedy for fuel from the blood and require a lot of support from companion cells. Hence, a lot of measurement of the site, amount and timing of brain activity is done via measuring electrical activity, neurotransmitter levels or blood flow.
We can consider this activity at three levels. The first is a single-cell level, wherein individual neurons communicate. But measurement at this level is difficult (laboratory-based) and provides a limited picture.
As such, we rely more on measurements done on a network level, where a series of neurons or networks are activated. Or, we measure whole-of-brain activity patterns which can incorporate one or more so-called “brain states”.
According to a recent definition, brain states are “recurring activity patterns distributed across the brain that emerge from physiological or cognitive processes”. These states are functionally relevant, which means they are related to behaviour.
Brain states involve the synchronisation of different brain regions, something that’s been most readily observed in animal models, usually rodents. Only now are we starting to see some evidence in human studies.
Various kinds of states
The most commonly-studied brain states in both rodents and humans are states of “arousal” and “resting”. You can picture these as various levels of alertness.
Studies show environmental factors and activity influence our brain states. Activities or environments with high cognitive demands drive “attentional” brain states (so-called task-induced brain states) with increased connectivity. Examples of task-induced brain states include complex behaviours such as reward anticipation, mood, hunger and so on.
In contrast, a brain state such as “mind-wandering” seems to be divorced from one’s environment and tasks. Dropping into daydreaming is, by definition, without connection to the real world.
We can’t currently disentangle multiple “states” that exist in the brain at any given time and place. As mentioned earlier, this is because of the trade-offs that come with recording spatial (brain region) versus temporal (timing) brain activity.
Brain states vs brain waves
Brain state work can be couched in terms such as alpha, delta and so forth. However, this is actually referring to brain waves which specifically come from measuring brain activity using EEG.
EEG picks up on changing electrical activity in the brain, which can be sorted into different frequencies (based on wavelength). Classically, these frequencies have had specific associations:
- gamma is linked with states or tasks that require more focused concentration
- beta is linked with higher anxiety and more active states, with attention often directed externally
- alpha is linked with being very relaxed, and passive attention (such as listening quietly but not engaging)
- theta is linked with deep relaxation and inward focus
- and delta is linked with deep sleep.
Brain wave patterns are used a lot to monitor sleep stages. When we fall asleep we go from drowsy, light attention that’s easily roused (alpha), to being relaxed and no longer alert (theta), to being deeply asleep (delta).
Can we control our brain states?
The question on many people’s minds is: can we judiciously and intentionally influence our brain states?
For now, it’s likely too simplistic to suggest we can do this, as the actual mechanisms that influence brain states remain hard to detangle. Nonetheless, researchers are investigating everything from the use of drugs, to environmental cues, to practising mindfulness, meditation and sensory manipulation.
Controversially, brain wave patterns are used in something called “neurofeedback” therapy. In these treatments, people are given feedback (such as visual or auditory) based on their brain wave activity and are then tasked with trying to maintain or change it. To stay in a required state they may be encouraged to control their thoughts, relax, or breathe in certain ways.
The applications of this work are predominantly around mental health, including for individuals who have experienced trauma, or who have difficulty self-regulating – which may manifest as poor attention or emotional turbulence.
However, although these techniques have intuitive appeal, they don’t account for the issue of multiple brain states being present at any given time. Overall, clinical studies have been largely inconclusive, and proponents of neurofeedback therapy remain frustrated by a lack of orthodox support.
Other forms of neurofeedback are delivered by MRI-generated data. Participants engaging in mental tasks are given signals based on their neural activity, which they use to try and “up-regulate” (activate) regions of the brain involved in positive emotions. This could, for instance, be useful for helping people with depression.
Another potential method claimed to purportedly change brain states involves different sensory inputs. Binaural beats are perhaps the most popular example, wherein two different wavelengths of sound are played in each ear. But the evidence for such techniques is similarly mixed.
Treatments such as neurofeedback therapy are often very costly, and their success likely relies as much on the therapeutic relationship than the actual therapy.
On the bright side, there’s no evidence these treatment do any harm – other than potentially delaying treatments which have been proven to be beneficial.
Susan Hillier, Professor: Neuroscience and Rehabilitation, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
GABA Against Stress/Anxiety
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A Neurotransmitter Less Talked-About
GABA is taken by many people as a supplement, mostly as a mood modifier, though its health claims go beyond the recreational—and also, we’re of the opinion that mental health is also just health, and if it works, it works. We’ll explore some of the claims and science behind them today…
What is GABA?
GABA stands for gamma-aminobutyric acid, and it’s a neurotransmitter. It’s a lot less talked-about than for example dopamine or serotonin, but it’s very important nonetheless.
We make it ourselves inside our body, and we can also get it from our food, or supplement it, and some drugs will also have an effect on its presence and/or activity in our body.
What foods is it found in?
- Animals, obviously (just like in human brains*)
- Fermented foods (many kinds)
- Yeast
- Tea
- Tomatoes
- Mulberries
For more details, see:
γ-Aminobutyric acid found in fermented foods and beverages: current trends
*However, we do not recommend eating human brains, due to the risk of CJD and prion diseases in general.
What claims are made about it and are they true?
For brevity, we’ll give a little spoiler up-front: all the popular claims for it appear to be valid, though there’s definitely room for a lot more human trials (we skipped over a lot of rodent studies today!).
So we’ll just drop some of its main benefits, and human studies to back those.
Reduction of stress and anxiety
GABA decreases task-related stress and anxiety within 30 minutes of being taken, both in subjective measures (i.e., self-reports) and in objective clinical physiological measures:
Cognitive enhancement
It’s not a does-everything nootropic like some, but it does have clear benefits to episodic memory:
❝GABA intake might help to distribute limited attentional resources more efficiently, and can specifically improve the identification and ordering of visual events that occur in close temporal succession❞
One of the things that makes this one important is that it also deals with the often-asked question of “does GABA pass the blood-brain barrier”:
❝The present findings do give further credence to the idea that oral ingestion does allow GABA to reach the brain and exert direct effects on cognition, which in the present case were specific to temporal attention.❞
Read more:
Supplementation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) affects temporal, but not spatial visual attention
Potential for more
We take care to give good quality sources, so the following study comes with a big caveat that it has since been retracted. Why was it retracted, you wonder?
It’s about the sample; they cite “30 healthy adults”, but neglected tp mention that this figure was initially 46. What happened to the other 16 participants is unclear, but given that this was challenged and the challenge not answered, it was sufficient for the journal (Nature) to pull the study, in case of deliberate sample bias.
However! Running the numbers in their results section, a probability of 0.03 is very compelling unless the disappearance of 16 subjects was outright fraudulent (which we regrettably cannot know either way).
Here’s the study (so take it with a pinch of salt, considering the above), and taken at face value, it shows how GABA supplementation improves accurate reactions to fast-moving visual and auditory stimuli:
RETRACTED ARTICLE: γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) administration improves action selection processes: a randomised controlled trial
…so, hopefully this experiment will be repeated, without disappearing participants!
The sweet spot
You may be wondering how something that slows a person down (having a relaxing effect) can also speed a person up. This has to do with what it is and isn’t affecting; think of it like a “focus mode” on your computer or other device that greys-out everything else a bit so that you can focus on what you’re doing.
It’s in some ways (by different neurochemical pathways, though) a similar effect to the “relaxed alertness” created by l-theanine supplementation.
There’s also a sweet spot whereby GABA is toning some things down just the right amount, without adversely affecting performance in areas we don’t want slowed down. For the science of this, see:
Is it safe?
GABA is “Generally Recognized As Safe”. However:
- you should speak with your pharmacist if you are taking any medications for blood pressure or epilepsy, as GABA supplementation may cause them to work too well.
- you should absolutely not take GABA with alcohol or opioids as (dose-dependent for all the substances involved, and also depending on your metabolic base rate and other factors) its acute depression of the CNS can mean you relax and slow down too much, and you may find yourself not breathing often enough to sustain life.
Aside from that, it is considered safe up to at least 1g/kg/day*. Given that popular doses are 120–750mg, and most people weigh more than 750g, this is very safe for most people:
United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Safety Review of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it, but for your convenience, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Infections Here, Infections There…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This week in health news, let’s take a look at infections outside and in, and how to walk away from it all (in a good way):
The bird that flu away
This one cannot be described as good news. Basically, bird flu is now already epidemic amongst cows in the US, with 845 herds (not 845 cows; 845 herds) testing positive across 16 states. The US Department of Agriculture earlier this month announced a federal order to test milk nationwide. Researchers welcomed the news, but said it should have happened months ago—before the virus was so entrenched. It currently has a fatality rate of 2–5% in cows; we don’t have enough data to reasonably talk about its fatality rate in humans—yet.
❝It’s disheartening to see so many of the same failures that emerged during the COVID-19 crisis re-emerge❞
~ Tom Bollyky, director of the Global Health Program at the Council on Foreign Relations
Read in full: How America lost control of the bird flu, setting the stage for another pandemic
Related: Cows’ Milk, Bird Flu, & You
Alzheimer’s from the gut upwards
Alzheimer’s is generally thought of as being a purely brain thing, but there’s a link between a [specific] chronic gut infection, and the development of Alzheimer’s disease. This infection is called human cytomegalovirus, or HCMV for short, and usually we’ve all been exposed to it by young adulthood. However, for some people, it lingers in an active state in the gut, wherefrom it may travel to the brain via the vagus nerve “gut-brain highway”. And once there, well, you can guess the rest:
Read in full: The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
Related: How To Reduce Your Alzheimer’s Risk
Walking back to happiness
Analyzing data from 96,138 adults around the world, showed that more steps meant less depression for participants.
You may be thinking “well yes, depressed people walk less”, but more specifically, increases in activity showed increases in anti-depressive benefits, with even small incremental increases showing correspondingly incremental benefits. Specifically, each additional 1,000 steps per day corresponded to a 9% reduction in depression:
Read in full: Higher daily step counts associated with fewer depressive symptoms
Related: Walking… Better.
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Goji Berries: Which Benefits Do They Really Have?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are Goji Berries Really A Superfood?
Goji berries are popularly considered a superfood, and sold for everything from anti-aging effects, to exciting benefits* that would get this email directed to your spam folder if we described them.
*We searched so you don’t have to: there doesn’t seem to be much research to back [that claim that we can’t mention], but we did find one paper on its “invigorating” benefits for elderly male rats. We prefer to stick to human studies where we can!
So how does the science stack up for the more mainstream claims?
Antioxidant effects
First and most obvious for this fruit that’s full of helpful polysaccharides, carotenoids, phenolic acids, and flavonoids, yes, they really do have strong antioxidant properties:
Immune benefits
Things that are antioxidant are generally also anti-inflammatory, and often have knock-on benefits for the immune system. That appears to be the case here.
For example, in this small-but-statistically-significant study (n=60) in healthy adults (aged 55–72 years)
❝The GoChi group showed a statistically significant increase in the number of lymphocytes and levels of interleukin-2 and immunoglobulin G compared to pre-intervention and the placebo group, whereas the number of CD4, CD8, and natural killer cells or levels of interleukin-4 and immunoglobulin A were not significantly altered. The placebo group showed no significant changes in any immune measures.
Whereas the GoChi group showed a significant increase in general feelings of well-being, such as fatigue and sleep, and showed a tendency for increased short-term memory and focus between pre- and post-intervention, the placebo group showed no significant positive changes in these measures.❞
“GoChi” here is a brand name for goji berries, and it’s not clear from the abstract whether the company funded the study:
Here’s another study, this time n=150, and ages 65–70 years old. This time it’s with a different brand (“Lacto-Wolfberry”, a milk-with-goji supplement drink) and it’s also unclear whether the company funded the study. However, taking the data at face value:
❝In conclusion, long-term dietary supplementation with Lacto-Wolfberry in elderly subjects enhances their capacity to respond to antigenic challenge without overaffecting their immune system, supporting a contribution to reinforcing immune defense in this population. ❞
In other words: it allowed those who took it to get measurably more benefit from the flu vaccinations that they received, without any ill effects.
Anticancer potential
This one’s less contentious (the immune benefits seemed very credible; we’d just like to see more transparent research to say for sure), so in the more clearly-evidenced case against cancer we’ll just drop a few quick studies, clipped for brevity:
- Goji berry (Lycium barbarum) inhibits the proliferation, adhesion, and migration of oral cancer cells
- A closer look at immunomodulatory properties of goji berries extract in human colon cancer cells
- Lycium barbarum polysaccharides induce apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells and inhibits prostate cancer growth
- Identification of goji berry cyclic peptides and anticervical carcinoma activity
- Antiproliferative effects of Lycium barbarum’s (goji berry) fractions on breast cancer Cell Lines
You get the idea: it helps!
Bonus benefit for the eyes
Goji berries also help against age-related macular degeneration. The research for this is in large part secondary, i.e. goji berries contain things x, y, and z, and then separate studies say that those things help against age-related macular degeneration.
We did find some goji-specific studies though! One of them was for our old friends the “Lacto-Wolfberry” people and again, wasn’t very transparent, so we’ll not take up extra time/space with that one here.
Instead, here’s a much clearer, transparent, and well-referenced study with no conflicts of interest, that found:
❝Overall, daily supplementation with Goji berry for 90d improves MPOD by increasing serum Z levels rather than serum L levels in early AMD patients. Goji berry may be an effective therapeutic intervention for preventing the progression of early AMD.❞
- MPOD = Macular Pigment Optical Density, a standard diagnostic tool for age-related macular degeneration
- AMD = Age-related Macular Degeneration
(that whole paper is very compelling reading, if you have time)
If you want a quicker read, we offer:
How To Avoid Age-Related Macular Degeneration
and also…
Where to get goji berries?
You can probably find them at your local health food store, if not the supermarket. However, if you’d like to buy them online, here’s an example product on Amazon for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fix Chronic Fatigue & Regain Your Energy, By Science
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic fatigue is on the rise. A lot of it appears to be Long COVID-related, but whether that’s the case for you or not, one thing that will make a big difference to your energy levels is something that French biochemist Jessie Inchauspé is here to explain:
Mitochondrial management
Inchauspé explains it in terms of a steam train; to keep running, it must have coal burning in its furnace. However, if more coal is delivered to the engine room faster than it can be put in the furnace and burned, and the coal just keeps on coming, the worker there will soon be overwhelmed trying to find places to put it all; the engine room will be full of coal, and the furnace will sputter and go out because the worker can’t even reach it on account of being buried in coal.
So it is with our glucose metabolism also. If we get spikes of glucose faster than our body can deal with them, it will overload the body’s ability to process that energy at all. Just like the steam train worker, our body will try! It’ll stuff that extra glucose wherever it can (storing as glycogen in the liver is a readily available option that’s easy to do and/but also gives you non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and isn’t quickly broken down into useable energy), and meanwhile, your actual mitochondria aren’t getting what they need (which is: a reliable, but gentle, influx of glucose).
You can imagine that the situation we described in the steam train isn’t good for the engine’s longevity, and the corresponding situation in the human body isn’t good for our mitochondria either (or our pancreas, or our liver, or… the list goes on). Indeed, damaged mitochondria affect exercise capacity and stress resilience—as well as being a long-term driver of cancer.
The remedy, of course, is blood sugar management. Specifically, avoiding glucose spikes. She has a list of 10 ways to do this (small changes to how we eat; what things to eat with what, in which order, etc) that make a huge measurable difference. For your convenience, we’ve linked those ten ways below; first though, if you’d like to hear it from Inchauspé directly (her style is very pleasant), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- 10 Ways To Balance Your Blood Sugars ← this is the longer list she’s referring to in the video!
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver ← also relevant
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
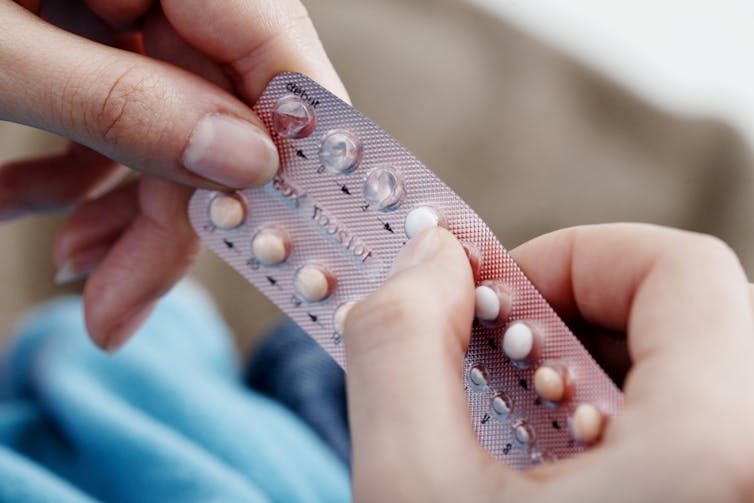
What is Ryeqo, the recently approved medicine for endometriosis?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For women diagnosed with endometriosis it is often a long sentence of chronic pain and cramping that impacts their daily life. It is a condition that is both difficult to diagnose and treat, with many women needing either surgery or regular medication.
A medicine called Ryeqo has just been approved for marketing specifically for endometriosis, although it was already available in Australia to treat a different condition.
Women who want the drug will need to consult their local doctor and, as it is not yet on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, they will need to pay the full cost of the script.
What does Ryeqo do?
Endometriosis affects 14% of women of reproductive age. While we don’t have a full understanding of the cause, the evidence suggests it’s due to body tissue that is similar to the lining of the uterus (called the endometrium) growing outside the uterus. This causes pain and inflammation, which reduces quality of life and can also affect fertility.
Ryeqo is a tablet containing three different active ingredients: relugolix, estradiol and norethisterone.
Relugolix is a drug that blocks a particular peptide from releasing other hormones. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Estradiol is a naturally occurring oestrogen hormone in women that helps regulate the menstrual cycle and is used in menopausal hormone therapy. Norethisterone is a synthetic hormone commonly used in birth control medications and to delay menstruation and help with heavy menstrual bleeding.
All three components work together to regulate the levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body that contribute to endometriosis, alleviating its symptoms.
Relugolix reduces the overall levels of oestrogen and progesterone in the body. The estradiol compensates for the loss of oestrogen because low oestrogen levels can cause hot flushes (also called hot flashes) and bone density loss. And norethisterone blocks the effects of estradiol on the uterus (where too much tissue growth is unwanted).
Is it really new?
The maker of Ryeqo claims it is the first new drug for endometriosis in Australia in 13 years.
But individually, all three active ingredients in Ryeqo have been in use since 2019 or earlier.
Ryeqo has been available in Australia since 2022, but until now was not specifically indicated for endometriosis. It was originally approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids, which share some common symptoms with endometriosis and have related causes.
In addition to Ryeqo, current medical guidance lists other drugs that are suitable for endometriosis and some reformulations of these have also only been recently approved.
The oral medicine Dienogest was approved in 2021, and there have been a number of injectable drugs for endometriosis recently approved, such as Sayana Press which was approved in a smaller dose form for self-injection in 2023.
You can’t take the contraceptive pill with Ryeqo but the endometriosis drug could replace it.
ShutterstockHow to take it and what not to do
Ryeqo is a once-a-day tablet. You can take it with, or without food, but it should be taken about the same time each day.
It is recommended you start taking Ryeqo within the first five days after the start of your next period. If you start at another time during your period, you may experience initial irregular or heavier bleeding.
Because it contains both synthetic and natural hormones, you can’t use the contraceptive pill and Ryeqo together. However, because Ryeqo does contain norethisterone it can be used as your contraception, although it will take at least one month of use to be effective. So, if you are on Ryeqo, you should use a non-hormonal contraceptive – such as condoms – for a month when starting the medicine.
Ryeqo may be incompatible with other medicines. It might not be suitable for you if you take medicines for epilepsy, HIV and AIDS, hepatitis C, fungal or bacterial infections, high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, angina (chest pain), or organ rejection. You should also not take Ryeqo if you have a liver tumour or liver disease.
The possible side effects of Ryeqo are similar to those of oral contraceptives. Blood clots are a risk with any medicine that contains an oestrogen or a progestogen, which Ryeqo does. Other potential side effects include bone loss, a reduction in menstrual blood loss or loss of your period.
It’s costly for now
Ryeqo can now be prescribed in Australia, so you should discuss whether Ryeqo is right for you with the doctor you usually consult for your endometriosis.
While the maker has made a submission to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee, it is not yet subsidised by the Australian government. This means that rather than paying the normal PBS price of up to A$31.60, it has been reported it may cost as much as $135 for a one-month supply. The committee will make a decision on whether to subsidise Ryeqo at its meeting next month.
Correction: this article has been updated to clarify the recent approval of specific formulations of drugs for endometriosis.
Nial Wheate, Associate Professor of the School of Pharmacy, University of Sydney and Jasmine Lee, Pharmacist and PhD Candidate, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: