Why are my muscles sore after exercise? Hint: it’s nothing to do with lactic acid
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As many of us hit the gym or go for a run to recover from the silly season, you might notice a bit of extra muscle soreness.
This is especially true if it has been a while between workouts.
A common misunderstanding is that such soreness is due to lactic acid build-up in the muscles.
Research, however, shows lactic acid has nothing to do with it. The truth is far more interesting, but also a bit more complex.
It’s not lactic acid
We’ve known for decades that lactic acid has nothing to do with muscle soreness after exercise.
In fact, as one of us (Robert Andrew Robergs) has long argued, cells produce lactate, not lactic acid. This process actually opposes not causes the build-up of acid in the muscles and bloodstream.
Unfortunately, historical inertia means people still use the term “lactic acid” in relation to exercise.
Lactate doesn’t cause major problems for the muscles you use when you exercise. You’d probably be worse off without it due to other benefits to your working muscles.
Lactate isn’t the reason you’re sore a few days after upping your weights or exercising after a long break.
So, if it’s not lactic acid and it’s not lactate, what is causing all that muscle soreness?
Muscle pain during and after exercise
When you exercise, a lot of chemical reactions occur in your muscle cells. All these chemical reactions accumulate products and by-products which cause water to enter into the cells.
That causes the pressure inside and between muscle cells to increase.
This pressure, combined with the movement of molecules from the muscle cells can stimulate nerve endings and cause discomfort during exercise.
The pain and discomfort you sometimes feel hours to days after an unfamiliar type or amount of exercise has a different list of causes.
If you exercise beyond your usual level or routine, you can cause microscopic damage to your muscles and their connections to tendons.
Such damage causes the release of ions and other molecules from the muscles, causing localised swelling and stimulation of nerve endings.
This is sometimes known as “delayed onset muscle soreness” or DOMS.
While the damage occurs during the exercise, the resulting response to the injury builds over the next one to two days (longer if the damage is severe). This can sometimes cause pain and difficulty with normal movement.
The upshot
Research is clear; the discomfort from delayed onset muscle soreness has nothing to do with lactate or lactic acid.
The good news, though, is that your muscles adapt rapidly to the activity that would initially cause delayed onset muscle soreness.
So, assuming you don’t wait too long (more than roughly two weeks) before being active again, the next time you do the same activity there will be much less damage and discomfort.
If you have an exercise goal (such as doing a particular hike or completing a half-marathon), ensure it is realistic and that you can work up to it by training over several months.
Such training will gradually build the muscle adaptations necessary to prevent delayed onset muscle soreness. And being less wrecked by exercise makes it more enjoyable and more easy to stick to a routine or habit.
Finally, remove “lactic acid” from your exercise vocabulary. Its supposed role in muscle soreness is a myth that’s hung around far too long already.
Robert Andrew Robergs, Associate Professor – Exercise Physiology, Queensland University of Technology and Samuel L. Torrens, PhD Candidate, Queensland University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Longevity As A Lifestyle Choice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
7 Keys To Healthy Longevity
This is Dr. Luigi Fontana. He’s a research professor of Geriatrics & Nutritional Science, and co-director of the Longevity Research Program at Washington University in St. Louis.
What does he want us to know?
He has a many-fold approach to healthy longevity, most of which may not be news to you, but you might want to prioritize some things:
Consider caloric restriction with optimal nutrition (CRON)
This is about reducing the metabolic load on your body, which frees up bodily resources for keeping yourself young.
Keeping your body young and healthy is your body’s favorite thing to do, but it can’t do that if it never gets a chance because of all the urgent metabolic tasks you’re giving it.
If CRON isn’t your thing (isn’t practicable for you, causes undue suffering, etc) then intermittent fasting is a great CR mimetic, and he recommends that too. See also:
- Is Cutting Calories The Key To Healthy Long Life?
- Fasting Without Crashing? We Sort The Science From The Hype
Keep your waistline small
Whichever approach you prefer to use to look after your metabolic health, keeping your waistline down is much more important for health than BMI.
Specifically, he recommends keeping it:
- under 31.5” for women
- under 37” for men
The disparity here is because of hormonal differences that influence both metabolism and fat distribution.
Exercise as part of your lifestyle
For Dr. Fontana, he loves mountain-biking (this writer could never!) and weight-lifting (also not my thing). But what’s key is not the specifics, but what’s going on:
- Some kind of frequent movement
- Some kind of high-intensity interval training
- Some kind of resistance training
Frequent movement because our bodies are evolved to be moving more often than not:
The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, & Move More
High-Intensity Interval Training because unlike most forms of exercise (which slow metabolism afterwards to compensate), it boosts metabolism for up to 2 hours after training:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Resistance training because strength (of muscles and bones) matters too:
Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Writer’s examples:
So while I don’t care for mountain-biking or weight-lifting, what I do is:
1) movement: walk (briskly!) everywhere and also use a standing desk
2) HIIT: 2-minute bursts of hindu squats and/or exercise bike sprints
3) resistance: pilates and other calisthenicsModeration is not key
Dr. Fontana advises that we do not smoke, and that we do not drink alcohol, for example. He also notes that just as the only healthy amount of alcohol is zero, less ultra-processed food is always better than more.
Maybe you don’t want to abstain completely, but mindful wilful consumption of something unhealthy is preferable to believing “moderate consumption is good for the health” and an unhealthy habit develops!
Greens and beans
Shocking absolutely nobody, Dr. Fontana advocates for (what has been the most evidence-based gold standard of healthy-aging diets for quite some years now) the Mediterranean diet.
See also: Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← this is about tweaking the Mediterranean diet per personal area of focus, e.g. anti-inflammatory bonus, best for gut, heart healthiest, and most neuroprotective.
Take it easy
Dr. Fontana advises us (again, with a wealth of evidence) Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction, and to get good sleep.
Not shocked?
To quote the good doctor,
❝There are no shortcuts. No magic pills or expensive procedures can replace the beneficial effects of a healthy diet, exercise, mindfulness, or a regenerating night’s sleep.❞
Always a good reminder!
Want to know more?
You might enjoy his book “The Path to Longevity: How to Reach 100 with the Health and Stamina of a 40-Year-Old”, which we reviewed previously
You might also like this video of his, about changing the conversation from “chronic disease” to “chronic health”:
Want to watch it, but not right now? Bookmark it for later
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Bright Line Eating – by Dr. Susan Peirce Thompson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a great title! It’s a great book too, but let’s talk about the title for a moment:
The “Bright Line” referenced (often used in the plural within the book) is the line one draws between what one will and will not do. It’s a line one doesn’t cross, and it’s a bright line, because it’s not a case of “oh woe is me I cannot have the thing”, but rather “oh yay is me for I being joyously healthy”.
And as for living happy, thin, and free? The author makes clear that “thin” is only a laudable goal if it’s bookended by “happy” and “free”. Eating things because we want to, and being happy about our choices.
To this end, while some of the book is about nutrition (and for example the strong recommendation to make the first “bright lines” one draws cutting out sugar and flour), the majority of it is about the psychology of eating.
This includes, hunger and satiety, willpower and lack thereof, disordered eating and addictions, body image issues and social considerations, the works. She realizes and explains, that if being healthy were just a matter of the right diet plan, everyone would be healthy. But it’s not; our eating behaviors don’t exist in a vacuum, and there’s a lot more to consider.
Despite all the odds, however, this is a cheerful and uplifting book throughout, while dispensing very practical, well-evidenced methods for getting your brain to get your body to do what you want it to.
Bottom line: this isn’t your average diet book, and it’s not just a motivational pep talk either. It’s an enjoyable read that’s also full of science and can make a huge difference to how you see food.
Click here to check out Bright Line Eating, and enjoy life, healthily!
Share This Post
-
Thinking of using an activity tracker to achieve your exercise goals? Here’s where it can help – and where it probably won’t
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s that time of year when many people are getting started on their resolutions for the year ahead. Doing more physical activity is a popular and worthwhile goal.
If you’re hoping to be more active in 2024, perhaps you’ve invested in an activity tracker, or you’re considering buying one.
But what are the benefits of activity trackers? And will a basic tracker do the trick, or do you need a fancy one with lots of features? Let’s take a look.
Why use an activity tracker?
One of the most powerful predictors for being active is whether or not you are monitoring how active you are.
Most people have a vague idea of how active they are, but this is inaccurate a lot of the time. Once people consciously start to keep track of how much activity they do, they often realise it’s less than what they thought, and this motivates them to be more active.
You can self-monitor without an activity tracker (just by writing down what you do), but this method is hard to keep up in the long run and it’s also a lot less accurate compared to devices that track your every move 24/7.
By tracking steps or “activity minutes” you can ascertain whether or not you are meeting the physical activity guidelines (150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week).
It also allows you to track how you’re progressing with any personal activity goals, and view your progress over time. All this would be difficult without an activity tracker.
Research has shown the most popular brands of activity trackers are generally reliable when it comes to tracking basic measures such as steps and activity minutes.
But wait, there’s more
Many activity trackers on the market nowadays track a range of other measures which their manufacturers promote as important in monitoring health and fitness. But is this really the case? Let’s look at some of these.
Resting heart rate
This is your heart rate at rest, which is normally somewhere between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Your resting heart rate will gradually go down as you become fitter, especially if you’re doing a lot of high-intensity exercise. Your risk of dying of any cause (all-cause mortality) is much lower when you have a low resting heart rate.
So, it is useful to keep an eye on your resting heart rate. Activity trackers are pretty good at tracking it, but you can also easily measure your heart rate by monitoring your pulse and using a stopwatch.
Heart rate during exercise
Activity trackers will also measure your heart rate when you’re active. To improve fitness efficiently, professional athletes focus on having their heart rate in certain “zones” when they’re exercising – so knowing their heart rate during exercise is important.
But if you just want to be more active and healthier, without a specific training goal in mind, you can exercise at a level that feels good to you and not worry about your heart rate during activity. The most important thing is that you’re being active.
Also, a dedicated heart rate monitor with a strap around your chest will do a much better job at measuring your actual heart rate compared to an activity tracker worn around your wrist.
Maximal heart rate
This is the hardest your heart could beat when you’re active, not something you could sustain very long. Your maximal heart rate is not influenced by how much exercise you do, or your fitness level.
Most activity trackers don’t measure it accurately anyway, so you might as well forget about this one.
VO₂max
Your muscles need oxygen to work. The more oxygen your body can process, the harder you can work, and therefore the fitter you are.
VO₂max is the volume (V) of oxygen (O₂) we could breathe maximally (max) over a one minute interval, expressed as millilitres of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min). Inactive women and men would have a VO₂max lower than 30 and 40 ml/kg/min, respectively. A reasonably good VO₂max would be mid thirties and higher for women and mid forties and higher for men.
VO₂max is another measure of fitness that correlates well with all-cause mortality: the higher it is, the lower your risk of dying.
For athletes, VO₂max is usually measured in a lab on a treadmill while wearing a mask that measures oxygen consumption. Activity trackers instead look at your running speed (using a GPS chip) and your heart rate and compare these measures to values from other people.
If you can run fast with a low heart rate your tracker will assume you are relatively fit, resulting in a higher VO₂max. These estimates are not very accurate as they are based on lots of assumptions. However, the error of the measurement is reasonably consistent. This means if your VO₂max is gradually increasing, you are likely to be getting fitter.
So what’s the take-home message? Focus on how many steps you take every day or the number of activity minutes you achieve. Even a basic activity tracker will measure these factors relatively accurately. There is no real need to track other measures and pay more for an activity tracker that records them, unless you are getting really serious about exercise.
Corneel Vandelanotte, Professorial Research Fellow: Physical Activity and Health, CQUniversity Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
What Most People Don’t Know About HIV
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What To Know About HIV This World AIDS Day
Yesterday, we asked 10almonds readers to engage in a hypothetical thought experiment with us, and putting aside for a moment any reason you might feel the scenario wouldn’t apply for you, asked:
❝You have unprotected sex with someone who, afterwards, conversationally mentions their HIV+ status. Do you…❞
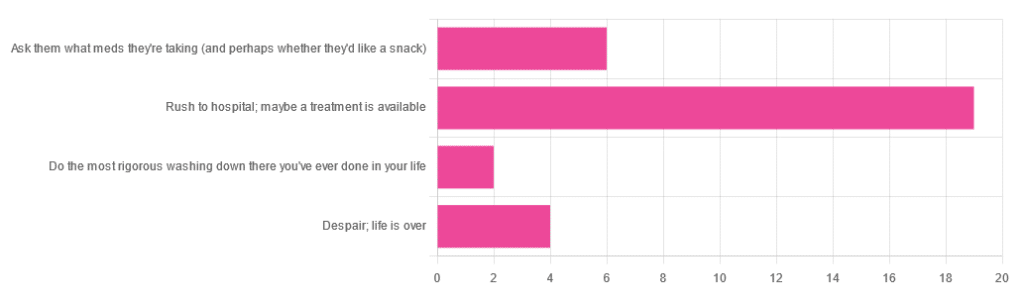
…and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses. Of those who responded…
- Just over 60% said “rush to hospital; maybe a treatment is available”
- Just under 20% said “ask them what meds they’re taking (and perhaps whether they’d like a snack)”
- Just over 10% said “despair; life is over”
- Two people said “do the most rigorous washing down there you’ve ever done in your life”
So, what does science say about it?
First, a quick note on terms
- HIV is the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. It does what it says on the tin; it gives humans immunodeficiency. Like many viruses that have become epidemic in humans, it started off in animals (called SIV, because there was no “H” involved yet), which were then eaten by humans, passing the virus to us when it one day mutated to allow that.
- It’s technically two viruses, but that’s beyond the scope of today’s article; for our purposes they are the same. HIV-1 is more virulent and infectious than HIV-2, and is the kind more commonly found in most of the world.
- AIDS is Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, and again, is what it sounds like. When a person is infected with HIV, then without treatment, they will often develop AIDS.
- Technically AIDS itself doesn’t kill people; it just renders people near-defenseless to opportunistic infections (and immune-related diseases such as cancer), since one no longer has a properly working immune system. Common causes of death in AIDS patients include cancer, influenza, pneumonia, and tuberculosis.
People who contract HIV will usually develop AIDS if untreated. Untreated life expectancy is about 11 years.
HIV/AIDS are only a problem for gay people: True or False?
False, unequivocally. Anyone can get HIV and develop AIDS.
The reason it’s more associated with gay men, aside from homophobia, is that since penetrative sex is more likely to pass it on, then if we go with the statistically most likely arrangements here:
- If a man penetrates a woman and passes on HIV, that woman will probably not go on to penetrate someone else
- If a man penetrates a man and passes on HIV, that man could go on to penetrate someone else—and so on
- This means that without any difference in safety practices or promiscuity, it’s going to spread more between men on average, by simple mathematics.
- This is why “men who have sex with men” is the generally-designated higher-risk category.
There is medication to cure HIV/AIDS: True or False?
False so far (though there have been individual case studies of gene treatments that may have cured people—time will tell).
But! There are medications that can prevent HIV from being a life-threatening problem:
- PrEP (Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis) is a medication that one can take in advance of potential exposure to HIV, to guard against it.
- This is a common choice for people aren’t sure about their partners’ statuses, or people working in risky environments.
- PEP (Post-Exposure Prophylaxis) is a medication that one can take after potential exposure to HIV, to “nip it in the bud”.
- Those of you who were rushing to hospital in our poll, this is what you’re rushing there for.
- ARVs (Anti-RetroVirals) are a class of medications (there are different options; we don’t have room to distinguish them) that reduce an HIV+ person’s viral load to undetectable levels.
- Those of you who were asking what meds your partner was taking, these will be those meds. Also, most of them are to be taken in the morning with food, so that’s what the snack was for.
If someone is HIV+, the risk of transmission in unprotected sex is high: True or False?
True or False, with false being the far more likely. It depends on their medications, and this is why you were asking. If someone is on ARVs and their viral load is undetectable (as is usual once someone has been on ARVs for 6 months), they cannot transmit HIV to you.
U=U is not a fancy new emoticon, it means “undetectable = untransmittable”, which is a mathematically true statement in the case of HIV viral loads.
See: NIH | HIV Undetectable=Untransmittable (U=U)
If you’re thinking “still sounds risky to me”, then consider this:
You are safer having unprotected sex with someone who is HIV+ and on ARVs with an undetectable viral load, than you are with someone you are merely assuming is HIV- (perhaps you assume it because “surely this polite blushing young virgin of a straight man won’t give me cooties” etc)
Note that even your monogamous partner of many decades could accidentally contract HIV due to blood contamination in a hospital or an accident at work etc, so it’s good practice to also get tested after things that involve getting stabbed with needles, cut in a risky environment, etc.
If you’re concerned about potential stigma associated with HIV testing, you can get kits online:
CDC | How do I find an HIV self-test?
(these are usually fingerprick blood tests, and you can either see the results yourself at home immediately, or send it in for analysis, depending on the kit)
If I get HIV, I will get AIDS and die: True or False?
False, assuming you get treatment promptly and keep taking it. So those of you who were at “despair; life is over” can breathe a sigh of relief now.
However, if you get HIV, it does currently mean you will have to take those meds every day for the rest of your (no reason it shouldn’t be long and happy) life.
So, HIV is definitely still something to avoid, because it’s not great to have to take a life-saving medication every day. For a little insight as to what that might be like:
HIV.gov | Taking HIV Medication Every Day: Tips & Challenges
(as you’ll see there, there are also longer-lasting injections available instead of daily pulls, but those are much less widely available)
Summary
Some quick take-away notes-in-a-nutshell:
- Getting HIV may have been a death sentence in the 1980s, but nowadays it’s been relegated to the level of “serious inconvenience”.
- Happily, it is very preventable, with PrEP, PEP, and viral loads so low that they can’t transmit HIV, thanks to ARVs.
- Washing will not help, by the way. Safe sex will, though!
- As will celibacy and/or sexual exclusivity in seroconcordant relationships, e.g. you have the same (known! That means actually tested recently! Not just assumed!) HIV status as each other.
- If you do get it, it is very manageable with ARVs, but prevention is better than treatment
- There is no certain cure—yet. Some people (small number of case studies) may have been cured already with gene therapy, but we can’t know for sure yet.
Want to know more? Check out:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What We Don’t Talk About When We Talk About Fat – by Aubrey Gordon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are books aplenty to encourage and help you to lose weight. This isn’t one of those.
There are also books aplenty to encourage and help you to accept yourself and your body at the weight you are, and forge self-esteem. This isn’t one of those, either—in fact, it starts by assuming you already have that.
There are fair arguments for body neutrality, and fat acceptance. Very worthy also is the constant fight for bodily sovereignty.
These are worthy causes, but they’re for the most-part not what our author concerns herself with here. Instead, she cares for a different and very practical goal: fat justice.
In a world where you may be turned away from medical treatment if you are over a certain size, told to lose half your bodyweight before you can have something you need, she demands better. The battle extends further than healthcare though, and indeed to all areas of life.
Ultimately, she argues, any society that will disregard the needs of the few because they’re a marginal demographic, is a society that will absolutely fail you if you ever differ from the norm in some way.
All in all, an important (and for many, perhaps eye-opening) book to read if you are fat, care about fat people, are a person of any size, or care about people in general.
Pick Up Your Copy of “What We Don’t Talk About When We Talk About Fat”, on Amazon Today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do You Need to Wear Sunscreen Indoors? An Analysis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michelle Wong—chemist, science educator, and cosmetician—explains the science:
Factors to take into account
UVA and UVB aren’t entirely interchangeable, so it’s important to know what you’re up against.
Sunscreen is rated by SPF, which indicates UVB protection—guarding against burning, skin cancer, and premature aging. Broad spectrum or UVA ratings measure protection against UVA rays, which cause tanning, contribute to melanoma, and can lead to skin aging and hyperpigmentation. However, most UV studies are based on white skin, which may not apply universally.
The need for sunscreen indoors depends on how much UV exposure you receive there:
- Direct exposure occurs when sunlight shines directly on you, such as when sitting by a window.
- Diffuse exposure happens when UV rays are scattered by air molecules or reflected off surfaces, which can still occur in shaded areas.
Indoors, walls and barriers do reduce UV exposure significantly. However, factors like window size, distance from windows, and the type of glass (which blocks UVB but not all UVA) play important roles in determining exposure.
The UV index (your phone’s weather app will probably have this) indicates the level of sunburn-causing UV in a specific area at a particular time. In Sydney, for example (where Dr. Wong is), the UV index can vary from 12 in summer to 2 in winter. Although UVA levels fluctuate less dramatically than UVB, they still peak during midday and in summer. Health guidelines in countries like Australia recommend wearing sunscreen when the UV index is 3 or above, but not necessarily every day.
Personal factors also influence the need for sunscreen indoors. People with darker skin, who have more melanin, may need less protection from incidental UV exposure but might still require UVA protection to prevent pigmentation. Those using skincare products that increase UV sensitivity, like alpha hydroxy acids, or those with specific medical conditions, such as photosensitivity or a family history of skin cancer, may also get particular benefit from wearing sunscreen indoors.
As to the downsides? There are some drawbacks to wearing sunscreen indoors, including cost, the effort required for application, and the risk of clogged pores. Though health concerns related to sunscreen are generally minor, they may tip the balance against wearing it if UV exposure is minimal.
For more on all of this plus visual teaching aids, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
Do We Need Sunscreen In Winter, Really? ← we tackle the science behind the answer to this similar* question
*But different, because now we need to take into account such things as axial tilt, the sun’s trajectory through the atmosphere (and thus how much gets reflected, refracted, diffused, etc—or not, as the case may be).
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: