What Your Doctor Wants You to Know to Crush Medical Debt – by Dr. Virgie Ellington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First things first: this one’s really only of relevance to people living in the US. That’s most of our readership, but if it’s not you, then apologies, this one won’t be of interest.
For the US Americans, though, Dr. Ellington starts strong with “you got a bill—now get the right bill”, and then gives a step-by-step process for finding the mistakes in your medical bills, fixing them, dealing with insurers who do not want to live up to their part of the bargain, and how to minimize what you need to pay, when you actually arrive at your final bill.
The biggest strength of this book is the wealth of insider knowledge (the author has worked as a primary care physician as well as as a health insurance executive), and while this information won’t stay current forever, its relatively recent publication date (2022) means that little has changed since then, and once you’re up to speed with how things are now, it’ll be easy to roll with whatever changes may come in the future.
Bottom line: if you’re living in the US and would like to not be ripped off as badly as possible when it comes to healthcare costs, this book is a very small, very powerful, investment.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Dr. Kim Foster’s Method For Balancing Hormones Naturally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not just sex hormones, but also hormones like cortisol (the stress hormone), and thyroid hormones (for metabolism regulation) too! The body is most of the time self-regulating when it comes to hormones, but there are things that we can do to help our body look after us correctly.
In short, if we give our body what it needs, it will (usually, barring serious illness!) give us what we need.
Dr. Foster recommends…
Foods:
- Healthy fats (especially avocados and nuts)
- Lean proteins (especially poultry, fish, and legumes)
- Fruits & vegetables (especially colorful ones)
- Probiotics (especially fermented foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, etc)
- Magnesium-rich foods (especially dark leafy greens, nuts, and yes, dark chocolate)
Teas:
- Camomile tea (especially beneficial against cortisol overproduction)
- Nettle tea (especially beneficial for estrogen production)
- Peppermint tea (especially beneficial for gut health, thus indirect hormone benefits)
Stress reduction:
- Breathing exercises (especially mindfulness exercises)
- Yoga (especially combining exercise with stretches)
- Spending time in nature (especially green spaces)
Dr. Foster explains more about all of these things, along with more illustrative examples, so if you can, do enjoy her video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to read more about this topic?
You might like our main feature: What Does “Balance Your Hormones” Even Mean?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
What happens when I stop taking a drug like Ozempic or Mounjaro?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are taking drugs like Ozempic to lose weight. But what do we actually know about them? This month, The Conversation’s experts explore their rise, impact and potential consequences.
Drugs like Ozempic are very effective at helping most people who take them lose weight. Semaglutide (sold as Wegovy and Ozempic) and tirzepatide (sold as Zepbound and Mounjaro) are the most well known in the class of drugs that mimic hormones to reduce feelings of hunger.
But does weight come back when you stop using it?
The short answer is yes. Stopping tirzepatide and semaglutide will result in weight regain in most people.
So are these medications simply another (expensive) form of yo-yo dieting? Let’s look at what the evidence shows so far.
It’s a long-term treatment, not a short course
If you have a bacterial infection, antibiotics will help your body fight off the germs causing your illness. You take the full course of medication, and the infection is gone.
For obesity, taking tirzepatide or semaglutide can help your body get rid of fat. However it doesn’t fix the reasons you gained weight in the first place because obesity is a chronic, complex condition. When you stop the medications, the weight returns.
Perhaps a more useful comparison is with high blood pressure, also known as hypertension. Treatment for hypertension is lifelong. It’s the same with obesity. Medications work, but only while you are taking them. (Though obesity is more complicated than hypertension, as many different factors both cause and perpetuate it.)
Obesity drugs only work while you’re taking them. KK Stock/Shutterstock Therefore, several concurrent approaches are needed; taking medication can be an important part of effective management but on its own, it’s often insufficient. And in an unwanted knock-on effect, stopping medication can undermine other strategies to lose weight, like eating less.
Why do people stop?
Research trials show anywhere from 6% to 13.5% of participants stop taking these drugs, primarily because of side effects.
But these studies don’t account for those forced to stop because of cost or widespread supply issues. We don’t know how many people have needed to stop this medication over the past few years for these reasons.
Understanding what stopping does to the body is therefore important.
So what happens when you stop?
When you stop using tirzepatide or semaglutide, it takes several days (or even a couple of weeks) to move out of your system. As it does, a number of things happen:
- you start feeling hungry again, because both your brain and your gut no longer have the medication working to make you feel full
When you stop taking it, you feel hungry again. Stock-Asso/Shutterstock - blood sugars increase, because the medication is no longer acting on the pancreas to help control this. If you have diabetes as well as obesity you may need to take other medications to keep these in an acceptable range. Whether you have diabetes or not, you may need to eat foods with a low glycemic index to stabilise your blood sugars
- over the longer term, most people experience a return to their previous blood pressure and cholesterol levels, as the weight comes back
- weight regain will mostly be in the form of fat, because it will be gained faster than skeletal muscle.
While you were on the medication, you will have lost proportionally less skeletal muscle than fat, muscle loss is inevitable when you lose weight, no matter whether you use medications or not. The problem is, when you stop the medication, your body preferentially puts on fat.
Is stopping and starting the medications a problem?
People whose weight fluctuates with tirzepatide or semaglutide may experience some of the downsides of yo-yo dieting.
When you keep going on and off diets, it’s like a rollercoaster ride for your body. Each time you regain weight, your body has to deal with spikes in blood pressure, heart rate, and how your body handles sugars and fats. This can stress your heart and overall cardiovascular system, as it has to respond to greater fluctuations than usual.
Interestingly, the risk to the body from weight fluctuations is greater for people who are not obese. This should be a caution to those who are not obese but still using tirzepatide or semaglutide to try to lose unwanted weight.
How can you avoid gaining weight when you stop?
Fear of regaining weight when stopping these medications is valid, and needs to be addressed directly. As obesity has many causes and perpetuating factors, many evidence-based approaches are needed to reduce weight regain. This might include:
- getting quality sleep
- exercising in a way that builds and maintains muscle. While on the medication, you will likely have lost muscle as well as fat, although this is not inevitable, especially if you exercise regularly while taking it
Prioritise building and maintaining muscle. EvMedvedeva/Shutterstock - addressing emotional and cultural aspects of life that contribute to over-eating and/or eating unhealthy foods, and how you view your body. Stigma and shame around body shape and size is not cured by taking this medication. Even if you have a healthy relationship with food, we live in a culture that is fat-phobic and discriminates against people in larger bodies
- eating in a healthy way, hopefully continuing with habits that were formed while on the medication. Eating meals that have high nutrition and fibre, for example, and lower overall portion sizes.
Many people will stop taking tirzepatide or semaglutide at some point, given it is expensive and in short supply. When you do, it is important to understand what will happen and what you can do to help avoid the consequences. Regular reviews with your GP are also important.
Read the other articles in The Conversation’s Ozempic series here.
Natasha Yates, General Practitioner, PhD Candidate, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Put Your Feet Up! (Against A Wall, For 20 Minutes)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Feel free to browse our articles while you do
Here are 10 good reasons to give it a try; there are another 10 in the short (3:18) video:
- Improves blood circulation
- Improves blood pressure
- Relaxes the body as a whole
- Alleviates lower back tension
- Eases headaches and migraines
- Reduces knee pain
- Relieves swelling in feet and ankles
- Improves lymphatic flow
- Stretches the hamstrings (and hip flexors, if you do it wide)
- Helps quiet the mind
As for the rest…
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
PS: about that circulation… As a general rule of thumb, anything that slightly confuses the heart (anatomically, not romantically) will tend to have a beneficial effect, in moderation. This goes for being upside-down (as is partly the case here), and also for high-intensity interval training (HIIT):
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Wise Old Fool
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
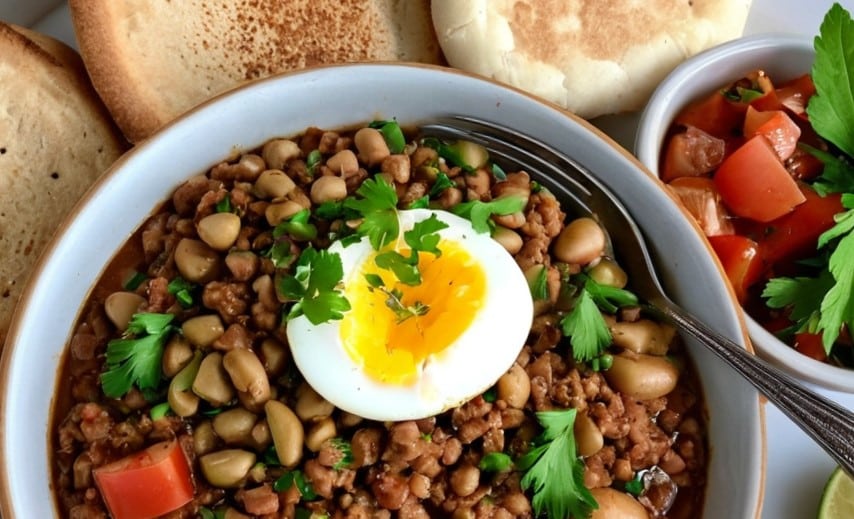
How old is this dish? Well, let’s put it this way, it used to be called “𓅮𓏏𓈖” and remnants of it have been found at neolithic burial sites in Egypt. Nowadays it’s called “فول مدمس”, which gets rendered a lot of different ways in the Latin alphabet, but “fūl mudammas” is one option. For short, it’s just called “fūl”, which is pronounced like the English word “fool”, and it’s about the beans.
From chana masala with poori to frijoles refritos to beans on toast, lots of cultures have some version of this breakfast food, and all can be great (yes, even the beans on toast). But today we’re about this particular kind of morning protein, fiber, fats, and healthful spices.
You will need
- 2x 14 oz cans fava beans (other kinds of beans work as substitute; kidney beans are common substitution, but this writer prefers black beans personally if she doesn’t have fava in), drained
- 4 garlic cloves, crushed
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 teaspoon sweet cinnamon (or ½ sweet cinnamon stick)
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp paprika
- 1 tsp black pepper
- Juice of ½ lemon
- For the relish: 1 medium tomato, finely chopped; 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil; 2 tbsp parsley, finely chopped
- To serve: 4 pitta breads, 2 eggs (omit if vegan), and a selection of pickled vegetables, drained
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add the olive oil to a saucepan over a medium heat; add the garlic, cumin seeds, and cinnamon. Keep these moving for a minute or two before moving to the next step.
2) Add the fava beans, as well as the other seasonings (chili flakes, paprika, black pepper), and mix thoroughly
3) Add 1 cup boiling water, and keep everything on a simmer for about 20 minutes, stirring often. Add the lemon juice while it’s simmering; when the beans start to break down and the mixture starts to thicken, it’s ready.
4) Mix the relish ingredients (finely chopped tomato, olive oil, parsley) thoroughly in a small bowl
5) Toast the pitta breads, and if using, soft-boil the eggs.
6) Serve! We suggest: fūl in a bowl, with one half of a soft-boiled egg per bowl, topped with the relish, and served with the pitta bread and pickled vegetables on the side.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Less Obvious Probiotic Benefits ← the pickled vegetables contain the probiotics here, while the beans are a great source of prebiotic fiber; this is why they work so well together
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons
- Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Apple vs Pear – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple to pear, we picked the pear.
Why?
Both are great! But there’s a category that puts pears ahead of apples…
Looking at their macros first, pears contain more carbs but also more fiber. Both are low glycemic index foods, though.
In the category of vitamins, things are moderately even: apples contain more of vitamins A, B1, B6, and E, while pears contain more of vitamins B3, B9, K, and choline. That’s a 4:4 split, and the two fruits are about equal in the other vitamins they both contain.
When it comes to minerals, pears contain more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. A resounding victory for pears, as apples are not higher in any mineral.
In short, if an apple a day keeps the doctor away, a pear should keep the doctor away for about a day and a half, based on the extra nutrients ← this is slightly facetious as medicine doesn’t work like that, but you get the idea: pears simply have more to offer. Apples are still great though! Enjoy both! Diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
From Apples To Bees, And High-Fructose Cs: Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
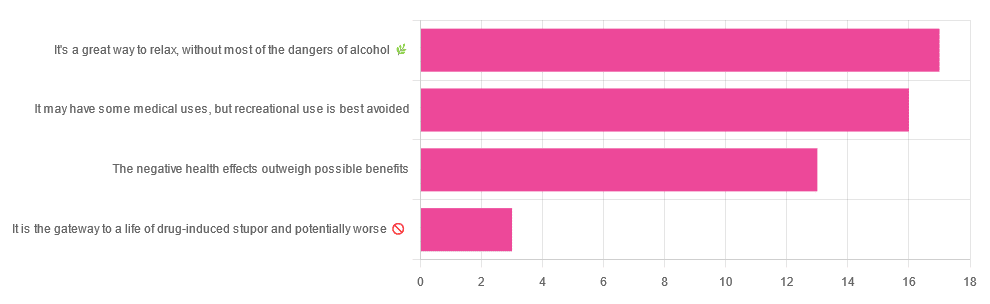
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: