What is ‘breathwork’? And do I need to do it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From “breathwork recipes” to breathing techniques, many social media and health websites are recommending breathwork to reduce stress.
But breathwork is not new. Rather it is the latest in a long history of breathing techniques such as Pranayama from India and qigong from China. Such practices have been used for thousands of years to promote a healthy mind and body.
The benefits can be immediate and obvious. Try taking a deep breath in through your nose and exhaling slowly. Do you feel a little calmer?
So, what’s the difference between the breathing we do to keep us alive and breathwork?

Breathwork is about control
Breathwork is not the same as other mindfulness practices. While the latter focus on observing the breath, breathwork is about controlling inhalation and exhalation.
Normally, breathing happens automatically via messages from the brain, outside our conscious control. But we can control our breath, by directing the movement of our diaphragm and mouth.
The diaphragm is a large muscle that separates our thoracic (chest) and abdominal (belly) cavities. When the diaphragm contracts, it expands the thoracic cavity and pulls air into the lungs.
Controlling how deep, how often, how fast and through what (nose or mouth) we inhale is the crux of breathwork, from fire breathing to the humming bee breath.
Breathwork can calm or excite
Even small bits of breathwork can have physical and mental health benefits and complete the stress cycle to avoid burnout.
Calming breathwork includes diaphragmatic (belly) breathing, slow breathing, pausing between breaths, and specifically slowing down the exhale.
In diaphragmatic breathing, you consciously contract your diaphragm down into your abdomen to inhale. This pushes your belly outwards and makes your breathing deeper and slower.
You can also slow the breath by doing:
- box breathing (count to four for each of four steps: breathe in, hold, breathe out, hold), or
- coherent breathing (controlled slow breathing of five or six breaths per minute), or
- alternate nostril breathing (close the left nostril and breathe in slowly through the right nostril, then close the right nostril and breathe out slowly through the left nostril, then repeat the opposite way).
You can slow down the exhalation specifically by counting, humming or pursing your lips as you breathe out.
In contrast to these calming breathing practices, energising fast-paced breathwork increases arousal. For example, fire breathing (breathe in and out quickly, but not deeply, through your nose in a consistent rhythm) and Lion’s breath (breathe out through your mouth, stick your tongue out and make a strong “haa” sound).
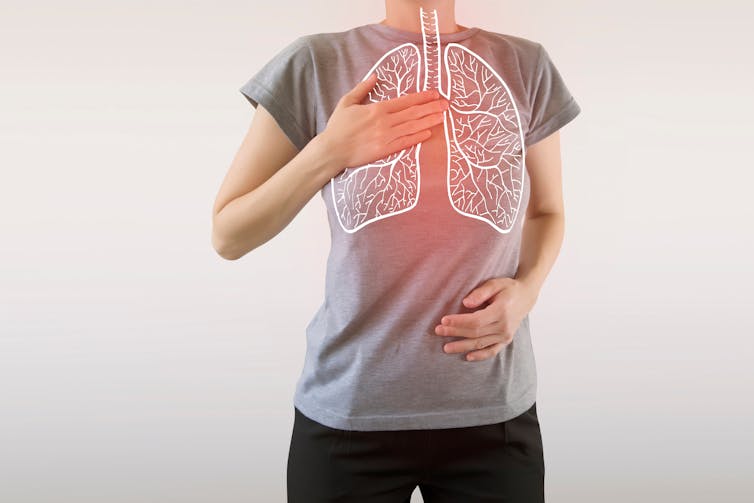
What is happening in the body?
Deep and slow breathing, especially with a long exhale, is the best way to stimulate the vagus nerves. The vagus nerves pass through the diaphragm and are the main nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Simulating the vagus nerves calms our sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) stress response. This improves mood, lowers the stress hormone cortisol and helps to regulate emotions and responses. It also promotes more coordinated brain activity, improves immune function and reduces inflammation.
Taking deep, diaphragmatic breaths also has physical benefits. This improves blood flow, lung function and exercise performance, increases oxygen in the body, and strengthens the diaphragm.
Slow breathing reduces heart rate and blood pressure and increases heart rate variability (normal variation in time between heart beats). These are linked to better heart health.
Taking shallow, quick, rhythmic breaths in and out through your nose stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. Short-term, controlled activation of the stress response is healthy and develops resilience to stress.
Breathing in through the nose
We are designed to inhale through our nose, not our mouth. Inside our nose are lots of blood vessels, mucous glands and tiny hairs called cilia. These warm and humidify the air we breathe and filter out germs and toxins.
We want the air that reaches our airways and lungs to be clean and moist. Cold and dry air is irritating to our nose and throat, and we don’t want germs to get into the body.
Nasal breathing increases parasympathetic activity and releases nitric oxide, which improves airway dilation and lowers blood pressure.
Consistently breathing through our mouth is not healthy. It can lead to pollutants and infections reaching the lungs, snoring, sleep apnoea, and dental issues including cavities and jaw joint problems.
A free workout
Slow breathing – even short sessions at home – can reduce stress, anxiety and depression in the general population and among those with clinical depression or anxiety. Research on breathwork in helping post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is also promising.
Diaphragmatic breathing to improve lung function and strengthen the diaphragm can improve breathing and exercise intolerance in chronic heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. It can also improve exercise performance and reduce oxidative stress (an imbalance of more free radicals and/or less antioxidants, which can damage cells) after exercise.

A mind-body connection you can access any time
If you feel stressed or anxious, you might subconsciously take shallow, quick breaths, but this can make you feel more anxious. Deep diaphragmatic breaths through your nose and focusing on strong exhalations can help break this cycle and bring calm and mental clarity.
Just a few minutes a day of breathwork can improve your physical and mental health and wellbeing. Daily deep breathing exercises in the workplace reduce blood pressure and stress, which is important since burnout rates are high.
Bottom line: any conscious control of your breath throughout the day is positive.
So, next time you are waiting in a line, at traffic lights or for the kettle to boil, take a moment to focus on your breath. Breathe deeply into your belly through your nose, exhale slowly, and enjoy the benefits.
Theresa Larkin, Associate professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong and Judy Pickard, Senior Lecturer, Clinical Psychology, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Counterclockwise – by Dr. Ellen Langer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written previously about Dr. Langer’s famous “Counterclockwise” study that saw reversals in biological markers of aging after a one-week intervention that consisted only of a (albeit rather intensive) mental reframe with regard to their age.
This book, as you might expect from the title, refers to that experiment a lot—but it doesn’t stop there. While the Counterclockwise experiment remains Dr. Langer’s most well-known, it’s not her most recent, and she draws from a wealth of research (her own and that of her colleagues in the field) to show the extent and limit of psychosomatic effect on aging.
Note:
- psychosomatic effect does not mean: “imagining it”
- psychosomatic effect means: “your brain regulates almost everything else in your body, directly or indirectly, including your autonomic functions, which includes immune function, tissue replacement, and more”
And as for when it comes to aging? Aging, like cancer, is in large part a problem of immune dysfunction; in both cases cells (be they senescent or cancerous, respectively) are not being killed when they are supposed to be, and in both cases, better instructions will improve the matter.
Many larger-scale markers of aging, such as mobility, are a case of the body only being able to do what the tissues allow, and the tissues are being constantly rebuilt (for better or for worse) according to autonomically-implemented specifications, and cells’ ability to carry out those orders.
Beyond the cellular physiology, this book discusses (a lot) the brain-down mechanisms by which the most powerful organ in our body can tell the rest of the body how old to be.
Dr. Langer also discusses the matter of “priming”, that is to say, how external factors prime us to believe certain things about our age and, with it, our health. These things can include popular media, conversations with friends and family, and healthcare providers’ framing of certain issues.
For example, a person just under a certain age and a person just over a certain age could both go to the doctor with the same complaint—a pain in a certain joint, let’s say. The doctor may refer the slightly younger patient for an x-ray because “let’s see what’s going on here”, and prescribe the slightly older patient some painkillers because “this is perfectly normal at your age”. One resultant problem is obvious: a difference in the standard of care. But the other resultant problem is less obvious: the older patient has now been primed to believe, by a confident authority figure, “it is natural for my body to be in a state of decline now, and this is what to expect”.
Thus, Dr. Langer prescribes mindfulness, not in the mindfulness meditation sense (though sure, do that too), but rather in the sense of consciously interacting with the world and making our own decisions about our own health and, yes, our own age. Because after all, our body neither knows nor cares how many times it has flown around the sun, and merely responds to physiological stimuli—including those we can influence with psychological reframing.
The book is not, per se, a “how-to” guide, rather it is an explanatory treatise, but it contains more than enough information to put it into practice, and indeed, she does also provide some exercises to do along the way.
The style is… Vivacious, without being especially upbeat. Dr. Langer is enthused about her work, yes, but she’s also angry at how many people are having their health sabotaged on the daily, and calls for a more health-first approach (as opposed to illness-first).
Bottom line: this is the book on our brain’s power over aging, so if that topic interests you, this book absolutely belongs on your bookshelf. Well, in your hands, and then on the bookshelf, and then back in your hands from time to time.
Click here to check out Counterclockwise, and age counterclockwise as her experimental subjects did!
Share This Post
-
Eat To Beat Cancer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Controlling What We Can, To Avoid Cancer
Every time a cell in our body is replaced, there’s a chance it will be cancerous. Exactly what that chance is depends on very many factors. Some of them we can’t control; others, we can.
Diet is a critical, modifiable factor
We can’t choose, for example, our genes. We can, for the most part, choose our diet. Why “for the most part”?
- Some people live in a food desert (the Arctic Circle is a good example where food choices are limited by supply)
- Some people have dietary restrictions (whether by health condition e.g. allergy, intolerance, etc or by personal-but-unwavering choice, e.g. vegetarian, vegan, kosher, halal, etc)
But for most of us, most of the time, we have a good control over our diet, and so that’s an area we can and should focus on.
Choose your animal protein wisely
If you are vegan, you can skip this section. If you are not, then the short version is:
- Fish: almost certainly fine
- Poultry: the jury is out; data is leaning towards fine, though
- Red meat: significantly increased cancer risk
- Processed meat: significantly increased cancer risk
For more details (and a run-down on the science behind the above super-summarized version):
- Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy? ← A mythbuster article that outlines many health properties (good and bad) of animal products
- The Whys and Hows of Cutting Meats Out Of Your Diet ← A life-hack article about acting on that information
Skip The Ultra-Processed Foods
Ok, so this one’s probably not a shocker in its simplest form:
❝Studies are showing us is that not only do the ultraprocessed foods increase the risk of cancer, but that after a cancer diagnosis such foods increase the risk of dying❞
Source: Is there a connection between ultraprocessed food and cancer?
There’s an unfortunate implication here! If you took the previous advice to heart and cut out [at least some] meat, and/but then replaced that with ultra-processed synthetic meat, then this was not a great improvement in cancer risk terms.
Ultra-processed meat is worse than unprocessed, regardless of whether it was from an animal or was synthetic.
In other words: if you buy textured soy pieces (a common synthetic meat), it pays to look at the ingredients, because there’s a difference between:
- INGREDIENTS: SOY
- INGREDIENTS: Rehydrated Textured SOY Protein (52%), Water, Rapeseed Oil, SOY Protein Concentrate, Seasoning (SULPHITES) (Dextrose, Flavourings, Salt, Onion Powder, Food Starch Modified, Yeast Extract, Colour: Red Iron Oxide), SOY Leghemoglobin, Fortified WHEAT Flour (WHEAT Flour, Calcium Carbonate, Iron, Niacin, Thiamin), Bamboo Fibre, Methylcellulose, Tomato Purée, Salt, Raising Agent: Ammonium Carbonates
Now, most of those original base ingredients are/were harmless per se (as are/were the grapes in wine—before processing into alcohol), but it has clearly been processed to Hell and back to do all that.
Choose the one that just says “soy”. Or eat soybeans. Or other beans. Or lentils. Really there are a lot of options.
About soy, by the way…
There is (mostly in the US, mostly funded by the animal agriculture industry) a lot of fearmongering about soy. Which is ironic, given the amount of soy that is fed to livestock to be fed to humans, but it does bear addressing:
❝Soy foods are safe for all cancer patients and are an excellent source of plant protein. Studies show soy may improve survival after breast cancer❞
Source: Food risks and cancer: What to avoid
(obviously, if you have a soy allergy then you should not consume soy—for most people, the above advice stands, though)
Advanced Glycation End-Products
These (which are Very Bad™ for very many things, including cancer) occur specifically as a result of processing animal proteins and fats.
Note: not even necessarily ultra-processing, just processing can do it. But ultra-processing is worse. What’s the difference, you wonder?
The difference between “ultra-processed” and just “processed”:
- Your average hotdog has been ultra-processed. It’s not only usually been changed with many artificial additives, it’s also been through a series of processes (physical and chemical) and ends up bearing little relation to the creature it came from.
- Your bacon (that you bought fresh from your local butcher, not a supermarket brand of unknown provenance, and definitely not the kind that might come on the top of frozen supermarket pizza) has been processed. It’s undergone a couple of simple processes on its journey “from farm to table”. Remember also that when you cook it, that too is one more process (and one that results in a lot of AGEs).
Read more: What’s so bad about AGEs?
Note if you really don’t want to cut out certain foods, changing the way you cook them (i.e., the last process your food undergoes before you eat it) can also reduce AGES:
Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Get More Fiber
❝The American Institute for Cancer Research shows that for every 10-gram increase in fiber in the diet, you improve survival after cancer diagnosis by 13%❞
Source: Plant-based diet is encouraged for patients with cancer
Yes, that’s post-diagnosis, but as a general rule of thumb, what is good/bad for cancer when you have it is good/bad for cancer beforehand, too.
If you’re thinking that increasing your fiber intake means having to add bran to everything, happily there are better ways:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Heart Rate Zones, Oxalates, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I think the heart may be an issue for lots of us. I know it is for me due to AFib. When I’m in my training zone like on a treadmill, I’m usually around 110 to 120. But there are occasionally times when I’m at 140 or 150. How dangerous is that? If I use that formula of 180 minus age, thats 103. I get nothing from that. My resting heart rate is in the 50 to 60 range.❞
First, for safety, let us draw attention to our medical disclaimer at the bottom of each email, and also specifically note that we are not cardiologists here, let alone your cardiologist. There’s a lot we can’t know or advise about. However, as general rules of thumb:
For people without serious health conditions, it is considered good and healthful for one’s heart rate to double (from its resting rate) during exercise, with even more than 2.5x resting rate being nothing more than a good cardio workout.
As for “180 minus age” (presuming you mean: to calculate the safe maximum heart rate), more common (and used by the American Heart Association) is 220 minus age. In your case, that’d give 143.
Having atrial fibrillation may change this however, and we can’t offer medical advice.
We can point to this AHA “AFib Resources For Patients and Professionals”, including this handy FAQ sheet which says:
“Am I able to exercise?” / “Yes, as long as you’re cleared by your doctor, you can perform normal activities of daily living that you can tolerate” (accompanied by a little graphic of a person using an exercise bike)
You personally probably know this already, of course, but it’s quite an extensive collection of resources, so we thought we’d include it.
It’s certainly a good idea for everyone to be aware of their healthy heart rate ranges, regardless of having a known heart condition or not, though!
American Heart Association: Target Heart Rates Chart
❝I would like to see some articles on osteoporosis❞
You might enjoy this mythbusting main feature we did a few weeks ago!
The Bare-Bones Truth About Osteoporosis
❝Interesting, but… Did you know spinach is high in oxylates? Some people are sensitive and can cause increased inflammation, joint pain or even kidney stones. Moderation is key. My sister and I like to eat healthy but found out by experience that too much spinach salad caused us joint and other aches.❞
It’s certainly good to be mindful of such things! For most people, a daily serving of spinach shouldn’t cause ill effects, and certainly there are other greens to eat.
We wondered whether there was a way to reduce the oxalate content, and we found:
How to Reduce Oxalic Acid in Spinach: Neutralizing Oxalates
…which led us this product on Amazon:
Nephure Oxalate Reducing Enzyme, Low Oxalate Diet Support
We wondered what “nephure” was, and whether it could be trusted, and came across this “Supplement Police” article about it:
Nephure Review – Oxalate Reducing Enzyme Powder Health Benefits?
…which honestly, seems to have been written as a paid advertisement. But! It did reference a study, which we were able to look up, and find:
In vitro and in vivo safety evaluation of Nephure™
…which seems to indicate that it was safe (for rats) in all the ways that they checked. They did not, however, check whether it actually reduced oxalate content in spinach or any other food.
The authors did declare a conflict of interest, in that they had a financial relationship with the sponsor of the study, Captozyme Inc.
All in all, it may be better to just have kale instead of spinach:
- 20 Foods High in Oxalates to Limit if You Have Kidney Stones
- The Kidney Dietician: The Best Low Oxalate Greens
We turn the tables and ask you a question!
We’ll then talk about this tomorrow:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Foods That Cause You to Lose Weight – by Dr. Neal Barnard
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We previously reviewed Dr. Barnard’s “The Power Foods Diet”, and this time his work is about weight loss.
This time there are more recipes (which take up most of the book, so this one could be reasonably described as a cookbook), but not until after nearly a hundred pages of concepts, principles, and tips.
The recipes themselves are again very respectable, even if some may be a little redundant (e.g. the double-page recipe for blueberry muffins is followed by a double-page recipe for banana and date muffins, instead of just saying “or substitute this”—things like that) and run the gamut from salad dressings to hearty main meals.
A strength of the book is that it’s about what you eat, not how much of it you eat, so if you love eating (which is a very healthy trait to have in general), then you’ll enjoy that aspect.
Bottom line: if you’d like to eat more and weigh less, then this is a top-tier book for you.
Click here to check out “Foods That Cause You To Lose Weight”, and enjoy eating!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
16/8 Intermittent Fasting For Beginners
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Health Insider explains in super-simple fashion why and how to do Intermittent Fasting (IF), which is something that can sound complicated at first, but becomes very simple and easy once understood.
What do we need to know?
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a good, well-evidenced way to ease your body’s metabolic load, and
give your organs a chance to recover from the strain of digestion and its effects. That’s not just your gastrointestinal organs! It’s your pancreas and liver too, amongst others—this is about glucose metabolism as much as it is about digestion.This, in turn, allows your body some downtime to do its favorite thing, which is: maintenance!
This maintenance takes the form of enhanced cellular apoptosis and autophagy, helping to keep cells young and cancer-free.
In other words, with well-practised intermittent fasting, we can reduce our risk of metabolic disease (including heart disease and diabetes) as well as cancer and neurodegeneration.
You may be wondering: this sounds miraculous; what’s the catch? There are a couple:
- While fasting from food, the body’s enhanced metabolism requires more water, so you’ll need to take extra care keep on top of your hydration (this is one reason why Ramadan fasting, while healthy for most people, is not as healthy as IF—because Ramadan fasting means abstaining from water, too).
- If you are diabetic, and especially if you have Type 1 Diabetes, fasting may not be a safe option for you, since if you get a hypo in the middle of your fasting period, it’s obviously not a good idea to wait another many hours before fixing it.
Extra note on that last one: it’s easy to think “can’t I just lower my bolus insulin instead of eating?” and while superficially yes that will raise your blood sugar levels, it’s because the sugar will be sticking around in your blood, and not actually getting released into the organs that need it. So while your blood glucose monitor may say you’re fine, you will be starving your organs and if you keep it up they may suffer serious damage.
Disclaimer: our standard legal/medical disclaimer applies, and this is intended for educational purposes only; please do speak with your endocrinologist before changing anything you usually do with regard to your blood sugar maintenance.
Ok, back onto the cheerier topic at hand:
Aside from the above: for most people, IF is a remarkably healthful practice in very many ways.
For more on the science, practicalities, and things to do/avoid, enjoy this short (4:53) video:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically
Want to know more?
Check out our previous main feature on this topic:
Intermittent Fasting: Mythbusting Edition
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Paleo Diet
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s The Real Deal With The Paleo Diet?
The Paleo diet is popular, and has some compelling arguments for it.
Detractors, meanwhile, have derided Paleo’s inclusion of modern innovations, and have also claimed it’s bad for the heart.
But where does the science stand?
First: what is it?
The Paleo diet looks to recreate the diet of the Paleolithic era—in terms of nutrients, anyway. So for example, you’re perfectly welcome to use modern cooking techniques and enjoy foods that aren’t from your immediate locale. Just, not foods that weren’t a thing yet. To give a general idea:
Paleo includes:
- Meat and animal fats
- Eggs
- Fruits and vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
- Herbs and spices
Paleo excludes:
- Processed foods
- Dairy products
- Refined sugar
- Grains of any kind
- Legumes, including any beans or peas
Enjoyers of the Mediterranean Diet or the DASH heart-healthy diet, or those with a keen interest in nutritional science in general, may notice they went off a bit with those last couple of items at the end there, by excluding things that scientific consensus holds should be making up a substantial portion of our daily diet.
But let’s break it down…
First thing: is it accurate?
Well, aside from the modern cooking techniques, the global market of goods, and the fact it does include food that didn’t exist yet (most fruits and vegetables in their modern form are the result of agricultural engineering a mere few thousand years ago, especially in the Americas)…
…no, no it isn’t. Best current scientific consensus is that in the Paleolithic we ate mostly plants, with about 3% of our diet coming from animal-based foods. Much like most modern apes.
Ok, so it’s not historically accurate. No biggie, we’re pragmatists. Is it healthy, though?
Well, health involves a lot of factors, so that depends on what you have in mind. But for example, it can be good for weight loss, almost certainly because of cutting out refined sugar and, by virtue of cutting out all grains, that means having cut out refined flour products, too:
Diet Review: Paleo Diet for Weight Loss
Measured head-to-head with the Mediterranean diet for all-cause mortality and specific mortality, it performed better than the control (Standard American Diet, or “SAD”), probably for the same reasons we just mentioned. However, it was outperformed by the Mediterranean Diet:
So in lay terms: the Paleo is definitely better than just eating lots of refined foods and sugar and stuff, but it’s still not as good as the Mediterranean Diet.
What about some of the health risk claims? Are they true or false?
A common knee-jerk criticism of the paleo-diet is that it’s heart-unhealthy. So much red meat, saturated fat, and no grains and legumes.
The science agrees.
For example, a recent study on long-term adherence to the Paleo diet concluded:
❝Results indicate long-term adherence is associated with different gut microbiota and increased serum trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), a gut-derived metabolite associated with cardiovascular disease. A variety of fiber components, including whole grain sources may be required to maintain gut and cardiovascular health.❞
Bottom line:
The Paleo Diet is an interesting concept, and certainly can be good for short-term weight loss. In the long-term, however (and: especially for our heart health) we need less meat and more grains and legumes.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: