This Is Your Brain on Food – by Dr. Uma Naidoo
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Diet will fix your brain” is a bold claim that often comes from wishful thinking and an optimistic place where anecdote is louder than evidence. But, diet does incontrovertibly also affect brain health. So, what does Dr. Naidoo bring to the table?
The author is a Harvard-trained psychiatrist, a professional chef who graduated with her culinary school’s most coveted award, and a trained-and-certified nutritionist. Between those three qualifications, it’s safe to she knows her stuff when it comes to the niche that is nutritional psychiatry. And it shows.
She takes us through the neurochemistry involved, what chemicals are consumed, made, affected, inhibited, upregulated, etc, what passes through the blood-brain barrier and what doesn’t, what part the gut really plays in its “second brain” role, and how we can leverage that—as well as mythbusting a lot of popular misconceptions about certain foods and moods.
There’s hard science in here, but presented in quite a pop-science way, making for a very light yet informative read.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand what your food is doing to your brain (and what it could be doing instead), then this is a top-tier book for you!
Click here to check out This Is Your Brain On Food, and get to know yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Stay off My Operating Table – by Dr. Philip Ovadia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
With heart disease as the #1 killer worldwide, and 88% of adults being metabolically unhealthy (leading cause of heart disease), this is serious!
Rather than taking a “quick fix” advise-and-go approach, Dr. Ovadia puts the knowledge and tools in our hands to do better in the long term.
As a heart surgeon himself, his motto here is:
❝What foods to put on your table so you don’t end up on mine❞
There’s a lot more to this book than the simple “eat the Mediterranean diet”:
- While the Mediterranean diet is generally considered the top choice for heart health, he also advises on how to eat healthily on all manner of diets… Carnivore, Keto, Paleo, Atkins, Gluten-Free, Vegan, you-name-it.
- A lot of the book is given to clearing up common misconceptions, things that sounded plausible but are just plain dangerous. This information alone is worth the price of the book, we think.
- There’s also a section given over to explaining the markers of metabolic health, so you can monitor yourself effectively
- Rather than one-size-fits-all, he also talks about common health conditions and medications that may change what you need to be doing
- He also offers advice about navigating the health system to get what you need—including dealing with unhelpful doctors!
Bottom line: A very comprehensive (yet readable!) manual of heart health.
Get your copy of Stay Off My Operating Table from Amazon today!
Share This Post
-
Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing coconut to avocado, we picked the avocado.
Why?
In terms of macros, avocado is lower in carbs and also in net carbs—coconut’s a little higher in fiber, but not enough to make up for the difference in carbs nor, when it comes to glycemic index and insulin index, the impact of coconut’s much higher fat content on insulin responses too. On which note, while coconut’s fats are broadly considered healthy (its impressive saturated fat content is formed of medium-chain triglycerides which, in moderation, are heart-healthy), avocado’s fats are even healthier, being mostly monounsaturated fat with some polyunsaturated (and about 15x less saturated fat). All in all, a fair win for avocado on the macros front, but coconut isn’t bad in moderation.
When it comes to vitamins, avocados are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline. Most of those differences are by very large margins. Coconuts are not higher in any vitamins. A huge, easy, “perfect score” win for avocados.
In the category of minerals, however, it’s coconut’s turn to sweep with more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, zinc, and selenium—though the margins are mostly not nearly as impressive as avocado’s vitamin margins. Speaking of avocados, they do have more potassium than coconuts do, but the margin isn’t very large. A compelling win for coconut’s mineral content.
Adding up the sections, we get to a very credible win for avocados, but coconuts are also very respectable. So, as ever, enjoy both (although we do recommend exercising moderation in the case of coconuts, mainly because of the saturated fat content), and if you’re choosing between them for some purpose, then avocado will generally be the best option.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy? ← defying Betteridge’s Law here!
- Avocado, Coconut & Lime Crumble Pots ← if you do want to enjoy both, here’s a fabulous way to do so in style
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Accidentally Overweight – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book’s main premise is that for most people who become overweight especially in midlife or later, if there wasn’t an obvious lifestyle change to precipitate this (e.g. started living on fast food for some reason), then in most cases, what’s needed is not drastic action, so much as some metabolic tweaks to correct things that have gone off-piste a little in our physiology.
The book covers nine factors that make an impact, and how each can be managed. They are:
- Insulin
- Stress hormones
- Calories
- Thyroid function
- Nervous system
- Emotions
- Sex hormones
- Liver function
- Gut bacteria
Some will be obvious, but as Dr. Weaver explains, are relative trivial compared to the others; “calories” in one such example of this “yes, it’s a factor, but very overrated” category.
Others are things that most people don’t think too much about, like liver function. And yet, it is indeed very much critical, and a major player in metabolism and adiposity.
The style is on the very light end of pop-science, but she does bring her professional knowledge to bear on topic (her doctorate is a PhD in biochemistry, so a lot of explanations come from that angle).
Bottom line: if you’ve found yourself “accidentally overweight”, and would like to tip the scales back in the other direction without doing anything extreme, then this book provides the tweaks that no amount of cardio or restrictive dieting will.
Click here to check out Accidentally Overweight, and re-adjust it back the other way!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Sunflower Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sunflower seeds to pumpkin seeds, we picked the pumpkin seeds.
Why?
Both seeds have a good spread of vitamins and minerals, but pumpkin seeds have more. Sunflower seeds come out on top for copper and manganese, but everything else that’s present in either of them (in the category of vitamins and minerals, anyway), pumpkin seeds have more.
There is one other thing that sunflower seeds have more of than pumpkin seeds, and that’s fat. The fat is mostly of healthy varieties, so it’s not a negative factor, but it does mean that if you’re eating a calorie-controlled diet, you’ll get more bang for your buck (i.e. better micronutrient-to-calorie ratio) if you pick pumpkin seeds.
If you’re not concerned about fat/calories, and/or you actively want to consume more of those, then sunflower seeds are still a fine choice.
When it comes down to it, a diverse diet is best, so enjoying both might be the best option of all.
Want to get some?
We don’t sell them, but here for your convenience are example products on Amazon:
Sunflower Seeds | Pumpkin Seeds
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
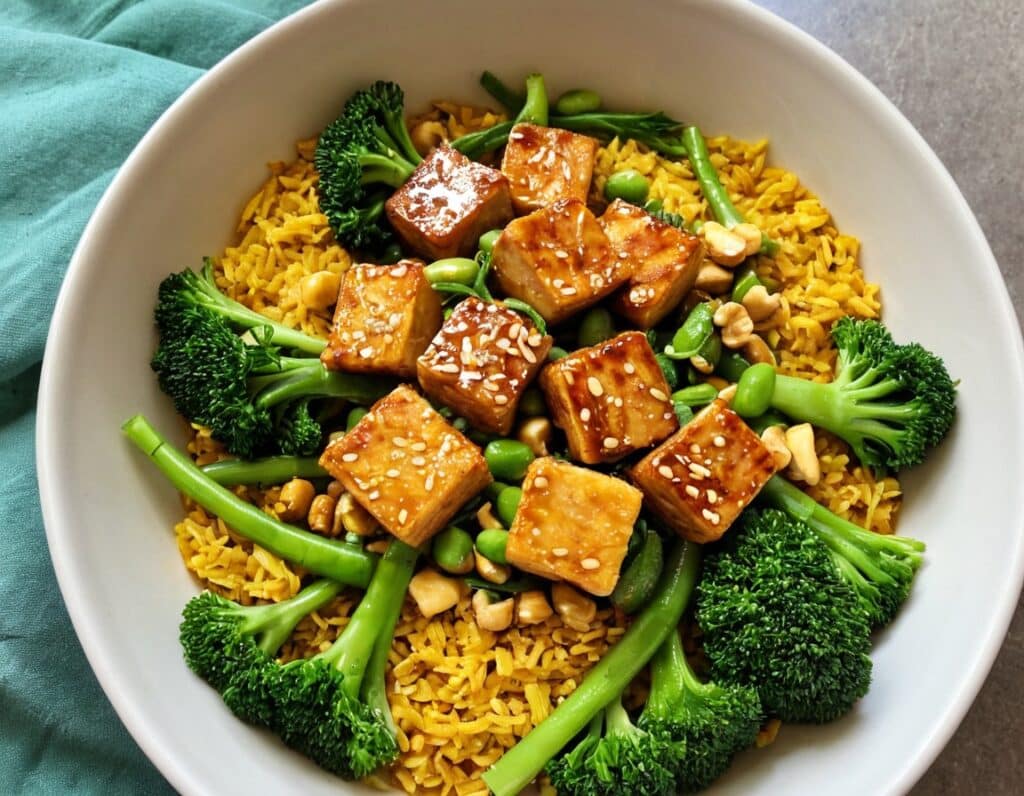
Sesame & Peanut Tofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Yesterday we learned how to elevate tofu from “nutrition” to “nutritious tasty snack” with our Basic Baked Tofu recipe; today we’re expanding on that, to take it from “nutritious tasty snack” to “very respectable meal”.
You will need
For the tofu:
- The Basic Baked Tofu that we made yesterday (consider making this to be “step zero” of today’s recipe if you don’t already have a portion in the fridge)
For the sauce:
- ⅓ cup peanut butter, ideally with no added sugar or salt (if allergic to peanuts specifically, use almond butter; if allergic to nuts generally, use tahini)
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated or crushed
- 1 tbsp tamarind paste
- 1½ tbsp tamari sauce (or low-sodium soy sauce, if a substitution is necessary)
- 1 tbsp sambal oelek (or sriracha sauce, if a substitution is necessary)
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground black pepper
- ½ tsp ground sweet cinnamon
- ½ tsp MSG (or else omit; do not substitute with salt in this case unless you have a particular craving)
- zest of 1 lime
For the vegetables:
- 14 oz broccolini / tenderstem broccoli, thick ends trimmed (failing that, any broccoli)
- 6 oz shelled edamame
- 1½ tsp toasted sesame oil
For serving:
- 4 cups cooked rice (we recommend our Tasty Versatile Rice recipe)
- ½ cup raw cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 5 minutes and then drained (if allergic, substitute cooked chickpeas, rinsed and drained)
- 1 tbsp toasted sesame seeds
- 1 handful chopped cilantro, unless you have the “this tastes like soap” gene, in which case substitute chopped parsley
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the sauce ingredients in a bowl and whisk well (or use a blender if you have one that’s comfortable with this relatively small quantity of ingredients). Taste it, and adjust the ingredient ratios if you’d like more saltiness, sweetness, sourness, spiciness, umami.
2) Prepare a bowl with cold water and some ice. Steam the broccolini and edamame for about 3 minutes; as soon as they become tender, dump them into the ice bathe to halt the cooking process. Let them chill for a few minutes, then drain, dry, and toss in the sesame oil.
3) Reheat the tofu if necessary (an air fryer is great for this), and then combine with half of the sauce in a bowl, tossing gently to coat well.
4) Add a little extra water to the remaining sauce, enough to make it pourable, whisking to an even consistency.
5) Assemble; do it per your preference, but we recommend the order: rice, vegetables, tofu, cashews, sauce, sesame seeds, herbs.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
- Sweet Cinnamon vs Regular Cinnamon – Which is Healthier?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Bird flu has been detected in a pig in the US. Why does that matter?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The United States Department of Agriculture last week reported that a pig on a backyard farm in Oregon was infected with bird flu.
As the bird flu situation has evolved, we’ve heard about the A/H5N1 strain of the virus infecting a range of animals, including a variety of birds, wild animals and dairy cattle.
Fortunately, we haven’t seen any sustained spread between humans at this stage. But the detection of the virus in a pig marks a worrying development in the trajectory of this virus.
David MG/Shutterstock How did we get here?
The most concerning type of bird flu currently circulating is clade 2.3.4.4b of A/H5N1, a strain of influenza A.
Since 2020, A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b has spread to a vast range of birds, wild animals and farm animals that have never been infected with bird flu before.
While Europe is a hotspot for A/H5N1, attention is currently focused on the US. Dairy cattle were infected for the first time in 2024, with more than 400 herds affected across at least 14 US states.
Bird flu has enormous impacts on farming and commercial food production, because infected poultry flocks have to be culled, and infected cows can result in contaminated diary products. That said, pasteurisation should make milk safe to drink.
While farmers have suffered major losses due to H5N1 bird flu, it also has the potential to mutate to cause a human pandemic.
Birds and humans have different types of receptors in their respiratory tract that flu viruses attach to, like a lock (receptors) and key (virus). The attachment of the virus allows it to invade a cell and the body and cause illness. Avian flu viruses are adapted to birds, and spread easily among birds, but not in humans.
So far, human cases have mainly occurred in people who have been in close contact with infected farm animals or birds. In the US, most have been farm workers.
The concern is that the virus will mutate and adapt to humans. One of the key steps for this to happen would be a shift in the virus’ affinity from the bird receptors to those found in the human respiratory tract. In other words, if the virus’ “key” mutated to better fit with the human “lock”.
A recent study of a sample of A/H5N1 2.3.4.4b from an infected human had worrying findings, identifying mutations in the virus with the potential to increase transmission between human hosts.
Why are pigs a problem?
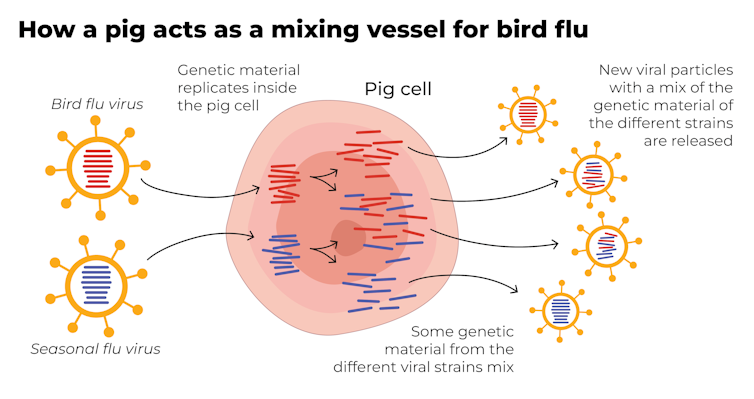
A human pandemic strain of influenza can arise in several ways. One involves close contact between humans and animals infected with their own specific flu viruses, creating opportunities for genetic mixing between avian and human viruses.
Pigs are the ideal genetic mixing vessel to generate a human pandemic influenza strain, because they have receptors in their respiratory tracts which both avian and human flu viruses can bind to.
This means pigs can be infected with a bird flu virus and a human flu virus at the same time. These viruses can exchange genetic material to mutate and become easily transmissible in humans.
The Conversation, CC BY-SA Interestingly, in the past pigs were less susceptible to A/H5N1 viruses. However, the virus has recently mutated to infect pigs more readily.
In the recent case in Oregon, A/H5N1 was detected in a pig on a non-commercial farm after an outbreak occurred among the poultry housed on the same farm. This strain of A/H5N1 was from wild birds, not the one that is widespread in US dairy cows.
The infection of a pig is a warning. If the virus enters commercial piggeries, it would create a far greater level of risk of a pandemic, especially as the US goes into winter, when human seasonal flu starts to rise.
How can we mitigate the risk?
Surveillance is key to early detection of a possible pandemic. This includes comprehensive testing and reporting of infections in birds and animals, alongside financial compensation and support measures for farmers to encourage timely reporting.
Strengthening global influenza surveillance is crucial, as unusual spikes in pneumonia and severe respiratory illnesses could signal a human pandemic. Our EPIWATCH system looks for early warnings of such activity, which can speed up vaccine development.
If a cluster of human cases occurs, and influenza A is detected, further testing (called subtyping) is essential to ascertain whether it’s a seasonal strain, an avian strain from a spillover event, or a novel pandemic strain.
Early identification can prevent a pandemic. Any delay in identifying an emerging pandemic strain enables the virus to spread widely across international borders.
Australia’s first human case of A/H5N1 occurred in a child who acquired the infection while travelling in India, and was hospitalised with illness in March 2024. At the time, testing revealed Influenza A (which could be seasonal flu or avian flu), but subtyping to identify A/H5N1 was delayed.
This kind of delay can be costly if a human-transmissible A/H5N1 arises and is assumed to be seasonal flu because the test is positive for influenza A. Only about 5% of tests positive for influenza A are subtyped further in Australia and most countries.
In light of the current situation, there should be a low threshold for subtyping influenza A strains in humans. Rapid tests which can distinguish between seasonal and H5 influenza A are emerging, and should form part of governments’ pandemic preparedness.
A higher risk than ever before
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the current risk posed by H5N1 to the general public remains low.
But with H5N1 now able to infect pigs, and showing worrying mutations for human adaptation, the level of risk has increased. Given the virus is so widespread in animals and birds, the statistical probability of a pandemic arising is higher than ever before.
The good news is, we are better prepared for an influenza pandemic than other pandemics, because vaccines can be made in the same way as seasonal flu vaccines. As soon as the genome of a pandemic influenza virus is known, the vaccines can be updated to match it.
Partially matched vaccines are already available, and some countries such as Finland are vaccinating high-risk farm workers.
C Raina MacIntyre, Professor of Global Biosecurity, NHMRC L3 Research Fellow, Head, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute, UNSW Sydney and Haley Stone, Research Associate, Biosecurity Program, Kirby Institute & CRUISE lab, Computer Science and Engineering, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: