Thinking about trying physiotherapy for endometriosis pain? Here’s what to expect
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Endometriosis is a condition that affects women and girls. It occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus ends up in other areas of the body. These areas include the ovaries, bladder, bowel and digestive tract.
Endometriosis will affect nearly one million Australian women and girls in their lifetime. Many high-profile Australians are affected by endometriosis including Bindi Irwin, Sophie Monk and former Yellow Wiggle, Emma Watkins.
Symptoms of endometriosis include intense pelvic, abdominal or low back pain (that is often worse during menstruation), bladder and bowel problems, pain during sex and infertility.
But women and girls wait an average of seven years to receive a diagnosis. Many are living with the burden of endometriosis and not receiving treatments that could improve their quality of life. This includes physiotherapy.

How is endometriosis treated?
No treatments cure endometriosis. Symptoms can be reduced by taking medications such as non-steriodal anti-inflammatories (ibuprofen, aspirin or naproxen) and hormonal medicines.
Surgery is sometimes used to diagnose endometriosis, remove endometrial lesions, reduce pain and improve fertility. But these lesions can grow back.
Whether they take medication or have surgery, many women and girls continue to experience pain and other symptoms.
Pelvic health physiotherapy is often recommended as a non-drug management technique to manage endometriosis pain, in consultation with a gynaecologist or general practitioner.
The goal of physiotherapy treatment depends on the symptoms but is usually to reduce and manage pain, improve ability to do activities, and ultimately improve quality of life.
What could you expect from your first appointment?
Physiotherapy management can differ based on the severity and location of symptoms. Prior to physical tests and treatments, your physiotherapist will comprehensively explain what is going to happen and seek your permission.
They will ask questions to better understand your case and specific needs. These will include your age, weight, height as well as the presence, location and intensity of symptoms.
You will also be asked about the history of your period pain, your first period, the length of your menstrual cycle, urinary and bowel symptoms, sexual function and details of any previous treatments and tests.
They may also assess your posture and movement to see how your muscles have changed because of the related symptoms.

They will press on your lower back and pelvic muscles to spot painful areas (trigger points) and muscle tightness.
If you consent to a vaginal examination, the physiotherapist will use one to two gloved fingers to assess the area inside and around your vagina. They will also test your ability to coordinate, contract and relax your pelvic muscles.
What type of treatments could you receive?
Depending on your symptoms, your physiotherapist may use the following treatments:
General education
Your physiotherapist will give your details about the disease, pelvic floor anatomy, the types of treatment and how these can improve pain and other symptoms. They might teach you about the changes to the brain and nerves as a result of being in long-term pain.
They will provide guidance to improve your ability to perform daily activities, including getting quality sleep.
If you experience pain during sex or difficulty using tampons, they may teach you how to use vaginal dilators to improve flexibility of those muscles.
Pelvic muscle exercises
Pelvic muscles often contract too hard as a result of pain. Pelvic floor exercises will help you contract and relax muscles appropriately and provide an awareness of how hard muscles are contracting.
This can be combined with machines that monitor muscle activity or vaginal pressure to provide detailed information on how the muscles are working.
Yoga, stretching and low-impact exercises
Yoga, stretching and low impact aerobic exercise can improve fitness, flexibility, pain and blood circulation. These have general pain-relieving properties and can be a great way to contract and relax bigger muscles affected by long-term endometriosis.
These exercises can help you regain function and control with a gradual progression to perform daily activities with reduced pain.
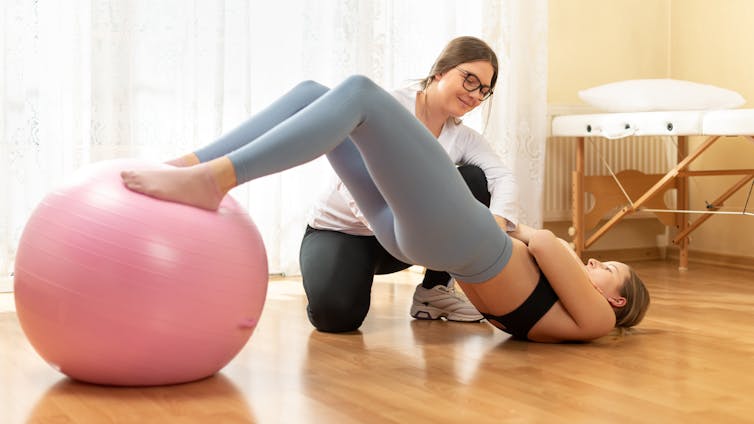

Hydrotherapy (physiotherapy in warm water)
Performing exercises in water improves blood circulation and muscle relaxation due to the pressure and warmth of the water. Hydrotherapy allows you to perform aerobic exercise with low impact, which will reduce pain while exercising.
However, while hydrotherapy shows positive results clinically, scientific studies to show its effectiveness studies are ongoing.
Manual therapy
Women frequently have small areas of muscle that are tight and painful (trigger points) inside and outside the vagina. Pain can be temporarily reduced by pressing, massaging or putting heat on the muscles.
Physiotherapists can teach patients how to do these techniques by themselves at home.
What does the evidence say?
Overall, patients report positive experiences pelvic health physiotherapists treatments. In a study of 42 women, 80% of those who received manual therapy had “much improved pain”.
In studies investigating yoga, one study showed pain was reduced in 28 patients by an average of 30 points on a 100-point pain scale. Another study showed yoga was beneficial for pain in all 15 patients.
But while some studies show this treatment is effective, a review concluded more studies were needed and the use of physiotherapy was “underestimated and underpublicised”.
What else do you need to know?
If you have or suspect you have endometriosis, consult your gynaecologist or GP. They may be able to suggest a pelvic health physiotherapist to help you manage your symptoms and improve quality of life.
As endometriosis is a chronic condition you may be entitled to five subsidised or free sessions per calendar year in clinics that accept Medicare.
If you go to a private pelvic health physiotherapist, you won’t need a referral from a gynaecologist or GP. Physiotherapy rebates can be available to those with private health insurance.
The Australian Physiotherapy Association has a Find a Physio section where you can search for women’s and pelvic physiotherapists. Endometriosis Australia also provides assistance and advice to women with Endometriosis.
Thanks to UTS Masters students Phoebe Walker and Kasey Collins, who are researching physiotherapy treatments for endometriosis, for their contribution to this article.
Peter Stubbs, Senior Lecturer in Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney and Caroline Wanderley Souto Ferreira, Visiting Professor of Physiotherapy, University of Technology Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Spreading Mental Health Awareness
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
Request: more people need to be aware of suicidal tendencies and what they can do to ward them off
That’s certainly a very important topic! We’ll cover that properly in one of our Psychology Sunday editions. In the meantime, we’ll mention a previous special that we did, that was mostly about handling depression (in oneself or a loved one), and obviously there’s a degree of crossover:
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
Share This Post
-
Revealed: The Soviet Secret Recipe For Success That The CIA Admits Put The US To Shame
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today’s edition of 10almonds brings you a blast from the past with a modern twist: an ancient Russian peasant food that became a Soviet staple, and today, is almost unknown in the West.
Before we get to that, let’s take a sneaky look at this declassified CIA memorandum from near the end of the Cold War:
(Click here to see a bigger version)
The take-away here is:
- Americans were eating 2–3 times more meat than Soviets
- Soviets were eating nearly double the amount of grain products and potatoes
…and both of these statistics meant that nutritionally speaking, the Soviets were doing better.
Americans also consumed more sugar and fats, which again, wasn’t the best dietary option.
But was the American diet tastier? Depends on whom you ask.
Which brings us to a literal recipe we’re going to be sharing with you today:
It’s not well-known in the West, but in Russia, it’s a famous national comfort food, a bastion of health and nutrition, and it rose to popularity because it was not only cheap and nutritious, but also, you could eat it for days without getting sick of it. And it could be easily frozen for reheating later without losing any of its appeal—it’d still be just as good.
In Russia there are sayings about it:
Щи да каша — пища наша (Shchi da kasha — pishcha nasha)
“Shchi and buckwheat are what we eat”
Top tip: buckwheat makes an excellent (and naturally sweet) alternative to porridge oats if prepared the same way!
Где щи, там и нас ищи (Gdye shchi, tam i nas ishchi)
“Where there’s shchi, us you’ll see”
Голь голью, а луковка во щах есть (Gol’ gol’yu, a lukovka vo shchakh yest’)
“I’m stark naked, but there’s shchi with onions”
There’s a very strong sentiment in Russia that really, all you need is shchi (shchi, shchi… shchi is all you need )
But what, you may ask, is shchi?
Our culinary cultural ambassador Nastja is here to offer her tried-and-tested recipe for…
…Russian cabbage soup (yes, really—bear with us now, and you can thank us later)
There are a lot of recipes for shchi (see for yourself what the Russian version of Lifehacker recommends), and we’ll be offering our favorite…
Nastja’s Nutritious and Delicious Homemade Shchi
Hi, Nastja here! I’m going to share with you my shchi recipe that is:
- Cheap
- So tasty
- Super nutritious*
- Vegan
- Gluten Free
You will also need:
- A cabbage (I use sweetheart, but any white cabbage will do)
- 1 cup (250g) red lentils (other kinds of lentils will work too)
- ½ lb or so (250–300g) tomatoes (I use baby plum tomatoes, but any kind will do)
- ½ lb or so (250–300g) mushrooms (the edible kind)
- An onion (I use a brown onion; any kind will do)
- Salt, pepper, rosemary, thyme, parsley, cumin
- Marmite or similar yeast extract (do you hate it? Me too. Trust me, it’ll be fine, you’ll love it. Omit if you’re a coward.)
- A little oil for sautéing (I use sunflower, but canola is fine, as is soy oil. Do not use olive oil or coconut oil, because the taste is too strong and the flashpoint too low)
First, what the French call mise-en-place, the prep work:
- Chop the cabbage into small strips, ⅛–¼ inch x 1 inch is a good guideline, but you can’t really go wrong unless you go to extremes
- Chop the tomatoes. If you’re using baby plum tomatoes (or cherry tomatoes), cut them in half. If using larger tomatoes, cut them into eighths (halve them, halve the halves, then halve the quarters)
- Chop the mushrooms. If using button mushrooms, half them. If using larger mushrooms, quarter them.
- Chop the onion finely.
- Gather the following kitchenware: A big pan (stock pot or similar), a sauté pan (a big wok or frying pan will do), a small frying pan (here a wok will not do), and a saucepan (a rice cook will also do)
Now, for actual cooking:
- Cook the red lentils until soft (I use a rice cooker, but a saucepan is fine) and set aside
- Sauté the cabbage, put it in the big pot (not yet on the heat!)
- Fry the mushrooms, put them in the big pot (still not yet on the heat!)
When you’ve done this a few times and/or if you’re feeling confident, you can do the above simultaneously to save time
- Blend the lentils into the water you cooked them in, and then add to the big pot.
- Turn the heat on low, and if necessary, add more water to make it into a rich soup
- Add the seasonings to taste, except the parsley. Go easy on the cumin, be generous with the rosemary and thyme, let your heart guide you with the salt and pepper.
- When it comes to the yeast extract: add about one teaspoon and stir it into the pot. Even if you don’t like Marmite, it barely changes the flavour (makes it slightly richer) and adds a healthy dose of vitamin B12.
We did not forget the tomatoes and the onion:
- Caramelize the onion (keep an eye on the big pot) and set it aside
- Fry the tomatoes and add them to the big pot
Last but definitely not least:
- Serve!
- The caramelized onion is a garnish, so put a little on top of each bowl of shchi
- The parsley is also a garnish, just add a little
Any shchi you don’t eat today will keep in the fridge for several days, or in the freezer for much longer.
*That nutritious goodness I talked about? Check it out:
- Lentils are high in protein and iron
- Cabbage is high in vitamin C and calcium
- Mushrooms are high in magnesium
- Tomatoes are good against inflammation
- Black pepper has a host of health benefits
- Yeast extract contains vitamin B12
Let us know how it went! We love to receive emails from our subscribers!
Share This Post
-
Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cashew nuts to coconut, we picked the cashews.
Why?
It can be argued this isn’t a fair comparison, as coconuts aren’t true nuts, but it’s at the very least a useful comparison, because they have very similar (often the same) culinary uses, so deciding between one or the other is something people will often do.
In terms of macros, cashews have 6x the protein and more than 2x the fiber, as well as slightly more fat (but the fats are healthy, as are those of coconut, by the way) and 2x the carbs. Depending on what you’re looking for, this head-to-head could come out differently, but we say it’s a win for cashews.
You may be wondering: if cashews have more of all those things, what are coconuts made of? And the answer is that coconuts have 8x the water (and yes, this is counting the coconut meat only, not including the milk inside). Of course, if you get dessicated coconut, then it won’t have that, but we’re comparing fresh to fresh.
In the category of vitamins, cashews have a lot more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, E, and K. Meanwhile, coconut has more vitamin C, but it’s not a lot. An easy win for cashews here.
When it comes to minerals, cashews have rather more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. On the other hand, coconut has more sodium. Another easy win for cashews.
Cashews also have the lower glycemic index.
All in all, cashews win the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
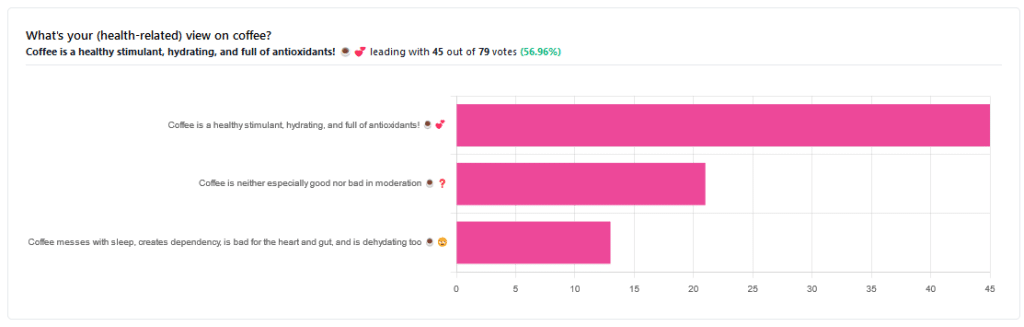
Yesterday, we asked you for your (health-related) views on coffee. The results were clear: if we assume the responses to be representative, we’re a large group of coffee-enthusiasts!
One subscriber who voted for “Coffee is a healthy stimulant, hydrating, and full of antioxidants” wrote:
❝Not so sure about how hydrating it is! Like most food and drink, moderation is key. More than 2 or 3 cups make me buzz! Just too much.❞
And that fine point brings us to our first potential myth:
Coffee is dehydrating: True or False?
False. With caveats…
Coffee, in whatever form we drink it, is wet. This may not come as a startling revelation, but it’s an important starting point. It’s mostly water. Water itself is not dehydrating.
Caffeine, however, is a diuretic—meaning you will tend to pee more. It achieves its diuretic effect by increasing blood flow to your kidneys, which prompts them to release more water through urination.
See: Effect of caffeine on bladder function in patients with overactive bladder symptoms
How much caffeine is required to have a diuretic effect? About 4.5 mg/kg.
What this means in practical terms: if you weigh 70kg (a little over 150lbs), 4.5×70 gives us 315.
315mg is about how much caffeine might be in six shots of espresso. We say “might” because while dosage calculations are an exact science, the actual amount in your shot of espresso can vary depending on many factors, including:
- The kind of coffee bean
- How and when it was roasted
- How and when it was ground
- The water used to make the espresso
- The pressure and temperature of the water
…and that’s all without looking at the most obvious factor: “is the coffee decaffeinated?”
If it doesn’t contain caffeine, it’s not diuretic. Decaffeinated coffee does usually contain tiny amounts of caffeine still, but with nearer 3mg than 300mg, it’s orders of magnitude away from having a diuretic effect.
If it does contain caffeine, then the next question becomes: “and how much water?”
For example, an Americano (espresso, with hot water added to make it a long drink) will be more hydrating than a ristretto (espresso, stopped halfway through pushing, meaning it is shorter and stronger than a normal espresso).
A subscriber who voted for “Coffee messes with sleep, creates dependency, is bad for the heart and gut, and is dehydrating too” wrote:
❝Coffee causes tachycardia for me so staying away is best. People with colon cancer are urged to stay away from coffee completely.❞
These are great points! It brings us to our next potential myth:
Coffee is bad for the heart: True or False?
False… For most people.
Some people, like our subscriber above, have an adverse reaction to caffeine, such as tachycardia. An important reason (beyond basic decency) for anyone providing coffee to honor requests for decaff.
For most people, caffeine is “heart neutral”. It doesn’t provide direct benefits or cause direct harm, provided it is enjoyed in moderation.
See also: Can you overdose on caffeine?
Some quick extra notes…
That’s all we have time for in myth-busting, but it’s worth noting before we close that coffee has a lot of health benefits; we didn’t cover them today because they’re not contentious, but they are interesting nevertheless:
- Coffee is the world’s biggest source of antioxidants
- 65% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for coffee-drinkers
- 67% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes for coffee-drinkers
- 43% reduced risk of liver cancer for coffee-drinkers
- 53% reduced suicide risk for coffee-drinkers
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Yoga Therapy for Arthritis – by Dr. Steffany Moonaz & Erin Byron
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Two quick notes to start with:
- One of the problems with arthritis and exercise is that arthritis can often impede exercise.
- Another of the problems with arthritis and exercise is that some kinds of exercise can exacerbate arthritis.
This book deals with both of those issues, by providing yoga specifically tailored to living with arthritis. Indeed, the first-listed author’s PhD in public health was the result of 8 years of study developing an evidence-based yoga program for people with arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
The authors take the view that arthritis is a whole-person disease (i.e. it affects all parts of you), and so addressing it requires a whole-person approach, which is what this book delivers.
As such, this is not just a book of asana (yoga postures). It does provide that, of course (as well as breathing exercises), but also its 328 pages additionally cover a lot of conscious work from the inside out, including attention to the brain, energy levels, pain, and so forth, and that the practice of yoga should not merely directly improve the joints via gentle physical exercise, but also should help to heal the whole person, including reducing stress levels, reducing physical tension, and with those two things, reducing inflammation also—and also, due to both that and the asana side of practice, better-functioning organs, which is always a bonus.
The style is interesting, as it refers to both science (8 pages of hard-science bibliography) and yogic principles (enough esoterica to put off, say, James Randi or Penn & Teller). This reviewer is very comfortable with both, and so if you, dear reader, are comfortable with both too, then you will surely enjoy this book.
Bottom line: if you or a loved one has arthritis, you’ll wish you got this book sooner.
Click here to check out Yoga Therapy For Arthritis, and live better!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
A Fresh Take On Hypothyroidism
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Three Rs To Boost Thyroid-Related Energy Levels
This is Dr. Izabella Wentz. She’s a doctor of pharmacology, and after her own diagnosis with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, she has taken it up as her personal goal to educate others on managing hypothyroidism.
Dr. Wentz is also trained in functional medicine through The Institute for Functional Medicine, Kalish Functional Medicine, and the American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine. She is a Fellow of the American Society of Consultant Pharmacists, and holds certifications in Medication Therapy Management as well as Advanced Diabetes Care through the American Pharmacists Association. In 2013, she received the Excellence in Innovation Award from the Illinois Pharmacists Association.
Dr. Wentz’s mission
Dr. Wentz was disenchanted by the general medical response to hypothyroidism in three main ways. She tells us:
- Thyroid patients are not diagnosed appropriately.
- For this, she criticises over-reliance on TSH tests that aren’t a reliable marker of thyroid function, especially if you have Hashimoto’s.
- Patients should be better optimized on their medications.
- For this, she criticizes many prescribed drugs that are actually pro-drugs*, that don’t get converted adequately if you have an underactive thyroid.
- Lifestyle interventions are often ignored by mainstream medicine.
- Medicines are great; they truly are. But medicating without adjusting lifestyle can be like painting over the cracks in a crumbling building.
*a “pro-drug” is what it’s called when the drug we take is not the actual drug the body needs, but is a precursor that will get converted to that actual drug we need, inside our body—usually by the liver, but not always. An example in this case is T4, which by definition is a pro-drug and won’t always get correctly converted to the T3 that a thyroid patient needs.
Well that does indeed sound worthy of criticism. But what does she advise instead?
First, she recommends a different diagnostic tool
Instead of (or at least, in addition to) TSH tests, she advises to ask for TPO tests (thyroid peroxidase), and a test for Tg antibodies (thyroglobulin). She says these are elevated for many years before a change in TSH is seen.
Next, identify the root cause and triggers
These can differ from person to person, but in countries that add iodine to salt, that’s often a big factor. And while gluten may or may not be a factor, there’s a strong correlation between celiac disease and Hashimoto’s disease, so it is worth checking too. Same goes for lactose.
By “checking”, here we mean testing eliminating it and seeing whether it makes a difference to energy levels—this can be slow, though, so give it time! It is best to do this under the guidance of a specialist if you can, of course.
Next, get to work on repairing your insides.
Remember we said “this can be slow”? It’s because your insides won’t necessarily bounce back immediately from whatever they’ve been suffering from for what’s likely many years. But, better late than never, and the time will pass anyway, so might as well get going on it.
For this, she recommends a gut-healthy diet with specific dietary interventions for hypothyroidism. Rather than repeat ourselves unduly here, we’ll link to a couple of previous articles of ours, as her recommendations match these:
She also recommends regular blood testing to see if you need supplementary TSH, TPO antibodies, and T3 and T4 hormones—as well as vitamin B12.
Short version
After diagnosis, she recommends the three Rs:
- Remove the causes and triggers of your hypothyroidism, so far as possible
- Repair the damage caused to your body, especially your gut
- Replace the thyroid hormones and related things in which your body has become deficient
Learn more
If you’d like to learn more about this, she offers a resource page, with resources ranging from on-screen information, to books you can get, to links to hook you up with blood tests if you need them, as well as recommended supplements to consider.
She also has a blog, which has an interesting relevant article added weekly.
Enjoy, and take care of yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Thyroid patients are not diagnosed appropriately.