The Telomere Effect – by Dr. Elizabeth Blackburn and Dr. Elissa Epel
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Telomeres can be pretty mystifying to the person with a lay interest in longevity. Beyond “they’re the little caps that sit on the end of your DNA, and longer is better, and when they get short, damage occurs, and aging”, how do they fit into the big picture?
Dr. Elizabeth Blackburn and Dr. Elissa Epel excel at explaining the marvelous world of telomeres…
- how they work
- what affects them
- and how and why
…and the extent to which changes are or aren’t reversible.
For some of us, the ship has sailed on avoiding a lot of early-life damage to our telomeres, and now we have a damage-mitigation task ahead. That’s where the authors get practical.
Indeed, the whole third part of the book is titled “Help Your Body Protect Its Cells“, and indeed covers not just “from now on” protection, but undoing some of the damage already done (yes, telomeres can be lengthened—it gets harder as we get older, but absolutely can be done).
In short: if you’d like to avoid further damage to your telomeres where possible, and reverse some of the damage done already, this book will set you on the right track.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why You Probably Need More Sleep
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sleep: yes, you really do still need it!
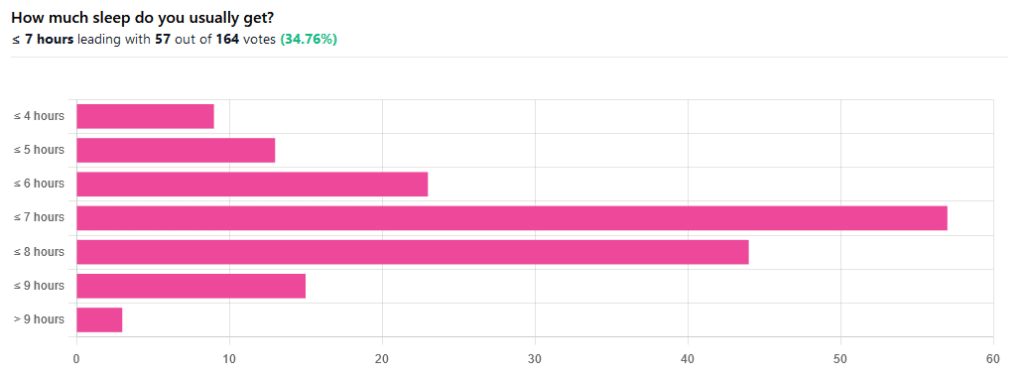
We asked you how much sleep you usually get, and got the above-pictured, below-described set of responses:
- A little of a third of all respondents selected the option “< 7 hours”
- However, because respondents also selected options such as < 6 hours, < 5 hours, and < 4 hours, so if we include those in the tally, the actual total percentage of respondents who reported getting under 7 hours, is actually more like 62%, or just under two thirds of all respondents.
- Nine respondents, which was about 5% of the total, reported usually getting under 4 hours sleep
- A little over quarter of respondents reported usually getting between 7 and 8 hours sleep
- Fifteen respondents, which was a little under 10% of the total, reported usually getting between 8 and 9 hours of sleep
- Three respondents, which was a little under 2% of the total, reported getting over 9 hours of sleep
- In terms of the classic “you should get 7–9 hours sleep”, approximately a third of respondents reported getting this amount.
You need to get 7–9 hours sleep: True or False?
True! Unless you have a (rare!) mutated ADRB1 gene, which reduces that.
The way to know whether you have this, without genomic testing to know for sure, is: do you regularly get under 6.5 hours sleep, and yet continue to go through life bright-eyed and bushy-tailed? If so, you probably have that gene. If you experience daytime fatigue, brain fog, and restlessness, you probably don’t.
About that mutated ADRB1 gene:
NIH | Gene identified in people who need little sleep
Quality of sleep matters as much as duration, and a lot of studies use the “RU-Sated” framework, which assesses six key dimensions of sleep that have been consistently associated with better health outcomes. These are:
- regularity / usual hours
- satisfaction with sleep
- alertness during waking hours
- timing of sleep
- efficiency of sleep
- duration of sleep
But, that doesn’t mean that you can skimp on the last one if the others are in order. In fact, getting a good 7 hours sleep can reduce your risk of getting a cold by three or four times (compared with six or fewer hours):
Behaviorally Assessed Sleep and Susceptibility to the Common Cold
^This study was about the common cold, but you may be aware there are more serious respiratory viruses freely available, and you don’t want those, either.
Napping is good for the health: True or False?
True or False, depending on how you’re doing it!
If you’re trying to do it to sleep less in total (per polyphasic sleep scheduling), then no, this will not work in any sustainable fashion and will be ruinous to the health. We did a Mythbusting Friday special on specifically this, a while back:
Could Just Two Hours Sleep Per Day Be Enough?
PS: you might remember Betteridge’s Law of Headlines
If you’re doing it as a energy-boosting supplement to a reasonable night’s sleep, napping can indeed be beneficial to the health, and can give benefits such as:
- Increased alertness
- Helps with learning
- Improved memory
- Boost to immunity
- Enhance athletic performance
However! There is still a right and a wrong way to go about it, and we wrote about this previously, for a Saturday Life Hacks edition of 10almonds:
How To Nap Like A Pro (No More “Sleep Hangovers”!)
As we get older, we need less sleep: True or False
False, with one small caveat.
The small caveat: children and adolescents need 9–12 hours sleep because, uncredited as it goes, they are doing some seriously impressive bodybuilding, and that is exhausting to the body. So, an adult (with a normal lifestyle, who is not a bodybuilder) will tend to need less sleep than a child/adolescent.
But, the statement “As we get older, we need less sleep” is generally taken to mean “People in the 65+ age bracket need less sleep than younger adults”, and this popular myth is based on anecdotal observational evidence: older people tend to sleep less (as our survey above shows! For any who aren’t aware, our readership is heavily weighted towards the 60+ demographic), and still continue functioning, after all.
Just because we survive something with a degree of resilience doesn’t mean it’s good for us.
In fact, there can be serious health risks from not getting enough sleep in later years, for example:
Sleep deficiency promotes Alzheimer’s disease development and progression
Want to get better sleep?
What gets measured, gets done. Sleep tracking apps can be a really good tool for getting one’s sleep on a healthier track. We compared and contrasted some popular ones:
The Head-To-Head Of Google and Apple’s Top Apps For Getting Your Head Down
Take good care of yourself!
Share This Post
-
Sticky Jackfruit Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All the taste and experience of pulled pork, without the increased risk of cancer and metabolic disease. On the contrary, jackfruit introduces lots of fiber, vitamins, carotenoids, and flavanones. We’ll have to do a main feature about jackfruit sometime; it’s an unusual fruit especially for its protein content, but for now, let’s get cooking!
You will need
- 1 can (14oz/400g) green jackfruit, drained (the flesh will not, in fact, be green—this is referring to the fruit being unripe and thus still firm in texture, which is what we want. The outside of the fruit, which will not be in the can, will have been green)
- 1/4 red cabbage, thinly sliced
- 1/2 carrot, grated
- 6 mangetout, thinly sliced
- 2 tbsp mayonnaise (your preference what kind, and yes, vegan is fine too)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp gochujang paste (if you can’t find gochujang paste locally, you can either order it online (here it is on Amazon) or substitute with harissa paste, which is not the same—it uses different spices—but will do the same job here re texture, umami taste, and level of spiciness)
- 1 tbsp soy sauce
- 1 tbsp balsamic vinegar
- 1 tsp apple cider vinegar
- 1 tsp garlic paste
- 1 tsp tomato paste
- 1 tsp ginger paste
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 3½ fl oz water
- 2 burger buns (unless you make them yourself, burger buns will probably not be healthy; you can, however, also look for small round wholemeal breads—the name of which varies far too much by region for us to try to get a catch-all name here—and use them in place of burger buns)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the garlic paste, ginger paste, tomato paste, gochujang paste, soy sauce, balsamic vinegar, and chili flakes in a saucepan
2) Boil the 3½ fl oz water we mentioned; add it to the saucepan, mixing well, turn on the heat and let it simmer for 5 minutes or until it is thick and sticky (it will thicken more as it cools, too, so don’t worry if it doesn’t seem thick enough yet). Set it aside.
3) Dry the jackfruit (using strong kitchen paper should be fine), add the olive oil to a skillet and bring it to a high heat; add the jackfruit and fry on both sides for a few minutes, until it looks cooked (remember, while this may look like animal meat, it’s not, so there’s no danger of undercooking here).
4) When the jackfruit looks a nice golden-brown, add two thirds of the sauce from the saucepan, and break apart the jackfruit a bit (this can be done with a wooden/bamboo spatula, so as to not damage your pan), When it all looks how you’d expect pulled jackfruit (or pulled pork) to look, take it off the heat.
5) Combine the carrot, cabbage, and mangetout in a small bowl, adding the apple cider vinegar and mixing well; this will be the coleslaw element
6) Mix the remaining sauce with the mayonnaise
7) (optional) toast the burger buns
8) Assemble the burgers; we recommend the following order: bottom bun, pulled jackfruit, coleslaw, gochujang mayo, top bun
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake, The Fun Way!
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Is Vitamin C Worth The Hype? (Doctorly Investigates)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Double Board-Certified Dermatologists Dr. Muneeb Shah & Dr. Luke Maxfield weigh in on vitamin C; is it worth the hype?
Yes it is, but…
There are some caveats, for example:
- It’s best to apply vitamin C on clean, dry skin and let it set before layering other products.
- Avoid mixing with oxidants like benzoyl peroxide (cancels out antioxidant effects).
- Avoid combining with copper (may negate brightening benefits).
- Do not use with hypochlorous acid (oxidative reactions cancel out benefits).
- Be cautious with retinol due to irritation risks.
However, used correctly, it does give very worthy benefits, and they recommend:
- Morning use: acts as an antioxidant, pairs well with sunscreen for better protection from sun and environmental damage.
- Night use: maximizes functions like improving tone, collagen production, texture, and reducing wrinkles.
That’s not to say that at night it stops being an antioxidant or during the day it isn’t critical for collagen synthesis, but it is to say: because of the different things our bodies typically encounter and/or do during the day or night, those are the best times to get the most out of those benefits.
They also review some popular products; here are some notes on their comments about them:
- Skinceuticals C E Ferulic: research-backed, $180, effective but potentially irritating.
- Skinceuticals Phloretin CF: includes 0.5% salicylic acid, good for acne-prone skin.
- Dermatology Vitamin C E Ferulic: relatively more affordable ($70), fragrance-free, includes peptides and ceramides.
- Drunk Elephant C-Firma: powder-to-serum formula, sued for patent infringement.
- Paula’s Choice C15 Booster: reformulated, fragrance-free, similar to Skinceuticals.
- Neutrogena Vitamin C Capsules: stabilized 20% ascorbic acid, single-use, travel-friendly.
- La Roche-Posay Vitamin C Serum: contains fragrance and alcohol, not ideal for sensitive skin.
- Matter of Fact Vitamin C Serum: includes ascorbic acid and ferulic acid, oily texture for dry skin.
- Medik8 Super C Ferulic: stable 30% ethyl ascorbic acid, lightweight texture.
- Naturium Vitamin C Complex: multi-form Vitamin C with niacinamide, alpha arbutin, and turmeric.
- Timeless Vitamin C Serum: affordable ($20), 20% ascorbic acid with E and ferulic acid.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
More Than Skin-Deep: Six Ways To Eat For Healthier Skin ← this one’s about a lot more than just vitamin C 😎
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Things You Can See Only When You Slow Down – by Haemin Sunim
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this one’s not about: noticing raindrops on roses and whiskers on kittens.
That’s great too, though. This writer particularly loves the cute faces of baby jumping spiders. Sounds unlikely, but have you seen them?
What it’s rather about: noticing what’s between your ears, and paying closer attention to that, so that we can go about our business more mindfully.
This is, fundamentally, a book about living a happier life, whatever the potentially crazy circumstances of the hustle and bustle around us. Not because of disinterest; quite the opposite. Sunim bids us ask the question of ourselves, what are we really doing and why?
The writing style is very light and easy, while being heavy-hitting in terms of the ideas it brings. Little wonder that this one is so highly-rated on Amazon, with more than 5,000 ratings.
Bottom line: if sometimes you feel like the world is a little hectic and all that is around you is out of your control, this is a great book for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How the HHS impacts your community’s health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services is responsible for programs that impact every community in the country. But most Americans aren’t aware of the department’s scope.
“Most of the power in the agency, most of the administrative authority comes from laws that Congress has passed,” former HHS Secretary Kathleen Sebelius told NPR. She added that the HHS secretary “could redefine terms that had a huge impact on people. And that could be done all administratively, not by going back to Congress.”
HHS is comprised of 13 agencies, all of which play an important role in promoting the health of all Americans. These are just some of the ways that HHS affects people’s lives and health.
Vaccines
One of HHS’s most salient roles is developing, approving, and monitoring vaccines after they are on the market. The National Institutes of Health funds and conducts research to develop new vaccines and improve existing ones. The NIH’s Vaccine Research Center spearheads research to develop vaccines against deadly diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis.
The Food and Drug Administration is responsible for overseeing clinical trials that test product safety and effectiveness, approving new vaccines, and monitoring the safety of all vaccines before and after approval. In conjunction with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the FDA also manages the national surveillance systems that record and flag potential vaccine side effects.
In addition to safety monitoring, the CDC conducts research on vaccine safety and effectiveness and issues vaccination guidance. The agency’s recommended immunization schedule guides school and child care vaccination requirements and health care provider recommendations nationwide.
Although the CDC does not have the authority over school and childcare vaccination requirements at the state level, changes to the agency’s recommendations could have wide-ranging impacts.
“If this recommendation changes, there’s downstream effects, like insurance companies could stop covering them. And adding cost could easily deter uptake,” epidemiologist and creator of the Your Local Epidemiologist newsletter Katelyn Jetelina told PBS.
However, CDC vaccine recommendations are just that: recommendations. The agency cannot dictate, for example, vaccine requirements for school enrollment. Those standards are set at the state level, with the possible exception during a national public health emergency.
Drug safety
The FDA oversees all clinical trials in the United States. Every prescription drug and many medical products undergo a rigorous, closely regulated, multistep trial to test their safety and effectiveness. At the end of that process, the FDA determines whether a drug meets its standards for approval. Without FDA approval, a drug cannot be sold in the U.S.
Like with vaccines, the FDA monitors potential safety concerns related to over-the-counter and prescription medications, medical devices, and other products the agency regulates. Health care providers, FDA-regulated companies, and patients can report suspected safety issues to the agency, which evaluates each report for further investigation.
The FDA also alerts the public to safety concerns related to medical products by releasing safety notices, adding warning labels, and issuing drug recalls.
Pandemic and public health emergency response
Several HHS agencies are tasked with preventing, preparing for, and responding to disease outbreaks. This responsibility includes tracking potentially dangerous infectious diseases in the U.S. and globally, developing pandemic response strategies, and issuing guidance to contain ongoing outbreaks.
Both the CDC and FDA inform the public about public health concerns, including pandemics. The Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response works with communities, medical facilities, local and state governments, and industry partners to enhance responses to disasters and public health emergencies.
The CDC also tracks pathogens like the flu, norovirus, and sexually transmitted infections to better understand where diseases are spreading, how they are evolving, and how best to prepare for outbreaks.
In the event of a public health emergency, the CDC may issue guidance on how to stay safe and minimize health impacts. For example, in January, the agency released tips on how to protect against smoke during the wildfires affecting southern California and how to avoid frostbite and hypothermia, as extreme cold weather affected much of the country.
The FDA can issue emergency use authorizations, which allow the use of “unapproved medical products or unapproved uses of approved medical products … to diagnose, treat, or prevent serious or life-threatening diseases … when certain criteria are met” during public health emergencies. These authorizations help ensure that the standard FDA approval process is not a barrier to the public receiving lifesaving medical products, such as authorizing specific vaccines during a pandemic.
Food and water safety
The FDA, along with the U.S. Department of Agriculture, plays an important role in regulating food safety. The agency approves and monitors the safety of food additives, like sweeteners, dyes, and preservatives. It also regulates how food is prepared, packaged, and stored, including conducting inspections of food facilities and farms.
FDA food safety testing detects dangerous foodborne illnesses like salmonella and E. coli. For example, in late December 2024, the FDA began testing raw (unpasteurized) milk products for bird flu contamination. The CDC investigates outbreaks of foodborne illnesses and, along with the FDA and USDA, provides the public with information about food safety.
The FDA also regulates most food labels, including nutrition facts, ingredient lists, and health claims on food packaging. In January, the agency proposed new front-of-package nutrition labels that highlight sugar, fat, and sodium content in packaged food products.
HHS and the USDA are responsible for updating the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, which are updated every five years. These guidelines are the basis of all federal food assistance programs for children, older adults, and low-income families.
HHS sets the guidelines for the maximum fluoride level in drinking water and periodically makes recommendations about fluoride levels. However, the department has no authority to require or ban fluoridation, which is regulated at the state and local level. U.S. cities began adding fluoride to drinking water in the 1940s to improve dental health and reduce cavities by 25 percent.
Health care access
The HHS secretary regulates the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, which provides health insurance to adults 65 and older, people with disabilities, low-income families, and eligible children through the Children’s Health Insurance Program. Together, Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP insure over 145 million Americans, or roughly 42 percent of the U.S. population. Changes to either of these programs could impact health care access and quality for millions of Americans.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Tooth Remineralization: How To Heal Your Teeth Naturally
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michelle Jorgensen, dentist, explains:
The bare-bones details:
Teeth cannot be regrown (yet!) but can be remineralized, which simply involves restoring lost minerals. When we’re talking about health, “minerals” is usually used to mean elemental minerals, like calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, etc, but the specific mineral that’s needed here is hydroxyapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral, the same as is found in bones).
Not only can acids from food and bacteria dissolve the minerals from the teeth, but also, the body itself may extract minerals from the teeth if it needs them for other functions it considers more critical and/or more urgent.
Cavities occur when acids create porous holes in teeth by dissolving minerals, which allows bacteria to invade, which means more acid, and cavities.
Remineralization can be achieved by doing the following things:
- Use hydroxyapatite-based products (tooth powder, mouthwash).
- Improve gut health to ensure proper mineral absorption.
- Reduce acidic food and drink intake.
- Maintain good oral hygiene to prevent bacteria build-up.
- Eat foods rich in vitamins A, D, E, and K, which help direct minerals to teeth and bones.
For more on all of the above, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
- Fluoride Toothpaste vs Non-Fluoride Toothpaste – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: